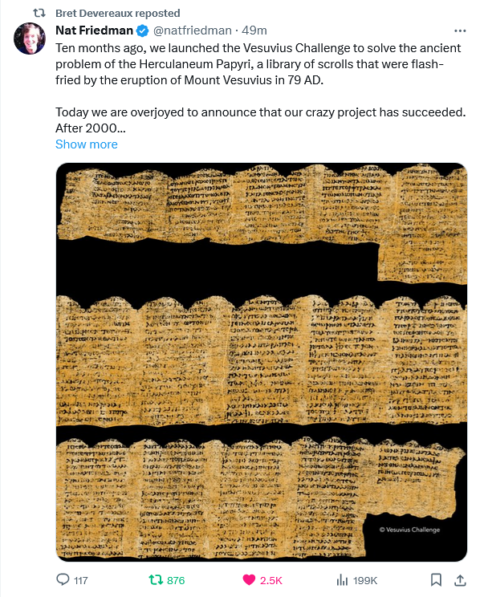
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes looks at the importance of salt in history:
There was a product in the seventeenth century that was universally considered a necessity as important as grain and fuel. Controlling the source of this product was one of the first priorities for many a military campaign, and sometimes even a motivation for starting a war. Improvements to the preparation and uses of this product would have increased population size and would have had a general and noticeable impact on people’s living standards. And this product underwent dramatic changes in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, becoming an obsession for many inventors and industrialists, while seemingly not featuring in many estimates of historical economic output or growth at all.
The product is salt.
Making salt does not seem, at first glance, all that interesting as an industry. Even ninety years ago, when salt was proportionately a much larger industry in terms of employment, consumption, and economic output, the author of a book on the history salt-making noted how a friend had advised keeping the word salt out of the title, “for people won’t believe it can ever have been important”.1 The bestselling Salt: A World History by Mark Kurlansky, published over twenty years ago, actively leaned into the idea that salt was boring, becoming so popular because it created such a surprisingly compelling narrative around an article that most people consider commonplace. (Kurlansky, it turns out, is behind essentially all of those one-word titles on the seemingly prosaic: cod, milk, paper, and even oysters).
But salt used to be important in a way that’s almost impossible to fully appreciate today.
Try to consider what life was like just a few hundred years ago, when food and drink alone accounted for 75-85% of the typical household’s spending — compared to just 10-15%, in much of the developed world today, and under 50% in all but a handful of even the very poorest countries. Anything that improved food and drink, even a little bit, was thus a very big deal. This might be said for all sorts of things — sugar, spices, herbs, new cooking methods — but salt was more like a general-purpose technology: something that enhances the natural flavours of all and any foods. Using salt, and using it well, is what makes all the difference to cooking, whether that’s judging the perfect amount for pasta water, or remembering to massage it into the turkey the night before Christmas. As chef Samin Nosrat puts it, “salt has a greater impact on flavour than any other ingredient. Learn to use it well, and food will taste good”. Or to quote the anonymous 1612 author of A Theological and Philosophical Treatise of the Nature and Goodness of Salt, salt is that which “gives all things their own true taste and perfect relish”. Salt is not just salty, like sugar is sweet or lemon is sour. Salt is the universal flavour enhancer, or as our 1612 author put it, “the seasoner of all things”.
Making food taste better was thus an especially big deal for people’s living standards, but I’ve never seen any attempt to chart salt’s historical effects on them. To put it in unsentimental economic terms, better access to salt effectively increased the productivity of agriculture — adding salt improved the eventual value of farmers’ and fishers’ produce — at a time when agriculture made up the vast majority of economic activity and employment. Before 1600, agriculture alone employed about two thirds of the English workforce, not to mention the millers, butchers, bakers, brewers and assorted others who transformed seeds into sustenance. Any improvements to the treatment or processing of food and drink would have been hugely significant — something difficult to fathom when agriculture accounts for barely 1% of economic activity in most developed economies today. (Where are all the innovative bakers in our history books?! They existed, but have been largely forgotten.)
And so far we’ve only mentioned salt’s direct effects on the tongue. It also increased the efficiency of agriculture by making food last longer. Properly salted flesh and fish could last for many months, sometimes even years. Salting reduced food waste — again consider just how much bigger a deal this used to be — and extended the range at which food could be transported, providing a whole host of other advantages. Salted provisions allowed sailors to cross oceans, cities to outlast sieges, and armies to go on longer campaigns. Salt’s preservative properties bordered on the necromantic: “it delivers dead bodies from corruption, and as a second soul enters into them and preserves them … from putrefaction, as the soul did when they were alive”.2
Because of salt’s preservative properties, many believed that salt had a crucial connection with life itself. The fluids associated with life — blood, sweat and tears — are all salty. And nowhere seemed to be more teeming with life as the open ocean. At a time when many believed in the spontaneous generation of many animals from inanimate matter, like mice from wheat or maggots from meat, this seemed a more convincing point. No house was said to generate as many rats as a ship passing over the salty sea, while no ship was said to have more rats than one whose cargo was salt.3 Salt seemed to have a kind of multiplying effect on life: something that could be applied not only to seasoning and preserving food, but to growing it.
Livestock, for example, were often fed salt: in Poland, thanks to the Wieliczka salt mines, great stones of salt lay all through the streets of Krakow and the surrounding villages so that “the cattle, passing to and fro, lick of those salt-stones”.4 Cheshire in north-west England, with salt springs at Nantwich, Middlewich and Northwich, has been known for at least half a millennium for its cheese: salt was an essential dietary supplement for the milch cows, also making it (less famously) one of the major production centres for England’s butter, too. In 1790s Bengal, where the East India Company monopolised salt and thereby suppressed its supply, one of the company’s own officials commented on the major effect this had on the region’s agricultural output: “I know nothing in which the rural economy of this country appears more defective than in the care and breed of cattle destined for tillage. Were the people able to give them a proper quantity of salt, they would … probably acquire greater strength and a larger size.”5 And to anyone keeping pigeons, great lumps of baked salt were placed in dovecotes to attract them and keep them coming back, while the dung of salt-eating pigeons, chickens, and other kept birds were considered excellent fertilisers.6
1. Edward Hughes, Studies in Administration and Finance 1558 – 1825, with Special Reference to the History of Salt Taxation in England (Manchester University Press, 1934), p.2
2. Anon., Theological and philosophical treatise of the nature and goodness of salt (1612), p.12
3. Blaise de Vigenère (trans. Edward Stephens), A Discovrse of Fire and Salt, discovering many secret mysteries, as well philosophical, as theological (1649), p.161
4. “A relation, concerning the Sal-Gemme-Mines in Poland”, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 5, 61 (July 1670), p.2001
5. Quoted in H. R. C. Wright, “Reforms in the Bengal Salt Monopoly, 1786-95”, Studies in Romanticism 1, no. 3 (1962), p.151
6. Gervase Markam, Markhams farwell to husbandry or, The inriching of all sorts of barren and sterill grounds in our kingdome (1620), p.22