CDR Salamander has a proposal to encourage cheapskate freeloaders like Justin Trudeau’s Canada (although it didn’t start with him … Canada has been freeloading militarily since the early 1970s) to take on more like a fair share of NATO’s needs:
President Vladimir Putin on Wednesday ordered Russia’s first mobilisation since World War Two and backed a plan to annex swathes of Ukraine, warning the West he was not bluffing when he said he’d be ready to use nuclear weapons to defend Russia.
In the biggest escalation of the Ukraine war since Moscow’s Feb. 24 invasion, Putin explicitly raised the spectre of a nuclear conflict, approved a plan to annex a chunk of Ukraine the size of Hungary, and called up 300,000 reservists.
This should not be a shock to anyone. If it is, perhaps you should consider investing your time in cat-blogging.
It should bring to the front that NATO can no longer allow unserious nations to play like they are anything but security free-riders. They need to contribute their fair share or pay some consequence. Alliances have benefits and responsibilities. You should not have one without the other.
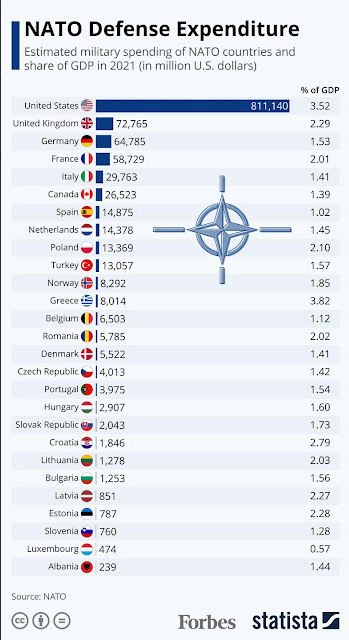
While percentage of GDP is an imperfect measure of contribution, it is better than all the other ones. It is as simple benchmark of national effort.
As these are the best numbers we have, let’s look at 2021 and then forward.
It is amazing that after all Russia has shown Western Europe — both of its nature and the nature of modern warfare — that so many of our NATO allies continue to slow walk defense spending, doing the very minimum to be a full and fair partner in the alliance.
Russian victory — however they define it — or Russian defeat — however Ukraine defines it — will not change the geography or nature of Russia. She is not going anywhere.
So, what’s to be done to encourage nations like Canada to put up or shut up? This might help:
“Out years” are where dragons live, so anyone not on guide-slope to 2%+ by the end of 2023 – when one way or another the Russo-Ukrainian War should be over – will find someway to not get there in a wave of excuses and bluffing.
We should call their bluff.
As such, and this is generous, we need to finally pursue PLAN SALAMANDER for NATO “Flags-to-Post” that I first proposed almost six years ago.
In NATO, General and Flag Officer billets are distributed amongst nations in a rather complicated way, but this formula is controlled by NATO – and as such – can be changed.
Entering argument: take the present formula for “fair distribution” and multiply by .75 any nation that spends 1.5% to 1.99% GDP on defense. Multiply by .5 any nation that spends between 1.25% to 1.499%. Multiply by .25 1.0% to 1.240%. If you fall below 1%, you get nothing and your OF5 (Col./Capt) billets are halved.
1.25x for 2.01%-2.25%. 1.5X for 2.26%-2.75%; 1.75x for 2.76% -3.0%. 2x for +3.01%.
The math gets funky when a lot of people get over 2%, but we can refine it later. Doesn’t cost a penny and will unquestionably get the attention of those nations. Trust me on this. By January 1st, 2024 no more excuses. A small and symbolic punishment, but a good start that may be all that is needed. This is not the second half of the 20th Century any more.