Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 19 Sep 2017Linguistically speaking, Alexander means “Defender of Men” from the Greek “alexo“, defend, and “aner/ander“, man. I’ll never be able to not internally think of his name as just meaning “Alex-Man”.
Oh, yeah, also he conquered an empire or something? IDK. I stopped paying attention after his bland name.
PATREON: www.patreon.com/OSP
MERCH LINKS:
Shirts – https://overlysarcasticproducts.threa…
All the other stuff – http://www.cafepress.com/OverlySarcas…Find us on Twitter @OSPYouTube!
February 9, 2021
History Summarized: Alexander the Great
February 7, 2021
Roman legion vs Macedonian phalanx
Epimetheus
Published 13 Aug 2018Roman legion vs Macedonian phalanx (Macedonian wars)
Battle of Pydna 168 BC and battle of Cynoscephalae 197 BCSupport new videos from Epimetheus on Patreon! 😀
https://www.patreon.com/Epimetheus1776roman legion, roman legion tactics, macedonian phalanx, Macedonian phalanx tactics, Macedonian phalanx vs roman legion, ancient Macedonian army, ancient roman army, roman army, Roman legionary, rome vs Greece, Rome vs Macedon, roman army weapons, Roman army tactics, Macedonian wars, battle Cynoscephalae, battle of Pydna, republican Roman army, Roman maniple, Roman republic, documentary, ancient Rome documentary, ancient Greece documentary, rome documentary, battle of magnesia, rome selucid empire, Roman empire vs selucid empire, diadochi, ancient,
January 27, 2021
Misunderstood Moments in History – The Spartan Myth
Invicta
Published 27 Oct 2017Start your 30 day free trial here: http://ow.ly/eCd230fiZ7Q
The Spartans are immortalized in history as super soldiers bred for war. However most of what we think we know about them is a lie. Today we will unmask the truth behind the Spartan Myth.
The Great Courses Plus is currently available to watch through a web browser to almost anyone in the world and optimized for the US market. The Great Courses Plus is currently working to both optimize the product globally and accept credit card payments globally.
Documentary Credits:
Research: Dr Roel Konijnendijk
Script: Invicta
Artwork: Milek J
Editing: Invicta
Music: Total War OST, SoundnoteDocumentary Bibliography:
Paul Anthony Cartledge, The Spartans: The World of the Warrior-heroes of Ancient Greece
Nigel Kennell, Spartans: A New History (2010)
S. Hodkinson, Property and Wealth in Classical Sparta (2000)
J. Ducat, Spartan Education: Youth and Society in the Classical Period (2006)
S.M. Rusch, Sparta at War: Strategy, Tactics and Campaigns, 550-362 BC (2011)
E. Rawson, The Spartan Tradition in European Thought (1969)
S. Hodkinson & I.M. Morris (eds.), Sparta in Modern Thought (2012)
January 26, 2021
QotD: “A world organized around institutional mass slavery”
An example: We’ve discussed all the cool steampunk shit the Greeks could’ve had, if only Archimedes had … well, that’s just the thing, isn’t it? We look at the aeolipile and see a prototype steam engine; they looked at it and saw, as best we can tell, a party trick. Back when, I suggested, Marxist-style, that labor costs were a sufficient explanation for why nobody took the obvious-to-us next step of hooking the thing up to something productive and kicking off the Industrial Revolution. Machines are labor-saving devices; the ancient world had a gross excess of labor. Calling the aeolipile a steam engine, then, is a category error.
New hypothesis: It’s a category error, all right, but not because they didn’t think in terms of labor costs. It’s because they couldn’t think in terms of labor costs.
A world organized around institutional mass slavery is, in a very real sense, a timeless world. Herodotus (I think) actually says somewhere that nothing worth mentioning happened before him, and you can see echoes of this attitude even as late as the Antebellum South. You see their attitude described as “conservative,” but since that’s egghead shorthand for “evil” you can ignore it. They weren’t consciously backward-looking; rather, they were deeply rooted to their place and station. To the outsider, it looked like they were trying to hold time back, but to the insider, time — clock time, industrial time, the time of the Protestant work ethic — barely existed at all.
So with the Classical World. The Romans, for instance, are endlessly frustrating to their admirers (of which I am an ardent one). Their only economic fix, for instance, was debasing the currency, i.e. a primitive form of inflation. You guys could figure out how to hew an artificial harbor out of some desert rocks — a trick we’d have a hard time pulling off today — but you couldn’t figure out fiat currency? Or a better political system than the tetrarchy? Or that the forts-and-legions paradigm just isn’t cutting it? Or … etc.
Stuff like that is why Spengler said classical, Apollonian culture was fundamentally different from, and incompatible with, our Faustian culture. According to Spengler, the master metaphor for the Apollonian is the human body, which is beautiful but changeless (emphasis mine, not Spengler’s). You can improve your body somewhat, but only within certain tight limits, and the body’s fundamental form is always the same (we could time warp Julius Caesar into the Current Year and still recognize him as a fellow homo sap., no matter how different his mind might be).
The Faustian, though — that would be us — organizes his worldview around space, infinite space. Practically speaking, this results in our attitude of innovation-for-innovation’s sake. We send a man to the moon because we can, but such an idea would never occur to the Romans, for the same reason they didn’t apply all their awesome engineering knowledge to the problems of governance. Hacking a harbor out of the desert is a tremendous feat, but it’s a local feat — a one-shot deal, a very specific response to a very specific local problem, with no broader applications.
This, I suggest, is because the timeless world of institutional mass slavery naturally selects for the kind of man who is at home in the world of institutional mass slavery. It’s a world of very low future time orientation, because “time” hardly exists at all. Forget machinery for a sec; the Roman world was full of enormous problems that had teeny-tiny, head-slappingly obvious fixes. Julius Caesar, for instance, was considered some kind of prodigy because he could sight-read books. Which really was a noteworthy feat, because Romans didn’t even put spaces between their words, much less use any sort of punctuation marks. And they were radical innovators compared to the Ancient Egyptians, since at least Roman writing all ran left-to-right; hieroglyphics can be read in any direction, including vertically, and I’m pretty sure there are examples of them changing text orientations in the middle of the same inscription. It’s not hard to imagine some legion commander actually losing a battle because he had to stop and sound out an important communique from a subordinate …
… and yet the Romans, for all their technical skill, never even figured that tiny change out. See also: The Chinese doing fuck-all with movable type, vs. (Faustian) Europeans using it to conquer the world. China, too, was a timeless society. As Derb says somewhere, Classical Chinese isn’t even really writing; it’s more of an aide-memoire — designed to remind readers of stuff they already know, not to communicate new information.
Your post-Roman European, by contrast, lived in a world where high future time orientation was an absolute must. You don’t need hypotheses like the famous “lead in the drinking water pipes” to explain the seemingly bizarre things the Romans did, or didn’t do; all you need is time orientation, a fundamental attitude of “this is a variation on an old problem” vs. “this is an entirely new situation that requires a new response.” Life in the post-Roman world was solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short — every man for himself; think through the consequences of your actions very carefully before you do them, or die horribly. Those who failed to do so died. Bake that into the genetic cake for a few generations, and you get Renaissance Man, who’d see a million possible applications for the aeolipile.
Severian, “Bio-Marxism”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-09-24.
January 24, 2021
The Great Wine Blight
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 9 Sep 2020In the 19th century, the Great Wine Blight threatened the very existence of grapes. But the pestilence brought into Europe by American vines was eradicated by the use of those very same vines. The History Guy recalls how American indigenous vines saved the wine industry, and how you can help to preserve its future.
This is original content based on research by The History Guy. Images in the Public Domain are carefully selected and provide illustration. As very few images of the actual event are available in the Public Domain, images of similar objects and events are used for illustration.
Special thanks to Stone Hill Winery, Hermann, Missouri:
https://stonehillwinery.comYou can purchase the bow tie worn in this episode at The Tie Bar:
All events are portrayed in historical context and for educational purposes. No images or content are primarily intended to shock and disgust. Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. Non censuram.
Find The History Guy at:
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TheHistoryGuyThe History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered is the place to find short snippets of forgotten history from five to fifteen minutes long. If you like history too, this is the channel for you.
Awesome The History Guy merchandise is available at:
teespring.com/stores/the-history-guy
Script by CDH
#history #thehistoryguy #wine
January 15, 2021
Germany Bankrupts Greece – Countless Die in Famine – War Against Humanity 026 – January 1942, pt. 1
World War Two
Published 14 Jan 2021The early weeks of 1942 show how much of a global War Against Humanity this really is. People in occupied zones across the globe suffer under the boot of their tormentors. In Greece, thousands die in a famine, while repressive tactics claim the lives of many more in the Balkans. The Holocaust continues in cities and the extermination camp of Chełmno, while the Japanese army wreaks havoc in South-East Asia as they advance on Allied positions.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Spartacus Olsson
Written by: Joram Appel
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Joram Appel and Valantis Athanasiou
Edited by: Miki Cackowski
Sound design: Marek Kamiński
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
Jaris Almazani (Artistic Man) – https://instagram.com/artistic.man
Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Daniel WeissSources:
Yad Vashem 4147/72, 953, 4613/629, 85EO6
IWM KF 199, FE 255, SE 4819
Bundesarchiv
Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
Museum of Yugoslavia
From the Noun Project: Skull by Muhamad UlumSoundtracks from the Epidemic Sound:
Johan Hynynen – “Dark Beginning”
Peter Sandberg – “Document This 1”
Skrya – “First Responders”
Cobby Costa – “From the Past”
Farrell Wooten – “Blunt Object”
Gunnar Johnsen – “Not Safe Yet”
Cobby Costa – “Flight Path”Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
January 3, 2021
QotD: Literary stasis in the Byzantine empire
Undoubtedly, the Mediaeval Romans – now exclusively Greek in their language – made little effort to be original in their literature. They had virtually the whole body of Classical Greek literature in their libraries and in their heads. For them, this was both a wonderful possession and a fetter on the imagination. It was in their language, and not in their language. Any educated person could understand it. But the language had moved on – changes of pronunciation and dynamics and vocabulary. The classics were the accepted model for composition. But to write like the ancients was furiously hard. Imagine a world in which we spoke Standard English, but felt compelled, for everything above a short e-mail, to write in the language of Shakespeare and the Authorised Version of the Bible. Some of us might manage a good pastiche. Most of us would simply memorise the whole of the Bible, and, overlooking its actual content, write by adapting and rearranging remembered clauses. It would encourage an original literature. Because Latin soon became a completely foreign language in the West – and because we in England were so barbarous, we had to write in our own language – Western Mediaeval literature is often a fine thing. The Mediaeval Romans never had a dark age in our sense. Their historians in the fifteenth century wrote up the fall of Constantinople to the Turks in the same language as Thucydides. Poor Greeks.
Sean Gabb, “The Mediaeval Roman Empire: An Unlikely Emergence and Survival”, SeanGabb.co.uk, 2018-09-14.
November 28, 2020
Miscellaneous Myths: The Zodiac
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 27 Nov 2020Thanks to longtime patron Volt for requesting this topic!
We know their names! We know their symbols! We know there’s a truly staggering number of websites dedicated to their stereotypical personality traits! But what do we know about their stories? Let’s discuss!
FUN FACT I GLOSSED OVER IN THE VIDEO: like I said, it’s REALLY hard to determine when these constellations entered Greece. Most people set the date at 300ish, when Eudoxus codified the Greek calendar based on the Babylonian one — but that clashes with the fact that Heracles’s labors predate that by at least three centuries, and they’ve had those zodiacal themes since that lost epic poem was initially written. We know, therefore, that the Babylonian zodiac entered greece between Homer’s time (when he conspicuously didn’t mention them — and neither did Hesiod in his Astronomia) and Peisander’s time (author of the lost Heracleia), basically the interval between 800 and 600 CE. The phoenician traders carrying that info is a reasonable assumption, especially considering how important the stars are to sailors navigating at night. But it is WILD to me how hard this is to research and how nobody seems to have really explored the timeline here!
Two Zodiac merch designs are available on our redbubble!
The modern constellations-only zodiac: https://www.redbubble.com/shop/ap/634…
The MUL*APIN Babylonian zodiac: https://www.redbubble.com/shop/ap/634…Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
November 27, 2020
Horse Lords: A Brief History of the Scythians
History Time
Published 30 Jan 2018This video is about the Scythians. One of the first horse cultures on Earth.
Are you a budding artist, illustrator, cartographer, or music producer? Send me a message! No matter how professional you are or even if you’re just starting out, I can always use new music and images in my videos. Get in touch! I’d love to hear from you.
If you liked this video and have a spare dollar you can help support the channel here:-
http://www.patreon.com/historytimeUKI’ve compiled a reading list of my favourite history books via the Amazon influencer program. If you do choose to purchase any of these incredible sources of information then Amazon will send me a tiny fraction of the earnings (as long as you do it through the link) (this means more and better content in the future) I’ll keep adding to and updating the list as time goes on:-
https://www.amazon.com/shop/historytimeMusic used:-
Ross Bugden – “Parallel”, “Last Dawn”, “Titans”, “Olympus”I try to use copyright free images at all times. However if I have used any of your artwork or maps then please don’t hesitate to contact me and I’ll be more than happy to give the appropriate credit.
—Join the History Time community on social media:-
Instagram:-
https://www.instagram.com/historytime…
Twitter:-
https://twitter.com/HistoryTimeUK
October 24, 2020
Andrew Sullivan on the potentials of therapeutic use of psilocybin
In the last free edition of his Weekly Dish newsletter — and probably the last time I’ll be able to link to it — Andrew Sullivan discusses the medical trials and legalization initiatives for psilocybin along with some of the history of its use in the Elusinian Mysteries in ancient Greece:
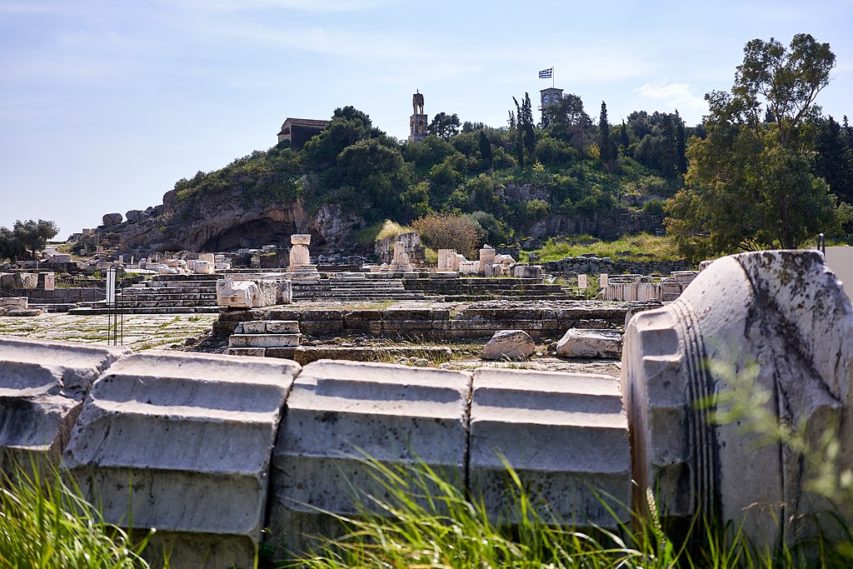

At the archaeological site of the Sanctuary of Demeter at Eleusis. The information board on the left stands on what was once the courtyard of the sanctuary. Over the staircase behind it stood the Greater Propylaea. Next to the cavern in the background stood the Sanctuary of Pluto (who abducted Persephone, Demeter’s daughter). The cavern represents the entrance to the Underworld. The path to the left of the cavern leads to the Telesterion where the faithful were initiated to the Eleusinian mysteries. The brown building up on the hill (left) is a church dedicated to the Virgin Mary (Church of Panagitsa Mesosporitissa) and stands over the area of the Telesterion.
Photo by George E. Koronaios via Wikimedia Commons.
There are many ways in which this election might portend the future, but there’s a seemingly small issue — only on the ballot in Oregon and the District of Columbia — that’s a sleeper, it seems to me, and worth keeping an eye on. It’s the decriminalization of naturally-occurring psychedelics, in particular, psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in some mushrooms which have long been dubbed “magic.”
This doesn’t come out of the blue. Huge strides have been taken in the last few years in the decriminalization of cannabis, with 33 states allowing medical use, of which 11 allow recreational as well. The FDA recently greenlit clinical trials for psilocybin as a “breakthrough therapy” for depression — with some wildly impressive results. Books like Michael Pollan’s magisterial How To Change Your Mind have helped shift the reputation of psychedelics from groovy, counter-cultural weirdness to mature, spiritual, and regulated mental health treatment. Ketamine — previously a party drug and an animal tranquilizer — has shown more promise as an anti-depressant than any therapy since the mid-1990s.
The familiar worry, of course, is that we might be ushering in an era of wild drug experimentation, with unforeseen and unknowable results. Some people fear that relaxing some of the legal restrictions on things that grow in nature could lead to social disruption or higher levels of addiction or worse. The great popularizer of psychedelics, Aldous Huxley, gave us a somewhat sobering description of what might be our future in Brave New World, and many in the West have been terrified of these substances for quite a while.
But new research suggests that this shift toward integrating psychedelics into a healthy, responsible life for Westerners may not be new at all. It would, in fact, be a return to a civilization that used these substances as a bulwark of social and personal peace. New literary investigations of ancient texts, new — and re-examined — archeological finds, and cutting edge bio-chemical technology that can detect and identify substances in long-buried artifacts, suggest that deploying psychedelics would, in fact, be a return to a Brave Old World we are only now rediscovering.
We’ve long known that human knowledge of psychedelic aspects of nature goes back into pre-history; and use of them just as far. But perhaps the most surprising find in this new area of research is that sacred tripping was not simply a function of prehistoric religious rituals and shamanism, but an integral, even central part, of the world of the ancient Greeks. The society that remains the basis for so much of Western civilization seems to have held psychedelics as critical to its vision of human flourishing. And that vision may have a role to play in bringing Western civilization back into balance.
A breakthrough in understanding this comes in the form of a rigorously scholarly new book, The Immortality Key: The Secret History of the Religion With No Name, by Brian Muraresku. What he shows is the centrality of psychedelic use for the ancient Greeks, in an elaborate and mysterious once-in-a-lifetime ceremony at the Temple of Eleusis, a short distance from Athens. We’ve long known about this temple of the Mysteries, as they were known, and the rite of passage they offered — because it’s everywhere in the record. Many leading Greeks and Romans went there, including Plato and Marcus Aurelius. Here is Cicero, no less, in De Legibus:
For it appears to me that among the many exceptional and divine things your Athens has produced and contributed to human life, nothing is better than those Mysteries. For by means of them we have been transformed from a rough and savage way of life to the state of humanity, and been civilized. Just as they are called initiations, so in actual fact we have learned from them the fundamentals of life, and have grasped the basis not only for living with joy, but also for dying with a better hope.
October 18, 2020
Miscellaneous Myths: Orion
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 10 Jul 2020Look! Up in the sky! It’s a giant! It’s a hunter! It’s Orion!
PINS: https://crowdmade.com/collections/ove…
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
MERCH LINKS: https://www.redbubble.com/people/OSPY…
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
From the comments:
Overly Sarcastic Productions
6 days ago
whoops, uh – YES, way back in my Endymion video I DID say that Artemis loved Orion, but in my defense, I was a much less diligent researcher back then, and that little nugget of “common knowledge” was EVERYWHERE I LOOKED. I had to do some serious digging this time to find where it came from and how unsupported it really was. I wasn’t kidding — that interpretation was so appealingly tropey that it eclipsed the MUCH larger body of work that completely contradicted it, and even completely unrelated articles and descriptions will mention “btw Artemis and Orion were totally smoochin” like it’s a Thing. Mythology is fun like that! 😅 -R
October 17, 2020
History Hijinks: Greek Wise Guys
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 16 Oct 2020When I first studied Ancient Philosophy in college I thought it was engaging and interesting to discuss and whatever, but only years later did I come to appreciate the true hilarity of these Wise-Guys.
SOURCES & Further Reading: Plato’s Dialogues (Apology & Republic), Aristotle’s Ethics, Gorgias’ Encomium of Helen, and when direct sources aren’t available, there’s a bucketload of great write-ups from Stanford: https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/pr…, https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/de…, https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/ar…, https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/pl…, https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/so…
This video was edited by Sophia Ricciardi AKA “Indigo”. https://www.sophiakricci.com/
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
PODCAST: https://overlysarcasticpodcast.transi…
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/kguuvvq
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
October 10, 2020
Miscellaneous Myths: The Minotaur
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 9 Oct 2020Ah, Theseus. Athens’ favorite trash man. Let’s talk about someone a little more interesting — literally anyone involved in this story will do.
Good news, I found the 1080P button! Bad news, the minute differences in image resolution are now threatening my sanity.
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/kguuvvq
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
A century on, Greece and Turkey are back at daggers drawn
John Psaropoulos on the ever-more-heightened tension in the Aegean Sea as Turkey looks to muscle in on Greek-claimed waters in search of natural gas (or a fight):
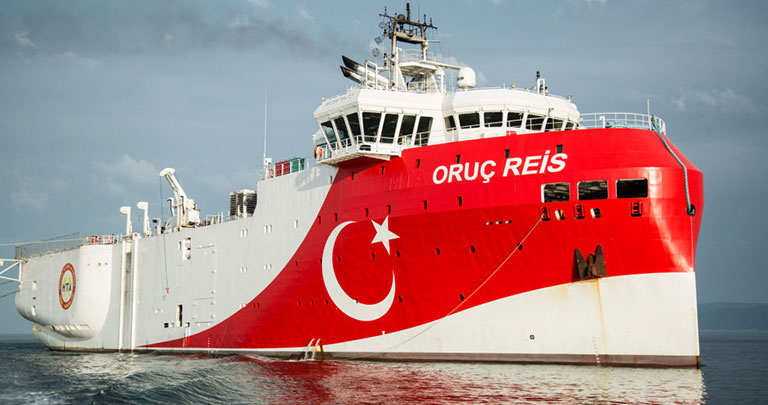
Last summer, Greece and Turkey came closer to war than they have done since 1974, when Turkey invaded Cyprus. The drama began to unfold on 21 July, when Turkey announced it was sending a seismic survey ship, the Oruc Reis, to look for oil and gas in areas the UN Law of the Sea awards to Greece.
Within hours, the Greek and Turkish navies had deployed throughout the Aegean and east of Crete. They remained so for two months. Greek helicopters pinned down Turkish submarines off the island of Evia. Frigates shadowed each other so closely, that on 12 August two of them collided when a Turkish frigate performed a manoeuvre across the bows of a Greek one. Greek and Turkish F-16s intercepted each other between Crete and Cyprus. Greece came close to invoking the European Union’s mutual defence clause.
On 13 September, Turkey withdrew the Oruc Reis, ostensibly for maintenance, and redeployed its navy. In the coming days, Greece and Turkey are to resume talks abandoned four and a half years ago on carving out their continental shelves – vast swathes of the east Mediterranean where they may exercise exclusive commercial rights to exploit undersea resources.
For now, there is de-escalation, but expectations for the outcome of these talks are low.
“Right now, Turkey doesn’t consider itself an extension of the West. It doesn’t consider that it has commitments and responsibilities towards the West,” says Konstantinos Filis, who directs the Institute of International Relations in Athens. “It believes it is an autonomous power in the region, that it is very potent, and that all its neighbours should respect it. The Turkish leadership doesn’t appear to be prepared for compromises with neighbours it considers inferior.”
The east Mediterranean is where the world’s most significant natural gas discoveries have occurred since the turn of the millennium. Israel and Egypt are now energy independent. Cyprus soon hopes to be. But Greece potentially dwarfs them all.
Seismic explorations it conducted six years ago suggest that Greece has natural gas reserves of 70-90 trillion cubic feet – as much as Israel, Egypt and Cyprus have discovered combined, with a pre-Covid-19 market value of about $200 billion. Assuming gas is viable for the next 25 years, Greece’s reserves, if proven, would cover its energy needs and turn gas into a lucrative export to the European Union. As much as a third of the value of the gas would go to the Greek state in taxes and royalties, allowing it to pay off a fifth of its external debt, now approaching twice its GDP.
This is clearly a future Turkey, with eight times Greece’s population and four times its economy, would rather claim for itself. Legally, it cannot do so. Under the rules of the UN’s Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), the lion’s share of east Mediterranean waters goes to Greece and Cyprus. Recep Tayyip Erdogan, Turkey’s leader for the past 18 years, feels that the Greeks are hemming him in.
September 28, 2020
The Elgin Marbles as oversized bargaining chips
Michael Curtis on the renewed demands that the British government return the Elgin Marbles to Athens:
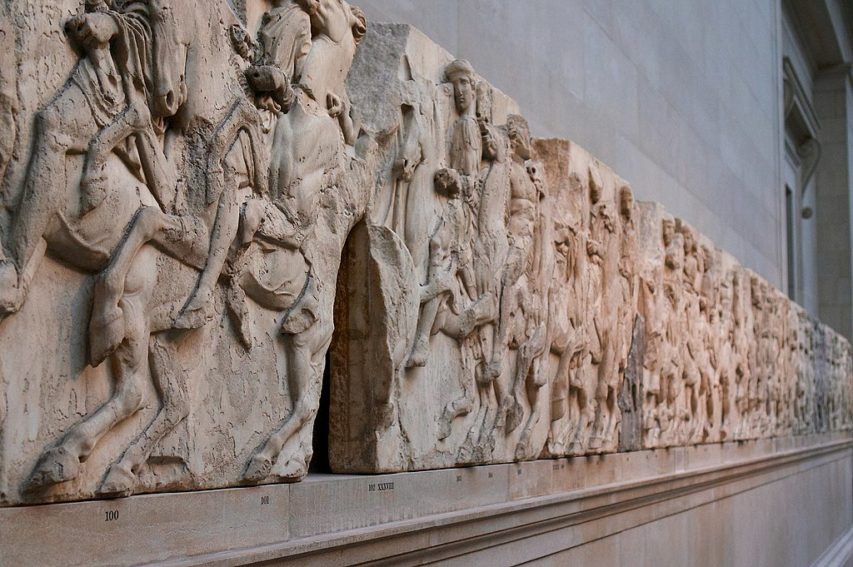

Some of the sculptures in the Elgin Marbles collection on display in the Duveen Gallery of the British Museum.
Photo by Paul Hudson via Wikimedia Commons.
The internecine wars in Washington, D.C., continue over government funding, a coronavirus relief bill, government shutdown, but on September 9, 2020 one form of political truce between Republicans and Democrats on foreign affairs was announced. Eighteen members of the U.S. Congress, bilateral members of the Congressional Caucus on Hellenic issues, including the chairs of the House Oversight and Rules committees, and Foreign Affairs subcommittee on issues relating to Europe, had written a letter to British Prime Minister Boris Johnson.
It informed him, in case he didn’t know, that the Elgin marbles, EM, had been the source of controversy among allies for many decades. The letter urged the British government, already saddled by labyrinth Brexit discussions, to negotiate with the Greek government in earnest over the return of the Elgin marbles to Greece by 2021, the 200th anniversary of the modern Greek nation. The eighteen Congress people joined other Americans intruding in British affairs. On September 16, 2020 both Joe Biden and Nancy Pelosi said there can be no US-UK trade deal if Brexit negotiations undermined the 1998 Good Friday peace agreement. However, the letter of the Congress group has raised the problem of the restitution of cultural objects taken from their country of origin.
Prime Minister Johnson does not need reminding that it was Thomas Bruce, Earl Elgin, British Ambassador to the Ottoman Empire, which included Greece, who took the marbles from the Parthenon in Athens, 1801-1805. The Parthenon, the central building of the Acropolis of Athens. was built around 488 B.C. to honor a goddess called Athena, and was at different times a Christian church and a mosque. The pillars and sculptures of the Parthenon were made of marble.
Elgin, with a passion for classical antiquities, made the case that the art works in the temples of Greece, then under Ottoman control would be destroyed because of Turkish indifference. Some had been destroyed in 1687 when the Venetians attacked Athens. The Sublime Porte granted Elgin’s request to take away pieces of stone with old inscriptions or figures. Perhaps this was gratitude for British action in blocking the advance of Napoleon in Egypt. Elgin took pediment sculptur friezes, metopes, and fragmented pieces from the walls of the Parthenon, and brought them to Britain. In 1816 he sold the sculptures to the British government which then sent them to the British Museum where they have remained.
Though the letter by the 18 members of Congress might be considered impertinent, it contained no threat of any kind but attempted to spark action on a disputed issue which has emotional appeal and symbolic importance, the presence of the Elgin marbles in the British Museum. In recent years the issue has been raised by officials of the European Union as well as by celebrated private citizens such as the actor George Clooney and his wife, and co-stars Bill Murray and Matt Damon, who while working on the 2014 film The Monuments Men, about art stolen by the Nazis, thought return of the Elgin marbles to Greece was the “right thing” to do.