The Tank Museum
Published May 3, 2024 19 productsUsed extensively by the German army of World War Two, the “tank destroyer” was developed to counter the increasing dominance of the tank on the battlefield.
Germany would field a massive 18 different types of tank destroyer in World War Two – compared with the 7 or 8 different types used by US, British and Commonwealth forces. One of these in particular, Sturmgeschütz III, would destroy more tanks than any other AFV in the entire conflict.
In this video we look at the development, strengths and weaknesses of German tank destroyers: from the 17 tonne Hetzer to the massive 70 tonne Jagdtiger — the heaviest tracked vehicle of the War.
00:00 | Introduction
00:59 | The First Tank Destroyers
04:14 | Avoiding Close Combat
06:59 | Jagdpanther
12:05 | Jagdtiger
15:31 | Hetzer
18:01 | Stug III
22:51 | ConclusionThis video features archive footage courtesy of British Pathé.
#tankmuseum #jagdpanther #stugiii #hetzer #jagdtiger
August 19, 2024
Evolution of WW2 German Tank Destroyers
August 16, 2024
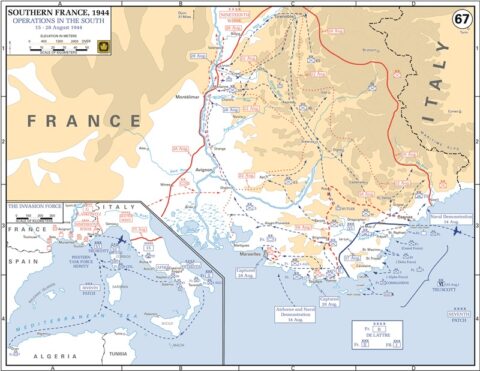
“Operation Dragoon … was described by Adolf Hitler as the worst day of his life”
The “other” D-Day landing in France that few people know much about: Operation Dragoon.
Often referred to as “the other D-Day”, Op Dragoon ran until 14 September 1944 and was a pivotal turning point in the Second World War.
Op Dragoon was a huge and complex operation by land, sea and air that liberated nearly two-thirds of France by linking up with troops from the Normandy invasion on 11 September and pushing the German forces right back to their frontier.
It also secured the ports of Marseilles and Toulon so Allied troops could flood into France.
This was a bitter blow for Hitler, who during conversations with his generals that were discovered in records written in shorthand, said: “The 15th of August was the worst day of my life”.
Dr Peter Caddick-Adams, a military historian and defence analyst, spoke to BFBS Forces News about Operation Dragoon, a largely French/American operation with support from countries including the UK and Canada.
He said: “It set the victory over Germany firmly on its way — and the end of the Second World War couldn’t really have been achieved without Operation Dragoon.
“This is the D-Day that you’ve never heard of.
“Originally there was planned to be two invasions of France on the same day — in Normandy and on the south coast of France along the Riviera.
“It was found that we didn’t have enough landing craft to do both at the same time simultaneously.”
It also didn’t help that Winston Churchill was against the idea and tried to cancel the operation.
The Prime Minister wanted the Italian campaign to remain dominant and was worried Dragoon would take troops and other resources away from Italy.
However, despite his best efforts, the Americans and French prevailed and Operation Dragoon went ahead.
Initially, the operation was given the codename Anvil, because Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy, was originally going to be called Sledgehammer.
The plan was for Germany’s armed forces to be smashed between the hammer and the anvil.
Churchill never changed his opinion about the operation despite its eventual success, as Dr Caddick-Adams explained: “At the last minute Churchill had the name changed to Dragoon and, legend has it, because he felt he was being dragooned into an operation that he didn’t want to undertake”.
August 15, 2024
August 8, 2024
Panzer III: Versatile stalwart of the Panzer force
The Tank Museum
Published Apr 19, 2024See inside the Panzer III and discover the story of the most numerous German armoured fighting vehicle of World War II.
Intended as the German army’s main gun tank, with its brother, the Panzer IV, acting as support, the Panzer III fought in Europe and North Africa but was effectively obsolete by 1942 in the face of better opposition like the Soviet T-34. So the two changed places – an up-gunned Panzer IV becoming the gun tank with the Panzer III — now with a short barrelled 75mm gun — in the support role. This wouldn’t last long — but the Panzer III chassis would form the basis of the highly successful Stug III.
00:00 | Introduction
00:15 | Background
02:12 | Two Similar Designs
02:57 | Panzer III Designs
10:22 | Take a Look Inside
14:46 | An Interview with Mike Hayton
23:52 | What’s it like to Drive?
26:00 | ConclusionThis video features archive footage courtesy of British Pathé.
#tankmuseum #panzeriii
August 7, 2024
Maxims in the Skies: the German LMG 08/15
Forgotten Weapons
Published Apr 24, 2024As soon as the MG08/15 “light” machine gun was adopted by Germany, it was recognized as an ideal basis for an aircraft gun. Weight was of the essence for WW1 aircraft, and a lightened Maxim was just the thing to use. So the Spandau Arsenal began producing the LMG08/15 (the “L” in which might stand for either air-cooled or lightweight; we really don’t know which) in May 1916. In addition to cutting a ton of lightening slots in the water jacket, the guns also had mechanisms added to allow a pilot to cycle both the bolt and the feed system from behind the gun (something not possible with a standard ground model). The example we are looking at today has a great example of an early style of such device completely intact …
(more…)
August 6, 2024
Me262 – Why It Was Rubbish
HardThrasher
Published Feb 16, 2024A brief and sober discussion of the multi-faceted nature of aircraft development in the 3rd Reich, and an assessment of the aircraft itself in context of the political and organisational challenges and changes from 1939-1945. Or to put it another way, why it was rubbish from start to finish.
Timestamps
00:00 – 00:22 – Trailer
00:22 – 01:49 – Introduction
01:49 – 05:14 – Willy Messerschmitt’s World Falls Apart
05:18 – 08:03 – Udet’s Flying Circus
08:07 – 11:26 – Me262’s Development
11:26 – 11:32 – Popcorn
11:33 – 13:37 – The Me163 Affair
13:42 – 19:30 – Milch Tries to Break His Willy
19:33 – 30:18 – Hitler’s Big Brain Moment
30:21 – 42:03 – Speeds and Feed of the Me262
42:05 – 46:53 – Operational History
46:54 – 48:50 – Survivor’s Club
(more…)
August 4, 2024
Mokusatsu! – WW2 – Week 310 – August 3, 1945
World War Two
Published 3 Aug 2024The Japanese reaction to the Allied ultimatum for unconditional surrender is … mokusatsu. This can be translated several ways, but all involve not giving a response. Meanwhile, materials for atomic bombs to be dropped on Japan are delivered to Tinian, though the ship making the delivery is sunk by a Japanese submarine days afterward. The active war continues in Burma and China, and the Potsdam Conference ends in Germany with the map of Poland very much re-drawn.
00:00 Intro
00:56 Mokusatsu
05:47 Delivering Atomic Material
07:22 Sinking The Indianapolis
09:26 Bombing Japan
12:22 The War In Burma And China
14:07 Potsdam Confernece Ends
17:02 Conclusion
(more…)
August 2, 2024
Why WW1 Turned Into Trench Warfare
The Great War
Published Apr 12, 2024Trench warfare is one of the lasting symbols of the First World War, especially on the Western Front. But when the war began, the German and French armies envisioned sweeping advances and defeating the enemy swiftly. So, how and why did the Western Front in 1914 turn into the trench system we associate with WW1?
(more…)
July 29, 2024
MG11: The Magnificent Swiss Maxim Gun
Forgotten Weapons
Published Apr 19, 2024The Swiss were one of the first countries to test Hiram Maxim’s new automatic machine gun in 1887, and they found it far superior to their just-recently-purchased Gardner guns. The first Swiss Maxims were delivered in 1889, and the country came back three more times for newer models. The MG94 was the first major adoption, followed by the MG00 for cavalry. Finally, after the Maxim patents expired and DWM introduced their improved 1909 commercial pattern, the Swiss adopted it as the MG11. The first 167 MG11s were produced by DWM, but deliveries ceased in 1915 because of the war. This prompted the Swiss National Assembly to order the government arsenal W.F. Bern to begin production, and between 1915 and 1946 the Swiss made 10,269 more MG11s domestically. They were absolutely beautifully made weapons.
In 1934/35, a modernization program made a number of improvements to the guns. The booster was simplified, the trigger was made one-hand friendly (so the second hand could be used to adjust aim while firing), a bracket for antiaircraft sights was added, and traverse and elevation stops were added to the tripods. Most significantly, the cloth belt was replaced by a fully metal belt. That belt is widely regarded as the best Maxim belt ever produced, and it is particularly valuable to shooters today, as it will function with essentially any caliber in any model of Maxim.
Swiss Maxims were never exported in quantity, and they are quite rare today.
(more…)
July 14, 2024
Britain’s First Naval Defeat in 100 years – Coronel 1914
Historigraph
Published Sep 26, 2020
July 13, 2024
Did you blink and miss Gender Empathy Gap Day?
Don’t worry, unlike so, so many other formal days (or months, or seasons …) in the calendar devoted to this or that or the other real and imagined causes, celebrations, or acknowledgements, Gender Empathy Gap Day isn’t observed anywhere:
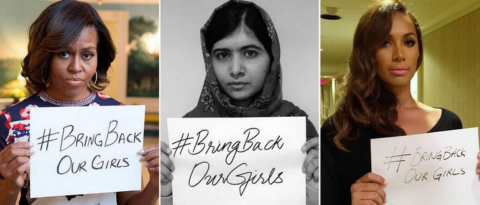
Remember these examples of virtue signalling? Can you imagine them doing the same for boys or young men?
Image from The Fiamengo File.
Few people have heard of Gender Empathy Gap Day, a day inaugurated in Germany in 2018 to raise awareness about our societies’ remarkable indifference to the suffering of men and boys. Not surprisingly, it has no official status in any country.
Most people, if asked, will insist that it is women and girls who suffer. We expect men and boys to apologize for their advantages and educate themselves about issues affecting women and girls. Animus against men is socially acceptable, even approved. “I bathe in male tears” is a popular feminist slogan, and university professors write mainstream opinion pieces with unironic titles like “Why Can’t We Hate Men?”
The Gender Empathy Gap Day doesn’t advocate a contest over which sex has it worse. It does advocate recognition of our collective inability or unwillingness to see the full humanity of men.
Academic researchers Alice Eagly and Antonio Mladinic have compiled data showing that both females and males tend to have more positive associations with women than with men. Researchers have also confirmed a much higher in-group bias amongst women, meaning that women feel more empathy towards other women than towards men, while men also feel more empathy for women.
Whether it’s homelessness (61% male), homicide (78% male victims), suicide (79% male), workplace fatalities (93% male), prison incarceration (93% male), or a host of other issues, men and boys do suffer. Yet according to the research of Dr. Tania Reynolds, we tend to associate agency with maleness and the capacity for victimhood with femaleness, seeing men and boys as active doers rather than as sufferers deserving concern.
As a result, we are tolerant of harsh punishments for male criminal offenders, but not for women. In 2012, Sonja Starr, a professor of Law, published the results of her study of discrepancies in criminal sentencing that showed a very large gender gap in the punishment of women for the same crimes committed by men. Starr’s extensive study found an average 63% sentencing gap that harshly disadvantaged men. She also discovered that “Female arrestees are […] significantly likelier to avoid charges and convictions entirely, and twice as likely to avoid incarceration if convicted”.
The gap in punishment results because we all — including prosecutors, judges, and juries — incline to the belief that women who commit crimes were led into their law-breaking by others, usually men, and had limited choices because of poverty, childhood abuse, mental illness, or addiction. We hesitate to deprive young children of the care of their mothers, while we are content to see fathers behind bars. As Starr points out, however, male offenders have also “suffered serious hardships, have mental health or addiction issues, have minor children, and/or have ‘followed’ others onto a criminal path”.
Author Glen Poole has noted that such indifference to male difficulties is built right into the stories our society tells about itself. He points out that when a large number of men are killed — whether in war, accident, or natural disaster — mainstream news sources report on people killed, making the sex of the victims invisible. It is not news when men and boys die.
When women or girls are killed or harmed, they are rarely if ever referred to as people. Their suffering is news.
July 11, 2024
In Germany, flying your national flag in June is considered a “grave offence against the human dignity” of the LGBT community
For reasons that I hope I don’t need to go into in any depth, displays of patriotism in Germany are viewed with deep suspicion by progressives and the various state and national government agencies. Even doing something like displaying the German national flag in any context other than a football match can draw official condemnation:
Many readers may not know about the German Stolzmonat, but I promise the backstory is worth it, so please bear with me.
As all of you do know, via some opaque imperial decree, every June across the Western world has become the monstrosity known as “Pride Month”. It is an occasion for the raucous celebration of every sexual minority and deviant proclivity imaginable. There are rainbow flags, lewd street parades, bizarre political speeches and all manner of astroturfed queer activism. I’m told that the festivities were massively scaled back this year in the Anglosphere, perhaps because they are awkward for elections, but on the Continent all such trends arrive very late and we had nothing but the usual excesses.
The eager flying of the rainbow colours is especially obnoxious in Germany, where the display of one’s national flag – except perhaps in a sports context – is discouraged and politically suspect. Some Germans have therefore responded to the perennial irritation of Pride Month by declaring June to be “Stolzmonat” instead. “Stolzmonat” is merely the German translation of “Pride Month”, but our clever cultural hackers have appropriated the term to indicate not gay but national pride. Those who celebrate Stolzmonat do not conduct any lavish public events and they give no speeches. Most of them simply change their social media profile pictures to present the colours black, red and gold. Now and again they also tweet the hashtag #Stolzmonat.
It’s primarily a German act of social media protest, but anybody can participate:
Enough people observe Stolzmonat to cause the corresponding hashtag to rise to the top of Twitter trends now and again. This has given the Rainbow Brigade indigestion, and as there is precious little division between the Rainbow Brigade and the German state, the domestic intelligence services of Lower Saxony have decided it is time to issue an ex cathedra condemnation of Stolzmonat – eight days after it ended. […] Below I translate this ridiculous woman’s statement. As you read, please remember that this is not just some random trans activist, but a functionary of the Lower Saxony Office for the Protection of the Constitution – an agency endowed with considerable powers to surveil and harass ordinary Germans for their alleged intellectual offences against “democracy” and the constitution:
Stop scrolling! We’re here to tell you all you need to know about the new right-wing campaign “Stolzmonat“. “Stolzmonat” is actually just the German translation of “Pride Month”. That’s what members of our queer community [1] say; they want to make the term “Stolzmonat” into what it should actually be – an expression of diversity, tolerance and strengthening of the rights of queer people.
Last year, the hashtag Stolzmonat temporarily landed at number one in the X-Trends – albeit as a polemical term of the extreme right wing. This year, the New Right in particular called for participation in Stolzmonat. The LGBTQIA+ community [2] is among the archetypal enemies of the right-wing extremist scene. In addition to discrimination against queer people, nationalism – that is to say, exaggerated national pride with simultaneous devaluation of other nations and the rejection of the values of liberal democracy – are core elements of Stolzmonat. They appropriate the German flag as a symbol for this campaign and associate it with the aforementioned elements. The new right use Queer hostility to associate themselves with existing prejudices in society and to activate ideologically like-minded people to participate in Stolzmonat. This is intended to create the impression of a large counter-movement to Pride Month. They use the hashtag and the German flag instead of the rainbow flag in their profile pictures. One of their messages: queer people are not a part of Germany. Right-wing extremists are thus pursuing a metapolitical approach [3] to exert influence on the pre-political sphere [4] and thus lay the foundation for anti-democratic positions.
There are so many dumb statements floating in this verbal morass that I don’t know where to begin. So just briefly: 1) The alphabet soup community is not “among the archetypal enemies of the right-wing extremist scene”. Pride Month has, however, became a deeply ridiculous and shallow cultural celebration of a great many things that are wrong with our society and a lot of people are extremely tired of it. 2) “Nationalism” in no way entails the “devaluation of other nations”, nor does it require the “rejection of the values of liberal democracy”. Liberal democracy grew up alongside nationalism, after all, and the Stolzmonat organisers explicitly encourage non-Germans to display their own national colours during Stolzmonat. 3) It is obviously not the point of Stolzmonat to argue that “queer people are not a part of Germany”.
Wittmann’s Tiger Rampage | Villers-Bocage, June 1944
The Tank Museum
Published Mar 30, 2024In the space of 15 minutes, Michael Wittmann took a single Tiger tank and stopped a major British advance, destroying 10 tanks, 10 halftracks, 8 Bren carriers, 1 scout car and a six-pounder anti-tank gun in the process. An eye-catching achievement … But was this a victory handed on a plate?
John Delaney outlines Wittmann’s audacious and decisive action at Villers Bocage against the British Desert Rats, examining its military significance. It’s become the stuff of legend. It was a gift to Nazi propagandists, who wasted no time in championing the achievements of their “tank ace”. For the British, it was an embarrassing blow to military prestige.
Wittmann got lucky. But luck runs out eventually …
00:00 | Introduction
00:42 | Arrival into Villers-Bocage
03:08 | Wittmann’s Rampage Begins
04:51 | Rampaging Through the Village
11:56 | Wittmann’s Luck Runs Out
14:09 | Was Wittmann Really a Tank Ace?
16:54 | ConclusionThis video features archive footage courtesy of British Pathé.
#tankmuseum #tankactions #johndelaney #michaelwittmann #tigertank
July 10, 2024
Two World Wars: Finnish C96 “Ukko-Mauser”
Forgotten Weapons
Published Mar 27, 2024A decent number of C96 Mauser pistols were present in Finland’s civil war, many of them coming into the country with the Finnish Jaegers, and others from a variety of sources, commercial and Russian. They were used by both the Reds and the Whites, and in both 9x19mm and 7.63x25mm. After the end of the civil war, when the military was standardizing, the C96s were handed over to the Civil Guard, where they generally remained until recalled to army inventories in 1939. They once again saw service in the Winter War and Continuation War, and went into military stores afterwards until eventually being surplussed as obsolete.
One of the interesting aspects of Finnish C96s is that many of them come from the so-called “Scandinavian Contract” batch (for which no contract has actually turned up). These appear to be guns made in 7.63mm that were numbered as part of the early production in the Prussian “Red 9” series, probably for delivery to specific German units or partner forces during World War One.
(more…)
July 6, 2024
Why Germany Lost the Battle of Verdun
The Great War
Published Mar 8, 2024The Battle of Verdun represents the worst of trench warfare and the suffering of the soldiers in the minds of millions – and for many, the cruel futility of the First World War. But why did Germany decide to attack Verdun in the first place and why didn’t they stop after their initial attack failed?
(more…)