Elizabeth Nickson calls for the destruction of the deep state, Cato the Censor-style: salt the earth and leave no stone standing upon another stone:
There has been some argument in my house about Trump’s tariffs on Canada, and indeed the rest of the world. I’m on the American side; why on earth should the Americans pay for everything? Because they do. They pay for Europe’s defence, they allow every single country to tariff American products while allowing their goods in for pennies. When anyone, anywhere is in trouble, who do they call? The Yanks. Where do the pleas of all the desperate people all over the world land? America. Who did the Israeli captives hope for? Trump and the Americans. (Actually just Trump. They didn’t think that the Biden people would lift a finger. Which they didn’t.)
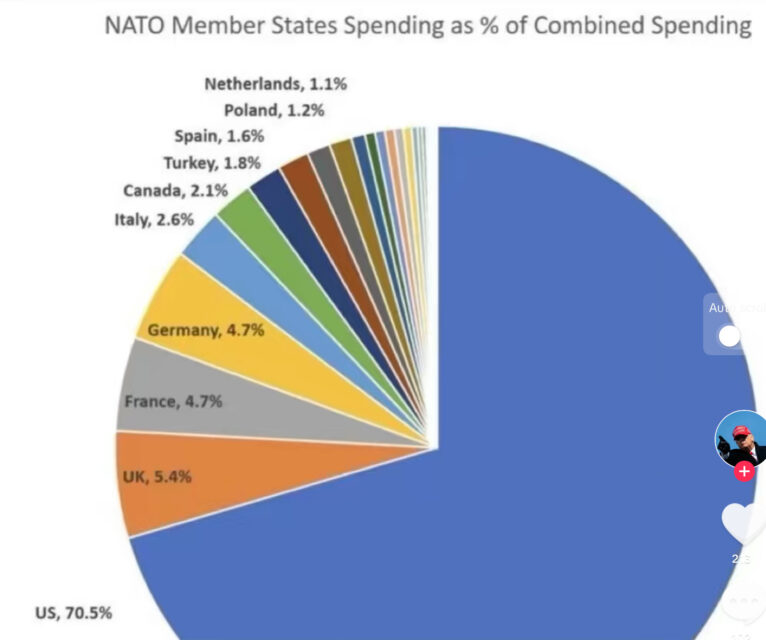
Please explain why these countries below, numbering 550 million people, cannot defend themselves?
Why can’t they defend themselves? They are broke.
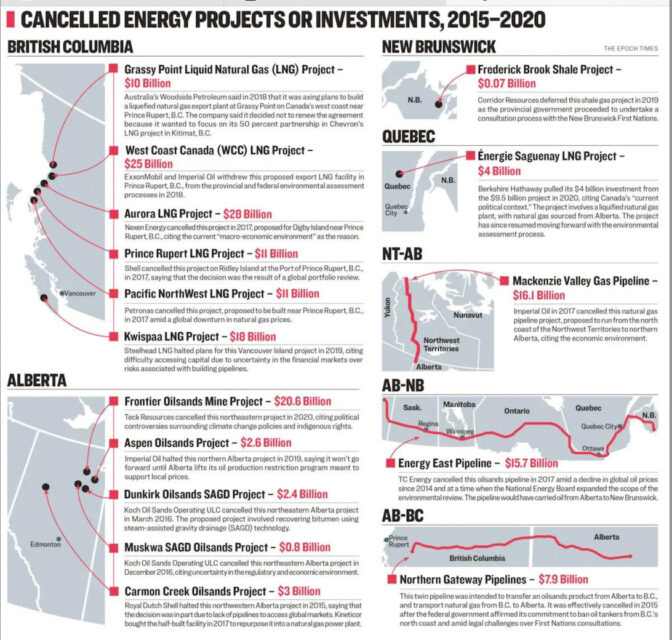
The following represents $150 billion in missed opportunity in the last FIVE years. Canada is so broke, it is broke-ass broke; it is a shriveling carbuncle on the American economy. We send 80% of our exports to you because we are TOO DAMNED LAZY to develop our own country.
If we had built those projects, Canada would be rich, the middle class would be crackling along, creativity would have soared and we would actually be proud. No one is proud of Canada except for the people paid to bloviate or who hope to be paid to bloviate, and those too stupid to bloviate. The rest of us are sullen and angry and so frustrated we don’t know what to do with ourselves.
But no. Climate Change. Look, I am sorry to say this, but anyone who “believes” in climate change being somehow catastrophic is stupid, malignant or has not done the required reading. Which means lazy. Which means childlike. There is no there there. Climate alarmism is nonsense, it is bullshit, it is utter crap made up by subsidized kids looking for “significance” and an endless supply of taxpayer dollars. The science is far too new to be reliable, there are thousands of real (not NGO) scientists in opposition to it and the policy implications are so vast we are looking at a new feudalism. Anyone promoting climate change is unserious.
Childhood is where we are. Canada is the only country in the Western Hemisphere which exacts a crippling carbon tax. And this:
The above is a perfect illustration of vanity, of a detachment from reality. And the only way people can detach from reality is that they are subsidized by the Americans. This means the Heartland people, the Flyover people. Those subsidies to the world added to a massive, unsustainable, insane, debt of thirty-seven trillion, created a giant fuzzy rainbow coloured cloud inhabited by perpetual children built by ghastly people like Samantha Powers, Al Gore, Hillary Clinton, and their legion of sick, larcenous, pedophile supporters, the ferociously stupid women on the east coat of America, the idiots at all the Ivies, and the two million federal workers who are about to be reduced by, I wish, 50%.