Army University Press
Published Jan 22, 2024Created for the Department of Command and Leadership and the Department of Military History at the US Army Command and General Staff College, The Korean War: The First Year is a short documentary focused on the major events of the Forgotten War. Designed to address the complex strategic and operational actions from June 1950 – June 1951, the film answers seven key questions that can be found in the timestamps below. Major events such as the initial North Korean invasion, the defense of the Pusan Perimeter, the Inchon landing, and the Chinese intervention are discussed.
Timestamps:
1. Why are there Two Koreas? – 00:25
2. Why did North Korea Attack South Korea? – 02:39
3. How did the UN stop the Communist invasion? – 06:30
4. Why did MacArthur attack at Inchon? – 10:24
5. Why did the UN attack into North Korea? – 14:27
6. Why did China enter the Korean War? – 18:51
7. How did the UN stop the Communist invasion … again? – 21:44
January 23, 2024
The Korean War: The First Year
January 22, 2024
“He lied. That was what he had to say at the time.”
At First Things, Robert Carle reviews Tania Brannigan’s Red Memory: The Afterlives of China’s Cultural Revolution:
At a 1979 White House dinner, actress Shirley MacLaine told Deng Xiaoping, China’s new leader and the guest of honor that evening, about a Chinese scientist she had met. He said that he’d been happier and more productive when he worked on a Chinese farm. Deng cut her short: “He lied. That was what he had to say at the time.” Deng spent three years working in a tractor factory during the Cultural Revolution, and he refused to romanticize it. The memoirs of Cultural Revolution survivors written in the 1980s echo Deng’s view that it was a brutal and pointless experiment.
Today, there is widespread nostalgia in China for the Cultural Revolution. President Xi Jinping has reflected positively on the time he spent exiled in the remote town of Liangjiahe in Shaanxi province, living in a cave, hauling coal carts, carrying manure, building dikes, enduring bitter winters, flea bites, and hunger. This experience, Xi claims, bonded him with China’s common people and prepared him to be an empathetic ruler. Liangjiahe is now a “red tourist” attraction where students can visit Xi’s old home and admire the well he built.
Xi’s glamorization of the Cultural Revolution is reflected in Beijing’s chic dining scene. In Red Classics Restaurant, for example, waitresses in Red Guard uniforms serve meat and vegetables in plain style to invoke an era of stark living. You can have a fully themed wedding in this restaurant, posing for photos in matching Mao suits on a tractor parked in one corner.
In her new book, Red Memory, Tania Branigan describes the clashing memories of the Cultural Revolution. Those who suffered under the brutality of the Red Guard describe an infernal decade when Mao turned his murderous paranoia on his own people, leading them to tear each other to pieces. Children denounced their parents, and students murdered their teachers. In Mao’s campaign against the four “olds” (Old Ideas, Old Culture, Old Customs, and Old Habits), traditional Chinese culture and morality became targets for destruction.
But Branigan also tells stories of people who are nostalgic for a time when life was more austere and when people lived for a cause other than individualism and materialism. Some former Red Guards have set up a bookstore and website called Utopia. Others organize trips to North Korea to admire society as it should be, or set up rural communes for students. One Utopia co-founder, a professor, made headlines for slapping an eighty-year-old “traitor” who had dared to criticize Mao.
Red Memory is full of chilling stories of brutality and betrayal. Fang Zhongmou witnessed the torture and beating of her husband by adolescent Red Guards. She endured years of interrogations at her workplace because her father had been a landowner. One night in 1970, while doing laundry at home, she launched into a tirade against Mao. Her son told her, “If you go against my dear Chairman Mao, I will smash your dog head in”. He reported her to officials. After two months of violent “struggle sessions”, Fang was executed. The son grew up to be a guilt-ridden adult who agonizes over his mother’s gravesite.
Song Binbin was eighteen when she viciously denounced her school’s deputy principal, Bian Zhongyun. Bian had told the students that they should run out of the building in the event of an earthquake. Because she did not instruct the students to take Mao portraits with them, Red Guards hunted her down and beat her to death with nailed clubs. As the Cultural Revolution swept China, beatings and executions became increasingly baroque. Students poured boiling water over teachers’ heads and made them swallow excrement, crawl over embers, drink ink and glue, and beat one another.
QotD: Mao’s theory of “protracted war” as adapted to Vietnamese conditions by Võ Nguyên Giáp
The primary architect of Vietnam’s strategy, initially against French colonial forces and then later against the United States and the US-backed South Vietnamese (Republic of Vietnam or RVN) government was Võ Nguyên Giáp.
Giáp was facing a different set of challenges in Vietnam facing either France or the United States which required the framework of protracted war to be modified. First, it must have been immediately apparent that it would never be possible for a Vietnamese-based army to match the conventional military capability of its enemies, pound-for-pound. Mao could imagine that at some point the Red Army would be able to win an all-out, head-on-head fight with the Nationalists, but the gap between French and American capabilities and Vietnamese Communist capabilities was so much wider.
At the same time, trading space for time wasn’t going to be much of an option either. China, of course, is a very large country, with many regions that are both vast, difficult to move in, and sparsely populated. It was thus possible for Mao to have his bases in places where Nationalist armies literally could not reach. That was never going to be possible in Vietnam, a country in which almost the entire landmass is within 200 miles of the coast (most of it is far, far less than that) and which is about 4% the size of China.
So the theory is going to have to be adjusted, but the basic groundwork – protract the war, focus on will rather than firepower, grind your enemy down slowly and proceed in phases – remains.
I’m going to need to simplify here, but Giáp makes several key alterations to Mao’s model of protracted war. First, even more than Mao, the political element in the struggle was emphasized as part of the strategy, raised to equality as a concern with the military side and fused with the military operation; together they were termed dau tranh, roughly “the struggle”. Those political activities were divided into three main components. Action among one’s own people consisted of propaganda and motivation designed to reinforce the will of the populace that supported the effort and to gain recruits. Then, action among the enemy people – here meaning Vietnamese who were under the control of the French colonial government or South Vietnam and not yet recruited into the struggle – a mix of propaganda and violent action to gain converts and create dissension. Finally, action against the enemy military, which consisted of what we might define as terroristic violence used as message-sending to negatively impact enemy morale and to encourage Vietnamese who supported the opposition to stop doing so for their own safety.
Part of the reason the political element of this strategy was so important was that Giáp knew that casualty ratios, especially among guerrilla forces – on which, as we’ll see, Giáp would have to rely more heavily – would be very unfavorable. Thus effective recruitment and strong support among the populace was essential not merely to conceal guerrilla forces but also to replace the expected severe losses that came with fighting at such a dramatic disadvantage in industrial firepower.
That concern in turn shaped force-structure. Giáp theorized an essentially three-tier system of force structure. At the bottom were the “popular troops”, essentially politically agitated peasants. Lightly armed, minimally trained but with a lot of local knowledge about enemy dispositions, who exactly supports the enemy and the local terrain, these troops could both accomplish a lot of the political objectives and provide information as well as functioning as local guerrillas in their own villages. Casualties among popular troops were expected to be high as they were likely to “absorb” reprisals from the enemy for guerrilla actions. Experienced veterans of these popular troops could then be recruited up into the “regional troops”, trained men who could now be deployed away from their home villages as full-time guerrillas, and in larger groups. While popular troops were expected to take heavy casualties, regional troops were carefully husbanded for important operations or used to organize new units of popular troops. Collectively these two groups are what are often known in the United States as the Viet Cong, though historians tend to prefer their own name for themselves, the National Liberation Front (Mặt trận Dân tộc Giải phóng miền Nam Việt Nam, “National Liberation Front for South Vietnam”) or NLF. Finally, once the French were forced to leave and Giáp had a territorial base he could operate from in North Vietnam, there were conventional forces, the regular army – the People’s Army of Vietnam (PAVN) – which would build up and wait for that third-phase transition to conventional warfare.
The greater focus on the structure of courses operating in enemy territory reflected Giáp’s adjustment of how the first phase of the protracted war would be fought. Since he had no mountain bases to fall back to, the first phase relied much more on political operations in territory controlled by the enemy and guerrilla operations, once again using the local supportive population as the cover to allow guerrillas and political agitators (generally the same folks, cadres drawn from the regional troops to organize more popular troops) to move undetected. Guerrilla operations would compel the less-casualty-tolerant enemy to concentrate their forces out of a desire for force preservation, creating the second phase strategic stalemate and also clearing territory in which larger mobile forces could be brought together to engage in mobile warfare, eventually culminating in a shift in the third phase to conventional warfare using the regional and regular troops.
Finally, unlike Mao, who could envision (and achieve) a situation where he pushed the Nationalists out of the territories they used to recruit and supply their armies, the Vietnamese Communists had no hope (or desire) to directly attack France or the United States. Indeed, doing so would have been wildly counter-productive as it likely would have fortified French or American will to continue the conflict.
That limitation would, however, demand substantial flexibility in how the Vietnamese Communists moved through the three phases of protracted war. This was not something realized ahead of time, but something learned through painful lessons. Leadership in the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV = North Vietnam) was a lot more split than among Mao’s post-Long-March Chinese Communist Party; another important figure, Lê Duẩn, who became general secretary in 1960, advocated for a strategy of “general offensive” paired with a “general uprising” – essentially jumping straight to the third phase. The effort to implement that strategy in 1964 nearly overran the South, with ARVN (Army of the Republic of Vietnam – the army of South Vietnam) being defeated by PAVN and NLF forces at the Battles of Bình Giã and Đồng Xoài (Dec. 1964 and June 1965, respectively), but this served to bring the United States more fully into the war – a tactical and operational victory that produced a massive strategic setback.
Lê Duẩn did it again in 1968 with the Tet Offensive, attempting a general uprising which, in an operational sense, mostly served to reveal NLF and PAVN formations, exposing them to US and ARVN firepower and thus to severe casualties, though politically and thus strategically the offensive ended up being a success because it undermined American will to continue the fight. American leaders had told the American public that the DRV and the NLF were largely defeated, broken forces – the sudden show of strength exposed those statements as lies, degrading support at home. Nevertheless, in the immediate term, the Tet Offensive’s failure on the ground nearly destroyed the NLF and forced the DRV to back down the phase-ladder to recover. Lê Duẩn actually did it again in 1972 with the Eastern Offensive when American ground troops were effectively gone, exposing his forces to American airpower and getting smashed up for his troubles.
It is difficult to see Lê Duẩn’s strategic impatience as much more than a series of blunders – but crucially Giáp’s framework allowed for recovery from these sorts of defeats. In each case, the NLF and PAVN forces were compelled to do something Mao’s model hadn’t really envisaged, which was to transition back down the phase system, dropping back to phase II or even phase I in response to failed transitions to phase III. By moving more flexibly between the phases (while retaining a focus on the conditions of eventual strategic victory), the DRV could recover from such blunders. I think Wayne Lee actually puts it quite well that whereas Mao’s plan relied on “many small victories” adding up to a large victory (without the quick decision of a single large victory), Giáp’s more flexible framework could survive many small defeats on the road to an eventual strategic victory when the will of the enemy to continue the conflict was exhausted.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: How the Weak Can Win – A Primer on Protracted War”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-03-03.
January 21, 2024
The Red Army Overruns Poland! – WW2 – Week 282 – January 20, 1945
World War Two
Published 20 Jan 2024The huge new Soviet offensives charge ahead this week, taking Warsaw and Krakow; in the west the Battle of the Bulge is officially called over … though there is still fighting there. On Luzon, the Americans push out of their beachhead, though there is heavy fighting to secure their flank.
(more…)
January 20, 2024
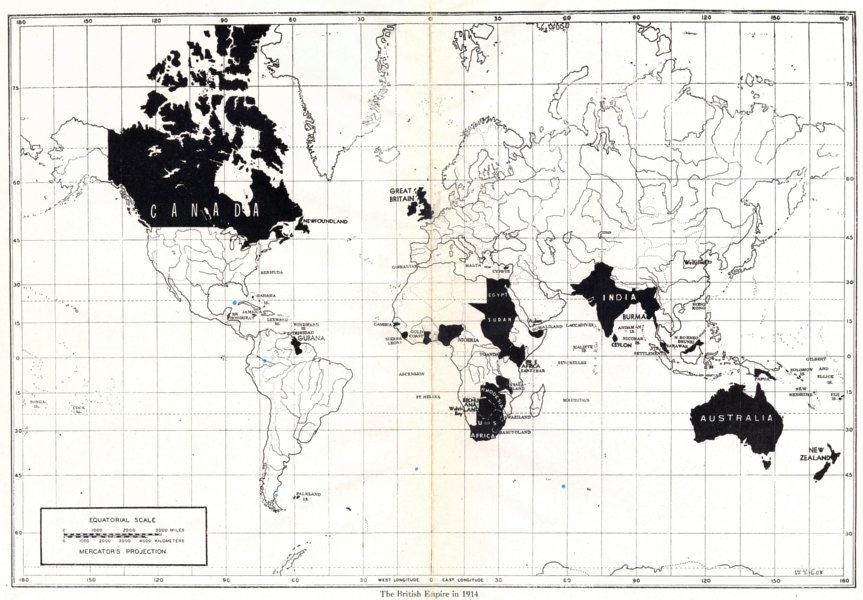
The British Empire would have failed a proper cost-benefit analysis
At the Institute of Economic Affairs, Kristian Niemietz is working on a paper on the economics of empire that, as he shows in this article, indicates that the empire was never a winning economic proposition for Britain as a whole, no matter how well certain well-connected individuals and companies benefitted:
But is it actually true that imperialism makes countries richer? Does imperialism make economic sense?
This question was already hotly debated at the heyday of imperialism. Adam Smith believed that the British Empire would not pass a cost-benefit test:
The pretended purpose of it was to encourage the manufactures, and to increase the commerce of Great Britain. But its real effect has been to raise the rate of mercantile profit, and to enable our merchants to turn into a branch of trade, of which the returns are more slow and distant than those of the greater part of other trades, a greater proportion of their capital than they otherwise would have done […]
Great Britain derives nothing but loss from the dominion which she assumes over her colonies.
He believed that Britain would be better off if it dissolved its Empire:
Great Britain would not only be immediately freed from the whole annual expense of the peace establishment of the colonies, but might settle with them such a treaty of commerce as would effectually secure to her a free trade, more advantageous to the great body of the people, though less so to the merchants, than the monopoly which she at present enjoys.
The liberal free-trade campaigner Richard Cobden agreed:
[O]ur naval force, on the West India station […], amounted to 29 vessels, carrying 474 guns, to protect a commerce just exceeding two millions per annum. This is not all. A considerable military force is kept up in those islands […]
Add to which, our civil expenditure, and the charges at the Colonial Office […]; and we find […] that our whole expenditure, in governing and protecting the trade of those islands, exceeds, considerably, the total amount of their imports of our produce and manufactures.
If imperialism was a loss-making activity – why did Britain and other European colonial empires engage in it for so long?
Smith and Cobden explained it in terms of clientele politics (or Public Choice Economics, as we would say today). Somebody obviously benefited, even if the nation as a whole did not. And the beneficiaries were politically better organised than those who footed the bill.
This proto-Public Choice case against imperialism was not limited to political liberals. Otto von Bismarck, the Minister President of Prussia and future Chancellor of the German Empire, hated liberals in the Smith-Cobden tradition, but he rejected colonialism in terms that almost make him sound like one of them:
The supposed benefits of colonies for the trade and industry of the mother country are, for the most part, illusory. The costs involved in founding, supporting and especially maintaining colonies […] very often exceed the benefits that the mother country derives from them, quite apart from the fact that it is difficult to justify imposing a considerable tax burden on the whole nation for the benefit of individual branches of trade and industry [translation mine].
In his writing about the economics of imperialism, even Michael Parenti, a Marxist-Leninist political scientist (who is, for obvious reasons, popular among Twitter hipsters), sounds almost like a Public Choice economist:
[E]mpires are not losing propositions for everyone. […] [T]he people who reap the benefits are not the same ones who foot the bill. […]
The transnationals monopolize the private returns of empire while carrying little, if any, of the public cost. The expenditures needed […] are paid […] by the taxpayers.
So it was with the British empire in India, the costs of which […] far exceeded what came back into the British treasury. […]
[T]here is nothing irrational about spending three dollars of public money to protect one dollar of private investment – at least not from the perspective of the investors.”
This leads us to a curious situation. Today’s woke progressives disagree with their comrade Parenti on the economics of empire, but they do agree with Britain’s old imperialists, who argued that the Empire was vital for Britain’s prosperity.
January 14, 2024
Soviet and American Massive Attacks – Week 281 – January 13, 1945
World War Two
Published 13 Jan 2024In the East, the Soviets launch a massive series of new offensives. In the West, Monty holds an ill-judged press conference about the Battle of the Bulge. Operation Nordwind, the German offensive in Alsace, continues. In Hungary, there’s house to house fighting as the Red Army besieges Budapest. In Asia, the Allies wrestle with the Kamikazes, begin their landings on Luzon, and advance in Burma.
00:54 Intro
01:12 Recap
01:22 Montgomery’s Press Conference
05:53 Operation Nordwind
07:07 The battle for Hungary
09:38 The huge Soviet offensive begins!
12:22 American landings on Luzon
15:29 Anti-Kamikaze tactics
18:11 Slim’s advance in Burma
21:11 Conclusion
(more…)
January 13, 2024
QotD: Brahmins and Mandarins
Traditional Hindu society knew hundreds of hereditary castes and subcastes, but all broadly fit into four major “varna” (“colors”, strata):
- Brahmins (scholars, clerisy)
- Kshatriya (warriors, rulers)
- Vaishya (traders, skilled artisans)
- Shudras (farmers)
- The un-counted fifth varna are the Dalit (“untouchables”, outcasts in both senses of the word)
Historical edge cases aside, membership in the Brahmin stratum was hereditary, even more so than in the nobility of feudal Europe. At least there, kings might raise a commoner to a knighthood or even the peerage for merit or political expedience: one need not wait for reincarnation into a higher caste.
The Sui dynasty in China, however, took a different route. Seeking both to curb the power of the hereditary nobles and to broaden the available talent pool for administrators, they instituted a system of civil service examinations. With interruptions (e.g. under the Mongol emperor Kublai Khan) and modifications, that system remained in place for thirteen centuries until finally abolished in 1904. Westerners refer to laureates of the Imperial Examinations (from the entry-level shengyuan to the top-level jinshi) by the collective term Mandarins. Ironically, this term comes not from any Chinese dialect but (via Malay and Portuguese) from the Sanskrit word mantri (counselor, minister) — cf. the Latin mandatum (command) and its English cognate “mandate”.
Initially, the exams were limited to the scholar and yeoman farmer classes: with time, they were at least in theory opened up to all commoners in the “four occupations” (scholars, farmers, artisans, merchants), with jianmin (those in “base occupations”) still excluded. The process also was ostensibly fair: exams were written, administered at purpose-built examination halls with individual three-walled examination cubicles to eliminate cribbing. Moreover, exam copies were identified by number rather than by name. […]
In practice, the years of study and the costs of hiring tutors for the exam limited this career path to the wealthy. Furthermore, the success rate was very low (between 0.03% and 1%, depending on the source) so one had better have a fallback trade or independent wealth. In some cases, rich families who for some reason were barred from the exams would sponsor a bright student from a poor family. Once the student became a government official, he would owe favors to the sponsor.
Moreover, the subject matter of the exam soon became ossified and tested more for conformity of thought, and ability to memorize text and compose poetry in approved forms, than for any skill actually relevant to practical governance. (Hmm, artists or scholars in a narrow abstruse discipline being touted as authorities on economic or foreign policy: verily, there is nothing new under the sun.)
Nitay Arbel, “Brahmandarins”, According to Hoyt, 2019-10-08.
January 11, 2024
Pushing back against the Colonialism Narrative
At Samizdata, Brendan Westbridge praises Nigel Biggar’s 2023 book Colonialism: A Moral Reckoning:
He examines the various claims that the “de-colonisers” make: Amritsar, slavery, Benin, Boer War, Irish famine. In all cases he finds that their claims are either entirely ungrounded or lack vital information that would cast events in a very different light. Amritsar? Dyer was dealing with political violence that had led to murder. Some victims had been set alight. Anyway, he was condemned for his actions by the British authorities and, indeed, his own standing orders. Slavery? Everyone had it and Britain was the first to get rid of it. Benin? They had killed unarmed ambassadors. Irish famine? They tried to relieve it but they were quite unequal to the size of the task. In the case of Benin he comes very close to accusing the leading de-coloniser of knowingly lying. The only one of these where I don’t think he is so convincing is the Boer War. He claims that Britain was concerned about the future of the Cape and especially the Simonstown naval base and also black rights. I think it was the pursuit of gold even if it does mean agreeing with the communist Eric Hobsbawm.
He is far too polite about the “de-colonisers”. They are desperate to hammer the square peg of reality into their round-hole of a theory. To this end they claim knowledge they don’t have, gloss over inconvenient facts, erect theories that don’t bear scrutiny and when all else fails: lie. Biggar tackles all of these offences against objectivity with a calmness and a politeness that you can bet his detractors would never return.
The communists – because they are obsessed with such things and are past masters at projection – like to claim that there was an “ideology” of Empire. Biggar thinks this is nonsense. As he says:
There was no essential motive or set of motives that drove the British Empire. The reasons why the British built an empire were many and various. They differed between trader, migrant, soldier, missionary, entrepreneur, financier, government official and statesman. They sometimes differed between London, Cairo, Cape Town and Calcutta. And all of the motives I have unearthed in this chapter were, in themselves, innocent: the aversion to poverty and persecution, the yearning for a better life, the desire to make one’s way in the world, the duty to satisfy shareholders, the lure of adventure, cultural curiosity, the need to make peace and keep it, the concomitant need to maintain martial prestige, the imperative of gaining military or political advantage over enemies and rivals, and the vocation to lift oppression and establish stable self-government. There is nothing morally wrong with any of these. Indeed, the last one is morally admirable.
One of the benefits of the British Empire is that it tended to put a stop to local wars. How many people lived because of that? But that leads us on to another aspect. Almost no one ever considers what went on before the Empire arrived. Was it better or worse than went before it? Given that places like Benin indulged in human sacrifice, I would say that in many cases the British Empire was an improvement. And if we are going to talk about what went before what about afterwards? He has little to say about what newly-independent countries have done with their independence. The United States, the “white” (for want of a better term) Commonwealth and Singapore have done reasonably well. Ireland is sub-par but OK. Africa, the Caribbean and the Indian sub-continent have very little to show for themselves. This may explain why Britain needed very few people to maintain the Empire. At one point he points out that at the height of the Raj the ratio of Briton to native was 1 to 1000. That implies a lot of consent. Tyrannies need a lot more people.
The truth of the matter is that talk of reparations is rooted in the failure of de-colonisation. If Jamaica were a nicer place to live than the UK, if Jamaica had a small boats crisis rather than the UK then no one would be breathing a word about reparations or colonial guilt. All this talk is pure deflection from the failure of local despots to make the lives of their subjects better.
Biggar has nothing to say about what came after the empire and he also has little to say about how it came about in the first place – so I’ll fill in that gap. Britain acquired an empire because it could. Britain was able to acquire an Empire because it mastered the technologies needed to do it to a higher level and on a greater scale than anyone else. Britain mastered technology because it made it possible to prosper by creating wealth. That in itself was a moral achievement.
January 8, 2024
QotD: Nomadic cultures’ territorial needs
This bears little resemblance to the strategic concerns of historical nomads. As a direct consequence of failing to understand the subsistence systems that nomads relied on, [George R.R.] Martin [in his descriptions of the Dothraki nomad culture] has also rendered their patterns of warfare functionally unintelligible.
The chief thing that nomads, both Great Plains Native Americans and Eurasian Steppe Nomads used violence to secure control of is the one thing the Dothraki never do: territory. To agrarian elites (who write most of our sources) and modern viewers, the vast expanses of grassland that nomads live on often look “empty” and “unused” (and thus not requiring protection), but that’s not correct at all. Those “empty” grasslands are very much in use; the nomads know this and are abundantly willing to defend those expanses of grass with lethal force to keep out interlopers. Remember: the knife’s edge of subsistence for nomads is very thin indeed, so it takes only a small disruption of the subsistence system to push the community into privation.
For the Eurasian Steppe nomad, the grass that isn’t near their encampment is in the process of regrowth for the season or year when it will be near their encampment and need to support their herds. Allowing some rival nomadic group to move their sheep and their horses over your grassland – eating the essential grass along the way – means that grass won’t be there for your sheep and your horses when you need it; and when the sheep starve, so will you. So if you are stronger than the foreign interloper, you will gather up all of your warriors and confront them directly. If you are weaker, you will gather your warriors and raid the interloper, trying to catch members of their group when they’re alone, to steal horses and sheep (we’ll come back to that); you are trying to inflict a cost for being on your territory so that they will go away and not come back.
The calculus for nomadic hunters like the Great Plains Native Americans is actually fairly similar. Land supports bison, bison support tribal groupings, so tribal groups defend access to land with violent reprisals against groups that stray into their territory or hunt “their” bison. And of course the reverse is true – these groups aren’t merely looking to hold on to their own territory, but to expand their subsistence base by taking new territory. Remember: the large tribe is the safe tribe; becoming the large tribe means having a larger subsistence base. And on either the plains or the steppe, the subsistence base is fundamentally measured in grass and the animals – be they herded sheep or wild bison – that grass supports. Both Secoy and McGinnis (op. cit.) are full of wars of these sorts on the Great Plains, where one group, gaining a momentary advantage, violently pushes others to gain greater territory (and thus food) for itself. For instance, Secoy (op. cit., 6-32) discusses how access to horses allowed the Plains Apache to rapidly violently expand over the southern Plains in the late 17th century, before being swept off of them by the fully nomadic Ute and Comanche in the first third of the 18th. As McGinnis notes (op. cit., 16ff), on the Northern Plains, prior to 1800 it initially was the Shoshone who were dominant and expanding, but around 1800 began to be pushed out by the Blackfoot, who in turn would, decades later, be pushed by the expanding Sioux.
This kind of warfare is different from the way that settled, agrarian armies take territory. Generally, the armies of agrarian states seek to seize (farm-) land with its population of farmers mostly intact and exert control both over the land and the people subsequently in order to extract the agricultural surplus. But generally (obviously there are notable exceptions) nomads both lack the administrative structures to exert that kind of control and are also very able to effectively resist that sort of control themselves (it is hard for even nomads to tax nomads), making “empire building” along agrarian lines difficult or undesirable (unless you are the Mongols). So instead, polities are trying to inflict losses (typically more through raiding and ambush than battle). Since rivals will tend to avoid areas that become unsafe due to frequent raiding, the successful tribe can essentially push back an opposing tribe with frequent raids. In extreme circumstances, a group may feel threatened enough to get up and move entirely – which of course creates conflict wherever they go, since their plan is to disposess the next group along the way of their territory.
Within that security context, larger scale groupings – alliances, confederations, and super-tribal “nations” – are common. On the Eurasian Steppe, such alliances tended to be personal, although there was a broad expectation that a given ethnic grouping would work together against other ethnic groupings (an expectation that Chinggis actually worked very hard, once he became the Great Khan of a multi-ethnic “Mongol” army, to break up through the decimal organization system; this reorganization is part of what made the Mongol Empire so much more successful than previous Steppe confederations). Likewise, even a cursory look at the Native Americans of the Great Plains produces both a set of standard enmities (the Sioux and the Crow, for instance) but also webs of peace agreements, treaties, alliances, confederations and so on. The presence of British, French, Spanish and American forces (both traders and military forces) fit naturally into that system; the Plains Apache allied with the Spanish against the Comanche, the Crow with the United States against the Sioux and so on. Such allies might not only help out in a conflict, but also deter war and raiding because their strength and friendship made lethal retaliation likely (don’t attack someone allied to Chinggis Khan and expect to survive the experience …).
Exactly none of that complexity appears with the Dothraki, who have no alliances, no peace agreements, no confederations and no territory to attack or defend. Instead, the Dothraki simply sail around the grass sea, fighting whenever they should chance to meet.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: That Dothraki Horde, Part IV: Screamers and Howlers”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-01-08.
January 7, 2024
1945 Begins! – WW2 – Week 280 – January 6, 1945
World War Two
Published 6 Jan 2024The Germans launch a new offensive, Operation Nordwind, in Alsace, even as their offensive in the Ardennes is stalled. The Allies in the west don’t just have to fight these, they are also having serious issues amongst themselves in High Command that threaten their unity. The siege of Budapest is in full swing and is a hard, fought, bloody battle, and the Soviets and the Americans have big plans for new offensives soon to kick off in Eastern Europe and the Philippines (respectively).
00:00 INTRO
01:20 The Siege of Budapest
04:51 German defense plans in the East
06:38 Montgomery versus Eisenhower
08:32 Eisenhower versus the French
10:35 New German Offensive in Alsace
13:49 Monty’s plans for the press
15:04 The Battle of the Bulge
17:45 Preparations for the Luzon Landings
20:56 Notes to end the week
21:51 Summary and conclusion
(more…)
QotD: The US Army between 1945 and 1950
One aftermath of the Korean War has been the passionate attempt in some military quarters to prove the softness and decadence of American society as a whole, because in the first six months of that war there were wholesale failures. It has been a pervasive and persuasive argument, and it has raised its own counterargument, equally passionate.
The trouble is, different men live by different myths.
There are men who would have a society pointed wholly to fighting and resistance to Communism, and this would be a very different society from the one Americans now enjoy. It might succeed on the battlefield, but its other failures can be predicted.
But the infantry battlefield also cannot be remade to the order of the prevailing midcentury opinion of American sociologists.
The recommendations of the so-called Doolittle Board of 1945-1946, which destroyed so much of the will — if not the actual power — of the military traditionalists, and left them bitter, and confused as to how to act, was based on experience in World War II. In that war, as in all others, millions of civilians were fitted arbitrarily into a military pattern already centuries old. It had once fitted Western society; it now coincided with American customs and thinking no longer.
What the Doolittle Board tried to do, in small measure, was to bring the professional Army back into the new society. What it could not do, in 1946, was to gauge the future.
By 1947 the United States Army had returned, in large measure, to the pattern it had known prior to 1939. The new teen-agers who now joined it were much the same stripe of men who had joined in the old days. They were not intellectuals, they were not completely fired with patriotism, or motivated by the draft; nor was an aroused public, eager to win a war, breathing down their necks.
A great many of them signed up for three squares and a sack.
Over several thousand years of history, man has found a way to make soldiers out of this kind of man, as he comes, basically unformed, to the colors. It is a way with great stresses and great strains. It cannot be said it is wholly good. Regimentation is not good, completely, for any man.
But no successful army has been able to avoid it. It is an unpleasant necessity, seemingly likely to go on forever, as long as men fight in fields and mud.
One thing should be made clear.
The Army could have fought World War III, just as it could have fought World War II, under the new rules. During 1941-1945 the average age of the United States soldier was in the late twenties, and the ranks were seasoned with maturity from every rank of life, as well as intelligence.
In World War III, or any war with national emotional support, this would have again been true. Soldiers would have brought their motivation with them, firmed by understanding and maturity.
The Army could have fought World War III in 1950, but it could not fight Korea.
T.R. Fehrenbach, This Kind of War: A Study in Unpreparedness, 1963.
January 5, 2024
QotD: Hong Kong and the “league table” of world economic freedom
The Fraser Institute issued its annual Economic Freedom of the World report last week. It didn’t get much attention; it never does these days. Considered as a league table, the report is very boring and static, and makes poor copy.
The same countries typically appear at the top from year to year, and are separated mostly by microscopic, irrelevant differences. For 2017, whence the data in the new report come, Canada sat in eighth place just a hair above Australia and a hair below the U.K. Ascending to the top, we meet other siblings of the English-speaking world, Ireland and the U.S.; the Swiss Republic stands in its typical fourth; the relatively wild child of the Commonwealth, New Zealand, remains third; and then, in the top two places, you have the twin beacons of radical economic freedom, Singapore and Hong Kong.
Ah, yes, Hong Kong. The Special Administrative Region seems, for now, to have won a short-term victory in its struggle to preserve the conditions of its reunion with mainland China. This has not, ostensively, been a struggle over economic freedom per se, but it is not a coincidence that the rioting ultimately originated in a conflict over bookstores. It is mighty hard to draw a line where “economic” freedom stops and purely personal or civil freedoms begin, and the design of the index reflects this. It has a large basic rule-of-law component, includes mobility rights under the free trade factor, and takes points away for imposing military conscription. (This is surely a tiny tribute to the shade of Milton Friedman, who was one of the originators of the index.)
Even if Hong Kong’s immediate quarrel with China has been resolved for now, it is only a manifestation of what is likely to be a longer game. Clever columnists always like exoticizing talk about how the Chinese think in generations, but when it comes to Hong Kong, the cliché has weight. The 2019 riots, in showing how attached young HKers are to their distinct identity and to the English-speaking world, have revealed a nightmarish, even delegitimizing failure by the Chinese Communists. Mainland influence on Hong Kong education and politics has been used with the intention of prolonging and deepening the spirit of ’97; China, so often deemed the super-country of the future by admiring or fearful intellectuals, has tested the results of this effort in the eyes of the world and been made a laughingstock.
Colby Cosh, “Hong Kong’s still king in economic freedom rankings … for now”, National Post, 2019-09-17.
January 1, 2024
Michael Palin’s Great-Uncle Harry
In The Critic, Peter Caddick-Adams reviews Michael Palin’s Great-Uncle Harry:
The first of last week’s volumes nestling on my desk, with its immediately identifiable Ripping Yarns cover illustration, was Sir Michael Palin’s story of his forebear, Great Uncle Harry, who travelled the world but disappeared on the Somme. Here, I felt an immediate connection, not least because Michael, I and his Great Uncle Harry Palin had hauled ourselves through the same academy of learning, Shrewsbury School, though at different times. There are plenty of 1914-18 memoirs and tributes around, but this is one of the best. The further the Great War (as it used to be called) recedes, the more we seem to need to torture ourselves with the staggering sacrifices it involved. I read my copy over Remembrance weekend, which made it doubly poignant.
In Great Uncle Harry, Palin’s gift is to give us the hinterland of his ancestor. Many First World War authors, here I could mention the great Lyn Macdonald, Richard Holmes and Martin Middlebrook, all of whom I place on pedestals, provide us with erudite studies, laced with gripping eyewitness accounts. I find myself doing the same with 1939-45, but of necessity there is no room to give the brave and the damned a back story. They are parachuted into the text. They fight and live or die and exit stage left. It is refreshing, therefore, to hold the hand of a first war warrior from birth unto death. Palin was lucky his Great Uncle Harry kept a series of notebooks and diaries of his time in khaki, and was able to research his globe-trotting years before battle. Our man was brought up in Herefordshire, and after school drifted out to British India. He had two stints, first working as a railway manager and latterly as overseer on tea plantations. The reader is fortunate that Palin the documentary-maker filmed in both environments and is able to look over his forebear’s shoulder and summon up the Edwardian social standards of the day, with its solar topees and chota pegs (sunset whiskeys), its heat and its dust. Palin the younger’s many diaries and written travelogues, of which I find New Europe (2007) the best, are equally good.
But Great Uncle Harry Palin was restless. The youngest and most headstrong of seven, he flounced out of each of his two jobs serving the Raj, and ended up trying his hand at farming in New Zealand. There he seemed more settled, but not quite. The Palin under the microscope, notes his great nephew, was one of the first to volunteer for war service with the 12th (Nelson) Regiment, a South Island infantry outfit, in August 1914 and sailed with them overseas, initially to Egypt. There they were absorbed into the Canterbury Battalion, and deployed to Gallipoli, from which Great Uncle Harry emerged without a scratch.
Gallipoli is a conjurer’s name. Now known by the Turks as their Gelibolu Peninsula, overlooking the ancient Hellespont (today’s Dardanelles Strait), its southern tip lies 200 miles from what was then Turkey’s capital, Constantinople, officially Istanbul after 1930. Only since the 1990s has this strategically significant sliver of land, across the Dardanelles from ancient Troy, and guarding entry to the Bosphorus and Black Sea, been opened up for tourists. The 1915 operation was dreamt up by Winston Churchill to break the stalemate of the Western Front. He advocated a naval advance on Constantinople, as a way of knocking the Austro-German alliance out of the war. Such a stratagem would then have offered Paris and London the ability to supply the troops of Tsar Nicholas the Last with modern arms and munitions to prevail against the Central Powers.
Instead of breaking the Western Front, Gallipoli broke Churchill. It was a campaign endlessly refought in the inter-war years, which generally concluded that amphibious warfare had no future, though Lieutenant Colonel George S. Patton in his 1936 General Staff study, The Defense of Gallipoli, found it fascinating. It was one reason why the allies had no maritime landing capability in 1939-40, to Britain’s detriment at Dunkirk, and later Germany’s disadvantage when planning a seaborne assault against southern England. Valuable lessons of what to do, and not to do, had to be relearned before D-Day in 1944 could be a success. My own assessment is right idea, wrong commanders. Gallipoli might have offered the success Churchill desired, but was executed poorly.
The original plan had been to overwhelm Constantinople with battleships, and there is evidence that the Turks were preparing to surrender. However, the Franco-British war fleet encountered German-supplied Krupp cannon along both shores of the Dardanelles and a minefield in the middle, and suffered catastrophic losses. A land campaign was then initiated to clear the Turkish land-based defences. This should have been foreseen and a simultaneous, rather than sequential, maritime-land attack might well have delivered the goods.
Instead, the few Turkish defenders on Gallipoli could see a landing was imminent, called in reinforcements and dug trenches ferociously. On the peninsula, amidst scrub, trench and memorials lie scattered British, Commonwealth, Ottoman and French (yes, they were there too) cemeteries, hinting at stirring tales of derring-do. Last time I was there, I encountered not only rifle cartridges, pieces of pottery rum jars, and shell cases, but human bones. My guide observed, “Probably wild pigs dislodging the topsoil. It happens all the time.” An indication of the 300,000 Allied and 255,000 Turkish killed, wounded and missing in a campaign where illness often took as many as combat wounds. Along the western coast, amidst shards of amphorae from pre-history, lie many wrecks associated with the 1915 campaign in crystal-clear water. It remains high on my recommended battlefields to visit.
December 31, 2023
Budapest Under Siege – WW2 – Week 279 – December 30, 1944
World War Two
Published 30 Dec 2023In the west, the Allies break the siege of Bastogne, but the fight for the Ardennes continues. and British commander Bernard Montgomery is maneuvering to take command of the Western Front ground forces. In Hungary Budapest is cut off by the Soviets and under siege, with hundreds of thousands of civilians still in the city. The fight in Italy is winding down for the winter, but the fight in the Philippines continues. In fact, American landings on Luzon are planned to go off soon.
00:00 INTRO
01:22 The Siege of Bastogne
03:10 The failure of 5th and 6th Panzer Armies
06:11 Montgomery wants command
09:27 Guderian appeals to Hitler, “stop the Ardennes Offensive!”
12:11 Budapest surrounded and under siege
17:04 Wrapping up the Gothic Line Campaign
19:29 Churchill in Athens
20:30 The fight in the Philippines
23:07 SUMMARY
(more…)
December 26, 2023
The awe-inducing power of volcanoes
Ed West considers just how much human history has been shaped by vulcanology, including one near-extinction event for the human race:
A huge volcano has erupted in Iceland and it looks fairly awesome, both in the traditional and American teenager senses of the word.
Many will remember their holidays being ruined 13 years ago by the explosion of another Icelandic volcano with the epic Norse name Eyjafjallajökull. While this one will apparently not be so disruptive, volcano eruptions are an under-appreciated factor in human history and their indirect consequences are often huge.
Around 75,000 years ago an eruption on Toba was so catastrophic as to reduce the global human population to just 4,000, with 500 women of childbearing age, according to Niall Ferguson. Kyle Harper put the number at 10,000, following an event that brought a “millennium of winter” and a bottleneck in the human population.
In his brilliant but rather depressing The Fate of Rome, Harper looked at the role of volcanoes in hastening the end of antiquity, reflecting that “With good reason, the ancients revered the fearsome goddess Fortuna, out of a sense that the sovereign powers of this world were ultimately capricious”.
Rome’s peak coincided with a period of especially clement climatic conditions in the Mediterranean, in part because of the lack of volcanic activity. Of the 20 largest volcanic eruptions of the last 2,500 years, “none fall between the death of Julius Caesar and the year AD 169”, although the most famous, the eruption of Vesuvius in AD 79, did. (Even today it continues to reveal knowledge about the ancient world, including a potential treasure of information.)
However, the later years of Antiquity were marked by “a spasm” of eruptions and as Harper wrote, “The AD 530s and 540s stand out against the entire late Holocene as a moment of unparalleled volcanic violence”.
In the Chinese chronicle Nan Shi (“The History of the Southern Dynasties”) it was reported in February 535 that “there twice was the sound of thunder” heard. Most likely this was a gigantic volcanic explosion in the faraway South Pacific, an event which had an immense impact around the world.
Vast numbers died following the volcanic winter that followed, with the year 536 the coldest of the last two millennia. Average summer temperature in Europe fell by 2.5 degrees, and the decade that followed was intensely cold, with the period of frigid weather lasting until the 680s.
The Byzantine historian Procopius wrote how “during the whole year the sun gave forth its light without brightness … It seemed exceedingly like the sun in eclipse, for the beams it shed were not clear”. Statesman Flavius Cassiodorus wrote how: “We marvel to see now shadow on our bodies at noon, to feel the mighty vigour of the sun’s heat wasted into feebleness”.
A second great volcanic eruption followed in 540 and (perhaps) a third in 547. This led to famine in Europe and China, the possible destruction of a city in Central America, and the migration of Mongolian tribes west. Then, just to top off what was already turning out to be a bad decade, the bubonic plague arrived, hitting Constantinople in 542, spreading west and reaching Britain by 544.
Combined with the Justinian Plague, the long winter hugely weakened the eastern Roman Empire, the combination of climatic disaster and plague leading to a spiritual and demographic crisis that paved the way for the rise of Islam. In the west the results were catastrophic, and urban centres vanished across the once heavily settled region of southern Gaul. Like in the Near East, the fall of civilisation opened the way for former barbarians to build anew, and “in the Frankish north, the seeds of a medieval order germinated. It was here that a new civilization started to grow, one not haunted by the incubus of plague”.