Paul Sellers
Published 4 Feb 2022Mortise guides were once an unknown aid in woodworking realms but they ensure parallelity to the outside face of any mortise you cut and increase your levels of accuracy to near perfection.
Paul invented this guide for woodworking students to improve their mortising work and saw thousands of them succeed in cutting perfect mortises but also found himself reaching for one daily too.
Make metric and imperial sets and customise them for specific jobs too.
——————–
Want to learn more about woodworking?
Go to Woodworking Masterclasses for weekly project episodes: http://bit.ly/2JeH3a9
Go to Common Woodworking for step-by-step beginner guides and courses: http://bit.ly/35VQV2o
http://bit.ly/2BXmuei for Paul’s latest ventures on his blog
——————–
Instagram: http://bit.ly/2oWpy7W
Twitter: http://bit.ly/33S7RFa
Pinterest: http://bit.ly/35X5uTf
June 9, 2022
The Paul Sellers Mortise Guide
QotD: Cicero and the end of the Roman Republic
De legibus (“On the Laws”) along with his earlier work, De re publica (“On the Republic”) show Cicero attempting to grapple with the nature of the Roman Republic and the prospect for reform. In a sense, De re publica looks backwards, with the discussion couched in a fictional dialogue set at the tail end of the life of Scipio Aemilianus (185-129 BC), although Cicero intends the subject – a rumination on the nature of the Republic and its proper workings, based on a discussion of its history – to be applicable in his own time.
De legibus is more aggressively forward looking. Set in Cicero’s own time (it is a dialogue between Cicero, his brother Quintus and their friend Atticus), De legibus first sets out a theory for the general foundation of law […] to use as the basis for a reformed model of the Roman Republic, which is summarized in the third book. Damage to the text means that De legibus cuts off in book three, and there are smaller gaps and fragments in the earlier books as well.
It’s important to get a sense of the situation in the 50s B.C. when Cicero is writing to understand why he feels this is necessary. The previous round of civil wars had ended in 82 B.C., with the victor, the arch-conservative L. Cornelius Sulla, imposing a revised republic with shocking brutality and bloodshed. By the 50s, it would have been clear to anyone paying attention that the peace and apparent stability of the Sullan reforms had been a mirage – the disruptions of the 60s (including the Catilinarian conspiracy, foiled by Cicero) were not one-offs, but merely the first rattlings of the wheels coming off the cart entirely. I don’t want to get too deep into the woods of how exactly this happened; there are any number of good books on the collapse of the Republic which deal with this period (Scullard’s From the Gracchi to Nero (1959) is a venerable and straight-forward narrative of the period; Syme, The Roman Revolution (1939) is probably the most influential – reading both can serve as a foundation for getting into the more recent and often more narrowly directed literature on the topic, note also Flowers, Roman Republics (2011)).
It’s in this context – as the Republic is clearly shaking apart – that Cicero is ruminating on the nature of the Republic, how it functions, what it is for, and how it might be set right. Despite this, Cicero should not be taken for a radical, or even really for much of a reformer; Cicero is a staunch conservative looking to restore the function of the old system, in many cases by a return to tradition as much as the renovation of it. Cicero’s corpus is a plea to save the Republic as it was, not to bury it; it was a plea, of course, that would go unanswered. In a real sense, the Republic died with Cicero.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: A Trip Through Cicero (Natural Law)”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-12-12.
June 8, 2022
The Climate Wars are dead, merely collateral damage from the Russia-Ukraine War
JoNova links to this Foreign Policy article by Ted Nordhous, signfiying the end of a “lame Cold War substitute” as the conflict in Ukraine pushes it decisively off the agenda for most western nations:
Four days after Russian tanks rolled into Ukraine, the U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released its latest assessment of the impacts of global warming. Leading media outlets did their best to pick out the most dire scenarios and findings from the report. But the outbreak of the first major European war since 1945 kept the report off the front page or, at the very least, below the fold. “Climate Change Is Harming the Planet Faster Than We Can Adapt” simply couldn’t compete with “Putin Is Brandishing the Nuclear Option”.
Meanwhile, the headlong rush across Western Europe to replace Russian oil, gas, and coal with alternative sources of these fuels has made a mockery of the net-zero emissions pledges made by the major European economies just three months before the invasion at the U.N. climate summit in Glasgow, Scotland. Instead, questions of energy security have returned with a vengeance as countries already struggling with energy shortages and price spikes now face a fossil fuel superpower gone rogue in Eastern Europe.
In the decades following the end of the Cold War, global stability and easy access to energy led many of us to forget the degree to which abundant energy is existential for modern societies. Growing concern about climate change and the push for renewable fuels also led many to underestimate just how dependent societies still are on fossil fuels. But access to oil, gas, and coal still determines the fate of nations. Two decades of worrying about carbon-fueled catastrophes — and trillions of dollars spent globally on transitioning to renewable power — haven’t changed that basic existential fact.
Virtually overnight, the war in Ukraine has brought the post-Cold War era to a close, not just by ending Europe’s long era of peace, but by bringing basic questions of energy access back to the fore. A new era, marked by geopolitically driven energy insecurity and resource competition, is moving climate concerns down on the list of priorities. If there is a silver lining in any of this, it’s that a shift of focus back to energy security imperatives might not be the worst thing for the climate. Given the scant effect international climate efforts have had on emissions over the past three decades, a turn back toward energy realpolitik — and away from the utopian schemes that have come to define climate advocacy and policymaking worldwide — could actually accelerate the shift to a lower-carbon global economy in the coming decades.
The issue of climate change burst into the global debate just as the Cold War was coming to an end. As one existential threat seemingly receded, another came into view. For much of the international community, particularly the United Nations and its agencies, climate change also became much more than an environmental issue, offering an opportunity to reshape the post-Cold War order to be more equitable, multilateral, and politically integrated.
Nonetheless, when the framework for climate action emerged in the early 1990s, it built on the experience of the Cold War era. U.S.-Soviet arms control agreements became the model for global cooperation on climate change. Just as the superpowers had signed treaties to gradually draw down their nuclear weapons stocks, nations would commit to draw down their emissions. Yet the first major agreement to propose legally binding limits on emissions — the 1997 Kyoto Protocol — was dead from the moment the U.S. Senate unanimously rejected its terms, even before the negotiations had been finalized. Combine U.S. opposition with the understandable reluctance of energy-hungry, fast-developing nations such as China and India to even consider limiting emissions, and the inefficacy of international climate action was set.
The Story Behind the Dambuster Raid – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 7 Jun 2022The thousand-bomber offensive was about to begin as Air-Marshall Harris was assembling his forces. Yet one man was to challenge his strategy. The aircraft designer Barnes Wallis thought: “What if there was a way to destroy Germany’s industrial might not by simply dropping thousands of bombs over its cities, but by a precision strike against its dams?” For this, a new kind of bouncing bomb was to be delivered.
(more…)
With the ACLU no longer fit for purpose, FIRE steps up to protect freedom of speech on and off the campus
Matt Taibbi talks to Nico Perrino about the Foundation for Individual Rights in Education (FIRE) moving beyond protecting free speech for university students to protecting those rights for all Americans:
After years of planning, the Foundation for Individual Rights in Education, better known as FIRE, announced a major expansion Monday, moving “beyond college campuses to protect free speech — for all Americans”.
FIRE was the brainchild of University of Pennsylvania history professor Alan Charles Kors and Boston civil liberties lawyer Harvey A. Silverglate, who co-authored the 1999 book, The Shadow University: The Betrayal of Liberty on America’s Campuses. To the modern reader the book reads like a collection of eccentric cases of students and teachers caught up in speech code issues, most (but not all) being conservative.
To take just one of countless nut-bar examples, Kors and Silverglate told the story of a professor in San Bernardino reprimanded for violating sexual harassment policies because, among other things, “he assigns provocative essays such as Jonathan Swift’s ‘A Modest Proposal'”, as the court case later put it. This was apparently the “cannibalism” portion of the accusation that he delved into such subjects as “obscenity, cannibalism, and consensual sex with children”.
The book triggered such an overwhelming number of responses from other faculty members and students that the pair decided to set up an organization to defend people who found themselves in tricky speech controversies on campuses. They soon found they had plenty of work and, by 2022, enough of a mandate to expand beyond colleges and universities into America at large. According to FIRE CEO Greg Lukianoff, as quoted in a Politico story, the group has already raised over $28 million toward a $75 million “litigation, opinion research and public education campaign aimed at boosting and solidifying support for free-speech values”.
As noted in another story I put out today, FIRE will be doing a lot of stepping into a role semi-vacated by the American Civil Liberties Union. I spoke with Nico Perrino of FIRE, producer and co-director of the excellent documentary about former ACLU chief Ira Glasser (see review here), to ask what the expansion would entail …
MAC 1950: Disassembly & History
Forgotten Weapons
Published 27 Feb 2017Shooting the MAC 1950: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sduZ4…
The PA MAC 1950 (Pistolet Automatique Modele 1950) was the result of a 1946 French effort to standardize on a single military pistol. By the end of WWII, the French military had accumulated a mess of different pistols of French, Spanish, American, and German origin; officially using the Luger, P38, Mauser HSc, 1911 (and A1), 1935A, 1935S, Star, Ruby, and Model 1892 revolver.
Trials were held in 1950, although the outcome was predetermined — this pistol, designed by St Etienne and largely derived from the Model 1935S, was to be the next French military sidearm. A design from the SACM company was also tested, as was a commercially purchased SIG SP47/8, but this was for comparison sake only. In fact, the SIG was the best performer in the testing, with the St Etienne design suffering from cracked parts and durability problems. It would be improved, however, and deemed suitable for adoption by early 1951.
Production began in 1953 at the Chatellerault arsenal (hence the “MAC” name used in the US). All of 221,900 were made by Chatellerault until it was shut down in 1963, when production transferred to St Etienne, where another 120,000 would be made by 1978.
Mechanically, the gun is largely taken form the Browning 1911, with a few improvements. The recoil spring is of a captive design, and the fire control group is all built into a single easily replaced unit (similar to the Tokarev and the 1935S). It is single action only, with hammer-block and magazine safeties and a 9-round magazine of standard 9x19mm ammunition. It is still in French service, having proven to be a reliable and dependable weapon, if outdated by today’s standards.
http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.bbtv.com/collections/forg…
If you enjoy Forgotten Weapons, check out its sister channel, InRangeTV! http://www.youtube.com/InRangeTVShow
QotD: Before the (politically correct) Current Era
I have noticed that the authors (or sub-editors) of practically all academic books, or books with intellectual pretensions, now eschew the use of BC and AD, as if to use them were to be either a member of, or an apologist for, the Spanish Inquisition (as popularly, if erroneously, conceived). They have been replaced by the odiously unctuous BCE and CE.
These new initials stand for Before the Common Era and the Common Era: but common to what, and common to whom? Nobody bothers to explain. By strange but happy coincidence, 300 BC turns out to be the same year as 300 BCE, and AD 400 as CE 400, or 400 CE. Why the change, then?
Do those who have promoted it and obeyed its dictates really think that all those sensitive Zoroastrians, who are supposedly so offended by the old style of dating, are also so stupid that they have failed to notice the coincidence and will therefore fail to be offended by it?
The academics, intellectuals and sub-editors of university presses who use the new style evidently believe that the world is populated by people of extreme psychological fragility, and whose self-esteem, which can be shattered by the mere usage of BC and AD, it is their duty to protect.
Thus does condescension and sentimentality unite with megalomania to produce absurd circumlocutions.
Theodore Dalrymple, “Before the current era”, The Critic, 2022-02-09.
June 7, 2022
D Day: The First Canadian Parachute Battalion and the Battle for the Village of Varaville
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 6 Jun 2022There are so many stories of heroism involved in the massive Operation Overlord, among them the extraordinary story of the little-known first Canadian Parachute Battalion. The lightly armed Canadians were among the first allied soldiers to hit the ground in France on D-Day.
Check out our new community for fans and supporters! https://thehistoryguyguild.locals.com/
This is original content based on research by The History Guy. Images in the Public Domain are carefully selected and provide illustration. As very few images of the actual event are available in the Public Domain, images of similar objects and events are used for illustration.
You can purchase the bow tie worn in this episode at The Tie Bar:
https://www.thetiebar.com/?utm_campai…All events are portrayed in historical context and for educational purposes. No images or content are primarily intended to shock and disgust. Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. Non censuram.
Find The History Guy at:
New community!: https://thehistoryguyguild.locals.com/
Please send suggestions for future episodes: Suggestions@TheHistoryGuy.netThe History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered is the place to find short snippets of forgotten history from five to fifteen minutes long. If you like history too, this is the channel for you.
Awesome The History Guy merchandise is available at:
teespring.com/stores/the-history-guyScript by THG
#history #thehistoryguy #DDay
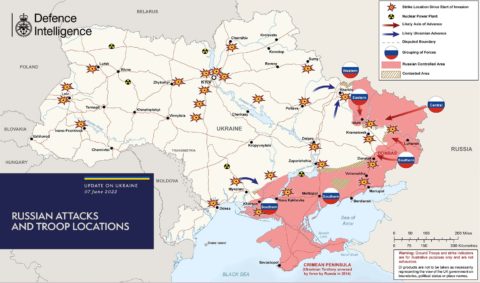
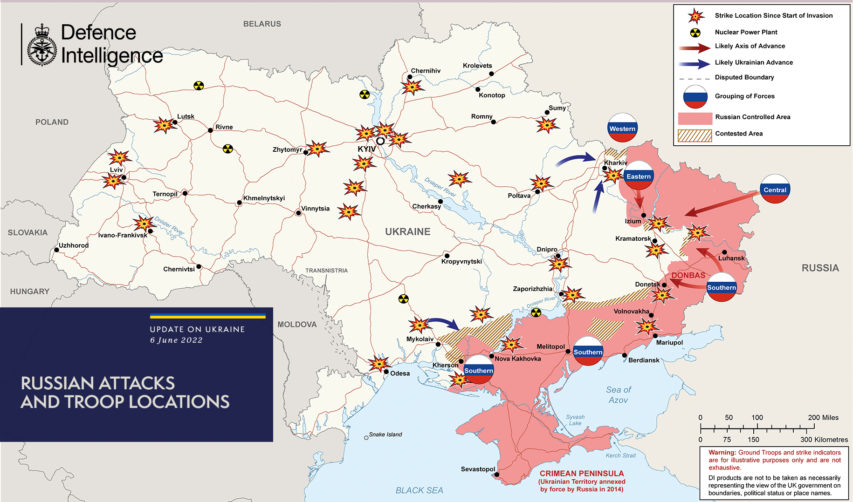
100 days of fighting in Ukraine
In The Line, Andrew Potter rounds up the latest open source data on the Russo-Ukrainian war of 2022, and notes that the briefly enthusiastic western nations — having all posted Ukraine flags on their social media accounts and boycotted Russian vodka — are now noticeably suffering from battle (cheerleading) fatigue and are all rather obviously hoping Ukraine will sue for peace with the Russian aggressor:
We are now just past the one hundred day mark of Vladimir Putin’s insane invasion of Ukraine. But even as the Ukrainian forces are fighting ferociously for Severodonetsk, with president Volodymyr Zelensky making an amazing visit to troops right on the edge of the front lines of the eastern salient, a few Western leaders marked the occasion by suggesting that it’s getting on time for them to think about giving up.
According to Zelensky, Russian forces currently control around one fifth of Ukrainian territory, mostly in the east and the south. As he pointed out last Thursday in an address to the Luxembourg parliament, this is an area that is much larger than the entire Benelux region.
For Russia, this has come at a considerable cost. Reliable open source intelligence estimates put Russian losses at over 31,000 soldiers killed, 3,300 armoured vehicles and another 2,500 trucks destroyed, 200 lost aircraft, 175 helicopters, and 13 ships or boats. All of this for a “special operation” that was supposed to take no more than a long weekend including the victory parade, with the invaders welcomed as liberators.
Dear as this has been for Russia, for Ukrainians the price has been much, much higher. Reliable estimates of Ukrainian military losses are hard to come by, but something around half of the Russian figures is probably in the ballpark, though they could easily be much higher. Zelensky has not been totally shy in talking about losses; the other day he said the Ukrainian forces were losing 60-100 fighters a day, with another 500+ wounded, in fighting in the east.
These are staggering losses (recall that Canada lost 158 soldiers over the course of more than a decade in Afghanistan), but they don’t even begin to compare with what has happened to Ukraine’s civilians and to its cities. This war has been going on for so long, reports of Russian outrages and war crimes now so numerous, that history-making acts of outright barbarism have come and gone from the news pages in a matter of days: Bucha, Kramatorsk, Mariupol … the list goes on and grows. When all this is done, how many dead, deported and disappeared Ukrainians will there be? If it is 50,000 dead in Mariupol alone, a million or more is not out of the question.
For a few days and even weeks, the narrative was that Putin had gravely miscalculated. He clearly expected the Ukrainians to roll over and for the neighbours to just shrug and look the other way. Instead, the Ukrainians fought back and NATO and the West were galvanized into support and action. If Putin was worried about Ukraine bringing NATO and the EU to his doorstep, well, his worst nightmare had come true, with Sweden and Finland applying for expedited admission to the alliance.
But as degraded his army, as inept his generals, as degenerate his kleptocracy might be, Putin has always had a couple of aces up his sleeve: The abiding and reliable perfidy of the Germans and the French, and the increasing inability of the American-led anglosphere to maintain its focus. As Putin sees it, as this war stretches on the Americans and the Brits will lose interest, and the burning desire of Emmanuel Macron and Olaf Scholz to help Putin “save face” — i.e. give Russia some Ukrainian territory — will grow increasingly appealing.
History of Rome in 15 Buildings 12. Santa Maria in Trastevere
toldinstone
Published 2 Oct 2018Wanted: candidate for Pope. Must be a good fundraiser, effective administrator, and shrewd politician. Deep pockets a must. Sanctity negotiable.
The medieval papacy lies at the heart of this twelfth episode of our History of Rome, in which we discuss the catastrophic schism that created the church of Santa Maria in Trastevere.
To see the story and photo essay associated with this video, go to:
https://toldinstone.com/santa-maria-i…
QotD: Mens’ fashion in Europe versus the USA
Men in Europe really like tight clothes. They really like suit jackets that are what Americas would see as a size too small. Even the portly guys have tight jackets and pants. The difference between Americans and Europeans is that the worst sin for a Euro is to be seen as boring, while the worst sin for an American is to be a phony. This shows up in men’s styles. European men look like they spent hours getting ready to go out, while American men want to look like they live in a house with no mirrors or hot water …
The Z Man, “Travelogue: Talinn”, The Z Blog, 2019-04-03.
June 6, 2022
“I ask, sir, what is the militia? It is the whole people except for a few public officials”
George Mason, quoted in the title of this post, had a very expansive view of the US militia. Most Americans of the day did not seem to share this view, as Chris Bray explains:

How Congress may have visualized the individual minutemen who would compose the militia of the United States after 1792.
Postcard image of French’s Concord Minuteman statue via Wikimedia Commons.
In the second Militia Act of 1792, Congress defined a uniform militia in all of the states:
That each and every free able-bodied white male citizen of the respective States, resident therein, who is or shall be of age of eighteen years, and under the age of forty-five years (except as is herein after excepted) shall severally and respectively be enrolled in the militia … That every citizen, so enrolled and notified, shall, within six months thereafter, provide himself with a good musket or firelock, a sufficient bayonet and belt, two spare flints, and a knapsack, a pouch, with a box therein, to contain not less than twenty four cartridges, suited to the bore of his musket or firelock, each cartridge to contain a proper quantity of powder and ball … and shall appear so armed, accoutred and provided, when called out to exercise or into service, except, that when called out on company days to exercise only, he may appear without a knapsack.
So, by federal law, every military-age white male in the country (except men who were exempted by the states, like clergymen) had to report to the local militia commander to be enrolled in their local company, and had to own a long list of equipment, and had to show up to train with that equipment when ordered.
They mostly didn’t. For decades, states reported their militia enrollment to the War Department, and it sometimes appeared that some states, by trying really hard, sometimes almost made it to something in the neighborhood of half participation. In 1826, the Barbour Board — named after Secretary of War James Barbour — evaluated the unmistakable failure of the federally defined uniform militia, and suggested trying again with a smaller group of select militiamen. The board’s report was universally ignored, because by 1826 the federal government, like, couldn’t even: Everyone knew the model of widely shared militia service had failed.
Historians have usually described the failure of universal white male militia service in the early republic as a top-down policy blunder in which political leaders didn’t try hard enough to make the thing work. But a marginal historian named Chris Bray, in a dissertation that generated no excitement of any kind in academia, argued that the universal white male militia obligation was doomed by something else: widespread irritation and popular resistance. The militia obligation reached into the lives of militiamen in ways they didn’t expect and wouldn’t tolerate, so they stopped showing up.
There are many different ways to tell this story, but let’s do it quickly.
Dr. Mengele Takes Command – WAH 063 – June 5, 1943
World War Two
Published 5 Jun 2022Despair in Germany, more death in the Jewish ghettos, and Dr. Mengele tales command in Auschwitz-Birkenau.
(more…)
Very convenient – “Only the cabinet can invoke the Emergencies Act, and if only the cabinet can be privy to the information that informs that decision, only the cabinet can judge whether the cabinet got it right”
In the free-to-cheapskates portion of The Line‘s weekly dispatch, the editors discuss the lack of evidence that the federal government was actually justified in its invokation of the Emergencies Act in February to break up the Freedom Convoy 2022 protests in Ottawa:

A screenshot from a YouTube video showing the protest in front of Parliament in Ottawa on 30 January, 2022.
Photo via Wikimedia Commons.
Your Line editors always understood that the situation in Ottawa (and at the borders) was indeed a crisis. We never doubted that. It was a very serious challenge that required a very serious response. But we have never seen the case for invoking the Emergencies Act. Under the law, which is very clear, a public-order emergency can only be invoked when the emergency cannot be met under existing laws. We really don’t know what, if anything, convinced Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and his cabinet that we had reached that point.
We have always been reasonable about this. The government may well be in possession of classified information that is not publicly known that convinced them, in good faith, that that condition had been met.
The problem is, they’re asking us to take it on their say-so. The position of the federal government thus far, as regards the inquiries and parliamentary reviews that are automatically triggered by invoking the act, is that they will not necessarily disclose all of the information that was known to the cabinet, and they may treat internal discussions as protected by cabinet confidentiality. This is setting up a perfect little loop of zero accountability. Only the cabinet can invoke the Emergencies Act, and if only the cabinet can be privy to the information that informs that decision, only the cabinet can judge whether the cabinet got it right.
You see the problem, right? As noted above, maybe they know something we don’t, and acted reasonably. Or maybe, under enormous political pressure, the PM whipped out the Emergencies Act to show us how big it is. That would be entirely within his character.
Do we think that’s what happened? We don’t know. Can we rule it out? No.
One of the only things the feds have yet said about their decision to invoke the Emergencies Act was that they did it because the police said it was necessary. But [former Ottawa Police Chief Peter] Sloly now says he never asked for it. The interim chief who succeeded him has said the same. The RCMP has said they did not ask for it. Who does that leave?
Maybe it was the OPP. Maybe it was one of the police agencies that patrols parliament itself. We don’t know. They just want us to take their word for it.
We’re sorry, but we don’t. The Emergencies Act is far too powerful to ever be invoked by a government on the basis of, “Trust us”. That’s not how things work in a democracy. And it should alarm all Canadians that the Liberals seem not to realize this, or are at least hoping that you don’t.
How Rescue Flotilla One saved more than 400 men on D-Day
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 2 Jun 2018The History Guy remembers the heroic service of Rescue Flotilla 1 of the United States Coast Guard during D-Day. It is history that deserves to be remembered.
The History Guy uses images that are in the Public Domain. As photos of actual events are sometimes not available, I will often use photographs of similar events and objects for illustration.
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TheHistoryGuy
The History Guy: Five Minutes of History is the place to find short snippets of forgotten history from five to fifteen minutes long. If you like history too, this is the channel for you.
Awesome The History Guy merchandise is available at:
teespring.com/stores/the-history-guyThe episode is intended for educational purposes. All events are presented in historical context.
#ushistory #militaryhistory #thehistoryguy