It would appear that Putin, Xi, etc. are coming to see themselves as the leaders in a worldwide battle against Juggalisme. That might be wishcasting — they are practical men, after all, and let me state, unequivocally and for the record, that I do NOT want to be ruled by Russians or Chinese. They are not my people. Nonetheless, it does seem clear they understand that the source of their problems is beyond what we think of as geopolitics. The United States is “agreement incapable”, as I guess the term d’art is, because it’s not rational, or even predictably irrational.
That was the monarchist critique of representative government that hit closest to home: Foreign policy needs to be supple and responsive; it must be able to move quickly, to make big changes in narrow time windows. In a real crisis, you simply don’t have time to convene a Parliament to debate stuff. N.b. they were saying this in the late 18th century; it’s so much worse now. And another observation from that time that is even truer today: A “democratic” foreign policy can never be consistent. You simply can’t plan long-term when there’s partial to complete governmental overhaul every few years.
That the US managed to muddle through for as long as it did was really a combo of two things: time (as a function of distance), and a near-peer enemy.
Neither of those is integral to the system, and neither is within the system’s control. Until recently, American foreign policy had to take into account the fact that on-the-spot commanders would have to make decisions on their own recognizance. Even with phone communications, the man on the ground in the Fulda Gap has to make decisions basically without reference to Washington. It forced him to be conservative — in other words, it discouraged adventurism.
Same way with the near-peer enemy. The looming shadow of the USSR forced regular reality checks inside the US Apparat. A whole bunch of possibilities were foreclosed by default — our response to any given situation had to take the likely Soviet reaction into account. As with the time/distance factor, this forced a kind of conservatism that looked a lot like sclerosis, but at least it deterred adventurism.
The history of the later 20th century is the history of those constraints being removed. In Vietnam, for instance, you had LBJ and McNamara sitting in a room in the White House, personally directing airstrikes in near-realtime. If “news” reports are to be believed, Obama was on the horn with that SEAL team going after Bin Laden right up to the very moment the chopper landed. Knowing these things are technically possible is catnip to politicians — they already assume they’re omnicompetent, and so now they want to be “advising” the commanding general even as the battle rages.
And if that’s catnip, then the end of the USSR was catnip on steroids. Why not play fuck-fuck games everywhere, all at once? Who’s gonna stop us? China? They chose to pass. They saw what happened to the USSR when it locked itself into an ideological death spiral vis-a-vis the Struggle Against International Capitalism. American policymakers only understand Soviet-style bluff and bluster. The Chinese play the long game.
NOT because they’re Inscrutable Orientals, I hasten to add — they’re as Juggalicious as our Clowns, in their way — but because the generation currently in power came up hard, and so they are adults. That’s all. They are not spoiled, petulant children. The next generation of Chinese leadership — assuming we live to see it — will really be something, and not in a good way.
So, what does Putin want? I dunno, and I’m not sure he knows, because I’m not sure he can know. I’m sure his broadest goal is “to stop getting fucked with by idiots”, but how can that be achieved? There shall be no durable peace in this world until there is Regime Change in [Washington, DC], and I’m not talking about the other half of the Uniparty winning an election or two. I think Putin knows that, but what can he really do about it? I think he’s going to be forced to annex a fair amount of territory and set up a totally demilitarized buffer zone. It won’t work, but it’s the least-worst practical option.
Severian, “Friday Mailbag”, Founding Questions, 2024-02-09.
May 12, 2024
QotD: What is Putin’s endgame in Ukraine?
January 22, 2024
“He lied. That was what he had to say at the time.”
At First Things, Robert Carle reviews Tania Brannigan’s Red Memory: The Afterlives of China’s Cultural Revolution:
At a 1979 White House dinner, actress Shirley MacLaine told Deng Xiaoping, China’s new leader and the guest of honor that evening, about a Chinese scientist she had met. He said that he’d been happier and more productive when he worked on a Chinese farm. Deng cut her short: “He lied. That was what he had to say at the time.” Deng spent three years working in a tractor factory during the Cultural Revolution, and he refused to romanticize it. The memoirs of Cultural Revolution survivors written in the 1980s echo Deng’s view that it was a brutal and pointless experiment.
Today, there is widespread nostalgia in China for the Cultural Revolution. President Xi Jinping has reflected positively on the time he spent exiled in the remote town of Liangjiahe in Shaanxi province, living in a cave, hauling coal carts, carrying manure, building dikes, enduring bitter winters, flea bites, and hunger. This experience, Xi claims, bonded him with China’s common people and prepared him to be an empathetic ruler. Liangjiahe is now a “red tourist” attraction where students can visit Xi’s old home and admire the well he built.
Xi’s glamorization of the Cultural Revolution is reflected in Beijing’s chic dining scene. In Red Classics Restaurant, for example, waitresses in Red Guard uniforms serve meat and vegetables in plain style to invoke an era of stark living. You can have a fully themed wedding in this restaurant, posing for photos in matching Mao suits on a tractor parked in one corner.
In her new book, Red Memory, Tania Branigan describes the clashing memories of the Cultural Revolution. Those who suffered under the brutality of the Red Guard describe an infernal decade when Mao turned his murderous paranoia on his own people, leading them to tear each other to pieces. Children denounced their parents, and students murdered their teachers. In Mao’s campaign against the four “olds” (Old Ideas, Old Culture, Old Customs, and Old Habits), traditional Chinese culture and morality became targets for destruction.
But Branigan also tells stories of people who are nostalgic for a time when life was more austere and when people lived for a cause other than individualism and materialism. Some former Red Guards have set up a bookstore and website called Utopia. Others organize trips to North Korea to admire society as it should be, or set up rural communes for students. One Utopia co-founder, a professor, made headlines for slapping an eighty-year-old “traitor” who had dared to criticize Mao.
Red Memory is full of chilling stories of brutality and betrayal. Fang Zhongmou witnessed the torture and beating of her husband by adolescent Red Guards. She endured years of interrogations at her workplace because her father had been a landowner. One night in 1970, while doing laundry at home, she launched into a tirade against Mao. Her son told her, “If you go against my dear Chairman Mao, I will smash your dog head in”. He reported her to officials. After two months of violent “struggle sessions”, Fang was executed. The son grew up to be a guilt-ridden adult who agonizes over his mother’s gravesite.
Song Binbin was eighteen when she viciously denounced her school’s deputy principal, Bian Zhongyun. Bian had told the students that they should run out of the building in the event of an earthquake. Because she did not instruct the students to take Mao portraits with them, Red Guards hunted her down and beat her to death with nailed clubs. As the Cultural Revolution swept China, beatings and executions became increasingly baroque. Students poured boiling water over teachers’ heads and made them swallow excrement, crawl over embers, drink ink and glue, and beat one another.
March 24, 2023
Only a paper dragon?
In UnHerd, Edward Luttwak suggests that China’s military may be much more apparent than real:
The day after Li Keqiang, China’s departing Prime Minister and the last of Beijing’s moderates, called for more market liberalisation to reach this year’s 5% growth target, Xi Jinping responded by announcing a muscle-flexing 7.2% increase in China’s defence spending. That is certainly consistent with Xi’s truculent stance (he replied to Nancy Pelosi’s recent Taiwan visit with a series of ballistic missile launches), and with his official promise to the Communist Party that China will become the world’s dominant power by 2049. But what do those percentages actually mean?
The declared total of China’s newly increased defence budget at 1.56 trillion yuan amounts to $230 billion, according to the current exchange rate. If that were the case, it would mean that China is falling further behind the United States, whose own fiscal 2023 defence spending is increasing to $797 billion (and actually more, since that figure does not include its funding for military construction or the added help to Ukraine).
China’s own figure is also generally assumed by experts to be greatly understated — not by fiddling the numbers one by one, but rather by wholesale exclusions, such as the attribution of research-and-development spending to civilian budgets. Even if a commando team of elite forensic accountants were sent into action to uncover China’s actual defence spending, with another team dispatched to determine what’s missing from the US budget, we would still only have a very loose indication of how much actual military strength China and the United States hope to add.
But one thing can be said with absolute certainty: each side is adding less than the rising numbers imply.
In China’s case, a manpower shortage undercuts military spending in the PLA’s ground forces and naval forces, and soon it will affect manned air units as well. The PLA ground forces now stand at some 975,000, a very small number for a country that has 13,743 miles of borders with 14 countries — including extreme high-mountain borders where internal combustion engines lose power, jungle-covered borders where remote observation is spoiled by foliage, Russian-river borders with endemic smuggling, and the border with India’s Ladakh where an accumulation of unresolved Chinese intrusions have forced each side to deploy substantial ground forces, with at least 80,000 on the Chinese side.Except for Ladakh, which now resembles a war-front, borders are not supposed to be guarded by army troops but by border police. And China did in fact have a substantial dedicated border force, but it was abolished for the same reason that the PLA ground army is so small: a crippling shortage of physically fit Chinese men willing to serve in these regions. Cities and towns, by contrast, do not seem afflicted by such severe manpower shortages, leading to the weird phenomenon on Nepal’s main border crossing to Tibet where, according to an acquaintance, a group of freezing Cantonese city policemen were checking travellers and “guarding the border”. (They said they had been “volunteered” for two months.)
November 30, 2022
The widespread anti-lockdown protests in China … and how Apple is helping suppress them
N.S. Lyons admires what can only be described as potentially revolutionary protests across many of China’s big cities and resisting further lockdowns by the government:
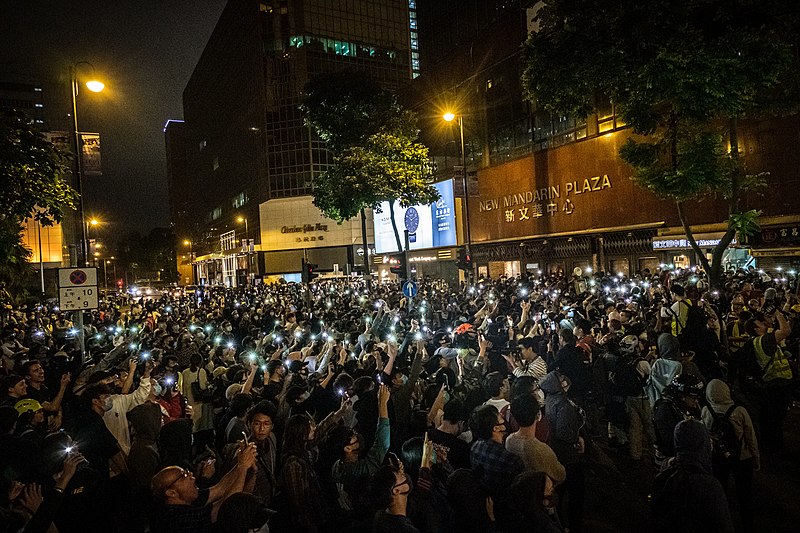
Something extraordinary happened in China over the weekend. Not long ago I wrote at length, if in a rather different context, about the vital importance of courage in the defense of the true and the human against the cold, mechanistic evil that is nihilistic technocracy, the machine whose Conditioners forever lust after total control – not only over men, but ultimately over reality itself. Well, now we have just seen a stunning example of such courage in the streets of China, where people rose up to reassert their human dignity in the face of the most dehumanizing machine of control in the world today: the Chinese Communist Party’s “zero-Covid” terror-state.
For three years now, the Chinese government has maintained its policy of draconian city-wide lockdowns, endless daily mass testing and biomedical surveillance, digital Covid-passes that arbitrarily govern every aspect of daily life, vast camps to house those dragged into quarantine for weeks (or longer) at a time, and, more recently, such innovations as “closed-loop” factories, where workers are forced to work, sleep, and “live” completely isolated from the outside world so that they can continue to produce your iPhones.
But now over the past several days protests have erupted in at least a dozen cities and 79 universities across the country, with spontaneous demonstrations – often begun by only a handful of people, or even a single individual – quickly drawing crowds of hundreds, even thousands, of people willing to fearlessly demand an end to the zero-Covid nightmare.
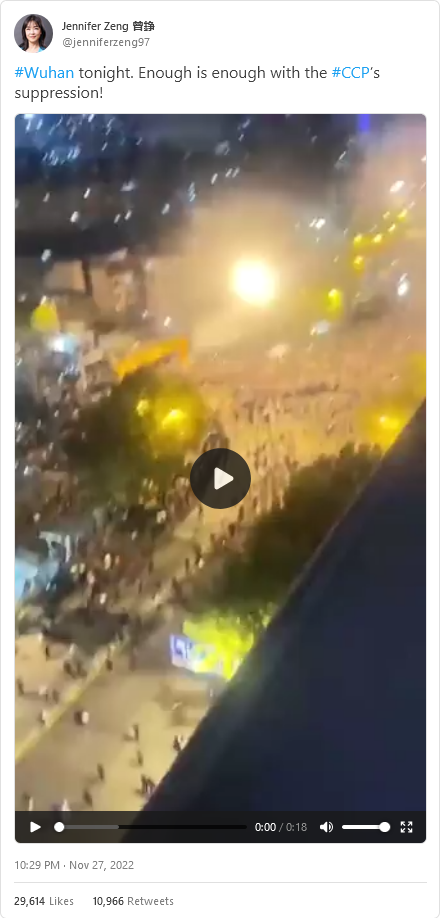
In Wuhan, where it all began, swarming crowds smashed down containment barriers and “liberated” locked-down neighborhoods:
[…]
All across the country, many thousands of these protesters spontaneously echoed many of the same lines:
We don’t want PCR tests. We want to eat.
We don’t want Cultural Revolution. We want reform.
We don’t want lockdowns. We want freedom.
We don’t want a Great Leader. We want the vote.
We don’t want lies. We want dignity.
We aren’t slaves. We are citizens.
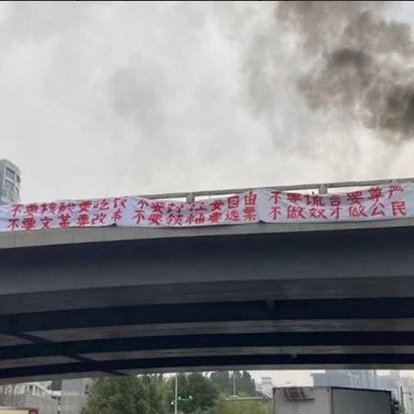
These are conspicuously the same lines as those of a banner hung from a Beijing bridge by a lone (since disappeared) protester, Peng Lifa, on the 13th of October, just ahead of the CCP’s 20th Party Congress and Xi Jinping’s re-coronation as Chinese leader for life.
Now, as recordings of the anti-lockdown protests are swiftly censored online, Chinese netizens have often simply been replying with “We saw it” – a phrase referring not just to the protests, but to Peng Lifa’s message.
His final and most striking line, on a second banner, happens to have been:
“Refuse to go to class. Go on strike. Remove the traitor Xi Jinping.”
And indeed in many protests over the last few days the people’s frustration with zero-Covid tyranny translated into something more: an outpouring of raw anger against the CCP and Xi.
Of course, China’s ruling Communist regime isn’t without its loyal supporters and useful idiots like Apple:
Maybe something will come of the COVID lockdown protests in China. Maybe not, if you’re old enough to remember the guy who stood in front of the tank in Tiananmen Square, and who was never identified nor ever seen again. More likely, the Chinese Communist Party will crack down again, and the people of China will become compliant again.
And the West will turn a blind eye. Again.
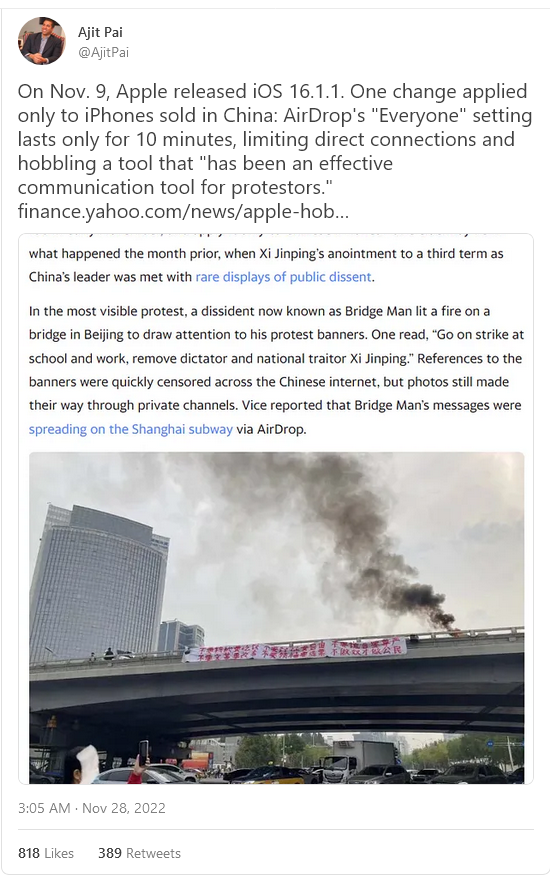
Here’s what was in the latest iPhone update, according to Zachary M. Seward of Quartz:
Hidden in the update was a change that only applies to iPhones sold in mainland China: AirDrop can only be set to receive messages from everyone for 10 minutes, before switching off. There’s no longer a way to keep the “everyone” setting on permanently on Chinese iPhones. The change, first noticed by Chinese readers of 9to5Mac, doesn’t apply anywhere else.
In other words, Chinese iPhone users can’t do or say anything without the CCP knowing about it. Dissent can be quashed before it even starts. The Chinese people can be kept under the CCP’s thumb. And Apple is helping.
November 28, 2022
Near Peer: China (Understanding the Chinese Military)
Army University Press
Published 29 Jul 2022This film examines the Chinese military. Subject matter experts discuss Chinese history, current affairs, and military doctrine. Topics range from Mao, to the PLA, to current advances in military technologies. “Near Peer: China” is the first film in a four-part series exploring America’s global competitors.
(more…)
July 9, 2022
QotD: Chinese “technocracy”
For a while, all (or almost all) of China’s top officials had engineering degrees.
When Xi Jinping first joined the Politburo Standing Committee in 2008, eight of its nine members were engineers. Paramount Leader Hu Jintao was a hydroelectric engineer. His second-in-command Wen Jiabao was a geological engineer. There were two electrical engineers, a petroleum engineer, a radio engineer, and two chemical engineers (including Xi himself). The only non-engineer was Li Keqiang, an economist.
And this was actually a low point in engineers’ dominance of Chinese power. The term before, 100% of Politburo Standing Committee officials had been engineers! What’s going on?
For one thing, Deng Xiaoping thought engineers were cool, and he was powerful enough to do whatever he wanted. A government made up entirely of engineers? Sure, whatever you say. And since the top echelons of Chinese government appoint their own successors, these engineers could appoint other engineers and so on.
But also: during the Cultural Revolution, about half of Chinese people who got degrees at all got engineering degrees. The Cultural Revolutionaries were really not big on education (according to one article, “Xi’s secondary education [was cut short] when all secondary classes were halted for students to criticise and fight their teachers.”) But engineering was useful for building factories, and so was grudgingly tolerated. That meant that of the people smart and ambitious enough to get into college at all, half did engineering.
The other half? I’m not sure. Law is a popular major for would-be politicians in the US, but here’s a Chinese person explaining why it doesn’t work that way in China (short version: China doesn’t have great rule of law, so lawyers don’t matter much and are low status).
Here is an article telling us not to take China’s engineer-kings too seriously. It argues that (aside from Deng’s original picks), most of them never did much engineering, and just studied the subject in school as a generic prestigious-sounding degree to springboard their government career. Chinese engineering curricula are easy, and powerful people frequently cheat or pay others to write their dissertations.Aside from a few of Deng’s personal picks, we should think of this less as “China is a magic place where rational scientists hold power”, and more as “for idiosyncratic reasons, social climbers in China got engineering degrees.” Certainly none of these people were selected for the Politburo on the basis of their engineering acumen. They got their power by bribing, flattering, and backstabbing people, just like everyone else.
In any case, Xi’s old Politburo class was the last one to be made primarily of engineers. The current Politburo has only one engineer — Xi himself.
Scott Alexander, “Dictator Book Club: Xi Jinping”, Astral Codex Ten, 2022-04-07.
April 8, 2022
The structure of the Chinese government
Scott Alexander reviews The Third Revolution, by Elizabeth Economy, although as he says up front, “It’s a look through recent Chinese history, with The Third Revolution as a very loose inspiration.”:
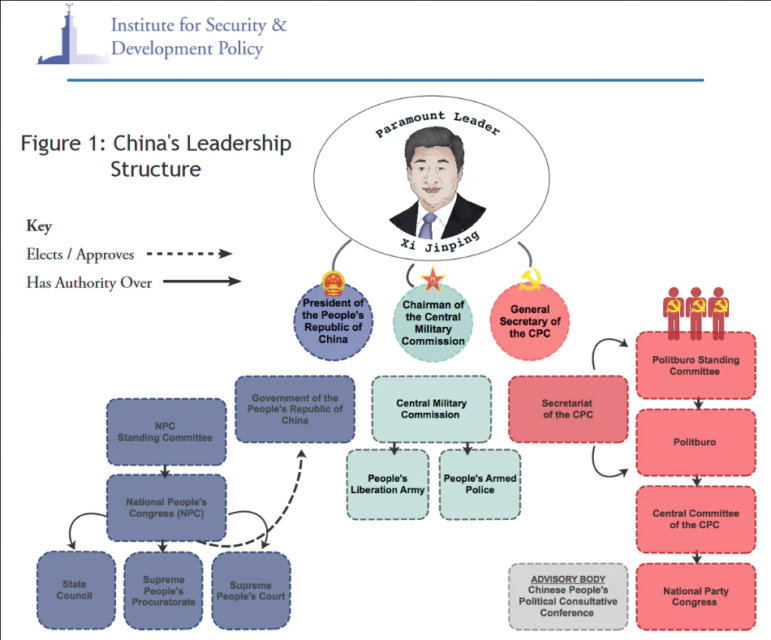
How Does China’s Government Work?
The traditional answer is a flowchart like this one (source):
But you could give a similarly convoluted flowchart for America, and it would tell people much less than words like “democracy” or “balance of powers”. What’s the Chinese equivalent?
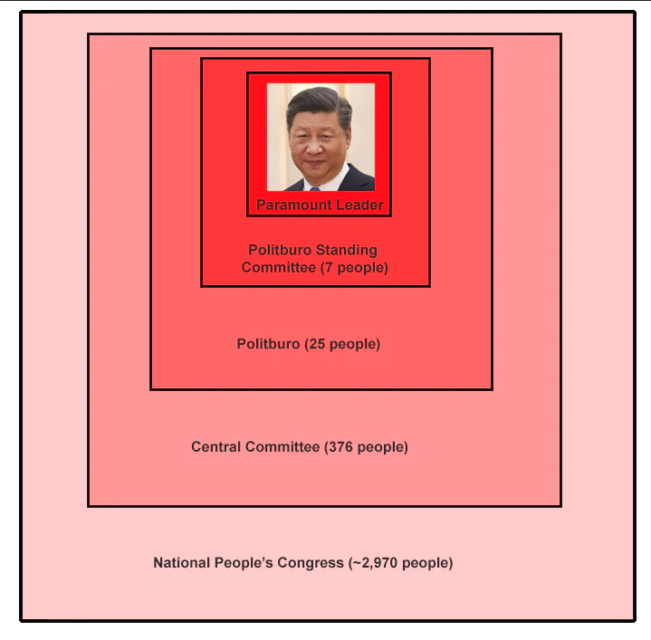
I found it a little more helpful to see it diagrammed it as a series of nested squares:
The inner levels have real power, and the outer layers are theoretically overseers but actually rubber stamps. Things get more and more rubber-stampy as you go out, culminating in the National People’s Congress, which recently voted to re-elect Xi by a vote of 2,970 in favor, 0 against — it’s so irrelevant that it’s literally called “the NPC”.
Who chooses the members of the inner groups? In theory, the outer groups; for example, the Central Committee is supposed to elect the Politburo Standing Committee. In practice, these selections tend to be of the “2,970 in favor, 0 against” variety, so they must be taking marching orders from someone. Who? The Chinese government doesn’t talk about it much, but probably the members of the Politburo Standing Committee hand-pick everyone, including the Paramount Leader and their own successors.
How do they pick? Mostly patron-client relationships. Every leading politician cultivates a network of loyal supporters; if he takes power, he tries to put as many of his people into top posts as he can. The seven Politburo members wheel and deal with each other about whose clients should get which positions, including any unoccupied Politburo seats.
If the two word description of US politics is “democracy, checks-and-balances”, then the two word description of Chinese politics is “oligarchy, patrons-and-clients”. If this seems exotic, it shouldn’t: it’s not much different from how the US fills unelected posts like “ambassador” and “White House staffer”. The Trump presidency put this into especially sharp relief, either because Trump did it more blatantly than usual or just because Trump’s clients were so obviously different from the normal Washington crowd. Consider eg the appointment of Jeff Sessions (among the first Congressmen to endorse Trump) as Attorney General.
In the US, this is a peripheral part of the system, checked by democracy. In China, it’s the whole game.
October 7, 2021
Understatement alert – “… many Canadians are less than confident in our prime minister’s ability to defend Canadian interests when up against Xi Jinping”
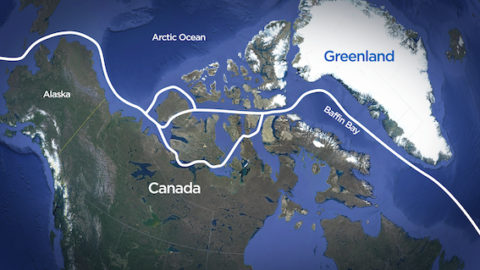
In The Line, Jaclyn Victor discusses Canada’s longstanding military freeloading habits and how Chinese interest in the Arctic are only the latest concerns pushing the government to start taking national sovereignty seriously:

Arctic Offshore Patrol Ship HMCS Harry DeWolf shortly after launch in 2018. The ship was commissioned into the Royal Canadian Navy in June, 2021.
If the West has learned anything about China in recent years, it’s that its leaders will stop at nothing to advance their interests, and will often do so in unpredictable ways. For Canada, the most obvious lesson here was the brazen hostage diplomacy that saw “the two Michaels”, Kovrig and Spavor, imprisoned for nearly three years in retaliation for Canada’s detention of Huawei executive Meng Wanzhou. But there’s another area in which China is flexing its muscles that is much closer to home: the Arctic.
Despite being nearly 1,500 kms from the Arctic Circle, China claims to be a “near-Arctic” state. This alone might not be concerning if it weren’t also for China’s efforts to increase its Arctic presence while simultaneously undermining that of legitimate Arctic states. Although Canada staunchly claims to have sovereignty over the Northwest Passage, China hasn’t accepted this, yet has (concerningly) demonstrated an increased interest in the Arctic. Canada’s periodic military exercises and lack of assertion in the North are clearly not effective in dissuading Chinese interest in the region. As the world recognizes the importance of the Arctic we must do more if we want to maintain our influence.
From claims that Trudeau has personal ties to the Chinese Communist Party to the general belief that he has no backbone in Chinese foreign policy matters, it is clear that many Canadians are less than confident in our prime minister’s ability to defend Canadian interests when up against Xi Jinping. Perhaps the most relevant example of this is the release of the Two Michaels after nearly three years in Chinese captivity — a momentous occasion that filled many Canadians with a renewed hope — but only happened thanks to support from President Biden. And what about China’s alleged election interference, which was aimed at supporting the Trudeau Liberals at the expense of the more hawkish Erin O’Toole? Simply put, China wouldn’t want Trudeau in power if they thought he’d put a damper on their interests.
Our allies, unfortunately, also recognize that our inaction is no match for China’s “coercive diplomacy” and military preparedness. Canada could have contributed to, and hugely benefited from, the recently signed AUKUS pact. The agreement was largely intended to provide Australia with nuclear submarines to fend off Chinese aggression, but it also committed the partners to collaborate on AI and other technologies. Canada seems to have been deliberately excluded. We’re skilled in many of the information-sharing focus areas specified in the agreement, and we clearly need increased submarine capabilities in order to help maintain the Arctic sovereignty we claim to have. On top of this, many of our closest allies have outright denied Canadian claims to the NWP, leaving us with limited defence partnerships as they relate to the Arctic.
In the meantime, China has been establishing itself in the Arctic in an effort to get a foothold. In 2018, China’s Arctic Policy was published — the first of its kind for an Asian state. The policy, which discusses Chinese interest in Arctic resource extraction, brings light to Chinese efforts to develop industry in the region. China currently controls about 90 per cent of the global trade of rare minerals, and they want to maintain this dominance. As Arctic ice melts and additional resources become accessible, one can bet that China will want a piece of the pie. China already has a robust starting point for strategic investments, with US $19 billion invested in Canadian Arctic mining projects. Until the NWP (or “golden waterway” as it’s been called) becomes ice-free in the summers, China will likely continue seeking additional investment opportunities to increase its hold and resulting influence. Once the strait inevitably becomes easy to transit, China will already have a legitimate reason to do so.
October 5, 2021
Chris Alexander – “The truth is that ‘normal’ in the People’s Republic of China, at least since 1959, has never included the rule of law”
Writing in The Line, Chris Alexander (former Minister of Citizenship and Immigration) explains why attempts to “return to normal” in Canada’s relationship with mainland China are foredoomed to failure:
Yuen Pau Woo was joined in these arguments by senators Peter Boehm and Peter Harder, both seasoned diplomats, who also urged Canada to suspend its judgement with regard to China’s persecution of the Uighurs. This includes the use of concentration camps and forced labour, as well as the repression of language, culture and religion. These are all blatant acts committed with the “intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group”, as the 1951 Genocide Convention defines this “odious scourge”.
Throughout this unfortunate saga, Beijing has had a Greek chorus of supporters across Canada — mostly from people with well-remunerated corporate or political backgrounds — for the preposterous notion of a “prisoner exchange” that would get relations with China back to “normal”.
In the end, the Senate’s genocide motion failed by a vote of 29 in favour to 33 opposed, with 13 abstentions. China’s Foreign Ministry praised Woo, Boehm and Harder as “people of vision” who had seen through the “despicable schemes of a few anti-China forces”. The “clumsy trick of attacking China for selfish political gains” and “the hype of ‘genocide’ in Xinjiang is unpopular and doomed to fail”, the Foreign Ministry spokesperson crowed.
Had Woo, a former president and CEO of the Asia Pacific Foundation of Canada, and the “two Peters”, both former deputy ministers of foreign affairs, voted in favour, the Senate’s genocide motion would have passed. Instead all three chose, on an issue directly threatening the identity and lives of millions, to take the position of the Communist Party of China over one unanimously endorsed by Canada’s elected House of Commons — all in the empty hope of getting back to “normal” with Beijing.
The truth is that “normal” in the People’s Republic of China, at least since 1959, has never included the rule of law. From China’s ferocious and brutal invasion of Tibet that same year, through the murderous Great Leap Forward ending in 1962, to the decade-long Cultural Revolution up to Mao’s death in 1976 (and beyond), China has been a legal void. Serious judicial reforms never featured in Deng Xiaoping’s economic relaunch. On the contrary, basic rights were decimated, as Tibetan, Mongolian, Uighur and other refugees attest.
According to Freedom House, the current General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party Xi Jinping’s relentless push for all-encompassing surveillance and censorship has made China the worst environment in the world for internet freedom for the seventh year running. Compliance with such global gag orders is enforced by the CCP’s Orwellian digital panopticon, the notorious United Front Work Department, which seeks to browbeat, buy, corrupt, blackmail, extort or otherwise leverage people and firms with connections to China in support of Xi’s agenda.
Thanks to United Front subterfuge, some prominent Canadians still take China’s side, even as Beijing’s favourability score in Canadian public opinion plummeted to 14 per cent, mirroring a worldwide nosedive for China’s image driven by the two Michaels’ ordeal and Beijing’s “wolf warrior” belligerence.
June 24, 2021
QotD: The fantasy world of Canadian geopolitical posturing
There are two basic things you need to know about Canada’s position in the world. The first is that we are bordered on three sides by ocean. The second is that we are bordered on the fourth side by the United States. That is a simple geopolitical reality whether we like it or not — and Canadians have expended a great deal of energy over the past half century or so making it clear just how much we dislike it.
Yet for all the reflexive anti-Americanism that has been the meat and mead of Canadian nationalism, Canada’s leadership class has usually been pretty good about understanding who is in charge. Over the course of the 20th century, from the Ogdensburg agreement of 1940 and the post-war establishment of NORAD to the Free Trade Agreement of 1988, we cemented that reality with a defence and economic alliance.
Paradoxically, what this continental defence and economic security arrangement has given us is the opportunity to let our internationalist pretensions run wild. One of the weirdest things about Canada is the extent to which we like to frame our place in the world in a-geographic terms. We imagine that we are as threatened as anyone by the mix of post-Cold War failed states, opportunistic terrorism, regional authoritarianism, and humanitarian disasters. By the same token, we like to presume that we are as well-positioned as any other country to do something about all of this.
As the dean of Canadian defence policy Kim Nossal points out in a recent paper, this a-geographic security fantasy is reflected in the official defence reviews that Canadian governments have released since the 1990s. Or take, for example, the 2017 Liberal policy statement, entitled Strong, Secure, Engaged, which rejects the idea that Canada’s privileged geographic location mitigates these global threats for us. As Nossal concludes, when you look at how Canadian governments actually talk about our security situation, you get little sense that, thanks to the Americans, Canada occupies “one of the safest spaces in contemporary global politics.”
You can see the logical leaps, then.
Once you’ve convinced yourself that Canada’s security is disconnected from the geographical imperative of the American security guarantee, it’s only a few steps to the conclusion that who we choose as our global strategic partner is actually a meaningful choice. And if it is true, as China’s president Xi Jinping has claimed, that the East is on the rise and the West is in decline, then why not throw your lot in with the new big dog on the block?
Andrew Potter, “Hedging our bets with China was a mistake”, The Line, 2021-03-23.
April 21, 2021
“The error in Western thinking was to view CCP officials as civilised counterparts”
In Quillette, Aaron Sarin traces the last twenty years of successful diplomacy, industrial espionage, and ever-increasing CCP media influence in China’s relationships with western nations:

President Donald Trump and PRC President Xi Jinping at the G20 Japan Summit in Osaka, 29 June, 2019.
Cropped from an official White House photo by Shealah Craighead via Wikimedia Commons.
By the end of 2020, China’s relationships with the US and Australia had reached their lowest point in living memory, while Sino-British relations weren’t far behind. Yet the European Commission chose this moment to sign a major new investment treaty with Beijing. The deal appeared to have been rushed to completion just before Joe Biden’s inauguration, as if to avoid the fuss that a new American administration would be sure to make. Indeed, incoming National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan felt sore enough to send a pointed tweet: “The Biden-Harris administration would welcome early consultations with our European partners on our common concerns about China’s economic practices.”
The truth is that Brussels has been drifting further and further from Washington ever since the election of Donald Trump, and there are few signs the winds will change now that Biden has taken office. In 2017, Merkel said that Europe could no longer rely on America. By 2020, it seemed truer to say that Europe would rely on China from now on. Indeed, diplomats like Emmanuel Bonne (Macron’s foreign policy adviser) have been most enthusiastic about “France’s readiness to step up strategic communication with China.” In his gushing deference, Bonne can sometimes sound like a man with a gun to his head: “France respects China’s sovereignty, appreciates the sensitivity of Hong Kong-related issues, and has no intention of interfering in Hong Kong affairs.” There are times when the language of neutrality reveals with painful clarity that a side has been chosen.
Brussels officials talk of “strategic autonomy,” of course. They hope to carve out a path to self-sufficiency while at the same time enjoying mutually beneficial relationships with partners like Beijing. The problem is that mutually beneficial relationships are not possible with predators. As successive American administrations have found, those who maintain close connections with the Communist Party will eventually suffer large-scale intellectual property theft and the loss of millions of manufacturing jobs.
Brussels can hardly expect that Beijing will respect this new agreement. Recall the various promises that were made regarding Hong Kong: all of them were broken. Party officials may have signed a legal document recognising the city’s special administrative status, but this was purely for show. In 2017, having apparently now ascended to a position above the law, they declared that the document had “no practical significance.” Remember how Barack Obama was given firm assurance that Beijing would never militarize the South China Sea? There were handshakes and smiles all round, and then Beijing proceeded to militarize the South China Sea.
Indeed, some of the commitments included as part of the new deal echo those made 20 years ago, when China first joined the World Trade Organisation. It was agreed in 2001 that prices in every sector would be determined by market forces; that state-owned enterprises would begin operating free of state influence; that international norms regarding intellectual property would be respected; and so on. After two decades, we can see that the Communist Party has kept not one of its promises.
The error in Western thinking was to view CCP officials as civilised counterparts. We failed to see that we were dealing with a pack of thugs and grifters — men for whom the rule of law is neither reality nor ideal, but façade. This lesson has now been learned in some quarters, but clearly not in the upper echelons of the European Union. This new investment deal even includes a reference to “commitments on forced labour,” which is little short of an insult when we consider the hundreds of thousands of Uyghurs who have been made to toil all day till dusk in the cotton fields of Xinjiang. The truth is that the EU has been fooled. There will be no “win-win situation.” Not when dealing with the Communist Party, which has always viewed geopolitics as a zero-sum game. In the words of Bilahari Kausikan, once Singapore’s top diplomat, “only the irredeemably corrupt or the terminally naïve take seriously Beijing’s rhetoric about a ‘community of common destiny.'”
July 31, 2020
Xi Jinping and the “Chinese dream”
Zineb Riboua outlines possible ways for the West to counter ongoing Chinese economic espionage:

President Donald Trump and PRC President Xi Jinping at the G20 Japan Summit in Osaka, 29 June, 2019.
Cropped from an official White House photo by Shealah Craighead via Wikimedia Commons.
Since 2012, Chinese President Xi Jinping’s favourite catchphrase has been “the Chinese dream”. In stark contrast to the evil, capitalistic American dream, Xi’s alternative vision of progress teaches that the only route to prosperity is through rigid adherence to collectivist ideology.
The Chinese state embodies a very particular ideology. Over the last few decades, it has aggressively ramped up its economic and political capital through business and enterprise, inextricably tying itself to the economic fortunes of both developed and developing countries. It is now seeking to use the economic capital it has accumulated to force its political agenda into reality.
That is why the role of private companies in China is unparalleled. Milton Friedman defined corporate social responsibility in terms of private companies’ sole duty to make a profit, and then increase that profit. Chinese companies appear to be exempt from this rule because they interact with the state in a unique and troubling way.
The current state of the Chinese political and economic landscape is no accident. When Deng Xiaoping spoke in the 1980s of building a “socialism with Chinese characteristics”, this is probably exactly what he had in mind. The Chinese Communist party has succeeded in weaponising local market forces in such a way that it now holds all the cards in its nation’s dealings with the outside world, both political and economic, because the line between the public and the private is non-existent.
This strategy has not gone unnoticed. Thanks to the Chinese Communist party’s recent conduct – unprecedented aggression in Hong Kong, the appalling genocide of the Uyghur people and a costly unwillingness to share information relating to the coronavirus outbreak – the state of its internal affairs has come into sharp focus on the international stage.
Unsurprisingly, the hawkish US has placed itself at the forefront of counter-Chinese rhetoric. Secretary of state Mike Pompeo said recently: “We gave the Chinese Communist party and the regime itself special economic treatment, only to see the CCP insist on silence over its human rights abuses as the price of admission for Western companies entering China.”
July 6, 2020
Cold War Two is upon us, but it’s not all Trump’s fault (believe it or not)
Niall Ferguson on the rapid drop in temperature in US/Chinese relations in the last eight years:

President Donald Trump and PRC President Xi Jinping at the G20 Japan Summit in Osaka, 29 June, 2019.
Cropped from an official White House photo by Shealah Craighead via Wikimedia Commons.
“We are in the foothills of a Cold War.” Those were the words of Henry Kissinger when I interviewed him at the Bloomberg New Economy Forum in Beijing last November.
The observation in itself was not wholly startling. It had seemed obvious to me since early last year that a new Cold War — between the U.S. and China — had begun. This insight wasn’t just based on interviews with elder statesmen. Counterintuitive as it may seem, I had picked up the idea from binge-reading Chinese science fiction.
First, the history. What had started out in early 2018 as a trade war over tariffs and intellectual property theft had by the end of the year metamorphosed into a technology war over the global dominance of the Chinese company Huawei Technologies Co. in 5G network telecommunications; an ideological confrontation in response to Beijing’s treatment of the Uighur minority in China’s Xinjiang region and the pro-democracy protesters in Hong Kong; and an escalation of old frictions over Taiwan and the South China Sea.
Nevertheless, for Kissinger, of all people, to acknowledge that we were in the opening phase of Cold War II was remarkable.
Since his first secret visit to Beijing in 1971, Kissinger has been the master-builder of that policy of U.S.-Chinese engagement which, for 45 years, was a leitmotif of U.S. foreign policy. It fundamentally altered the balance of power at the mid-point of the Cold War, to the disadvantage of the Soviet Union. It created the geopolitical conditions for China’s industrial revolution, the biggest and fastest in history. And it led, after China’s accession to the World Trade Organization, to that extraordinary financial symbiosis which Moritz Schularick and I christened “Chimerica” in 2007.
How did relations between Beijing and Washington sour so quickly that even Kissinger now speaks of Cold War?
The conventional answer to that question is that President Donald Trump has swung like a wrecking ball into the “liberal international order” and that Cold War II is only one of the adverse consequences of his “America First” strategy.
Yet that view attaches too much importance to the change in U.S. foreign policy since 2016, and not enough to the change in Chinese foreign policy that came four years earlier, when Xi Jinping became general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party. Future historians will discern that the decline and fall of Chimerica began in the wake of the global financial crisis, as a new Chinese leader drew the conclusion that there was no longer any need to hide the light of China’s ambition under the bushel that Deng Xiaoping had famously recommended.
February 23, 2020
China’s government and the coronavirus epidemic
In Quillette, Aaron Sarin shows how the Chinese government has systematically failed to respond adequately to the epidemic which broke out late in 2019in Wuhan and risks “losing the Mandate of Heaven”:
As of this writing, the epidemic’s death toll is still rising, and many of these deaths can ultimately be traced to the paranoid rigidity of the Xi Jinping administration. By late December 2019, doctors in Wuhan were already sounding the alarm over cases of what appeared to them to be SARS. Instead of listening to their warnings, the authorities summoned eight of these doctors for a dressing-down. They were warned of the punishments they could face for “rumour-mongering.” News of their detention was broadcast to tens of millions: a clear message to anyone else who might have been thinking about discussing viruses in public.
The Party’s leaders actually knew enough to be worried by this point — they alerted the World Health Organisation on December 31st — and yet still they hid the truth from the public. This neurotic obsession with secrecy has certainly cost lives. If the medical community had been informed of the outbreak back in December, hospitals could have stockpiled the necessary supplies. But now there are drastic shortages, and patients are dying in hallways and waiting rooms.
Even the critics of authoritarian dictatorship will usually agree that the system beats democracy for sheer efficiency, but the coronavirus debacle has turned that old wisdom on its head. Where we might have expected cold and methodical governance, we have found dithering bureaucrats, unable to take a step in any direction, paralysed by what Xu Zhangrun calls “systemic impotence.” Weeks went by and citizens swarmed in and out of Wuhan, picking up the virus and transporting it to the far corners of the country. Local government officials stayed quiet, wary of the heavy hand of Xi Jinping. On January 23rd, a citywide quarantine was finally announced, but eight long hours passed before it was enacted — time enough for a million or more to flee the city.
The Wuhan lockdown was repeated in other parts of the country (most recently the southern megacity of Guangzhou), and some observers praised the speed with which new hospitals were constructed from scratch. These very visible displays of its power aside, the Party has moved far too slowly at every stage of the crisis. Diagnostic testing required samples to be sent all the way to a laboratory in Beijing, and this delayed the distribution of testing kits to many of the hospitals in Wuhan. Even when testing kits were available, patients still found themselves trapped in a Kafka-esque web of bureaucracy. According to Reuters, the tests have been refused to people who fail to make it through a complex reporting system involving hospital authorities, district authorities, city health authorities, and disease control officials.
None of this should come as a surprise. The cliché about the efficiency of authoritarian systems was always, on closer analysis, something of a low-resolution image. In the old days of the Soviet Union, speedy industrial growth obscured the reality of a fragile system largely devoid of autonomous decision making. During the 1920s, the Communist Party’s state planning committee Gosplan was established with the impressive-sounding mission of creating a series of five-year plans to govern the economy. But over the next 70 years, the vast majority of these plans were radically revised and rewritten, or more frequently ignored altogether in favour of Joseph Stalin’s arbitrary dictates. Indeed, Gosplan actively tried to avoid making decisions at all, because committee members knew Stalin would have them shot and replaced if their ideas produced unwelcome results. In the end, fear saps the efficiency of all authoritarian regimes, and the Chinese Communist Party is no exception.
Li Wenliang has emerged as the most vivid symbol of the Party’s latest failure. Li was one of the Wuhan doctors disgraced for discussing the coronavirus on social media. A few days after his police warning, he contracted the virus himself, and on February 6th he died. It was during the period of Li’s short illness that the Party apparently realised its error and decided to absolve the doctors, but still the central government would accept no blame for the tragedy. Instead, the Supreme Court (which is controlled by the CCP) scolded the local government in Wuhan — an unusual move, no doubt designed to create a scapegoat for surging public anger. The truth is that the city’s officials had been faced with an impossible job. They obediently followed orders, and now they will be punished for it.
December 29, 2019
Changing western views about China
John Gray charts the image of China that has held steady for years among western countries but which has been severely shaken with the unrest in Hong Kong and the Chinese government’s reactions:

“The Chinese People’s Liberation Army is the great school of Mao Zedong Thought”, 1969.
A poster from the Cultural Revolution, featuring an image of Chairman Mao, published by the government of the People’s Republic of China.
Image via Wikimedia Commons.
The most important year of the decade is the one that is just ending. The struggle that will most deeply shape the global scene in years to come is not occurring in Britain, the US, Europe or any Western country. It is underway in Hong Kong, where a popular demand for democracy is confronting the immovable power of the world’s most highly developed authoritarian state.
It is a struggle no government wants to see escalate. More realistic than its Western counterparts, the Chinese leadership shows few signs of believing the conflict can be definitively resolved any time soon. Incremental concessions and large-scale repression both carry high levels of risk for Xi Jinping’s regime. The ideal end-state for Beijing is probably long-term containment. But the situation in the former colony is not stable, and it is difficult to exaggerate the impact that suppressing the protestors by force would have on China’s position in the world.
It is often pointed out that Hong Kong’s economic importance has dwindled with the rise of mainland cities such as Shanghai. But this leaves out how much two-system governance shapes global perceptions of China and its future. Xi’s progress towards a neo-totalitarian surveillance state has deflated the Western elites’ confidence that China is on a path of slow evolution towards liberal democracy. Yet the fantasy still lingers. The likelihood that China will be an authoritarian great power in any realistically imaginable future is too disturbing to contemplate.
“Hong Kong night Panorama” by Andos_pics is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
It is worth recalling the comforting tale on which Western governments have modelled China’s development. The country was getting rapidly richer, and while average incomes remained low by international standards, the middle class was steadily growing. This process of embourgeoisement would lead to stronger demands for democratic freedoms, and China would become ever more like the West. Embedded in practically every Western government and regularly invoked by the Western businesses that operate in China, this is a story with almost no basis in reality.
It is true that the rise of the middle classes in early 19th-century Europe coincided with an expansion of liberal freedoms in some countries. This was the main thrust of Marx’s analysis of bourgeois democracy. (A little-noted aspect of recent liberal thinking is that it relies heavily on a crude version of Marxian class analysis.) But there is nothing in the historical record that says the middle classes are inherently a force promoting liberalism. In the late 19th century, they backed the restoration of monarchy and empire in France and militarism In Prussia. In the early 20th century, large sections of the European middle classes embraced ethnic nationalism and then fascism. There was not much sign of the freedom-loving bourgeoisie in interwar Europe.
While it is so far less developed, a similar pattern of bourgeois support for illiberal politics has emerged in many European countries since the collapse of the Soviet Union. Across the continent, far-Right parties enjoy the support of significant sections of the middle classes. In America, Trump’s constituency includes many from precarious middle income groups.
So, the linkage between the middle classes and liberal values is tenuous throughout Western countries. In the UK and other English-speaking countries, it is middle class students, professors and administrators that have shut down freedom of inquiry and expression in higher education. Woke capitalism and much of the mainstream media are continuing this trend. Threatened by what they call populism, bourgeois liberals have ditched the values that once defined them. Far from being a universal law, middle class support for liberalism looks like a brief historical accident.