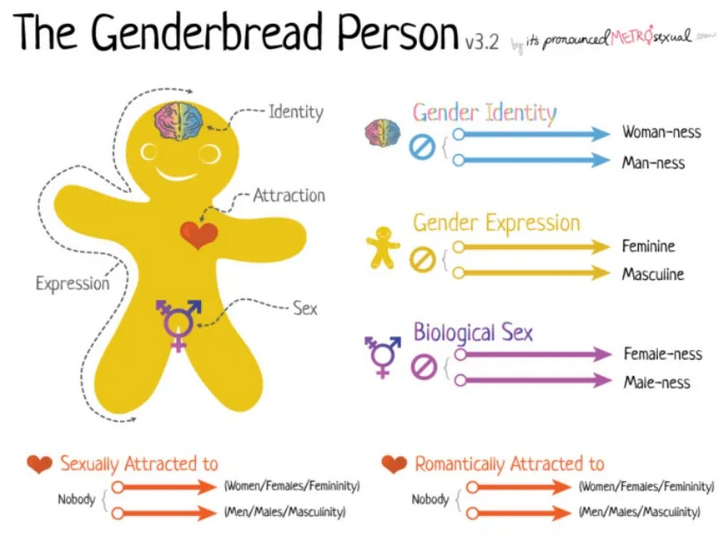
Janice Fiamengo on the far-from-impartial emphasis of concern on young people being pushed toward radical “solutions” to gender dysphoria:
Last year, conservative educational institution Prager U published “Why Girls Become Boys“, a short video by journalist Abigail Shrier, the author of Irreversible Damage: The Transgender Craze Seducing Our Daughters, published in 2020. Shrier’s focus is evident from the titles: girls. Previously, Shrier had been profiled in an interview with Candace Owens when she was still working on the book. Though the interview is now three years old, its canvassing of teen transitioning — in a discussion that moves from concern about girls being “seduced” into trans, to anger at society’s failure to protect girls from boys who transition — provides a fairly accurate representation, I believe, of conservative positioning on this subject. Girls who transition are seen as victims; while boys who transition are seen (if they are seen at all) as predators.
This double emphasis is clear in the interview. Shrier and Owens describe the collusion of media influencers, the public school system, woke punditry, and medical authorities to encourage girls (but not boys, it seems) to consider their gender identity “fluid”. Feelings of discomfort are too readily interpreted as signs of a trans identity. Girls can be made to believe themselves trans very quickly, sometimes simply from viewing one or more internet videos; and schools are not required to tell parents if their daughter begins identifying as male. From age fifteen, girls can find gender clinics willing to prescribe testosterone without their parents’ consent; a girl can have her breasts amputated as early as age sixteen. The lifetime of dependency on hormones (their consequences unknown), the risky surgeries, and the tragic missed opportunities — of motherhood in particular, but even of having breasts — were emphasized by both pundits.
It’s almost impossible to imagine these two women discussing the tragedy of losing a penis, of being denied the opportunity to become a father, of being denied the joy of male sexuality.
From this point, the conversation moved seamlessly into discussing the victimhood of girls forced to share their private spaces — and of course their sporting competitions — with biological males (often called “men” as in “Men are invading girls’ sports”). These males are not discussed as vulnerable innocents duped into taking body-altering hormones or undergoing dangerous surgeries. No imaginative effort was spent on why these boys want to live as trans female. The underlying assumption seemed to be that boys’ transition, far from being an attempt to relieve real distress, is an act of appropriation of female experience. The boys were depicted as aggressors who invade girls’ locker-rooms and deny girls opportunities (or, even worse, masquerade as trans in order to prey on girls sexually). Are there boys made uncomfortable in their change rooms or other private spaces by the presence of biological girls? The question seems never to have occurred to Shrier and Owens.
Shrier and Owens agree in decrying feminism for failing to protect girls and for failing (allegedly) to affirm femininity and girlhood. “Girls aren’t being told how wonderful it is to be a girl!” Their own feminist — or at least female-centered — assumptions are clearly evident in their conviction that the trans phenomenon is about multiple harms to females, harms which must always take precedence over the legitimate needs and experiences of males. And in fact, contrary to what Shrier and Owens seem to believe, there are many feminists who vehemently denounce biological male incursions into female bodies and spaces; many of them, such as Meghan Murphy, Julie Bindel, and Sheila Jeffreys, to name only a few, advocate from an avowedly anti-male perspective.
Shrier might respond that the overwhelming majority of adolescents who believe themselves to be trans are female (as she states in her Prager U video). This may be true (a recent Psychology Today article puts the number at greater than 80% female) but does not mitigate my objection. Teen suicide is about 80% male (more on this later), but it is hard to imagine concerned pundits ignoring the troubles of girls. Many discussions of teen suicide, in fact, make much of the fact that girls attempt suicide more often than boys, downplaying the fact that boys carry out their suicides in such distinctively high numbers. Don’t get me wrong: I have no objection to a focus on girls’ difficulties in adolescence — except when it improperly ignores and even maligns boys.
It wasn’t all that long ago that the vast majority of young people seeking “gender-affirming” therapy were males hoping to become trans-females. In the last few years, that proportion has flipped completely.