World War Two
Published 3 Dec 2022The Teheran Conference is in full swing and the Allied leadership and plan for a cross channel invasion of Europe is agreed upon by Stalin, Churchill, and Roosevelt. There are new Allied attacks across Italy, but at Bari a German air raid releases deadly poison gas.
(more…)
December 4, 2022
Operation Overlord Confirmed at Teheran – WW2 – 223 – December 3, 1943
December 2, 2022
Bombing Berlin with Ed Murrow of CBS – War Against Humanity 089
World War Two
Published 1 Dec 2022Ed Murrow accompanies the RAF on a bombing raid on Berlin, and files one of his most iconic broadcasts with CBS. In Teheran, Winston Churchill walks out on a dinner with Joseph Stalin, after the USSR Premiere suggests mass murdering German officers.
(more…)
November 29, 2022
Near Peer: Russia
Army University Press
Published 25 Nov 2022AUP’s Near Peer film series continues with a timely discussion of Russia and its military. Subject matter experts discuss Russian history, current affairs, and military doctrine. Putin’s declarations, advances in military technology, and Russia’s remembrance of the Great Patriotic War are also addressed. “Near Peer: Russia” is the second film in a four-part series exploring America’s global competitors.
November 27, 2022
Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn and One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich
In Quillette, Robin Ashenden discusses the life experiences of Aleksandr Slozhenitsyn that informed the novel that made him famous:
The book was published less than 10 years after the death of Joseph Stalin, the dictator who had frozen his country in fear for nearly three decades and subjected his people to widespread deportation, imprisonment, and death. His successor Nikita Khrushchev — a man who, by his own admission, came to the job “elbow deep in blood” — had set out on a redemptive mission to liberalise the country. The Gulags had been opened and a swathe of prisoners freed; Khrushchev had denounced his predecessor publicly as a tyrant and a criminal and, at the 22nd Party Congress in October 1961, a full programme of de-Stalinisation had been announced. As for the Arts, previously neutered by the Kremlin’s policy of “Socialist Realism” — in which the values of Communism had to be resoundingly affirmed — they too were changing. Now, a new openness and a new realism was called for by Khrushchev’s supporters: books must tell the truth, even the uncomfortable truth about Communist reality … up to a point. That this point advanced or retreated as Khrushchev’s power ebbed and flowed was something no writer or publisher could afford to miss.
Solzhenitsyn’s book told the story of a single day in the 10-year prison-camp sentence of a Gulag inmate (or zek) named Ivan Denisovich Shukhov. Following decades of silence about Stalin’s prison-camp system and the innocent citizens languishing within it, the book’s appearance seemed to make the ground shake and fissure beneath people’s feet. “My face was smothered in tears,” one woman wrote to the author after she read it. “I didn’t wipe them away or feel ashamed because all this, packed into a small number of pages … was mine, intimately mine, mine for every day of the fifteen years I spent in the camps.” Another compared his book to an “atomic bomb”. For such a slender volume — about 180 pages — the seismic wave it created was a freak event.
As was the story of its publication. By the time it came out, there was virtually no trauma its author — a 44-year-old married maths teacher working in the provincial city of Ryazan — had not survived. After a youth spent in Rostov during the High Terror of Stalin’s 1930s, Solzhenitsyn had gone on to serve eagerly in the Red Army at the East Prussian front, before disaster struck in 1945. Arrested for some ill-considered words about Stalin in a letter to a friend, he was handed an eight-year Gulag sentence. In 1953, he was sent into Central Asian exile, only to be diagnosed with cancer and given three weeks to live. After a miraculous recovery, he vowed to dedicate this “second life” to a higher purpose. His writing, honed in the camps, now took on the ruthless character of a holy mission. In this, he was fortified by the Russian Orthodox faith he’d rediscovered during his sentence, and which had replaced his once-beloved, now abandoned Marxism.
Solzhenitsyn had, since his youth, wanted to make his mark as a Russian writer. In the Gulag, he’d written cantos of poetry in his head, memorized with the help of matchsticks and rosary beads to hide it from the authorities. During his Uzbekistan exile, he’d follow a full day’s work with hours of secret nocturnal writing about the darker realities of Soviet life, burying his tightly rolled manuscripts in a champagne bottle in the garden. Later, reunited with the wife he’d married before the war, he warned her to expect no more than an hour of his company a day — “I must not swerve from my purpose.” No friendships — especially close ones — were allowed to develop with his fellow Ryazan teachers, lest they take up valuable writing time, discover his perilous obsession, or blow his cover. Subterfuge became second nature: “The pig that keeps its head down grubs up the tastiest root.” Yet throughout it all, he was sceptical that his work would ever be available to the general public: “Publication in my lifetime I must put out of my mind.”
After the 22nd Party Congress, however, Solzhenitsyn recognised that the circumstances were at last propitious, if all too fleeting. “I read and reread those speeches,” he wrote later, “and the walls of my secret world swayed like curtains in the theatre … had it arrived, then, the long-awaited moment of terrible joy, the moment when my head must break water?” It seemed that it had. He got out one of his eccentric-looking manuscripts — double-sided, typed without margins, and showing all the signs of its concealment — and sent it to the literary journal of his choice. That publication was the widely read, epoch-making Novy Mir (“New World”), a magazine whose progressive staff hoped to drag society away from Stalinism. They had kept up a steady backwards-forwards dance with the Khrushchev regime throughout the 1950s, invigorated by the thought that each new issue might be their last.
November 15, 2022
How Was The Soviet Union Founded?
The Great War
Published 11 Nov 2022Vladimir Lenin had led the Bolshevik movement through the October Revolution and the Russian Civil War but by 1922 his health was failing and infighting among Bolshevik leadership caused friction. In the end Josef Stalin was able to prevail over Leon Trotsky and lead the newly founded Soviet Union until his death in 1953.
(more…)
November 12, 2022
QotD: The short careers of secret police chiefs
The first thing you learn on even the most cursory look at any secret police is: they aren’t. Secret, that is. Otherwise they wouldn’t be effective. Oh, they’d probably be a lot better at gathering certain kinds of intel, but intelligence gathering is really only their secondary function. Their primary function, of course, is intimidation. That’s why every Hans and Franz on the street in Nazi Germany could tell you exactly where the nearest Gestapo office was.
(The Romanian Securitate had public intimidation down to an art form. They’d follow random guys around using big, obvious details, the better to prove to the proletariat that everyone was suspect. It is to them, not Mafia dons or aspiring rappers, that we owe the now-standard Eurotrash track suit look).
Secret police goons suffer from two serious structural problems, though, that not even the guys in Stove’s book [The Unsleeping Eye] really ever solved. The first is the obvious one, that guys who know where the bodies are buried are always at risk of using that knowledge. Napoleon’s guy Joseph Fourche, and FDR’s main man J. Edgar, lived out their natural lives (as did Elizabeth’s spymaster Sir Francis Walsingham), but of them, only Fourche lived in anything approaching what we would call an ideologized society, and that was small beer.
The rest of those guys died in harness, because of course they did. Adolf Hitler was an especially stupid dictator, and Heinrich Himmler an especially servile little freak, but I have no doubt that if the Reich had gone on much longer [Himmler] would’ve shanked [Hitler]. If Heydrich hadn’t gotten perforated in Prague, he no doubt would’ve gone after [Himmler] even sooner. Lenin and especially Stalin burned through secret police chiefs on the regular, because they pretty much had to.
I don’t know about the goons in the Chinese etc. secret police, but I’d be shocked to find anyone with more than a few years’ tenure, because purges are simply a way of life in totally ideologized societies. For every Khrushchev who manages to hang on – n.b. he was a Red Army commissar during the war, i.e. a not-so-secret police goon — there are fifty guys who live fast and die hard, because that’s just how totalitarians rule.
The stoyaknik, of course, is well served to consider the current scene as if he were watching the Politburo of an exceptionally deluded Commie regime, one made up almost entirely of ruthless yet clueless retards … who still believe, for the most part, in Communism.
That was always the problem for Kremlinologists in evaluating the USSR — whatever the Boss of the moment decided would, of course, immediately be retconned into the Scriptures by the Academicians, but what did the Big Guy himself think about it? That constrained his choices. Stalin and Khrushchev were true Communists, there’s no question about that, but they came up in the school of the hardest possible knocks — if they needed to do something directly contrary to Leninism in order to hang on to power, then Comrade Ilych can suck it.
For anything short of mortal, though, they’d more often than not behave as stereotypical Commies, so the first thing any Kremlinologist had to do was determine the seriousness of the situation from the Politburo’s perspective. Not an easy task, as you might imagine, and what made it worse was: as the USSR gained stability and Communism matured, the old school hardasses all died off and were replaced by True Believers. Mikhail Gorbachev, for instance, didn’t start making his mark until after Stalin’s death, and he wasn’t a real up-and-comer until after Khrushchev — that is, he started rising through the ranks only after the hard boys were gone.
Thus, while Khrushchev was a true Commie, he still had some hard reality to constrain him. Gorby didn’t. He really believed all that Marxist-Leninist horseshit about democracy and etc.; he was far more doctrinaire than the earlier generation could possibly be. Thus Kremlinologists were forever baffled when he did stupid things that made no sense from the Realpolitik perspective, but were perfectly in keeping with the Scriptures. They thought Perestroika was some big 4D chess feint, for instance, instead of just a soft boy doing something noodle-headed.
Severian, “Book Review: The Unsleeping Eye by R.J. Stove”, Founding Questions, 2022-08-09.
September 19, 2022
Albania – Hitler’s Latest Ally? – WAH 078 – September 18, 1943
World War Two
Published 18 Sep 2022The German Nazi Genocide of the Jews surpasses four million deaths, while the Soviet Union and US step up oppression against some their own citizens.
(more…)
July 18, 2022
Russian Invasion of Finland – The Winter War 1939-40
Mark Felton Productions
Published 24 Mar 2022Find out why Russia invaded neutral Finland in late 1939, and how the outnumbered and outgunned Finns managed to defend their country for 3 months until making peace with Stalin.
(more…)
April 20, 2022
Khrushchev – Stalin’s Loyal Enforcer?
World War Two
Published 19 Apr 2022Nikita Khrushchev has served Joseph Stalin faithfully for the past decade. He’s a career commissar and party man. So, when war breaks out, are commissars like Khrushchev little more than Stalinist enforcers? Or is there more to the institution than that?
(more…)
April 19, 2022
When the Germans had to surrender twice
The end of the war in Europe is usually noted as being the 8th of May, 1945, when General Eisenhower received the surrender of German forces, but the Soviets (and now the Russians) mark the anniversary on the 9th:

ADN-ZB/Archiv
II.Weltkrieg 1939-1945
Die bedingungslose Kapitulation der faschistischen deutschen Wehrmacht wird am 8. Mai 1945 in Berlin-Karlhorst unterzeichnet.
Links: Der Vertreter des Oberkommandos der Roten Armee, Marschall der Sowjetunion G. K. Shukow, am Tischende Generalfeldmarschall Wilhelm Keitel.
J 0422/600/2 N
It was at three in the morning on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, that Generaloberst Alfred Jodl of the German High Command, signed a surrender document at General Dwight Eisenhower’s headquarters in Rheims, France. The European war was over. It was VE-Day. Stalin’s representative, General Ivan Susloparov, cabled his chief the great news.
However, the Russian leader flew into a rage. He wanted his own observance and insisted on a further ceremony at the Soviet military HQ in Karlshorst, a former Wehrmacht officers’ mess, six miles south-east of central Berlin. Chosen simply because it was one of the few buildings in the capital left with windows and a roof, the formalities were presided over by the captor of the city, Marshal Georgy Zhukov.
This time, it was Generalfeldmarschall Wilhelm Keitel, Jodl’s superior, who read over a near-identical document. Susloparov was again present, along with Carl Spaatz for the Americans and Jean de Lattre de Tassigny, representing France. Newsmen were unaware of the diplomatic spat that delayed proceedings.
De Lattre refused to sign unless the French tricolore was in evidence among the standards and pennants decorating the surrender room. The first Soviet solution hilariously produced a Dutch flag. To pacify an even-more outraged de Lattre, a Red Army seamstress was summoned to run up the appropriate banner. More delays ensued while the Allies bickered over the order of signatures and witnesses, only agreed after the mollifying effects of vodka and some food.
This is why the final ceremony began shortly after midnight. Cameras captured Keitel in full dress uniform, arriving in pompous mood. Flashlights caught the glint of his many medals, and the arrogant flourish of his marshal’s baton, held with gloved hands. He gazed around the room, haughty contempt written across his face. The field marshal removed only his right glove, screwed his monocle into his left eye and applied a fountain pen to the two-page, typewritten document. It was 00:16 local time on Wednesday, 9 May, which became Soviet Victory Day and remains so in Eastern Europe.
Each subsequent year on Victory Day, Red Square has echoed to the “Hurrahs” of vast numbers of Russian soldiers, sailors, marines and paratroopers, national guardsmen and airmen. They are drawn up to listen to their commander-in-chief and inspected by generals. Banners are saluted; swords flash through the air. Serenaded by massed bands playing stirring tunes, they march past the top brass, assembled on the roof of Lenin’s Mausoleum.
March 11, 2022
QotD: In 1939, Stalin never imagined Finland would refuse his demands
The one thing Stalin had not reckoned on was that any of these neighbors might object. Certainly he did not expect resistance from the Baltic states. As early as September 24th, 1939, three days before Warsaw surrendered to Germany, Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov had advised the Estonian foreign minister, Karl Selter, to “yield to the wishes of the Soviet Union in order to avoid something worse.” Latvia was next in line. When Lithuania’s foreign minister, Juozas Urbšys, objected that Soviet occupation would “reduce Lithuania to a vassal state,” Stalin replied brutally, “You talk too much.”
[…]
When Molotov summoned a Finnish delegation to the Kremlin on October 12th, 1939, Stalin made a personal appearance to heighten the intimidation factor, and he handed the Finns a brutal ultimatum demanding, among other things, “that the frontier between Russia and Finland in the Karelian Isthmus region be moved westward to a point only 20 miles east of Viipuri, and that all existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus be destroyed.” Stalin made it clear that this was the price that Finland had to pay to avoid the fate of Poland.
Aggressive and insulting as the Soviet demands on Finland were, Stalin and Molotov fully expected them to be accepted. As the Ukrainian party boss and future general secretary Nikita Khrushchev later recalled, the mood in the Politburo at the time was that “all we had to do was raise our voice a little bit and the Finns would obey. If that didn’t work, we could fire one shot and the Finns would put up their hands and surrender.” Stalin ruled, after all, a heavily armed empire of more than 170 million that had been in a state of near-constant mobilization since early September. The Red Army had already deployed 21,000 modern tanks, while the tiny Finnish Army did not possess an anti-tank gun. The Finnish Air Force had maybe a dozen fighter planes, facing a Red Air armada of 15,000, with 10,362 brand-new warplanes built in 1939 alone. Finnish Army reserves still mostly drilled with wooden rifles dating to the 19th century. By contrast, the Red Army was, in late 1939, the largest in the world, the most mechanized, the most heavily armored, and the most lavishly armed, even if surely not — because of Stalin’s purges — the best led.
One can imagine, therefore, Stalin’s shock when the Finns said no. Stunned by this unexpected resistance, Stalin and Molotov did not, at first, know quite what to do. With his highly placed spies in London, Stalin must have known that the mood in foreign capitals was becoming agitated by Soviet moves in the Baltic region. On October 31st, 1939, the British war cabinet took up the question of “Soviet Aggression Against Finland or Other Scandinavian Countries”. And earlier in the month, FDR had written to Moscow, demanding clarification of the Soviet posture on Finland. At this point, the Finnish cause seemed to have the potential to transform the so-far desultory and hypocritical British-French resistance to Hitler alone into a principled war against armed aggression by both totalitarian regimes.
On November 3rd, after yet another encounter in the Kremlin had gone sour with the Finns, Molotov warned the delegates that “we civilians can’t seem to do any more. Now it seems to be up to the soldiers. Now it is their turn to speak.” However, the truth was that, in November 1939, neither side was ready to wage war. Having expected the Finns to come around, Stalin had issued no orders to begin invasion preparations until after talks had finally broken down.
Sean McMeekin, “Stopped Cold: Remembering Russia’s Catastrophic 1939 Campaign Against Finland”, Quillette, 2021-04-20.
March 5, 2022
March 1, 2022
Genocide in Ukraine: The Holodomor | Into Context | War in Ukraine 01
TimeGhost History
Published 28 Feb 2022What do you get when you combine vigorous grain-tax policies, bad harvests with Stalin’s fear and animosity for the rural population of Ukraine? A man-created murder famine, designed to kill millions of Ukrainian men, women and children.
(more…)
February 16, 2022
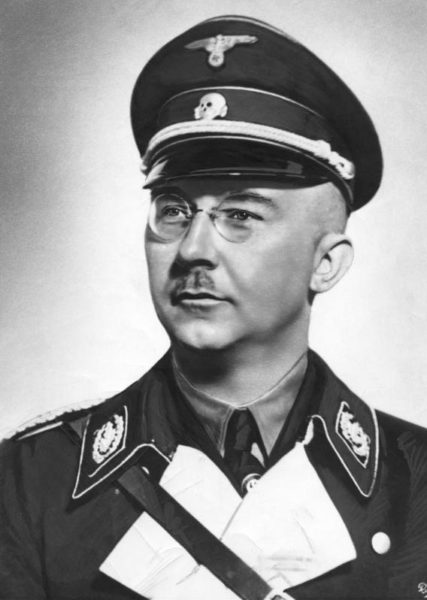
Germany’s dual economy during WW2 (and why Himmler would have succeeded Hitler if the Nazis had won WW2)
At Founding Questions, Severian looks at the way the Nazi economy was actually two entities — the “wartime” economy and the effectively separate SS economy under the control of Heinrich Himmler:
Here’s where the Nazis really blew it. “Nazism” should really be called “Hitlerism”, as it was a true cult of personality; there was no ideology without the specific individual man. That’s the tension at the heart of any collectivist ideology — somebody’s got to be The Boss, however temporarily — but Nazi Germany suffered it worse than most. Had the Nazis won the war, the bloodbath at the top would’ve been as spectacular per capita as the war itself. As thoroughgoing Social Darwinists, they only had one possible principle of succession …
Let’s provisionally call that the first consequence of an ideology in power: The personal is the political and vice versa. That seems trite, I realize, but I’m putting it here to emphasize its literalness – in an ideological state, building your own “affinity”, Bastard Feudalism-style, just IS politics. There’s no other possible political activity. And as much as the Nazis seemed to have screwed it up by going all in on the Fuhrerprinzip at the very top, their out-and-proud Organizational Darwinism (for lack of a better term) made them super-efficient at the lower levels.
Let’s bring Khrushchev back in. In many ways, he’s the Soviet Himmler. He was one of Stalin’s right hand men throughout the war, but somehow didn’t get tagged as a major player in the succession crisis until it was too late for all the other contenders for the purple to take effective countermeasures. In the same way, Hitler did announce a successor, sort of. In fact he did it twice: Before the war, it was Rudolf Hess; during the war, Hermann Goering. Neither of those guys had anything approaching the power Himmler had, but like Khrushchev, his personality was such that the other bigshots couldn’t help overlooking him. Just as the rest of the Politburo couldn’t wrap their heads around the idea of this uncouth quasi-Ukrainian peasant being a major threat, so the rest of the Nazi leaders couldn’t help seeing Himmler as this fussy little file clerk.
It’s a hell of a trick, and I’ll admit, I’m buffaloed. Even if Himmler (Khrushchev) was one hell of an actor, and the egos on the other top Nazis (Soviets) were gravity-defying, they still should’ve been able to see that this fussy little file clerk had some seriously hard boys working for him. Reinhard Heydrich was as ruthless a fuck as was ever born, and Himmler kept him in check. Ditto barbarians like Odilo Globocnik and Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski — they don’t come any nastier than those two, yet Himmler managed them easily. What other conclusion can you possibly draw about Himmler, other than that he was nastier than all of them put together? And yet, apparently, nobody did …
The only explanation for this that I can think of is the Nazis’ ideologization of governmental structures. As opposed to the Soviet experience, where the Party and the Bureaucracy were supposed to be, and often actually were, distinct. After some disastrous experiments with demoting technical experts to field hands, and vice versa, the Russian Communists learned that ideological correctness and “soviet power” does not, in fact, obviate the need for stuff like math. (See also: Mao’s backyard blast furnaces). So the Soviets made sure to separate what they called the “technical intelligentsia” from the Party. The head honcho at Gosplan, Gossnab, etc. would be a Party hack from way back, of course, but the actual brainworkers wouldn’t be. I don’t know just how many of them had Party membership cards, or if any of them did, but nobody I know of rose through the Party’s ranks via Gosplan.
Once a Gosplanner, always a Gosplanner. The technical intelligentsia got all kinds of perks in the Soviet system, but one thing they did not do was get perks inside the Party. You can be a technical expert, or you can be an up-and-coming Party man, but you can’t be both.
The Nazis did the exact opposite of that. The way the Third Reich actually functioned is still opaque in a lot of ways (especially to non-specialists), and of course the pressures of wartime forced a lot of ad hoc measures, but it seems like the SS was supposed to be a sort of All-Purpose Expert Corps. Not only did they have their own army and intelligence service, but they had their own economy — the brief history of the Third Reich makes a lot more sense when you realize that half or more of the official Reich economy was hamstrung by the informal but very real SS economy, operating largely (but far from exclusively) through the labor camps.
Indeed, the SS had their own administration. As incredible as it seems, the Nazis had no grand plan for what to do once they’d conquered Europe. Himmler did, at least as far as the East was concerned, and he tried his damnedest to put it into action in Poland (which is why the General Government was so legendarily brutal). Hitler apparently thought in terms of Germany’s lost late 19th century colonies, when he bothered to think about it at all … which wasn’t often. In his typical Fuhrer-riffic style, he just ignored the problem, trusting to Organizational Darwinism to sort it out …
… which is where the All-Purpose Experts of the SS stepped in. The General Government, for instance, was headed by a civilian lawyer, Hans Frank, but the day to day governance largely fell to the SS, because that’s who stepped up. Poland was an occupied zone, with vital war industries, but it was far behind the front for most of the war; the army couldn’t waste vital manpower garrisoning it. Thus the SSPF (the SS and Police Leader) stepped in, drawing manpower as needed from a wide variety of sources — the camp guards, the Wehrmacht (when garrison troops were available, and when they could wrangle them from the various army commanders), the civilian police, the “General SS”, and so on.
The details aren’t nearly as important as the big picture, which is: Unlike the technical intelligentsia in the Soviet Union, members of the SS could climb to the highest ranks of the Party. Indeed they were expected to: the SS was rapidly becoming a Party-within-the-Party at the outbreak of the war, not least because Himmler awarded a “ceremonial” SS rank to anyone who mattered politically in the various departments. The savvier guys refused the “honor,” of course, because they didn’t want to be subordinate to Himmler, even ceremonially, but many didn’t. Which meant that had the Nazis won the war, not only would Himmler have been the next Fuhrer, but the SS would’ve closed ranks, essentially taking over The Party — they’d be the Inner Party, as opposed to the “mere Nazis” of the Outer Party.
December 24, 2021
How Hitler, Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin Spent Christmas – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 23 Dec 2021They might be four of the most powerful politicians and/or military leaders on earth, but they are also citizens of their respective countries and today we take a look at what they do over the traditional Christmas holidays in 1942.
(more…)