Lorenzo Warby analyzes the three claims that underpin the intellectual structure of all the sub-categories derived from Critical Theory:
Universities across Anglo-America, and across the West more broadly, have become increasingly dominated by a Critical Theory magisterium: a teaching authority that claims ultimate or trumping moral authority. This magisterium is based on Critical Theory and its derivatives — Critical Race Theory, Critical Pedagogy, Queer Theory, Post-Colonial Theory, Settler-Colonial Theory, and so on: which constitutes the Critical Social Justice matrix.
This magisterium has come to increasingly dominate academe for a range of reasons. It generates intolerant zealots, so benefits from the dynamics of an intolerant minority.
It offers a powerful shared status game — affirm beliefs X, Y, Z and that makes you A Good Person. This status game spreads a supporting censorious intolerance, for if affirming beliefs X, Y, Z and makes you A Good Person, then denying X, Y, or Z makes you A Bad Person.
This justifies shaming and shunning anyone who denies X, Y, Z, because they are Bad People and its shows your commitment to what makes someone A Good Person. It shows commitment to the shared status game. This status game generates moralised cognitive assets, and you protect the value of those assets by participating in — or at least going along with — the shaming and the shunning.
The status game generates moral projects that the central administrations of universities can use to expand their authority, range of action, and so resources. An opportunity they have enthusiastically embraced. An opportunity that corporate, non-profit and government bureaucracies have also enthusiastically embraced.
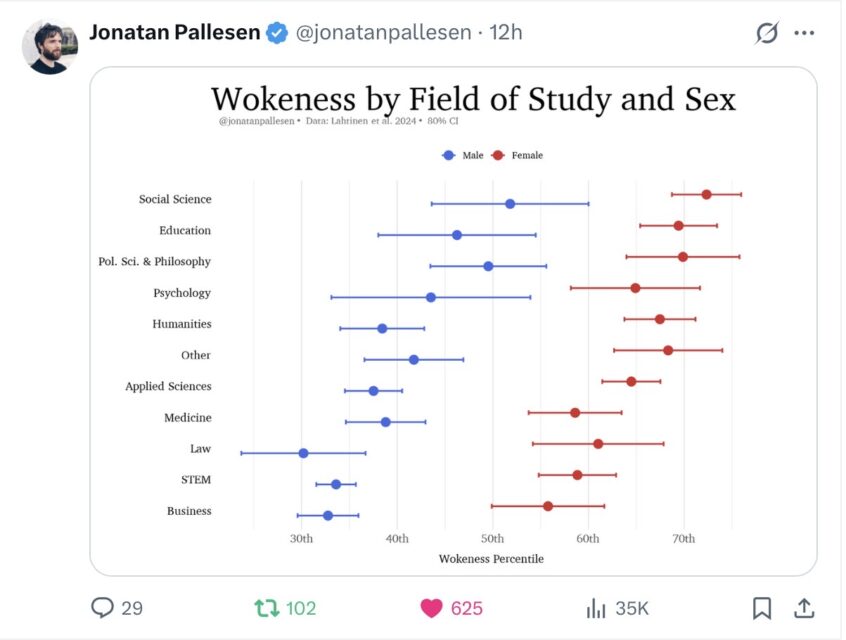
The emotions this status game attaches to those moralised cognitive assets — care, compassion, concern for the marginalised, if you affirm those beliefs, the opposite if you deny them — also plays into fears about threatening emotions (and safety through norm conformity) which are much stronger among men than women. Women are thus systematically more hostile to freedom of speech than men.
It is an exaggeration to claim that “wokery” is just the consequence of feminisation of institutions and occupations. It is, however, true that what works for — what is emotionally resonant in — increasingly feminised institutions and occupations has been selected for.
Source: data taken from this paper.
But the Critical Theory magisterium has expanded across academe — and beyond — due to the nature of its three foundational claims:
- A blank slate view of human nature.
- A view of social dynamics as dominated by conflict.
- An activist relationship with information: that the trumping purpose is not to describe the world, but to change it.
The blank slate view of human nature — not merely that we are not born without inborn ideas, but that everything that forms us is social — means that any level of social transformation that can be conceived is attainable. Provided enough social power can be assembled—to move human action, speech and thought in the correct direction—the socially-transformative society free of oppression and alienation can be created.
The grander the conceived purpose, the more energising and motivating it is. But also the more it rhetorically trumps anyone who is willing to “settle” for less than complete human liberation. This then feeds back into energising and motivating, as it provides an endless sense of being moral trumps.
A recurring version of such blank slate claims is that our “true” nature has been obscured or repressed by oppressive forces. This might be the alienation via private property (Marx) or by patriarchy, or white supremacy, or heteronormativity or whatever.
The most dramatic statement of the “repressed true nature” claim is also the earliest, in the first sentence of Jean-Jacques Rousseau‘s The Social Contract (1762):
Man is born free and everywhere he is in chains. (l’homme est né libre, et partout il est dans les fers.)
The view that oppressive forces are blocking our true nature goes naturally with the claim that social dynamics are dominated by conflict. This dominated-by-conflict claim was classically stated by Marx and Engels as the first sentence of the first chapter of The Communist Manifesto:
The history of all hitherto existing society is the history of class struggles.
If conflict dominates social dynamics, then the prosecution of such conflict so as to achieve human liberation becomes the ultimate moral good. Coordinating the fighters for human liberation becomes a moral urgency. To prosecute that struggle becomes the most important thing one can do.
Both of these claims naturally lead to, and gain strength from the claim, that the morally trumping thing to do with information is to prosecute the struggle for human liberation. Marx famously said:
The philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways; the point is to change it. Theses on Feuerbach, Thesis Eleven, 1845.
Max Horkheimer, in his seminal essay Traditional and Critical Theory (1937) tells us that:
Critical thinking, on the contrary, is motivated today by the effort really to transcend the tension and to abolish the opposition between the individual’s purposefulness, spontaneity, and rationality, and those work-process relationships on which society is built. Critical thought has a concept of man as in conflict with himself until this opposition is removed. If activity governed by reason is proper to man, then existent social practice, which forms the individual’s life down to its least details, is inhuman, and this inhumanity affects everything that goes on in the society.
Critical Theory is activist Theory, aimed at human liberation from the unwanted constraints of existing society and epitomises the activist relationship with information. All scholarship is trumped by this aim and so the most authoritative scholarship is that which is most committed to this aim.
Source. Notice the delusional claim of the first listed article. The intrusion of such updated Lysenkoism into contemporary science and medicine is even more rampant with matters Trans.