Real Time History
Published 7 Oct 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimehistory
In early October 1870, the German states are still confident the Franco-Prussian War is as good as over. But two events might cross their plans: One of the leaders of the new French Republic, Leon Gambetta, escapes the Siege of Paris in a hot-air balloon to coordinate the French Armies outside of Paris. And in Ablis, French guerrilla fighters, the so-called Franc-Tireurs, ambush a German patrol in their sleep — with swift German retribution.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Arand, Tobias: Gestorben für “Vaterland” und “Patrie” – Die toten Krieger aus dem Feldzug von 1870/71 auf dem “Alten Friedhof” in Ludwigsburg. Ludwigsburg 2012
Hahn, Joachim: Jüdisches Leben in Ludwigsburg. Geschichte, Quellen, Dokumentation. Karlsruhe 1998
Schneider, Fernand Thiébaut: “Der Krieg in französischer Sicht”, in: Entscheidung 1870. Der deutsch-französische Krieg, hrsg. v. Wolfgang von Groote und Ursula von Gersdorff. Stuttgart 1970. S. 165-203
» SOURCES
Engels, Friedrich: Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg. Sechzig Artikel aus der “Pall Mall Gazette”. Berlin (Ost) 1957Huber, Rudolf (Hrsg.): Dokumente zur deutschen Verfassungsgeschichte. Bd. 2. 1851-1900. Stuttgart 1964
Kürschner, Joseph (Hrsg.): Der große Krieg 1870-71 in Zeitzeugenberichten. Leipzig o.J. (1895)
N.N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870/71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Philippson, G.: “Jom Kippur 1870 vor Metz”, in: Wegweiser für die Jugendliteratur, Heft 4, 6 (1910). S. 26-27
Steenackers, François-Frédéric/Le Goff, F.: Histoire du gouvernement de la Défense nationale en province, 4 Septembre 1870 – 8 Février 1871. Bd. II. Paris 1884
Tissandier, Gaston: Souvenirs et récits d’un aérostier militaire de l’armée de la Loire. Paris 1891
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
October 8, 2021
Rise of Guerrilla Warfare & Daring Balloon Escapes – The Franco-Prussian War Early October 1870
October 1, 2021
This French General Saved Strasbourg From Total Destruction During the Franco-Prussian War 1870
Real Time History
Published 30 Sep 2021The symbolic city of Strasbourg had been besieged since the early stages of the Franco-Prussian War. The German siege troops are ready to breach the walls of the city and take it by storm. To avoid the destruction of the city, French general Uhrich surrenders and chooses, in his view, honor above glory.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: Gestorben für “Vaterland” und “Patrie”. Die toten Krieger aus dem Feldzug von 1870/71 auf dem “Alten Friedhof” in Ludwigsburg. Ludwigsburg 2012Ders.: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018
Chrastil, Rachel: The Siege of Strasbourg. Cambridge, 2014
» SOURCES
Busch, Moritz: Graf Bismarck und seine Leute vor Paris. Bd. 1. Leipzig 1878Du Casse, Albert: Journal authentique du Siège de Straßbourg. Paris 1871
Fischbach, Gustave: Le siège et le bombardement de Strasbourg, Paris, 1871
Fontane, Theodor: Der Krieg gegen Frankreich 1870-1871. Bd. 2. Berlin 1874
Kriegsgeschichtliche Abtheilung des Großen Generalstabs (Hrsg.): Der deutsch-französische Krieg 1870-71. II.1. Berlin 1878
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Das Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
N.N. Straßbourg. Paris 1874
N.N. (Hrsg.): Theodor Fontane. Kriegsgefangen – Erlebtes 1870. Briefe 1870/71. Berlin (0st) 1984
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
September 18, 2021
Paris Fights Back – The French Battle Against German Encirclement I Franco-Prussian War 1870
Real Time History
Published 16 Sep 2021Support Glory & Defeat: https://realtimehistory.net/gloryandd…
The German armies are on their way to encircle the French capital Paris after their victory at Sedan. The new French government is raising new troops all across the country and in Paris itself to stem the tide. Poorly equipped and poorly trained troops fight the Germans at Sceaux/Chatillon. Meanwhile, the German states start their negotiations for German unification.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französischen Krieges erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Bourguinat, Nicolas/Vogt, Gilles: La guerre franco-allemande de 1870. Une histoire globale. Paris 2020
Gouttman, Alain. La grande défaite de 1870-1871. Paris 2015
Haselhorst, Olaf: Operationen der deutschen Heere im Krieg gegen Frankreich 1870/71, in: Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg 1870/71.
Vorgeschichte, Verlauf, Folgen, hrsg. v. J. Ganschow unter anderem Graz 2009, S. 83–120
Milza, Pierre: L’année terrible. Paris 2009
» SOURCES
Chuquet, Arthur: La Guerre 1870-71. Paris 1895Busch, Moritz: Bismarck und seine Leute während des Kriegs mit Frankreich Band. 1. Leipzig 1878.
Goncourt, Edmonde de: Memoires de la vie Litteraire. Paris 1890
Kriegsgeschichtliche Abtheilung des Großen Generalstabes (Hrsg.): Der deutsch-französische Krieg 1870-71. II.1 Berlin. 1878
Russell, William Howard: My diary during the last great war. London and New York, 1874
Sternegg, Generalmajor von: Schlachten-Atlas des 19. Jahrhunderts. Band 10. Deutsch-Französischer Krieg1870/71. Leipzig u.a. o.J. [1885]
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
September 10, 2021
Why France Did Not Surrender After Sedan – Empress Eugénie Flees The Country I Franco-Prussian War
realtimehistory
Published 9 Sep 2021Sign up for a free 1 month trial for Skillshare: https://skl.sh/realtimehistory08211
After the French defeat at Sedan, the German states expect peace negotiations. But instead the new French republic declares an early form of “total war” and continues the fight. Meanwhile Empress Eugénie flees the country for Britain.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018
Arand, Tobias/Bunnenberg, Christian (Hrsg.): Karl Klein. Die Fröschweiler Chronik. Hamburg 2021
Herre, Franz: Eugénie. Kaiserin der Franzosen. München 2000
Howard, Michael: The Franco-Prussian War. London 1961
Milza, Pierre: L’année terrible. La guerre franco-prussienne. Septembre 1870 – mars 1871. Paris 2009» SOURCES
Braun, Lily (Hrsg.): Kriegsbriefe aus den Jahren 1870/71 von Hans v. Kretschman. Berlin 1911
Hérisson, Maurice Graf d’: Journal d’un officier d’ordonannce. Juillet 1870 – Février 1871. Paris 1885
Goncourt, Edmond de: Journal des Goncourt. Memoire de la vie litteraire. 2.1. 1870-1871. Paris 1890
Russell, William Howard: Meine sieben Kriege. Die ersten Reportagen von den Schlachtfeldern des 19. Jahrhunderts. Frankfurt a. M. 2000» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
September 9, 2021
Did Freudian Psychology Create Modern Art? | B2W: ZEITGEIST! I E.25 Harvest 1924
TimeGhost History
Published 8 Sep 2021The Surrealist Movement is born this season with unsurprising eccentric drama. Salvador Dali will one day be a part of it, but for now he is still in art school and has actually only just come out of prison. Also this season, a crime which sees police chasing America’s first ever “Public Enemy No. 1”
(more…)
September 4, 2021
Battle of Sedan – German Victory and Fall of the French Empire (Franco-Prussian War)
realtimehistory
Published 2 Sep 2021The Battle of Sedan was one of the pivotal moments in the 19th century. The French 2nd Empire’s defeat at Sedan (and the capture of Emperor Napoleon III) unleashed social tensions in Paris and a new French republic was proclaimed. And while the victory of the German Armies was resounding, the cost at places like Bazeilles was also high.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französischen Krieges erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Barry, Quintin: The Franco-Prussian War 1870-1871. Vol 1: the Campaign of Sedan. Solihull 2006
Bourguinat, Nicolas/Vogt, Gilles: La guerre franco-allemande de 1870. Une histoire globale. Paris 2020
Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite de 1870-1871. Paris 2015
Howard, Michael: The Franco-Prussian War. London 1961
Herre, Franz: Eugénie. Kaiserin der Franzosen. Stuttgart, München 2000
Milza, Pierre: L’année terrible. Paris 2009
» SOURCES
Chuquet, Arthur. La Guerre 1870-71. Paris 1895Fontane, Theodor: Der Krieg gegen Frankreich. Bd. Berlin 1874
Kühnhauser, Florian: Kriegs-Erinnerungen eines Soldaten des königlich bayerischen Infanterie-Leib-Regiments. Patenkirchen 1898
N.N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870-71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Sheridan, Philip H.: Von Gravelotte nach Paris. Erinnerungen aus dem deutsch-französischen Kriege. Leipzig 1889
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
July 19, 2021
May 26, 2021
QotD: Modern architecture is ugly … or worse
The British author Douglas Adams had this to say about airports: “Airports are ugly. Some are very ugly. Some attain a degree of ugliness that can only be the result of special effort.” Sadly, this truth is not applicable merely to airports: it can also be said of most contemporary architecture.
Take the Tour Montparnasse, a black, slickly glass-panelled skyscraper, looming over the beautiful Paris cityscape like a giant domino waiting to fall. Parisians hated it so much that the city was subsequently forced to enact an ordinance forbidding any further skyscrapers higher than 36 meters.
Or take Boston’s City Hall Plaza. Downtown Boston is generally an attractive place, with old buildings and a waterfront and a beautiful public garden. But Boston’s City Hall is a hideous concrete edifice of mind-bogglingly inscrutable shape, like an ominous component found left over after you’ve painstakingly assembled a complicated household appliance. In the 1960s, before the first batch of concrete had even dried in the mold, people were already begging preemptively for the damn thing to be torn down. There’s a whole additional complex of equally unpleasant federal buildings attached to the same plaza, designed by Walter Gropius, an architect whose chuckle-inducing surname belies the utter cheerlessness of his designs. The John F. Kennedy Building, for example — featurelessly grim on the outside, infuriatingly unnavigable on the inside — is where, among other things, terrified immigrants attend their deportation hearings, and where traumatized veterans come to apply for benefits. Such an inhospitable building sends a very clear message, which is: the government wants its lowly supplicants to feel confused, alienated, and afraid.
Brianna Rennix and Nathan J. Robinson, “Why You Hate Contemporary Architecture”, Current Affairs, 2017-10-31.
March 25, 2021
Modern Artists: The Original Shitposters! | B2W: ZEITGEIST! I E.14 – Winter 1922
TimeGhost History
Published 24 Mar 2021The interwar era has seen an explosion of art movements all vying to offer the most revolutionary response to modern society. The competition is intense and, as we shall see, often spills over into open conflict.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Francis van Berkel
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Francis van Berkel
Edited by: Michał Zbojna
Sound design: Marek KamińskiColorizations:
Daniel Weiss – https://www.facebook.com/TheYankeeCol…Sources:
Some images from the Library of CongressSoundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
“Epic Adventure Theme 3” – Håkan Eriksson
“Crimp” – Hysics
“Substage” – Jay Varton
“Appeased Soundscape 01” – August Wilhelmsson
“Stranger Days” – Alexandra Woodward
“Superior” – Silver Maple
“Rememberance” – Fabien Tell
“Ghost Dungeons” – Ethan Sloan
“Ancient Discoveries” – Gabriel LewisArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
TimeGhost History
2 days ago (edited)
The original idea for this episode came from me (Francis here, hello) stumbling across a passing reference to the 1922 trial of André Breton buried deep in a Wikipedia article. It led me down a huge rabbit hole on the history of the chaotic artists milling around in Paris, New York, Zurich, and beyond.Considering that it also takes place in the same season as the publication of Ulysses, the release of Nosferatu, the birth of Brazillian Modernism, and more, I realized that it was the perfect opportunity to dedicate an entire episode to the weird and wonderful artistic movements of the modern era. If this kind is new to you then consider this episode your introduction to the topic. Indy talks about the Cubist revolution, then Dadaism, Expressionism, and more.
In case all that seems a bit too niche for your liking then look at it this way: if you want to understand how people processed the horrors of the Great War, the rise of mass production, and modern geopolitical machinations, then diving into the art of the time is a great place to start.
Watch the video to find out why.
March 16, 2021
“… because who doesn’t like to see both wine snobs and the French taken down a peg or two?”
In The Critic, Henry Jeffreys sadly notes the passing of Steven Spurrier, perhaps best known for organizing the “Judgement of Paris” in 1976:
The wine world lost one of its giants this week in Steven Spurrier. He’s one of the very few people who managed to put the subject on the front pages of the world’s newspapers when he organised the so-called Judgement of Paris competition in 1976.
This was a blind tasting judged by the great and good of the French wine world pitting the might of Bordeaux and Burgundy, against California, a place whose wines most Europeans had never even tasted. Surely France could not lose. But thrillingly, and deliciously, it did, with Californian wines coming top in both the white and red categories. It inspired a book and a feature film Bottle Shock starring Alan Rickman as Spurrier. In fact, the media, particularly over here and in the US, has never lost interest. Perhaps because who doesn’t like to see both wine snobs and the French taken down a peg or two?
More significantly, it marked the arrival of American and later Australian, Chilean and other New World wines. Fittingly, I first met Spurrier at a round table tasting for an upmarket Chilean wine. These tastings could be nerve-wracking affairs for new writers. They still fill me with anxiety. I never know what to say as the big beasts of the wine world opine. Sometimes, the cellar rooms where such tastings are often held seem much too small for all those jostling egos.
I was sat next to Spurrier and, much to my surprise, he asked me my opinion on the wines, something I don’t think any other writer had done up to that point. He then engaged with what I said, and said something like, “yes, I think you’ve got it there.” Or words to that effect. It’s quite hard to express how startling this experience was to someone outside the wine world. It’s like Martin Scorsese asking your opinion on film making.
December 2, 2020
The Nazis: Most Notorious Art Thieves in History – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 1 Dec 2020During their occupation of large parts of Europe, the Nazis systematically looted foreign countries for art, gold and other items holding financial or cultural value. Often not for any larger purpose, but for their own, egocentric, criminal gain.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Joram Appel
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Joram Appel
Edited by: Karolina Dołęga
Sound design: Marek Kamiński
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
– Klimbim
– Daniel Weiss
– Norman Stewart – https://oldtimesincolor.blogspot.com/
– Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
– Spartacus OlssonSources:
– Bundesarchiv
– Yad Vashem: 73_1_34, 72GO8, 03_198, 73_1_23, 99co5, 186_271, 99co6, 16_28,
– United States Holocaust Memorial Museum ID EA 65940
– RijksmuseumSoundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
– “The Inspector 4” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “London” – Howard Harper-Barnes
– “Moving to Disturbia” – Experia
– “Break Free” – Fabien Tell
– “Remembrance” – Fabien Tell
– “Disciples of Sun Tzu” – Christian AndersenArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
1 hour ago
Throughout history, people have obsessed with hidden treasure of past thieves. There were plenty of hidden art and gold collections left behind by the Nazis, often in caves or vaults. Many were found after the war by the several Allied units tasked with locating valuables. While finding some Nazi gold stash still sounds exciting, we should not forget the story behind this loot. Writing this episode, the exciting nature of it quickly faded once I fully realised how thousands of normal people were robbed of everything they owned – including their lives. The thievery of valuables can not be seen outside of the context of Nazi racial policies and ultimately the murder of millions in the Holocaust. The top Nazis truly reconfirm their true criminal nature in this episode, not caring a bit about anything other than themselves.Cheers,
Joram
September 18, 2020
August 25, 2020
How we used to “dine out” (and someday might be able to again)
In The Critic, Alexander Larman reviews The Restaurant: A history of eating out by William Sitwell:
The recent enforced lockdown closure was a potential death blow to the entire [restaurant] industry. Which makes William Sitwell’s luxurious book both a celebration and an unintentional requiem for what may be a bygone time.
His central thesis is clear: the history of dining out is also a social history of evolving cultures and tastes. This means that the subjects he writes about range from ancient Pompeii to the growth of the sushi conveyor belt restaurant, encompassing everything from medieval taverns and the French Revolution to the rise of Anglo-Indian cuisine.
It is a broad and impressive spectrum, but perhaps Sitwell has, like some of the less fortunate people he describes, bitten off more than he can chew. His opening chapter about Pompeii is rich in surprising detail (graffiti uncovered outside one tavern when it was excavated ranged from the poetic — “Lovers are like bees in that they lead a honeyed life” — to the crude — “I screwed the barmaid”) and an insightful evocation of the dining culture in Ancient Rome.
He is then, unfortunately, faced with the insurmountable difficulty that the restaurant, as we know it today, did not exist until the late eighteenth century, meaning that his definition of “eating out” has to do some extremely heavy lifting.
There is as much padding in the early chapters as there is around some of his subjects’ waistlines. Much of what he writes is very interesting and often amusing, such as the way in which coffee, first drunk in London around the time of the Restoration, became associated both with health-giving properties and reportedly making men impotent, withered “cock-sparrows”. Yet there are also lengthy sections that have little or nothing to do with restaurants, such as a potted history of the Industrial Revolution.
Nevertheless, when Sitwell finally gets into his stride and begins to write about eateries proper, his authority and enthusiasm are palpable. He describes the dawn of fine dining in Paris in the nineteenth century evocatively. London lagged behind, although gentlemen’s clubs such as the Athenaeum and Reform offered some delights for the wealthy thanks to chefs (French, naturally) such as Alexis Soyer who implemented what one biographer called “the most famous and influential working kitchen in Europe” in 1841, complete with gas-fired stoves, butcher’s rooms and a fireplace devoted to the roasting of game and poultry.
August 21, 2020
“Uprising” Pt. 2 – The Liberation of Paris 1944 – Sabaton History 081 [Official]
Sabaton History
Posted 20 Aug 2020Mid-August 1944. The battle for France enters its decisive phase. With the Allied spearheads just 100 km away from Paris, the Résistance prepares for its long-awaited uprising. While collaborators and fascist officials flee the city in panic, many insurgents are eager to immediately rise up against the occupation and fight the Germans in the streets. But there is need for caution. The Germans are still there in force, and they have tanks and machine guns. The fear that this might turn into “another Warsaw” if the Allies don’t show up in time is very real.
Support Sabaton History on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/sabatonhistory
Listen to “Uprising” on the album Coat Of Arms:
https://music.sabaton.net/CoatOfArmsWatch the Official Music Video of “Uprising”:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=01IaK…Listen to Sabaton on Spotify: http://smarturl.it/SabatonSpotify
Official Sabaton Merchandise Shop: http://bit.ly/SabatonOfficialShopHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Markus Linke and Indy Neidell
Directed by: Astrid Deinhard and Wieke Kapteijns
Produced by: Pär Sundström, Astrid Deinhard, and Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Executive Producers: Pär Sundström, Joakim Broden, Tomas Sunmo, Indy Neidell, Astrid Deinhard, and Spartacus Olsson
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Editor: Iryna Dulka
Sound Editor: Marek Kaminski
Archive by: Reuters/Screenocean https://www.screenocean.com
Community Manager: Maria Kyhle
All music by SabatonSources:
– Imperial War Museum: B 9298
– Bundesarchiv, CC-BY-SA 3.0: Bild_101I-027-1477-16, Bild_183-2008-0710-500, Bild_183-2003-1112-500
– lubini from freesound.orgAn OnLion Entertainment GmbH and Raging Beaver Publishing AB co-Production.
© Raging Beaver Publishing AB, 2019 – all rights reserved.
July 18, 2020
“Agglomerationists” today and in the Middle Ages
In his latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes compares the views of today’s “urbanists” with the “agglomerationists” of the late Medieval period:
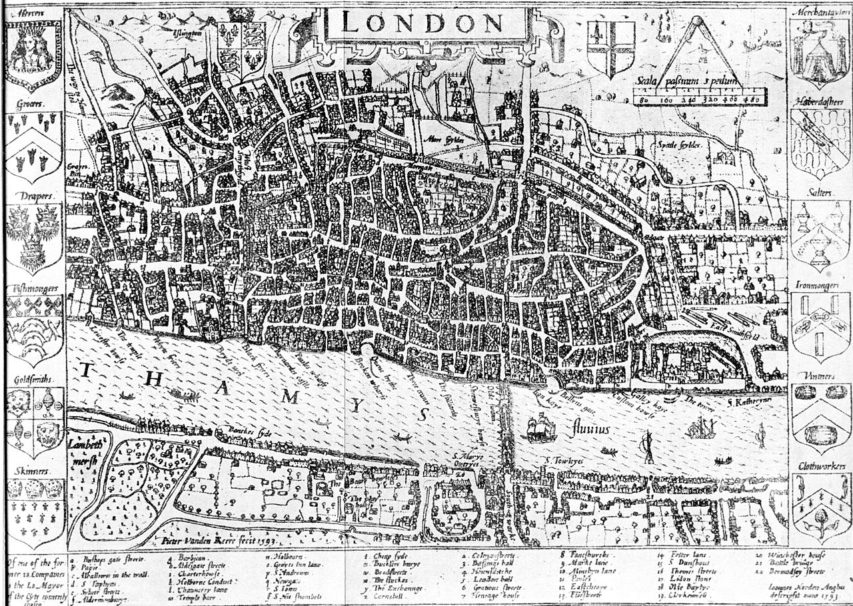
John Norden’s map of London in 1593. There is only one bridge across the Thames, but parts of Southwark on the south bank of the river have been developed.
Wikimedia Commons.
The other day, economic historian Tim Leunig tagged me into a comment on twitter with the line “intellectually I think the biggest change since settled agriculture was the idea that most people could live in cities and not produce food”. What’s interesting about that, I think, is the idea that this was not just an economic change, but an intellectual one. In fact, I’ve been increasingly noticing a sort of ideology, if one can call it that, which seemingly took hold in Britain in the late sixteenth century and then became increasingly influential. It was not the sort of ideology that manifested itself in elections, or even in factions, but it was certainly there. It had both vocal adherents and strenuous opponents, the adherents pushing particular policies and justifying them with reference to a common intellectual tradition. Indeed, I can think of many political and economic commentators who are its adherents today, whether or not they explicitly identify as such.
Today, the people who hold this ideology will occasionally refer to themselves as “urbanists”. They are in favour of large cities, large populations, and especially density. They believe strongly in what economists like to call “agglomeration effects” — that is, if you concentrate people more closely together, particularly in cities, then you are likely to see all sorts of benefits from their interactions. More ideas, more trade, more innovation, more growth.
Yet urbanism as a word doesn’t quite capture the full scope of the ideology. The group also heavily overlaps with natalists — people who think we should all have more babies, regardless of whether they happen to live in cities — and a whole host of other groups, from pro-immigration campaigners, to people setting up charter cities, to advocates of cheaper housing, to enthusiasts for mass transit infrastructure like buses, trams, or trains. The overall ideology is thus not just about cities per se — it seems a bit broader than that. Given the assumptions and aims that these groups hold in common, perhaps a more accurate label for their constellation of opinions and interests would be agglomerationism.
So much for today. What is the agglomerationist intellectual tradition? In the sixteenth century, one of the mantras that keeps cropping up is the idea that “the honour and strength of a prince consists in the multitude of the people” — a sentiment attributed to king Solomon. It’s a phrase that keeps cropping up in some shape or form throughout the centuries, and used to justify a whole host of agglomerationist policies. And most interestingly, it’s a phrase that begins cropping up when England was not at all urban, in the mid-sixteenth century — only about 3.5% of the English population lived in cities in 1550, far lower than the rates in the Netherlands, Italy, or Spain, each of which had urbanisation rates of over 10%. Even England’s largest city by far, London, was by European standards quite small. Both Paris and Naples were at least three times as populous (don’t even mention the vast sixteenth-century metropolises of China, or Constantinople).
Given their lack of population or density, English agglomerationists had a number of role models. One was the city of Nuremburg — through manufactures alone, it seemed, a great urban centre had emerged in a barren land. Another was France, which in the early seventeenth century seemed to draw in the riches to support itself through sheer exports. One English ambassador to France in 1609 noted that its “corn and grain alone robs all Spain of their silver and gold”, and warned that it was trying to create still new export industries like silk-making and tapestry weaving. (The English rapidly tried to do the same, though with less success.) France may not have been especially urban either, but Paris was already huge and on the rise, and the country’s massive overall population made it “the greatest united and entire force of any realm or dominion” in Christendom. Today, the population of France and Britain are about the same, but in 1600 France’s was about four times as large. Some 20 millions compared to a paltry 5. If Solomon was right, then England had a lot of catching up to do to even approach France in honour.















