This week and next, we’re going to look at an issue not of battles, but of settings: pre-modern cities – particularly the trope of the city, town or castle set out all alone in the middle of empty spaces. Why does the city or castle-town set amidst a sea of grass feel so off? And what should that terrain look like – especially in how it is shaped by the human activity taking place in a town’s hinterland. This is less of a military history topic (though we’ll see that factors in), and more of an economic history one. If that’s your jam – stay tuned, there will be more. If it’s not – don’t worry, we won’t abandon military topics either.
I find myself interested in pre-modern economies and militaries in roughly equal measure (in part because both are such crucial elements of state or societal success or failure). One of the reasons is that they are so interconnected: how military force is raised, supplied, maintained and projected is deeply dependent on how the underlying economy (which supplies the men, food, weapons and money) is structured and organized. And military institution and activities often play an important role in shaping economic structures in turn. So even if you are just here for the clashing of swords, remember: every sword must be forged, and every swordsman must be fed.
(Additional aside: I am assuming a west-of-the-Indus set of cereals: grain, barley and millet chiefly. Specifically, I am not going to bring in rice cultivation – the irrigation demands and density of rice farming changes a lot (the same is also true, in the opposite direction, to agriculture based around sorghum or yams). Most (western) fantasy and historic dramas are not set in rice-planting regions (and many East Asian works seem to have a much better grasp on where rice fields go and need no correction), so I’m going to leave rice out for now. I’m honestly not qualified to speak on it anyway – it is too different from my own area of research focus, which is on a Mediterranean agricultural mix (wheat, barely, olives, grapes), and I haven’t had the chance to read up on it sufficiently).
Lonely Cities
There’s a certain look that castles and cities in either historical dramas or fantasy settings set in the ancient or medieval world seem to have: the great walls of the city or castle rise up, majestically, from a vast, empty sea of grassland. […] These “lonely cities” are everywhere in fantasy and historical drama. I think we all know something is off here: cities and other large population centers do not simply pop up in the middle of open fields of grass, generally speaking. So if this shouldn’t all be grassland, what should be here? Who should be here?
What is a City For?
I think we need to start by thinking about why pre-modern towns and cities exist and what their economic role is. I’ll keep this relatively brief for now, because this is a topic I’m sure we’ll return to in the future. As modern people, we are used to the main roles cities play in the modern world, some of which are shared by pre-modern cities, and some of which are not. Modern cities are huge production centers, containing in them both the majority of the labor and the majority of the productive power of a society; this is very much not true of pre-modern cities – most people and most production still takes place in the countryside, because most people are farmers and most production is agricultural. Production happens in pre-modern cities, but it comes nowhere close to dominating the economy.
The role of infrastructure is also different. We are also used to cities as the center-point lynch-pins of infrastructure networks – roads, rail, sea routes, fiber-optic cable, etc. That isn’t false when applied to pre-modern cities, but it is much less true, if just because modern infrastructure is so much more powerful than its pre-modern precursors. Modern infrastructure is also a lot more exclusive: a man with a cart might visit a village where the road does not go, but a train or a truck cannot. The Phoenician traders of the early iron age could pull their trade ships up on the beach in places where there was no port; do not try this with a modern container ship. Infrastructure is largely a result of cities, not their original purpose or cause.
So what are the core functions of a pre-modern city? I see five key functions:
- Administrative Center. This is probably the oldest purpose cities have served: as a focal point for political and religious authorities. With limited communications technology, it makes sense to keep that leadership in one place, creating a hub of people who control a disproportionate amount of resources, which leads to
- Defensive/Military Center. Once you have all of those important people and resources (read: stockpiled food) in one place, it makes sense to focus defenses on that point. It also makes sense to keep – or form up – the army where most of the resources and leaders are. People, in turn, tend to want to live close to the defenses, which leads to
- Market Center. Putting a lot of people and resources in one place makes the city a natural point for trade – the more buyers and sellers in one place, the more likely you are to find the buyer or seller you want. As a market, the city experiences “network” effects: each person living there makes the city more attractive for others. Still, it is important to note: the town is a market hub for the countryside, where most people still live. Which only now leads to
- Production Center. But not big industrial production like modern cities. Instead it is the small, niche production – the sort of things you only buy once-in-a-while or only the rich buy – that get focused into cities. Blacksmiths making tools, producers of fine-ware and goods for export, that sort of thing. These products and producers need big markets or deep pockets to make end meet. The majority of the core needs of most people (things like food, shelter and clothes) are still produced by the peasants, for the peasants, where they live, in the country. Still, you want to produce goods made for sale rather than personal use near the market, and maybe sell them abroad, which leads to
- Infrastructure Center. With so much goods and communications moving to and from the city, it starts making sense for the state to build dedicated transit infrastructure (roads, ports, artificial harbors). This infrastructure almost always begins as administrative/military infrastructure, but still gets used to economic ends. Nevertheless, this comes relatively late – things like the Persian Royal Road (6th/5th century BC) and the earliest Roman roads (late 4th century BC) come late in most urban development.
Of course, all of these functions depend, in part, on the city as a concentration of people. but what I want to stress – before we move on to our main topic – is that in all of these functions the pre-modern city effectively serves the countryside, because that is still where most people are and where most production (and the most important production – food) is. The administration in the city is administering the countryside – usually by gathering and redistributing surplus agricultural production (from the countryside!). The defenses in the city are meant to defend the production of the countryside and the people of the countryside (when they flee to it). The people using the market – at least until the city grows very large – are mostly coming in from the country (this is why most medieval and ancient markets are only open on certain days – for the Romans, this was the “ninth day”, the Nundinae – customers have to transit into town, so you want everyone there on the same day).
(An aside: I have framed this as the city serving the economic needs of the countryside, but it is equally valid to see the city as the exploiter of the countryside. The narrative above can easily be read as one in which the religious, political and military elite use their power to violently extract surplus agricultural production, which in turn gives rise to a city that is essentially a parasite (this is Max Weber’s model for a “consumer city”) that contributes little but siphons off the production of the countryside. The study of ancient and medieval cities is still very much embroiled in a debate between those who see cities as filling a valuable economic function and those who see them as fundamentally exploitative and rent-seeking; I fall among the former, but the latter do have some very valid points about how harshly and exploitatively cities (and city elites) could treat their hinterlands.)
Consequently, the place and role of almost every kind of population center (city, town or castle-town) is dictated by how it relates to the countryside around it (the city’s hinterland; the Greeks called this the city’s khora (χώρα)).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Lonely City, Part I: The Ideal City”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-07-12.
June 12, 2023
QotD: Cities in the pre-modern era
May 25, 2023
The greatest economic moment of the 20th Century was when Thomas Edison invented the chicken
What’s that, you say? Edison didn’t invent the chicken? Yes, yes, okay. Technically it wasn’t Edison and technically the chicken already existed long before then, but Robert Graboyes explains why it’s kinda true:
No, Thomas Edison didn’t invent the chicken, despite my fake, AI-generated photographs above. But around the time of the Apollo moon landings, a future Nobel laureate allegedly declared that the most important invention of the 20th century was the chicken. This cryptic statement offers profound wisdom about possible paths of healthcare innovation in the 21st century. The chicken quote was attributed to Robert Mundell, 1999 Nobel economist, by Dick Zecher, who was my boss at Chase Manhattan Bank and, before that, Mundell’s colleague at the University of Chicago.
How is the chicken — first domesticated more than 5,000 years ago — a 20th-century invention at all? And how was the chicken more important than the airplane, computer, atomic bomb, television, interplanetary rocket — or the countless works of Edison and his crew?
Dick told me that the comment, delivered during an Economics Department seminar, attracted the blank stares that often met Mundell’s odd, enigmatic, and always-profound observations. After a prolonged silence, the befuddled seminar speaker asked what Mundell meant.
His insight was that in the 20th century, modern production methods so drastically reduced the price of chicken that the bird became, for all practical purposes, an entirely new good. According to W. Michael Cox and Richard Alm (“Myths Of Rich And Poor: Why We’re Better Off Than We Think“), a typical American in 1900 worked 160 minutes to earn enough money for a 3-pound chicken. An equivalent worker in 2000 needed only 14 minutes of wages to buy that chicken. Pre-1950s, consumers generally had to eviscerate a commercially bought bird or have a butcher do it. (My mother used to shudder when she recalled the itinerant butcher who would slaughter chickens for my grandmother in their kitchen sink.) Herbert Hoover’s promise of “a chicken in every pot” rings dull to our ears, but in 1928, the phrase sounded like “a flying car in every garage” sounds to ours.
Revolutionary production, distribution and storage methods changed chicken from a Sunday luxury item to the everyman’s protein. Our concept of chicken bears little resemblance to our great-grandparents’ image. Massive reductions in food prices explain why rates of malnutrition and starvation have plummeted worldwide since the mid-20th century.
February 14, 2023
You need a tailor. And a cobbler.
At least, that’s Tom Knighton‘s take:

“The Desbecker-Block Tailoring Co. Buffalo, N. Y. Tailors to all America. We’ve a man on the spot. He takes your measure – we do the rest.” by Boston Public Library is licensed under CC BY 2.0 .
I’m now of the opinion that every man needs a tailor and a cobbler to go along with their barber.
Why? Because quality has a quantity all its own.
Yeah, I know that phrase usually goes the other way around, but we’re not talking about warfare where you need a lot of tanks and airplanes. We’re talking about clothes and accouterments. You can only wear one suit and one pair of shoes at a time. You’ve only got one head to wear a hat on. You don’t need 500 of each to have a well-rounded wardrobe.
So why do we? Why do we, as a society, insist on buying so much so cheaply?
What’s more, are you someone who supports those in the trades while simultaneously engaging in activity that threatens some of them?
Look, I get that not everyone can drop $500 for shoes or $5,000 for suits. I sure can’t, after all, so there’s no way I’d expect anyone else to. In fact, no one has to do any such thing.
However, what they can do is buy the best quality they can find, particularly in a grade that can be repaired and/or altered if needed.
We can start utilizing these tradesmen, hopefully needing them more often than our plumbers or auto mechanics. Not only will we dress better, but we’ll also show more young people there are other ways to go forward in life without spending tens of thousands of dollars to get a college degree that qualifies them for little more than to ask, “Do you want fries with that?”
I’m certainly in agreement with Tom on where the needle should rest on the quality-quantity meter, in that I’ve always preferred to buy higher quality whenever I could afford it rather than cheaper but lower quality items. It’s mostly paid off for me, although others in my family were of the other persuasion, where “more now” was better than “lasts longer”.
In a later post, he quotes Sam Vimes and again, I largely agree:
Despite that, I can buy quality. I may have to pay a bit more upfront, but it’s like the Vimes theory of boots written by Sir Terry Pratchett that’s been talked about here a couple of times:
The reason that the rich were so rich, Vimes reasoned, was because they managed to spend less money. Take boots, for example. He earned thirty-eight dollars a month plus allowances. A really good pair of leather boots cost fifty dollars. But an affordable pair of boots, which were sort of OK for a season or two and then leaked like hell when the cardboard gave out, cost about ten dollars. Those were the kind of boots Vimes always bought, and wore until the soles were so thin that he could tell where he was in Ankh-Morpork on a foggy night by the feel of the cobbles. But the thing was that good boots lasted for years and years. A man who could afford fifty dollars had a pair of boots that’d still be keeping his feet dry in ten years’ time, while a poor man who could only afford cheap boots would have spent a hundred dollars on boots in the same time and would still have wet feet. This was the Captain Samuel Vimes “Boots” theory of socioeconomic unfairness.
So, spend the money on the leather boots and skip having to spend it later.
As a result, though, that’s kind of luxurious.
January 15, 2023
“Zoomers and Millennials are further to the left to begin with and, more critically, don’t seem to be moving rightward as they age”
Andrew Sullivan on the significant leftward orientation of younger Millennials and Gen Z’ers which does not track to historical models of political belief:

“Millennials” by EpicTop10.com is licensed under CC BY 2.0
It’s dawning on many on the political center and right that the current younger generation in America is not like previous younger generations. They’re immaturing with age. Zoomers and Millennials are further to the left to begin with and, more critically, don’t seem to be moving rightward as they age. A recent, viral piece in the FT added a new spark to the conversation, arguing that if Millennials matured like previous generations, then by the age of 35, they
should be around five points less conservative than the national average, and can be relied upon to gradually become more conservative. In fact, they’re more like 15 points less conservative, and in both Britain and the US are by far the least conservative 35-year-olds in recorded history … millennials have developed different values to previous generations, shaped by experiences unique to them, and they do not feel conservatives share these.
And the key experiences, it seems to me, are: entering the job market in the wake of the financial crisis; being poorer than your parents when they were the same age; lacking access to affordable housing and childcare; growing up in a far more multiracial and multicultural world than anyone before them; seeing gay equality come to marriage and the military; experiencing the first black president and nearly the first woman; and the psychological and cultural impact of Trump and Brexit.
These are all 21st century phenomena — and simply not experienced by the generations immediately before them. Socially and culturally more diverse, the young are also understandably down on the catastrophic success of neoliberal economics. So of course they are going to be different. When it was their turn on the wealth escalator, it essentially stopped.
Sometimes we forget that these deep factors are what are most seriously in play. And the biggest mistake many of us on the center or right tend to make is assuming that all of the young’s stickier leftiness — especially the most irritating varieties of it — are entirely a function of woke brainwashing, and not related to genuinely unique challenges. A lot is — the indoctrination is real and relentless — but a lot isn’t. And it’s vital to distinguish the two.
The left’s advantage is that they have directly addressed this generation’s challenges, and the right simply hasn’t. The woke, however misguided, are addressing the inevitable cultural and social challenges of a majority-minority generation; and the socialists have long been addressing the soaring inequality that neoliberalism has created. Meanwhile, the right has too often ducked these substantive issues or rested on cheap culture-war populism as a diversionary response. I don’t believe that the young are inherently as left as they currently are. It’s just that the right hasn’t offered them an appealing enough alternative that is actually relevant to them.
That doesn’t mean cringe pandering. It means smarter policies. Some obvious options: encourage much more house-building with YIMBY-style deregulation; expand access to childcare for young, struggling families; tout entrepreneurial and scientific innovation to tackle climate change; expand maternity and paternity leave; redistribute wealth from the super-rich to working Americans to stabilize society and prevent capitalism from undoing itself; and, above all, celebrate a diverse society — and the unique individuals and interactions that make it so dynamic and life-giving.
January 5, 2023
QotD: The Broken Window Fallacy
The broken window fallacy is a classic hurricane-season misstep. “Hurricanes may do damage”, the reasoning goes, “but look on the bright side. Think of how many jobs will be created because of the destruction. Think about all the demand that will be stimulated. Things may look bleak, but this is actually good for the economy.”
Bastiat debunked this reasoning in his 1848 essay “That Which Is Seen and that Which Is Not Seen“, and countless economists since have echoed his remarks. In the essay, he tells the parable of a shopkeeper whose careless son breaks a window, and he asks the reader whether this is good for the economy. At first glance, it’s tempting to say yes. But as Bastiat shows in the story, this conclusion ignores the unseen effects of the broken window.
“If … you come to the conclusion,” he writes, “as is too often the case, that it is a good thing to break windows, that it causes money to circulate, and that the encouragement of industry in general will be the result of it, you will oblige me to call out, ‘Stop there! your theory is confined to that which is seen; it takes no account of that which is not seen.'”
What is not seen, briefly, is the lost opportunities, the things that could have been done with our resources had they not been needed to replace the broken window. Taking those into account, it becomes clear that the broken window is harmful to the economy. After all, there is now one less window in our stockpile of goods.
The same reasoning applies on a larger scale. There may be plenty of jobs and demand when a hurricane destroys a town, but saying this is “good” for the economy is simply wrong. If this logic were true, the more destruction we experience the better off we’d be! But economic reasoning — and plain common sense — tells us this can’t be right.
Patrick Carroll, “3 Economic Fallacies to Watch Out for during Hurrican Season”, Foundation for Economic Education, 2022-09-30.
August 27, 2022
QotD: The key functions of cities in pre-modern economies
As modern people, we are used to the main roles cities play in the modern world, some of which are shared by pre-modern cities, and some of which are not. Modern cities are huge production centers, containing in them both the majority of the labor and the majority of the productive power of a society; this is very much not true of pre-modern cities – most people and most production still takes place in the countryside, because most people are farmers and most production is agricultural. Production happens in pre-modern cities, but it comes nowhere close to dominating the economy.
The role of infrastructure is also different. We are also used to cities as the center-point lynch-pins of infrastructure networks – roads, rail, sea routes, fiber-optic cable, etc. That isn’t false when applied to pre-modern cities, but it is much less true, if just because modern infrastructure is so much more powerful than its pre-modern precursors. Modern infrastructure is also a lot more exclusive: a man with a cart might visit a village where the road does not go, but a train or a truck cannot. The Phoenician traders of the early iron age could pull their trade ships up on the beach in places where there was no port; do not try this with a modern container-ship. Infrastructure is largely a result of cities, not their original purpose or cause.
So what are the core functions of a pre-modern city? I see five key functions:
- Administrative Center. This is probably the oldest purpose cities have served: as a focal point for political and religious authorities. With limited communications technology, it makes sense to keep that leadership in one place, creating a hub of people who control a disproportionate amount of resources, which leads to
- Defensive/Military Center. Once you have all of those important people and resources (read: stockpiled food) in one place, it makes sense to focus defenses on that point. It also makes sense to keep – or form up – the army where most of the resources and leaders are. People, in turn, tend to want to live close to the defenses, which leads to
- Market Center. Putting a lot of people and resources in one place makes the city a natural point for trade – the more buyers and sellers in one place, the more likely you are to find the buyer or seller you want. As a market, the city experiences “network” effects: each person living there makes the city more attractive for others. Still, it is important to note: the town is a market hub for the countryside, where most people still live. Which only now leads to
- Production Center. But not big industrial production like modern cities. Instead it is the small, niche production – the sort of things you only buy once-and-a-while or only the rich buy – that get focused into cities. Blacksmiths making tools, producers of fine-ware and goods for export, that sort of thing. These products and producers need big markets or deep pockets to make end meet. The majority of the core needs of most people (things like food, shelter and clothes) are still produced by the peasants, for the peasants, where they live, in the country. Still, you want to produce goods made for sale rather than personal use near the market, and maybe sell them abroad, which leads to
- Infrastructure Center. With so much goods and communications moving to and from the city, it starts making sense for the state to build dedicated transit infrastructure (roads, ports, artificial harbors). This infrastructure almost always begins as administrative/military infrastructure, but still gets used to economic ends. Nevertheless, this comes relatively late – things like the Persian Royal Road (6th/5th century BC) and the earliest Roman roads (late 4th century BC) come late in most urban development.
Of course, all of these functions depend, in part, on the city as a concentration of people, but what I want to stress […] is that in all of these functions the pre-modern city effectively serves the countryside, because that is still where most people are and where most production (and the most important production – food) is. The administration in the city is administering the countryside – usually by gathering and redistributing surplus agricultural production (from the countryside!). The defenses in the city are meant to defend the production of the countryside and the people of the countryside (when they flee to it). The people using the market – at least until the city grows very large – are mostly coming in from the country (this is why most medieval and ancient markets are only open on certain days – for the Romans, this was the “ninth day”, the Nundinae – customers have to transit into town, so you want everyone there on the same day).
(An aside: I have framed this as the city serving the economic needs of the countryside, but it is equally valid to see the city as the exploiter of the countryside. The narrative above can easily be read as one in which the religious, political and military elite use their power to violently extract surplus agricultural production, which in turn gives rise to a city that is essentially a parasite (this is Max Weber’s model for a “consumer city”) that contributes little but siphons off the production of the countryside. The study of ancient and medieval cities is still very much embroiled in a debate between those who see cities as filling a valuable economic function and those who see them as fundamentally exploitative and rent-seeking; I fall among the former, but the latter do have some very valid points about how harshly and exploitatively cities (and city elites) could treat their hinterlands.)
Consequently, the place and role of almost every kind of population center (city, town or castle-town) is dictated by how it relates to the countryside around it (the city’s hinterland; the Greeks called this the city’s khora (χώρα)).
Bret Devereaux, Collections: The Lonely City, Part I: The Ideal City”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-07-12.
May 30, 2022
Technocratic meddling in developing countries at the local level
One of the readers of Scott Alexander’s Astral Codex Ten has contributed a review of James Ferguson’s The Anti-Politics Machine. The reviewer looked at a few development economics stories that illustrate some of the more common problems western technocrats encounter when they provide their “expert advice” to people in developing countries. This is one of perhaps a dozen or so anonymous reviews that Scott publishes every year with the readers voting for the best review and the names of the contributors withheld until after the voting is finished:
But even if the project was in some sense a “failure” as an agricultural development project, it is indisputable that many of its “side effects” had a powerful and far-reaching impact on the Thaba-Tseka region. […] Indeed, it may be that in a place like Mashai, the most visible of all the project’s effects was the indirect one of increased Government military presence in the region
As the program continued to unfold, the development officials became more and more disillusioned — not with their own choices, but with the people of Thaba-Tseka, who they perceived as petty, apathetic, and outright self-destructive. A project meant to provide firewood failed because locals kept breaking into the woodlots and uprooting the saplings. An experiment in pony-breeding fell apart when “unknown parties” drove the entire herd of ponies off of cliffs to their deaths. Why, Ferguson’s official contacts bemoaned, weren’t the people of Thaba-Tseka committed to their own “development”?
Who could possibly be opposed to trees and horses? Perhaps, the practitioners theorized, the people of Thaba-Tseka were just lazy. Perhaps they “didn’t want to be better”. Perhaps they weren’t in their right mind or had made a mistake. Perhaps poverty makes a person do strange things.
Or, as Ferguson points out, perhaps their anger had something to do with the fact that the best plots of land in the village had been forcibly confiscated to make room for wood and pony lots, without any sort of compensation. The central government was all too happy to help find land for the projects, which they took from political enemies and put in the control of party elites, especially when it could use a legitimate anti-poverty program as cover. In Ferguson’s words, the development project was functioning as an “anti-politics machine” the government could use to pretend political power moves were just “objective” solutions to technical problems.
A local student’s term paper captured the general discontent:
In spite of the superb aim of helping the people to become self-reliant, the first thing the project did was to take their very good arable land. When the people protested about their fields being taken, the project promised them employment. […] It employed them for two months, found them unfit for the work, and dismissed them. Without their fields and without employment they may turn up to be very self-reliant. It is rather hard to know.
Two things stand out to me from this story. First, the “development discourse” lens served to focus the practitioners’ attention on a handful of technical variables (quantity of wood, quality of pony), and kept them from thinking about any repercussions they hadn’t thought to measure.
This is a serious problem, because “negative effects on things that aren’t your primary outcome” are pretty common in the development literature. High-paying medical NGOs can pull talent away from government jobs. Foreign aid can worsen ongoing conflicts. Unconditional cash transfers can hurt neighbors who didn’t receive the cash. And the literature we have is implicitly conditioned on “only examining the variables academics have thought to look at” — surely our tools have rendered other effects completely invisible!
Second, the project organizers somewhat naively ignored the political goals of the government they’d partnered with, and therefore the extent to which these goals were shaping the project.
Lesotho’s recent political history had been tumultuous. The Basotho Nationalist Party (BNP), having gained power upon independence in 1965, refused to give up power after losing the 1970 elections to the Basotho Congress Party (BCP). Blaming the election results on “communists”, BNP Prime Minister Leabua Jonathan declared a state of emergency and began a campaign of terror, raiding the homes of opposition figures and funding paramilitary groups to intimidate, arrest, and potentially kill anyone who spoke up against BNP rule.
This had significant effects in Thaba-Tseka, where “villages […] were sharply divided over politics, but it was not a thing which was discussed openly” due to a fully justified fear of violence. The BNP, correctly sensing the presence of a substantial underground opposition, placed “development committees” in each village, which served primarily as local wings of the national party. These committees spied on potential supporters of the now-outlawed BCP and had deep connections to paramilitary “police” units.
When the Thaba-Tseka Development Project started, its international backers partnered directly with the BNP leadership, reasoning that sustainable development and public goods provision could only happen through a government whose role they primarily viewed as bureaucratic. As a result, nearly every decision had to make its way through the village development committees, who used the project to pursue their own goals: jobs and project funds found their way primarily to BNP supporters, while the “necessary costs of development” always seemed to be paid by opposition figures.
The funding coalition ended up paying for a number of projects that reinforced BNP power, from establishing a new “district capital” (which conveniently also served as a military base) to constructing new and better roads linking Thaba-Tseka to the district and national capitals (primarily helping the central government tax and police an opposition stronghold). Anything that could be remotely linked to “economic development” became part of the project as funders and practitioners failed to ask whether government power might have alternate, more concerning effects.
As we saw earlier, the population being “served” saw this much more clearly than the “servants”, and started to rebel against a project whose “help” seemed to be aimed more at consolidating BNP control than meeting their own needs. When they ultimately resorted to killing ponies and uprooting trees, project officials infatuated with “development” were left with “no idea why people would do such a thing”, completely oblivious to the real and lasting harm their “purely technical decisions” had inflicted.
May 18, 2022
May 6, 2022
QotD: “… the Spartiates were quite possibly the least productive people to ever exist”
I think it is worth stressing just how extreme the division of labor was [in ancient Sparta]. Helots did all of the labor, because the Spartiates were quite possibly the least productive people to ever exist (the perioikoi presumably also produced a lot of goods for the spartiates, but being free, one imagines they had to be compensated for that out of the only economic resource the spartiates possessed: the produce of helot labor). The spartiates were forbidden from taking up any kind of productive activity at all (Plut. Lyc. 24.2). Lysander is shocked that the Persian prince Cyrus gardens as a hobby (Xen. Oec. 4.20-5), because why sully your hands with labor if you don’t have to? Given the normal divisions of household labor (textile production in the Greek household was typically done by women), it is equally striking that not one of Plutarch’s “Sayings of Spartan Women” in the Moralia concerns weaving, save for one – where a Spartan woman shames an Ionian one for being proud of her skill in it (Plut. Mor. 241d). Xenophon confirms that spartiate women did not weave, but relied on helot labor for that too (Xen. Lac. 1.4).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part II: Spartan Equality”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-08-23.
January 30, 2022
“I stand corrected. All retail sucks, not just book retail”
Following up to the issue of book store-to-publisher returns last week (here), Kenneth Whyte discovered that other retailers are not that different from the book business after all:

“Indigo Books and Music” by Open Grid Scheduler / Grid Engine is licensed under CC0 1.0
Last week I wrote about the horrible, wasteful publishing-wide policy of booksellers returning unsold books for full refunds rather than putting them on sale. Some 30 percent of books in stores are sent back to publishers who bury, pulp, or remainder them. I compared this practice to other retail sectors:
If I were in the ugly sweater business, I’d sell 500 ugly sweaters to Saks at $200-a-piece. Saks pays me 500x$200=$100,000, marks the ugly sweaters up to $500, and lays them out on tidy glass shelves under track lighting. Whatever is left after the Christmas season is marked down to half price on crowded sales racks. If Saks still has some ugly sweaters in January, it will ship them to the outlet store where they’re offered at still greater discounts.
Our friend, author and regular SHuSH reader Ken McGoogan, sent my comments to a mature student he teaches. She comes from the fashion industry and says it’s not so simple:
The reality is, if Saks cannot sell that ugly sweater, they will ask for mark-down money from the brand (the wholesaler) who sold them that ugly sweater. If the brand is not willing to give Saks that mark-down money, they will never carry anything from the brand again. Is mark-down money better than returns? Honestly, it’s not that much better. The amount of the mark-down money is an often shocking figure. And this is not just for Saks, all big retailers do it, without exception.
Barnes & Noble or Chapters are just like department stores. The business model is the same. The only thing is, if the readers found out how much waste the book returns are generating every year, it’ll be a big turn off for the customers. They’d rather force themselves to read e-books or audio books than be part of the wasteful culture. Especially for the younger generation, they are buying less garments because of the fashion industry’s wasteful level. Fyi, a lot of new clothes and unsold inventories are burned every year as they are running out of storage spaces.
I stand corrected. All retail sucks, not just book retail. And the book industry had better sort this out before the aforementioned younger generation begins to focus on it.
January 23, 2022
The oddity of the bookselling business
Unlike so many other retail operations, book stores have a different sales cycle because they can generally return unsold books (in good condition) to the publisher for a full refund. This means that 30% or more of the books on the shelf at Christmas will be shipped back to the publisher early in the new year, only to appear again on the discount shelves a year or two later for a fraction of the original retail price (and often in rather worse shape for all the additional handling). In the latest SHuSH newsletter, Kennethy Whyte calls this the worst problem in book publishing:

“Indigo Books and Music” by Open Grid Scheduler / Grid Engine is licensed under CC0 1.0
Book publishing doesn’t work like most other retail businesses. If I were in the ugly sweater business, I’d sell 500 ugly sweaters to Saks at $200-a-piece. Saks pays me 500x$200=$100,000, marks the ugly sweaters up to $500, and lays them out on tidy glass shelves under track lighting. Whatever is left after the Christmas season is marked down to half price on crowded sales racks. If Saks still has some ugly sweaters in January, it will ship them to the outlet store where they’re offered at still greater discounts.
What happens to them if they don’t sell at the outlet doesn’t interest me because I’ve got my $100,000. If Saks ordered far too many ugly sweaters, that’s Saks’ problem.
In the book world, I sell 1,000 copies of a book to a retail chain like Barnes & Indigo for $15-a-piece, half the retail price. Barnes & Indigo pays me 1,000x$15=$15,000 and maybe puts some of the books on a front table, or maybe buries them on a bottom shelf in the darkest corner of the store. I might sell a two hundred, four hundred, or six hundred copies.
Let’s be generous and say 600 sell at Barnes & Indigo through the autumn and over the holidays. Come January, the store doesn’t put the remaining stock on sale: it packs up the unsold 400 and ships them back to me for a full refund. The 400 returns, or at least those of them that aren’t crumpled or coffee-stained, go back into the warehouse, which charges me fees to process the returns and more fees to store them. Sometime later, I get a notice of the returns and regret that extra glass of wine I ordered at dinner the night I thought I sold Barnes & Indigo $15,000 worth of books when, in fact, I only sold $9,000 worth of books, perhaps leaving me under-water on that particular title. I also regret boasting of the $15,000 sale to the author, who probably did some royalty math in his head and thought he was getting 40% more than he’ll actually receive.
Returns at publishing houses run somewhere between 25% and 30% annually, across all titles. That’s despite Amazon with its ruthlessly efficient algorithms seldom buying many more copies than it needs, and despite ebooks and audiobooks (which amount to a quarter of sales for many publishers) having almost zero returns.
Millions of books are returned to publishers at this time of year. Sales are slower in January and February, so bookstores hurriedly return all their remaining holiday-season stock and whatever else hasn’t moved to keep themselves in cash. Some of the returns go back into storage. Eventually, most are remaindered, or pulped, or buried. It’s a colossal waste of paper and ink, a headache in terms of shipping/handling/accounting, and dispiriting as heck. You might think you had a great year, hit all your sales targets, exceeded them, even, and then in about the third week of January begins the drip drip drip of returns, and it continues steadily through March. That’s if you’re lucky and it’s drips, not waves. And while the returns are concentrated in the first quarter, your books are returnable year-round, so even a pleasant summer afternoon can be ruined by the unexpected arrival of a pallet of unwanted stock.
January 12, 2022
QotD: Baumol’s cost disease in architecture and furniture
Remember, the Baumol effect [Wiki] happens when new technology makes some industries more productive. Since the high-tech industries are so lucrative, wages go up. Then low-tech industries have to raise their wages so that their workers don’t all desert them for the high-tech industries. But since low-tech industries aren’t improving their productivity, they just because more expensive, full stop.
If stonemasonry is a low-tech industry, and new high-tech industries are arising all around it, stonemason wages could get prohibitively high (compared to everything else) until nobody wants to hire them anymore. This would create pressure for architectural styles that require as little masonry (or, generalized, human labor) as possible.
This has gotten me thinking about furniture.
I got a new place recently and have been looking for furnishings. Sometimes I look at people’s furniture Pinterests. If Pinterest is any kind of representative window into the soul of the modern furniture-enthusiast, people really like Art Nouveau. […] As far as I can tell, you can’t buy any of these anywhere — they’re a combination of antiques and concept pieces. The people who pin these and pine after these end up getting minimalist Scandinavian furniture with names like UJLIBLÖK, just like everyone else.
Anything that even comes close to the above costs high four to five digits. I don’t know if this is because it’s antique, because it requires more labor, or both.
I’m harping on furniture because it avoids a lot of the complicating factors in architecture. There isn’t some vague collection of “elites” making our furniture decisions. It’s a pretty free market! There are lots of normal middle-class people spending big chunks of money on furniture, lots of them really really like the old stuff, and the old stuff is still either unavailable or unaffordable. It seems like it used to be affordable — it wasn’t just kings and dukes who had the old Art Nouveau stuff — but for some reason that’s changed. I think Baumol effects offer a tidy explanation here, and if we use them to explain furniture, then they start looking really attractive for architecture.
I want this one to be true, because it exonerates our civilization. If we could make things like the Art Nouveau furniture above, or the Taj Mahal, relatively cheaply and easily, then the question of why we aren’t doing that demands an answer. If it’s just a quirk of basic economics, then our civilization is fine, and maybe we can hope that stoneworking technology advances to the point where we can do this kind of thing again cheaply.
Scott Alexander, “Highlights From The Comments On Modern Architecture”, Astral Codex Ten, 2021-10-04.
December 26, 2021
Repost – The market failure of Christmas
Not to encourage miserliness and general miserability at Christmastime, but here’s a realistic take on the deadweight loss of Christmas gift-giving:
In strict economic terms, the most efficient gift is cold, hard cash, but exchanging equivalent sums of money lacks festive spirit and so people take their chance on the high street. This is where the market fails. Buyers have sub-optimal information about your wants and less incentive than you to maximise utility. They cannot always be sure that you do not already have the gift they have in mind, nor do they know if someone else is planning to give you the same thing. And since the joy is in the giving, they might be more interested in eliciting a fleeting sense of amusement when the present is opened than in providing lasting satisfaction. This is where Billy Bass comes in.
But note the reason for this inefficient spending. Resources are misallocated because one person has to decide what someone else wants without having the knowledge or incentive to spend as carefully as they would if buying for themselves. The market failure of Christmas is therefore an example of what happens when other people spend money on our behalf. The best person to buy things for you is you. Your friends and family might make a decent stab at it. Distant bureaucrats who have never met us — and who are spending other people’s money — perhaps can’t.
So when you open your presents next week and find yourself with another garish tie or an awful bottle of perfume, consider this: If your loved ones don’t know you well enough to make spending choices for you, what chance does the government have?
December 23, 2021
Repost — The lousy economics of gift-giving
Tim Worstall explains why gift-giving at Christmas is so economically inefficient:
The point being made is dual, that individuals have agency and that utility is entirely personal.
To unravel that jargon.
Individuals, peeps, are able to make choices. We delight in making choices in fact, “agency” is the opposite of “anomie”, that feeling that society determines what we may or can do that so depresses the human spirits. We get to choose to get up at 6 am or 8. Have coffee or tea when we do. Go buy the latest platters from the newly popular beat combo, pay the ‘leccie bill or have the coffee out at an emporium.
Having choices, making them, makes people happier.
Secondly, utility. The result of those choices, which of them will maximise happiness, is different for each and every individual. Sure, we can aggregate some of them – food is usually pretty high up everyones’ list, that first litre of water a day tops most. But the higher up Maslow’s Pyramid we go the more tastes – and thus happiness devoured – differ.
So, we make humans happier by their having the choice to do what they want, not what others think they should want or have.
Thus, give people cash at Christmas not socks.
Balancing that is the obvious point that the care and attention with which a present is considered is part of that consumption of happiness. The boyfriend who actually listens to the type of clothing desired and goes gets it provides that joy that a bloke has, for once, been listening. Or the book that would never have been individually considered but was chosen because it might – and does.
Sure.
But the point isn’t about Christmas at all. That’s a way of wrapping the point so it can be left underneath the tree of knowledge.
October 9, 2021
The incredible growth of London after 1550
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes considers some alternative explanations for London’s spectacular growth beginning in the reign of Queen Elizabeth I:
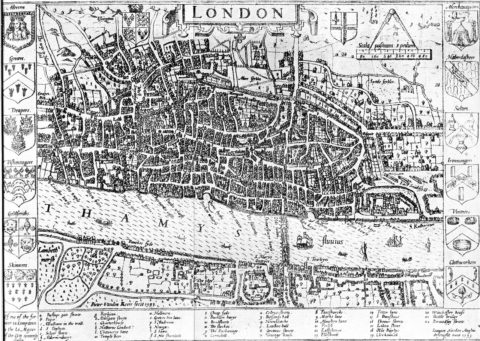
John Norden’s map of London in 1593. There is only one bridge across the Thames, but parts of Southwark on the south bank of the river have been developed.
Wikimedia Commons.
As regular readers will know, I’ve lately been obsessed with England’s various economic transformations between 1550 and 1650 — the dramatic eightfold growth of London, in particular, and the fall in the proportion of workers engaged in agriculture despite the growth of the overall population.
As I’ve argued before, I think that the original stimulus for many of these changes was the increased trading range of English overseas merchants. Thanks to advances in navigational techniques, they were able to find new markets and higher prices for their exports, particularly in the Mediterranean and then farter afield. And they were able to buy England’s imports much more cheaply, by going directly to their source. Although the total value of imports rose dramatically — by 150% in just 1600-38 — the value of exports seems to have risen by even more, as there’s plenty of evidence to suggest that for most of the period England had a trade surplus. The supply of money increased, even though Britain had no major gold or silver mines of its own.
The growing commerce was the major spur to London’s growth, with English merchants spending their profits in the city, and ever-cheaper and more varied luxury imports enticing the nobility from their country estates. Altogether, the concentration of people and wealth in London must have resulted in all sorts of spill-over effects to further drive its growth. After the initial push from overseas trade, I suspect that by the late seventeenth century the city was large enough that it was running on its own steam.
But on twitter, economic historian Joe Francis offered a slightly different narrative. Although he agrees that a change to overseas trade was the prime mover, he suggests that the trade itself was too small as a proportion of the economy to account for much of London’s growth. I disagree, for various reasons that I won’t go into now, but Joe brought to my attention various changes on the monetary side. Inspired by the work of Nuno Palma, he suspects that it was not the trade per se, but the fact of an export surplus that was doing the heavy lifting, by increasing the country’s money supply.
An increased money supply should have facilitated England’s internal trades, reducing their costs, and allowing for greater regional specialisation. Joe essentially thinks that I’ve got the mechanism slightly back to front: instead of London’s growing demands having reshaped the countryside, he contends that the specialisation of the entire country is what allowed for the better allocation of economic resources and workers to where they were most productive — a process from which a large city like London quite naturally then emerged.
I have some doubts about whether this process could really have been led from the countryside. The regional specialisation that we see in agriculture, for example, only really starts to become obvious from the 1600s onwards, by which stage London’s population had already begun to balloon from a puny 50,000 in 1550, to 200,000 and rising. I also haven’t found much evidence of other internal trade costs falling. Internal transportation — by packhorse, river, or down the coast — doesn’t seem to have become all that more efficient. Roads and waggon services don’t show much sign of improvement until the eighteenth century, and not many rivers were made more navigable before the mid-seventeenth century either. This is not to say that England’s internal trade didn’t increase. It certainly did, as London sucked in food and fuel in ever larger quantities, and from farther and farther afield. But it still looks like this was led by London demand, rather than by falling costs elsewhere.
Besides, the influxes of bullion from abroad would have all been channelled through London first, along with most of the country’s trade. To the extent that monetisation made a difference to the costs of trade then, this would have made a difference first in the city, before emanating out to its main suppliers, and then outwards. I thus see the Palma narrative as potentially complementary to my own.