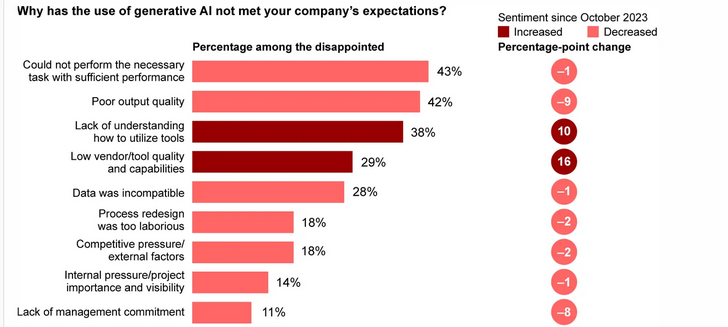
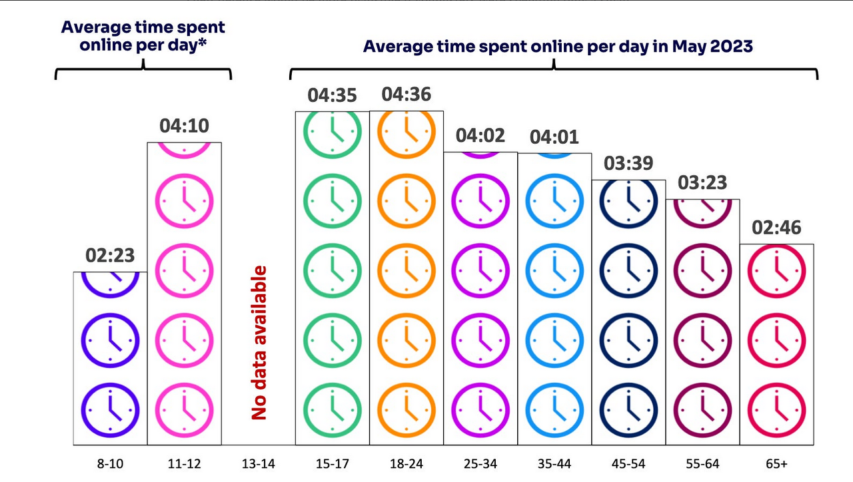
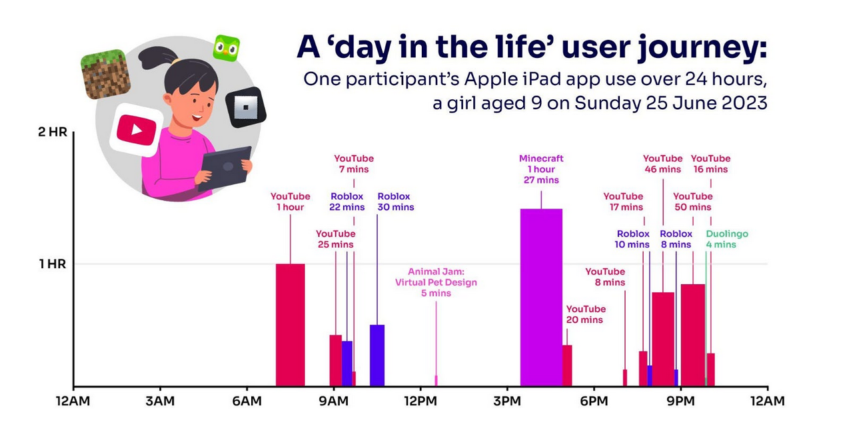
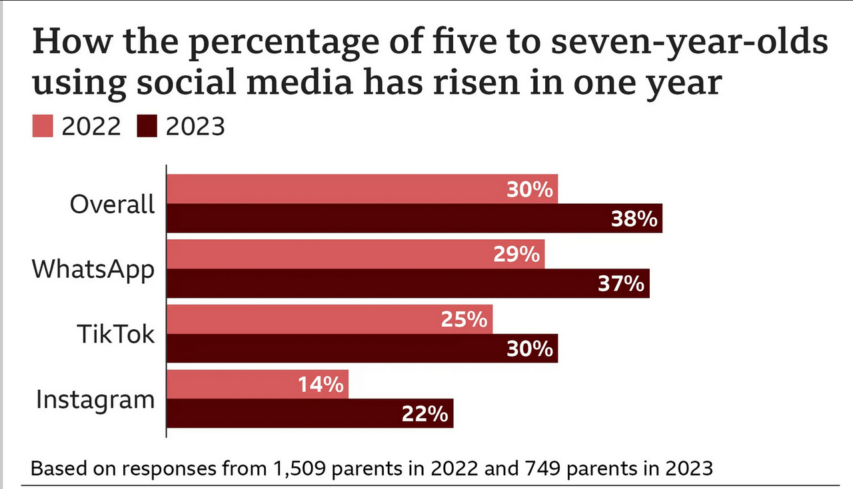Ted Gioia is covering the AI beat like nobody else. In this post he shares several near-term predictions involving AI development and deployment:
The world has gone mad. But nothing is as crazy as the AI news.
Every day those AI bots and their human posse of true believers get wilder and bolder — and recently they’ve been flexing like body builders on Muscle Beach.
The results are sometimes hard to believe. But all this is true:
- The movie trailer for Francis Ford Coppola’s new film got pulled from theaters because “the studio had been duped by an AI bot“.
- Just one person in North Carolina was able to steal $10 million in royalties from human musicians with AI-generated songs. They got billions of streams.
- The promoters of National Novel Writing Month angrily declared that opposition to AI books is classist and ableist.
- Children are now routinely using AI to make nude photos of other youngsters.
- Nearly half of the safety team at OpenAI left their jobs — and almost nobody seems to care or notice.
- AI tech titan Nvidia lost a half trillion in market capitalization over the course of just a few days — including the largest daily decline in the history of capitalism.
- By pure coincidence, Nvidia’s CEO sold $633 million worth of stock in the weeks leading up to the current decline.
We truly live in interesting times — which is one of the three apocryphal Chinese curses.
(The other two, according to Terry Pratchett, are: “May you come to the attention of those in authority” and “May the gods give you everything you ask for”. By tradition, the last is the most dangerous of all.)
I get some credit for anticipating this. On August 4, I made the following prediction:
But it’s going to get even more interesting, and very soon. That’s because the next step in AI has arrived — the unleashing of AI agents.
And like the gods, these AI agents will give us everything we ask for.
Up until now, AI was all talk and no action. These charming bots answered your questions, and spewed out text, but were easy to ignore.
That’s now changing. AI agents will go out in the world and do things. That’s their new mission.
It’s like giving unreliable teens the keys to the family car. Up until now we’ve just had to deal with these resident deadbeats talking back, but now they are going to smash up everything in their path.
But AI agents will be even worse than the most foolhardy teen. That’s because there will be millions of these unruly bots on our digital highways.