Shady Maples on the frequent issue needing a particular piece of equipment, but … bureaucracy:
Have you heard the one about the soldier and supply technician?
Soldier: I need a sleeping bag.
Supply Tech: We’re not issuing sleeping bags right now.
Soldier: I can see a sleeping bag on the shelf right there.
Supply Tech: But that’s my last sleeping bag! If I issued that one then I wouldn’t have any left in stock. I need to keep at least one sleeping bag in stock in case someone needs it.
Soldier: Yes! That someone is me! I need the sleeping bag!
Supply Tech: Look, my job is to keep the shelves stocked. See the sign on the door? It says Stores, not Gives. If I give you that sleeping bag then we’ll be out of stock.
Soldier: But I need the sleeping bag.
Supply Tech: You’ll have to come back after we restock.
Soldier: Fine, when are you restocking sleeping bags?
Supply Tech: When we’ve depleted our current stock.
This is barely a joke, I’m convinced it’s a script that supply techs learn in Borden.1 A common variant involves a soldier trying to get a piece of kit ahead of a training exercise. The supply tech tells them they can’t have the kit because they don’t need it. If the soldier needed the kit then it would be issued to them and since it’s not issued to them they don’t need it. I have personally had that conversation multiple times with everyone from lowly supply techs to quartermasters up to Life Cycle Material Managers in ADM(Mat). A notable one involved asking the depot in Montreal to send my unit a specific piece of optical equipment2 which we desperately needed, only to be told that they could not release that kit to us because the Army divesting it. My unit had just taken on a new capability that required this kit, why were they throwing this equipment away? “Nobody uses it anymore.” But I’ll use it, I’m telling you that I’m going to use it! My appeal failed, the depot had to divest because no one used the kit and they wouldn’t let us use the kit because they had to divest. I subsisted by borrowing equipment from other units off-the-books.
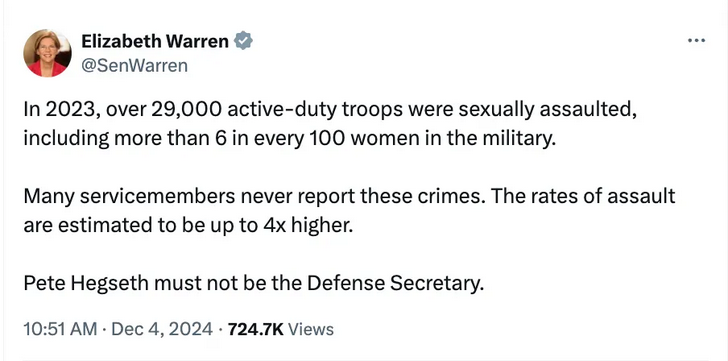
Pic related, from Patrick McKenzie.
There is a deep and difficult-to-articulate emotion that I feel whenever I have interactions like this. It’s a middle shade of anger, frustration, sadness, and loathing triggered by a people who so are so lost in process that they stop caring about real-world outcomes. Via Scott Alexander’s Links For December, I just learned? that Scott Aaaronson coined the term “blankface” for people like this:
What exactly is a blankface? He or she is often a mid-level bureaucrat, but not every bureaucrat is a blankface, and not every blankface is a bureaucrat. A blankface is anyone who enjoys wielding the power entrusted in them to make others miserable by acting like a cog in a broken machine, rather than like a human being with courage, judgment, and responsibility for their actions. A blankface meets every appeal to facts, logic, and plain compassion with the same repetition of rules and regulations and the same blank stare — a blank stare that, more often than not, conceals a contemptuous smile.
Once, my 2IC3 was trying to access a childcare benefit intended to reimburse members for babysitting when they are in the field or called in for overnight duties. My 2IC enquired about reimbursement but word came down from Ottawa that she wasn’t eligible since since had not used a licenced childcare provider. Nevermind that there are no licenced providers offering overnight childcare in our geographic area. When my 2IC submitted a grievance for her exclusion from the policy, the grievance analyst rejected it on the grounds that, since she never applied for the benefit (after being told she wasn’t eligible), she had not technically been denied anything. The analyst recommended applying for the benefit in order to be denied and then submitting another grievance based on that denial. At a time when the CAF is desperately trying to attract and retain female leaders, you know what really makes our case? Nickle-and-diming single moms over $70 of childcare. The analyst’s rejection letter made me feel like maybe Ted Kacynski had a point.
In his blog post, Scott Aaronson used Dolores Umbridge as the canonical example of a blankface. Umbridge is conspicuous do-gooder who uses her positional authority to make life miserable for everyone around her. As the story progresses and she accrues more power to her office, it becomes apparent that her virtuous posturing conceals a cruel authoritarian heart. Scott noted that:
The most despicable villain in the Harry Potter universe is not Lord Voldemort, who’s mostly just a faraway cipher and abstract embodiment of pure evil, no more hateable than an earthquake. Rather, it’s Dolores Jane Umbridge, the toadlike Ministry of Magic bureaucrat who takes over Hogwarts school, forces out Dumbledore as headmaster, and terrorizes the students with increasingly draconian “Educational Decrees”. Umbridge’s decrees are mostly aimed at punishing Harry Potter and his friends, who’ve embarrassed the Ministry by telling everyone the truth that Voldemort has returned and by readying themselves to fight him, thereby defying the Ministry’s head-in-the-sand policy.
Voldemort is evil, yes, but he is a moral agent who chooses and sacrifices according to his principles. The series pits his perverse will-to-power against the protagonists heroic defence of good. Unlike Voldemort, Umbridge doesn’t have any vision or principles, her only goal appears to be rigorous application of Ministry rules and procedures. She is not an agent of evil so much as its midwife, allowing evil to spread by obstructing any effort to stop it.
1. CFB Borden is the home of Canadian Forces Logistics Training Centre, a place that nobody says anything good about, especially the loggies.
2. This piece of kit was specialized enough that I would effectively dox myself if I told you what it was.
3. 2IC: Second-In-Command.





 Private William Penman,
Private William Penman, 

