Professor Mark Crispin Miller teaches media studies at New York University (NYU) and is an expert in propaganda. Dr. Miller says just about everything concerning Covid was simply an elaborate exercise in propaganda. Dr. Miller explains, “The propaganda dimension is crucial to our understanding of what went down. Some people like to say this is a result of a number of ‘blunders’ by the health authorities and the government. ‘Blunders’. No, these are not ‘blunders’. When everything they recommend is deleterious and destructive of people’s health … When they suppress the truth about life saving remedies in furtherance of this so-called ‘vaccination program’, and when the so-called ‘vaccines’ have abysmal records for safety and effectiveness and those records are all hidden, we cannot reasonably conclude this is all the result of ‘blunders’. I have called the period from 2020 through the present a ‘Propaganda Masterpiece’. … Covid and every aspect of that whole crisis was engineered with extreme brilliance and sophistication of a propaganda operation. This was followed by the George Floyd moment. This served a number of purposes quite in line with the Covid crisis, which is to shut down society, cripple the economy and destroy the middle class … Also, another important aspect of this whole propaganda epic has been to divide the American people … No matter what side of the struggle we are on, what matters is the struggle took place at all. It is deeply divisive …”
Dr. Miller goes on to say, “I know a lot about propaganda, and this is unprecedented in the history of mass persuasion. There has never been anything like this because this is global. This has never happened before. We had Stalin’s crimes … We had Hitler’s aggression and the Holocaust. We had 911 and the ‘War on Terror’. None of those actually begin to compare to what we have now because what we have now is planetary. It’s worldwide.”
Dr. Miller does not call the CV19 bioweapon/vax a genocide. He says it is really a global democide. Meaning everyone and anyone is being murdered with the CV19 bioweapon/vax. Dr. Miller says, “My Substack is called ‘Died Suddenly’. I started it in February of 2022 when I noticed many, many people were dying suddenly for no given reason. In the history of obituaries, certainly in the United States, that is unprecedented. Obituaries always tell you why somebody died. Even if the person is very, very old, you have a cause of death. Now, all kinds of people are dropping dead for no reason and often very young … We do a weekly overview with as many pictures of these people as possible. This is the point. There are many statistical claims of the numbers of people who are dying … But as Stalin said, ‘One death is a tragedy, a million deaths is a statistic’. This is brutal, cynical wisdom, and he was absolutely right. If you read 1 million people starved in Ukraine, you say that’s too bad. If you look at page after page after page of people’s faces and names with the names of their survivors, it’s not so easy to shrug off.”
Greg Hunter, “CV19 – A Propaganda Masterpiece – Mark Crispin Miller”, USAWatchdog, 2023-06-10.
October 5, 2023
QotD: The Wuhan Coronavirus pandemic was a “propaganda masterpiece”
October 3, 2023
“Just play safe” is difficult when the definition of “safe” is uncertain
David Friedman on the difficulty of “playing safe”:
It’s a no brainer. Just play safe
It is a common argument in many different contexts. In its strongest form, the claim is that the choice being argued for is unambiguously right, eliminates the possibility of a bad outcome at no cost. More plausibly, the claim is that one can trade the risk of something very bad for a certainty of something only a little bad. By agreeing to pay the insurance company a hundred dollars a year now you can make sure that if your house burns down you will have the money to replace it.
Doing that is sometimes is possible but, in an uncertain world, often not; you do not, cannot, know all the consequences of what you are doing. You may be exchanging the known risk of one bad outcome for the unknown risk of another.
Some examples:
Erythritol
Erythritol was the best of the sugar alcohols, substitutes tolerably well for sugar in cooking, has almost zero calories or glycemic load. For anyone worried about diabetes or obesity, using it instead of sugar is an obvious win. Diabetes and obesity are dangerous, sometimes life threatening.
Just play safe.
I did. Until an research came out offering evidence that it was not the best sugar alcohol but the worst:
People with the highest erythritol levels (top 25%) were about twice as likely to have cardiovascular events over three years of follow-up as those with the lowest (bottom 25%). (Erythritol and cardiovascular events, NIH)
A single article might turn out to be wrong, of course; to be confident that erythritol is dangerous requires more research. But a single article was enough to tell me that using erythritol was not playing safe. I threw out the erythritol I had, then discovered that all the brands of “keto ice cream” — I was on a low glycemic diet and foods low in carbohydrates are also low in glycemic load — used erythritol as their sugar substitute.
Frozen bananas, put through a food processor or super blender along with a couple of ice cubes and some milk, cream, or yogurt, make a pretty good ice cream substitute.1 Or eat ice cream and keep down your weight or glycemic load by eating less of something else.
It’s safer.
Lethal Caution: The Butter/Margarine Story
For quite a long time the standard nutritional advice was to replace butter with margarine, eliminating the saturated fat that caused high cholesterol and hence heart attacks. It turned out to be very bad advice. Saturated fats may be bad for you — the jury is still out on that, with one recent survey of the evidence concluding that they have no effect on overall mortality — but transfats are much worse. The margarine we were told to switch to was largely transfats.2
“Consumption of trans unsaturated fatty acids, however, was associated with a 34% increase in all cause mortality”3
If that figure is correct, the nutritional advice we were given for decades killed several million people.
1. Bananas get sweeter as they get riper so for either a keto or low glycemic diet, freeze them before they get too ripe.
2. Some more recent margarines contain neither saturated fats nor transfats.
3. “Intake of saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies”, BMJ 2015; 351 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h3978 (Published 12 August 2015)
Narcissism
Rob Henderson discusses the psychology of narcissistic individuals:

“Echo and Narcissus” by John William Waterhouse, 1903.
Oil painting from the Walker Art Gallery via Wikimedia Commons.
One of my favorite blogs from the Before Times was The Last Psychiatrist. He is most known for his writings on narcissism. When I discovered him in 2015, I read through most of his archive over the course of a few weeks. You can read my review of his book here.
On narcissistic injury and narcissistic rage:
A narcissistic injury occurs when the narcissist is confronted with the reality that he is not the main character in his movie … The worst thing that could happen to a narcissist is not that his wife cheats on him and leaves him for another man … He’s still the main character in his movie; it was a romantic comedy but now it’s a break-up film … The worst thing that could happen to a narcissist is that his wife cheats on him secretly and never tells him, and she doesn’t act any differently towards him, so that he couldn’t even tell. If she can do all that, that means she exists independently of him. He is not the main character in the movie. She has her own movie and he’s not even in it. That’s a narcissistic injury … But all narcissistic injuries lead to rage … The violence serves two necessary psychological functions: first, it’s the natural byproduct of rage. Second, the violence perpetuates the link, the relationship, keeps him in the lead role. “That slut may have had a whole life outside me, but I will make her forever afraid of me.” Or he kills himself — not because he can’t live without her, but because from now on she won’t be able to live without thinking about him. See? Now it’s a drama, but the movie goes on. So if you cause a narcissist to have a narcissistic injury, get ready for a fight.
Psychological researchers have found that there are two categories of narcissist:
- Grandiose narcissists: Dominant, extraverted, overconfident, exploitative, egotistical, low emotional distress. This is the version of narcissism people tend to be most familiar with.
- Vulnerable narcissists: Self-centered, introverted, defensive, resentful, high emotional distress. Psychologists sometimes refer to them “hidden” or “shy” or “covert” narcissists because they don’t self-promote the way the grandiose types do.
Grandiose narcissists enjoy seeking any kind of attention. Their positive self-image is resistant to criticism. They always think they’re amazing no matter what people say.
In contrast, vulnerable narcissists have mixed feelings about seeking attention. They are overly excited at the prospect of positive feedback but excessively sensitive to negative feedback. They have a high opinion of themselves but this high opinion can be thwarted if the external world does not validate it.
Both types tend to be exploitative, hold high opinions of themselves, and see themselves as deserving of special treatment.
Compared to grandiose narcissists, vulnerable narcissists are more sensitive to insults, ruminate more about perceived unfairness, and report more anger when they do not receive what they think they deserve. Although vulnerable narcissists require external feedback to maintain their sense of self, they are often dissatisfied with the feedback they receive.
QotD: The meteorologically mild 20th century
English needs, I think, a word for “beliefs which are motivated by the terror of being powerless against large threats”. I think I tripped over this in an odd place today, and it makes me wonder if our society may be talking itself into a belief system not essentially different from sorcerism.
[…] I read a lot of history and thus know a fair bit about how weather impact has been perceived by humans over time. It is a fact that the 20th century was an abnormally lucky hundred years, meteorologically speaking. The facts I managed to jam into tweets included (a) the superstorm that flooded 300 square miles of the Central Valley in California in the 1860s, (b) rainfall levels we’d consider drought conditions were normal in the U.S. Midwest before about 1905, and (c) storms of a violence we’d find hard to believe were commonly reported in the 1800s. I had specifically in mind something I learned from the book Wicked River: The Mississippi When It Last Ran Wild, which relays eyewitness accounts of thunderstorms so intense that travelers had to steeple their hands over their noses in order to breathe air instead of water; but a sense that storms of really theatrical violence were once common comes through in many other histories.
We had a quiet century geophysically as well – no earthquakes even nearly as bad as the New Madrid event of 1812, which broke windows as far north as Montreal. And no solar storms to compare with the Carrington Event of 1859, which seriously damaged the then-nascent telegraph infrastructure and if it recurred today would knock out power and telecomms so badly that we’d be years recovering and casualties would number in the hundreds of thousands, possibly the millions.
(I’m concentrating on 19th-century reports because those tended to be well-documented, but earlier records tell us it was the 20th century calm that was unusual, not the 19th-century violence.)
The awkward truth is that there are very large forces in play in the biosphere, and when they wander out of the ranges we’re adapted to, we suffer and die a lot and there really isn’t a great deal we can do about it; we don’t operate at the required energy scales. For that matter, I can think of several astronomical catastrophes that could be lurking just outside our light-cone only to wipe out all multicellular life on Earth next week. Reality is like that.
But none of this would fit in a tweet, so what I said in summary was that this may be the new normal – or, rather, the old normal returning. Humans didn’t do it.
Eric S. Raymond, “Heavy weather and bad juju”, Armed and Dangerous, 2011-02-03.
September 29, 2023
September 27, 2023
The fascinating world of trees
The latest book review from Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf examines Tristan Gooley’s How to Read a Tree:
Okay, I admit it: I read this book because I wanted to know more about the trees in my yard.
I’m afraid that’s not how Tristan Gooley means it to be used. He’s an expert in what he terms “natural navigation“, which means finding your way wherever you’re going using the sun, moon, stars, weather, land, sea, plants and animals. He teaches classes in it. He tested Viking navigation methods in a small boat in the north Atlantic and wrote a scholarly paper about it. He traveled the desert with the Tuareg. He’s the only living person to have crossed the Atlantic solo in both a plane and a sailboat.1 Meanwhile, I consistently walk a block in the wrong direction when I come out of the subway. But I am interested in trees!
Do you think much about trees? Could you draw one from memory and come up with something besides a fat green lollipop? Can you describe a tree you walk past every day with something more than its species and “leaves turn a pretty color in the fall” or “had its whole middle chopped out because planting trees directly under power lines is a terrible idea”? (Or if you live somewhere urban enough to have buried power lines, “they really, really should have made sure all these ginkgos were male”.)2 My guess is that you can’t, because most of us couldn’t, but trees deserve some real thought. They are actually fabulously, unintuitively weird, and learning just a little bit about how they work will dramatically enhance your ability to understand why the world around you is the way it is. I don’t expect I’ll use a tree to find my way any time soon, but since reading the book I’ve started spotting things in my yard and my neighborhood that I’d never noticed before — and noticing things is halfway to understanding them. (Which is, of course, why you must not be permitted to notice that which you are not supposed to understand.)
The most fundamental insight here is that trees are not like animals. This sounds breathtakingly obvious (and indeed, when I shared this pearl of wisdom at the dinner table everyone laughed at me), but it’s hard to internalize. Our increasingly urbanized and domesticated lives have so impoverished our natural imaginary — the available stock of symbols, metaphors, and archetypes through which we understand the natural world — that we’re more or less limited to commensals and charismatic megafauna, and are therefore vaguely surprised when we encounter organisms that work differently.3 And trees really do work differently, in a wide variety of ways that make perfect sense when Gooley points them out.
What are these differences? Well, for one thing, where animals have their physical architecture written into their genes, trees — like all plants — have potential. Sure, they have general growth habits4 (you’d never mistake a willow for a maple), but compare two trees of the same species — even two genetically identical trees cloned from grafts or cuttings of the same parent — and you’ll find dramatic structural differences depending on how the individual tree grew. This isn’t true for animals: one lion might be smaller than another, or bear the scars of an old injury, but all lions have four legs with the same joint anatomy. A lion will never grow a new leg, drop an old one, or add new tendons to support a particularly overworked limb. Trees, on the other hand, do all of those and more, following general rules dictated by species but growing in response to the conditions they encounter. And because only the top of the tree continues to grow up — a branch five feet off the ground will still be five feet off the ground in a decade, though quite a lot thicker — you can read a tree’s whole history in its structure. As with looking at a genome, looking at a tree is a way of looking into the past.
Trees seek the light. Just down the street, my neighbor’s entire front yard is shaded by three enormous oak trees planted in a rough triangle and each arching gently away from the others (with a surprising similarity to the Air Force Memorial) as they try to escape each others’ shade. A few blocks away is a survivor of a similar situation, an old pine tree that’s branchless most of the way up its trunk so you can really see the alarming 15° lean with which it grew. Some long-gone giant cast the shade that sculpted this tree into its present funny shape, and if we were in the woods we might be able to see its stump — Gooley encourages the reader to greet a woodland stump by looking for the “footprint” of the missing tree in its surroundings — but I suspect this one was probably removed to make way for the foundation of the nearby house. (Given the apparent age of the pine and the house, its old neighbor probably met its end around the time the new streetcars turned this farming village on a railroad into a proper suburb.)
1. The late Steve Fossett did it first, but since he holds about a billion other records it feels churlish to take this from Gooley.
2. Only female gingkos drop those awful berries. There are entire all-male cultivars that make fabulous trees, and somehow, inexplicably, I spent every autumn of my childhood scraping horrible stinky mush off the bottoms of my shoes. Why.
3. Also on this front, I recommend Merlin Sheldrake’s Entangled Life, which is exactly the sort of book about fungi you would expect someone named Merlin Sheldrake to write.
4. In fact “tree” is really just a growth habit, evolved independently by thousands of unrelated species of plants, because trees are the crabs of the plant kingdom. [NR: Do read that thread, it’s quite amusing}
September 26, 2023
“Passport Bros”
Few online people are less tuned-in to the mainsteam zeitgeist than me, so perhaps I’m once again one of the last people to be clued-in about “passport bros”. Here’s Janice Fiamengo‘s post on the “bros” and the women who apparently spend a lot of time criticizing them:
Female commentary on so-called Passport Bros is not hard to find on the internet: women are angry, contemptuous, and incredulous that men are looking for women overseas and encouraging other men to do the same — not for sex tourism (which feminists loved to criticize until they discovered that women are doing it too, in which case it is acceptable), but for a long-term relationship, including, in many cases, marriage and children. These men will partially or entirely relocate to the women’s home country in order to start a new, non-western (and non-feminist) life. The angry internet women claim not to care personally: let the losers go is their expressed attitude. Yet the sheer number and vehemence of their responses suggests they do care.
The angry commentary follows a standard pattern in which the women claim to know why a significant minority of men are giving up on western women as mates. The reason never has anything to do, of course, with faults in western women or their unrealistic expectations […]
Likewise, the reason never has anything to do with western divorce laws — in which a man can be ejected from his home, imprisoned, forced to undergo a psychiatric exam, fleeced, and deprived of his children by a grasping ex-wife — or with the fact that women are the ones who initiate divorce in upwards of 70% of cases (and are often applauded for doing so).
The reason has nothing to do with women’s openly expressed attitudes of superiority, resentment, and anti-male bigotry, which are rampant in western cultures, especially Anglophone ones. It has nothing to do with the #MeToo/Believe Women climate of baseless accusation that regularly sees men accused and disgraced purely on a woman’s say-so. It has nothing to do with the institutionalized discrimination of “equity” hiring that makes it difficult for men to find and advance in careers in order to be acceptably successful to the kind of women who now deride them for their failure.
According to the angry women online, men are leaving the west (particularly North America) to find partners because they aren’t good enough for western women. The men are allegedly “terrible, and don’t want to stop being terrible”, according to one gleefully irate commentator. Their only chance is with women so poor as to be grateful for a “terrible” man; in return, such women will have to “subject themselves to [his] advances”, according to another critic’s Victorian-style phrasing.
[…]
Many such women — protected by our pro-woman culture and deferred to by men terrified of female wrath — reach adulthood without ever having received any serious criticism. If and when they are criticized, their response is a howl of outrage and wounded self-regard. This is precisely what is happening in reaction to the Passport Bros.
Underneath the anger, there is perhaps a hint of fear. It’s not fear that men will leave the west in droves (they don’t see that happening yet, and neither do I), but it’s fear that men are not, after all, entirely under female control. Not yet, and maybe never. Some men are sick of the anti-male abuse and starting to do something about it. They are critically examining women’s characters and attitude; they’re drawing back from the acquiescence they’ve always been expected (and been willing) to give. Some are walking away and telling other men to do the same.
These women are used to dishing out the denunciation, reveling in justified grievance; they are infuriated to find that now they are the ones being judged and found wanting.
Don’t be that girl.
September 24, 2023
Architect Breaks Down Why All American Diners Look Like That | Architectural Digest
Architectural Digest
Published 1 Jun 2023Today Michael Wyetzner of Michielli + Wyetzner Architects returns to Architectural Digest to explore the design evolution of American diners. A cornerstone of American dining culture, their distinctive style has been emulated around the world making them a popular salute to the USA. Michael provides an expert look into the history behind their design evolution from the 1920s through to the 1960s and explains why all diners came to look like that.
(more…)
September 23, 2023
“Even before it began, the protest was denounced as a hatefest”
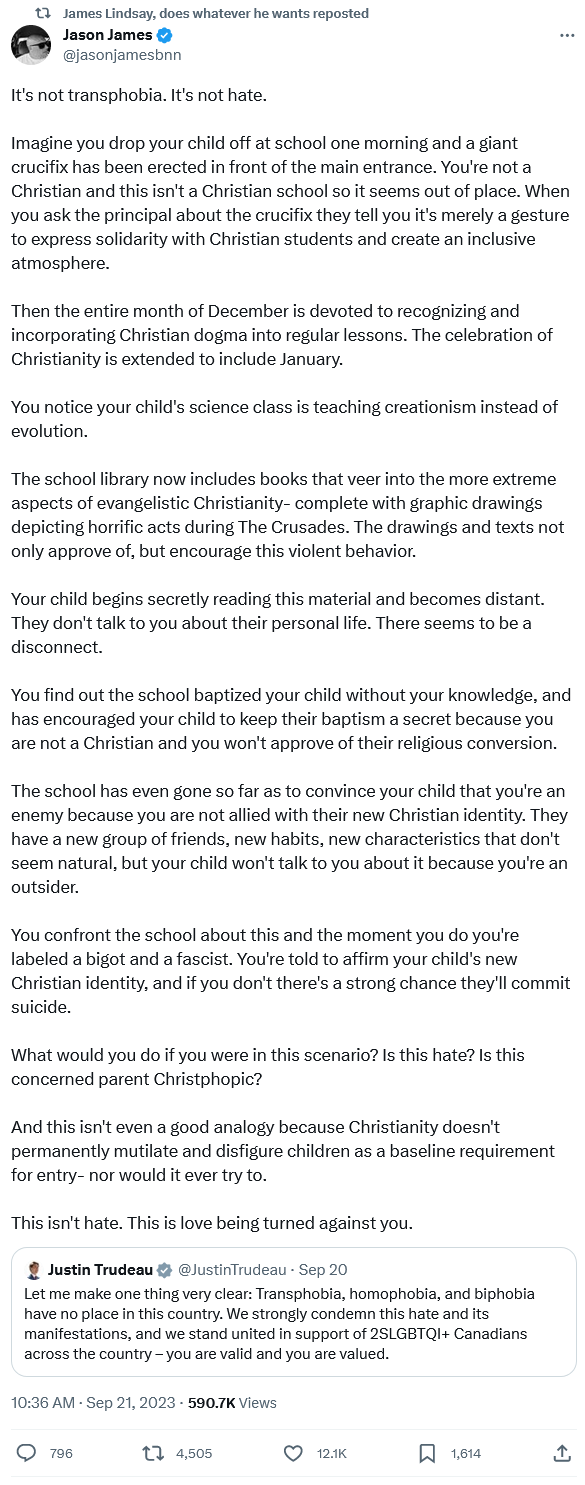
Tasha Kheiriddin on the parents’ 1 Million March 4 Children protest against teaching LGBT issues to school children and the counter-protest by teachers, unions, and a disturbing number of sitting politicians:
On Wednesday, thousands of parents and supporters took to the streets across Canada for the 1 Million March 4 Children protest, chanting “leave the kids alone.” They were protesting the teaching of “gender ideology” in schools, including lessons about gender identity, transgenderism and schools’ refusal to inform parents of their children’s use of preferred pronouns.
Even before it began, the protest was denounced as a hatefest. School boards sent letters to parents decrying the event. The Ontario Federation of Labour organized counter-protests with the slogan “Trans rights are workers’ rights.” NDP leader Jagmeet Singh stood on Parliament Hill, chanting, “Hey hey, ho ho, transphobia has got to go!” Prime Minister Justin Trudeau tweeted, “We strongly condemn this hate and its manifestations.”
Here’s something we can all agree on: there is no room for hate in schools. If a kid bullies another kid for any reason, including gender identity, they should be disciplined. But the counter-protestors go further: in their view, unless you actively instruct children about gender, sexuality and inclusiveness at an early age, it is you who is being hateful. There are no shades of grey: you are either a full-on supporter of drag story time or a transphobic bigot.
When it comes to gender identity, it is wrong for educators to dismiss all parental concerns as homophobia. Yes, there are some bigoted parents who teach their kids that being gay or trans is a sin. Some of them were in the crowd Wednesday.
But there are also many parents who are legitimately concerned that encouraging children to question their sexual identity at a very young age is confusing and inappropriate. We label movies PG-13 or higher when they contain sexuality and nudity. Why then introduce sexual identities such as aromantic (absence of romantic attraction) asexual (absence of sexual attraction), pansexual (attraction to any gender) or demisexual (attraction that requires an emotional bond) to grade school kids? And more importantly, why is this the purview of the school system at all?
On Twit-, er, I mean “X”, Jason James responded to a Justin Trudeau Xpost with this counterfactual:
September 22, 2023
Political psychosis and the never-ending “narrative”
Chris Bray points out several instances of the legacy media continuing to push “the narrative” despite any inconvenient facts that cast doubt on the official story:
Every day is opposite day. Every day is a bucket of fake. The narrative is the narrative; once it’s established, nothing penetrates it. It rattles on down the road, impervious to inputs, convinced of its own truth without regard to events outside the shell. Psychologists have a term for this.
So Politico warns this week that faith in vaccines is falling, and anti-vaxxer narratives are “on the rise.” Sample paragraph, this one describing Health Secretary Xavier Becerra:
The summer of 2023, a claim made in June and credulously repeated in the bottom half of September: If you take Covid vaccines, you can’t get sick, but if you don’t take Covid vaccines, you die. Government leaders who don’t push the 7th and 8th doses of the mRNA injections “choose not to take care of their people”.
[…]
But the narrative rolls on, unperturbed. If you’re dying of Covid, it’s because you hesitated to get your 7,369th dose, anti-vaxxer! Maybe you should have stopped being such a Nazi! In the news media, it’s 2021 forever, and the virtuous science-lovers are rolling up their sleeves to rebuke the science-hating morons, who will not survive the … okay, well, who will not survive the next … okay, well, YOU’LL PROBABLY DIE AT SOME POINT because you didn’t get it. You’re facing a winter of severe illness and death by 2054, at the latest. No amount of evidence will force the storytellers to stop telling this story. It’s the story, so they tell it. The Politico thing ends by quoting Peter Hotez, by the way, as you knew it would.
Similarly, The Atlantic warns now that Donald Trump was a time bomb who kept nearly going off for four years, and only the courage of General Mark Milley kept him under control. Look at the premise at the top of the piece: Disobeying, resisting, and undermining the President of the United States, a military officer protected the Constitution.
How well does the story parse the constitutional issues at stake? This well:
The military decided to have an abortion travel policy, and to fund it. A senator is now interfering in military policy and the unilateral executive appropriations of the Department of Defense, a sign of the ongoing constitutional crisis that began with Trump. Typically, you see, in our constitutional order, the military does whatever it wants, and spends money on its own authority however it feels like spending it, but Tuberville is engaging in the “unprecedented” act of suggesting that Congress should decide how to appropriate federal funds and regulate the armed forces, which means that he hates the Constitution. Article I, Section 8 would like a word, in this obviously extremist description of the authority of Congress:
To raise and support Armies, but no Appropriation of Money to that Use shall be for a longer Term than two Years;
To provide and maintain a Navy;
To make Rules for the Government and Regulation of the land and naval Forces;
And so on. Why is Tommy Tuberville being such a Nazi?
September 19, 2023
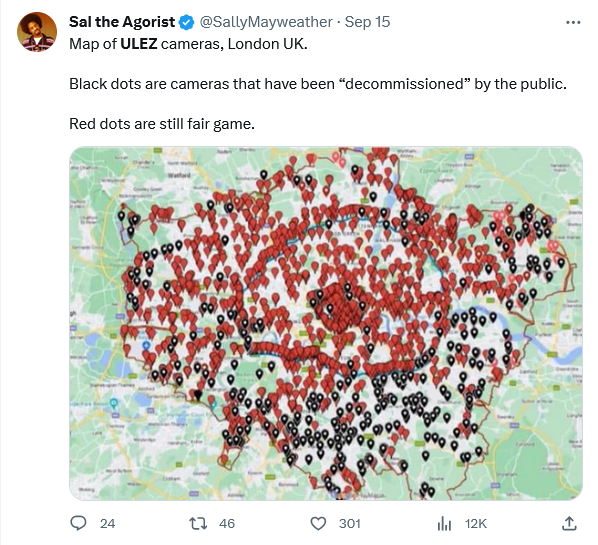
For some reason, ordinary Londoners don’t seem to appreciate Mayor Khan’s ULEZ initiatives
It’s hard to believe that anyone could possibly want to avoid London Mayor Sadiq Khan’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) expansion beyond the initial areas of the city, but a quick search of Twit-, er, I mean “X” shows evidence of what Justin Trudeau might characterize as a “small fringe minority … holding unacceptable views”:
Weird, isn’t it. All those “decommissioned” cameras. And people physically blocking access to workers:
London has put up with a lot over the centuries, but Mayor Khan’s ULEZ somehow seems to have awakened the resistance in a major way:
Brian Peckford republished this article from Yudi Sherman on the pushback against London’s ULEZ expansion:
London taxpayers are damaging the city’s surveillance vans in an escalating feud between Mayor Sadiq Khan and the city’s residents.
Last month Khan peppered the city with ultra-low emission zones (ULEZs), areas in London accessible only to low-emission vehicles. Cars that do not meet the city’s environmental standards are charged £12.50 ($16) for entering the ULEZ. Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) cameras positioned around the zones read license plates and check them against the vehicles’ make and model in real time. If a vehicle does not meet the environmental threshold, the fine is levied against the car owner. Failure to pay can lead to fines as high as £258 ($331).
The ULEZ climate mandate has drawn heavy protests from residents, including hunger strikes and refusal to pay fines. Taxpayers have also taken to disabling the ANPR surveillance cameras which Transport for London (TfL), the city’s transportation department, said will be used both for climate and law enforcement.
In response, the city deployed mobile surveillance vans mounted with ANPR cameras across London in the hopes of evading attacks, but the vans are being targeted as well. Some have been spotted covered in graffiti with their tires slashed, while others have been completely covered in tarp, reports the Daily Mail.
The activists are said to belong to a group calling itself the Blade Runners and have promised not to rest until every ULEZ camera is removed or destroyed “no matter what”. The group is being widely cheered by its compatriots, including media personality and political commentator Katie Hopkins. Over 4,000 people have joined a Facebook group to report ULEZ van sightings.
Between April 1st and August 31st, police recorded 351 incidents of destruction to ULEZ cameras and 159 removals, reports Sky News, an average of over 100 a month. Of those incidents, 171 reportedly occurred since August 17th alone, just before the ULEZ mandate officially expanded to include all outer London boroughs. Two individuals have been arrested in connection with the incidents, one of whom was charged.
One reported Blade Runner said, “In terms of damage it’s way more than what [London Mayor Saidq Khan and TfL] have stated.”
September 17, 2023
QotD: One of the most successful propaganda campaigns in history
[In the 1960s and 70s, mob-controlled cigarette smuggling seriously cut into tobacco taxes.] What the PTB should’ve done at that point, of course, was simply repealed the taxes, learned to live within their means, and stopped trying to nag their citizens into good behavior …
Ok, ok, is everyone done laughing yet? Go ahead, get it all out of your system; I’ll wait. Everyone back? Ok, moving on:
What the PTB actually did, of course, was a multi-level propaganda campaign. It was brilliant. It took a few years, of course, but the evidence is all around you. Quick: When’s the last time you saw anyone smoking in a mainstream movie? Even period films about the Forties, say — the ones where they take infinite pains to get just the right period-appropriate shade of Formica on the diner’s countertops — ignore the obvious historical reality of people puffing away like chimneys.
Indeed, it’s all but universal now, and has been for a long time, that characters who smoke are the bad guys.
Here again, look at college kids. I hate to keep beating this dead horse, but it’s really the best example I know of the phenomenon. Any time I taught the Early Modern period, I had to mention the massive economic and cultural effects of tobacco. So I encouraged kids to try it for themselves — everyone here is over 18, I said, so it’s perfectly legal. Want to know what all the hype was about? Just run down to the gas station, buy a pack, and light one up!
Around the turn of the century, I always had a few smokers in class, so I could say “bum one off So-and-So”. Even that would get me a few uneasy chuckles. A few years later, and not only were there no smokers in my classes, but the kids would be actively uncomfortable with the suggestion. By the end of my teaching career, when I couldn’t care less anymore, I was openly taunting them about it. You people have no problem with potheads, I’d say. I bet well over half of you are on Ritalin, Prozac, Xanax, Klonopin, shit that’s bad for you, in ways we don’t even understand yet, but you’re balking at one cigarette? It’s unsafe? Oh, come on, some of you are going to leave here and go light up a completely unfiltered ditch weed, and as for the rest of you, you know all about crazy sex fetishes I’ve never even heard of. You get blackout drunk at the football games every weekend, but oh no, you can’t have one cigarette, it’s so unhealthy.
Such is the power of propaganda, and it’s the only repression that works for the PTB when they’ve truly set their faces against a behavior …
Severian, “The Mob, Faux-tism, and the Ever-Rising Costs of Compliance”, Founding Questions, 2021-02-02.
September 16, 2023
Public health officials don’t seem to realize just how badly they’ve damaged their credibility
Chris Selley on the apparantly huge gap between how ordinary Canadians view their public health officials and how those officials think they’re viewed:
Throughout the pandemic, polls have shown a decline in confidence in public health: Researchers at McMaster University and Vox Pop Labs found that in March 2020, 59 per cent of Canadians had “a great deal of trust” in public health officials. Two years later that had plummeted to 37 per cent.
We have recently enjoyed months of being able to ignore COVID-19. Even the relentlessly, uniquely pessimistic Canadian media seemed to have exhausted themselves. So I found it a bit jarring to see Dr. Theresa Tam, Canada’s chief public health officer, suddenly back on the TV this week admonishing us to “get your mask ready” for fall and book yourself in for a booster. Dr. Kieran Moore, Tam’s counterpart at Queen’s Park, is due in the coming days to give Ontarians what will likely be a similar update.
If this year’s flu/RSV/COVID season is as bad as last, it will be fascinating to see how Canadians react. Perfervid opposition to masking and vaccination are minority positions: In the midst of last year’s autumn surge in childhood hospitalizations, a Nanos Research poll found 69 per cent of Canadians would support a return of mask mandates “if authorities deem(ed) it necessary”.
But are people ready to hear it, again, from the same public-health officials who have all-but destroyed their entire field in the last three years — seemingly without realizing it? It will be intriguing to see.
Tam’s original sins remain totally unexplained — at an official inquiry, for example, hint hint — never mind expiated. For days and weeks in early 2020, while our peer countries were closing borders and preparing for a pandemic, Tam assured us “the risk to Canada is low”. She lied that World Health Organization rules prohibited us from closing borders. She told us masks were worse than useless, and the only excuse anyone can offer is that she was fibbing to prevent Canadians from hoarding PPE. (I think she actually believed it. Either explanation is a firing offence.)
Remember the utterly incoherent advice the Public Health Agency of Canada provided to incoming travellers in the early days? Remember the built-to-fail, purely political quarantine hotels that Tam said weren’t necessary until they suddenly were — just as she said 14-day quarantine at home wasn’t necessary until it suddenly was? We were weeks if not months behind most of our peer countries. Regardless of your position on any given restriction, none of it made any sense.
September 15, 2023
September 14, 2023
Scott Alexander reviews the (old) Elon Musk biography
It’s okay, he makes it clear from the start that he’s talking about Ashlee Vance’s earlier work, not the one that just hit the shelves this year:
This isn’t the new Musk biography everyone’s talking about. This is the 2015 Musk biography by Ashlee Vance. I started reading it in July, before I knew there was a new one. It’s fine: Musk never changes. He’s always been exactly the same person he is now.1
I read the book to try to figure out who that was. Musk is a paradox. He spearheaded the creation of the world’s most advanced rockets, which suggests that he is smart. He’s the richest man on Earth, which suggests that he makes good business decisions. But we constantly see this smart, good-business-decision-making person make seemingly stupid business decisions. He picks unnecessary fights with regulators. Files junk lawsuits he can’t possibly win. Abuses indispensable employees. Renames one of the most recognizable brands ever.
Musk creates cognitive dissonance: how can someone be so smart and so dumb at the same time? To reduce the dissonance, people have spawned a whole industry of Musk-bashing, trying to explain away each of his accomplishments: Peter Thiel gets all the credit for PayPal, Martin Eberhard gets all the credit for Tesla, NASA cash keeps SpaceX afloat, something something blood emeralds. Others try to come up with reasons he’s wholly smart – a 4D chessmaster whose apparent drunken stumbles lead inexorably to victory.
Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, And The Quest For A Fantastic Future delights in its refusal to resolve the dissonance. Musk has always been exactly the same person he is now, and exactly what he looks like. He is without deception, without subtlety, without unexpected depths.
The main answer to the paradox of “how does he succeed while making so many bad decisions?” is that he’s the most focused person in the world. When he decides to do something, he comes up with an absurdly optimistic timeline for how quickly it can happen if everything goes as well as the laws of physics allow. He – I think the book provides ample evidence for this – genuinely believes this timeline,2 or at least half-believingly wills for it to be true. Then, when things go less quickly than that, it’s like red-hot knives stabbing his brain. He gets obsessed, screams at everyone involved, puts in twenty hour days for months on end trying to try to get the project “back on track”. He comes up with absurd shortcuts nobody else would ever consider, trying to win back a few days or weeks. If a specific person stands in his way, he fires that person (if they are an employee), unleashes nonstop verbal abuse on them3 (if they will listen) or sues them (if they’re anyone else). The end result never quite reaches the original goal, but still happens faster than anyone except Elon thought possible. A Tesla employee described his style as demanding a car go from LA to NYC on a single charge, which is impossible, but he puts in such a strong effort that the car makes it to New Mexico.
This is the Musk Strategy For Business Success; the rest is just commentary.
1. Vance starts with the story of the biography itself. When Musk learned he was being profiled, he called Vance, threatened that he could “make [his] life very difficult”, and demanded the right to include footnotes wherever he wanted telling his side of the story. When Vance said that wasn’t how things worked, Elon invited him to dinner to talk about it. Elon arrived late, and spent the first few courses talking about the risk of artificial superintelligence. When Vance tried to redirect the conversation to the biography, Elon abruptly agreed, gave him unprecedented access to everyone, and won him over so thoroughly that the book ends with a prediction that Musk will succeed at everything and become the richest man in the world (a bold claim back in 2015).
I like this story but find myself dwelling on Musk’s request — why shouldn’t he be allowed to read his own biography before publication and include footnotes giving his side of the story where he disagrees? That sounds like it should be standard practice! If I ever write a post about any of you and you disagree with it, feel free to ask me to add a footnote giving your side of the story (or realistically I’ll put it in an Open Thread).
2. The book gives several examples of times Musk almost went bankrupt by underestimating how long a project would take, then got saved by an amazing stroke of luck at the last second. When Vance asked him about his original plan to get the Falcon 1 done in a year, he said:
“Reminded about the initial 2003 target date to fly the Falcon 1, Musk acted shocked. ‘Are you serious?’ he said. ‘We said that? Okay, that’s ridiculous. I think I just didn’t know what the hell I was talking about. The only thing I had prior experience in was software, and, yeah, you can write a bunch of software and launch a website in a year. No problem. This isn’t like software. It doesn’t work that way with rockets.”
But also, the employees who Vance interviewed admit that whenever Musk asks how long something will take, they give him a super-optimistic timeline, because otherwise he will yell at them.
3. I wondered whether Elon was self-aware. The answer seems to be yes. Here’s an email he wrote a friend:
“I am by nature obsessive compulsive. In terms of being an asshole or screwing up, I’m personally as guilty of that as anyone, and am somewhat thick-skinned in this regard due to large amounts of scar tissue. What matters to me is winning, and not in a small way. God knows why … it’s probably [rooted] in some very disturbing psychoanalytical black hole or neural short circuit.”