Calum
Published 22 Aug 2020Pre-war shipwrecks are disappearing from the seabed. Why? A look at the sad reality of illegal salvaging that is destroying numerous war graves and historical wrecks around the world, told from the site of some of the most famous shipwrecks in the world; Scapa Flow.
The Guardian has done some amazing work in documenting this problem, worth a read if you have the time:
https://www.theguardian.com/world/201…
00:00 – Introduction & History of Scapa Flow
01:00 – Scuttling & Salvaging of the German High Fleet
02:45 – The Value of Pre-War Steel
03:54 – The Disappearing Shipwrecks
06:03 – HMS Royal Oak
10:16 – Disappearing Wargraves
10:58 – OutroTwitter………………….►https://twitter.com/calumraasay
Instagram…………….►http://instagram.com/calumraasay
Website………………..►http://calumgillies.com
March 23, 2021
Why are Pre-War Shipwrecks Disappearing?
March 20, 2021
Iron cannon, improved celestial navigation techniques, and “race-built” galleons
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes considers some of the technological innovations which helped English sailors to overcome powerful adversaries of the Spanish and Portuguese navies in the late 1500s and early 1600s:
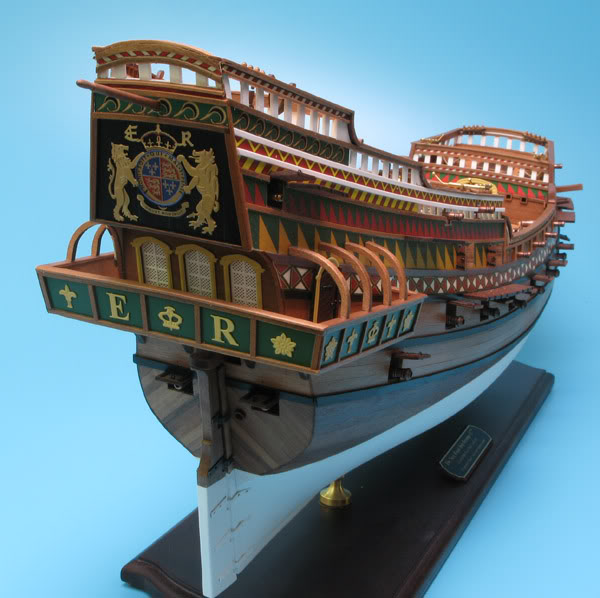

Stern view of a model of the Revenge as an example of a race-built galleon, 1577.
Image from modellmarine.de
Apart from the adoption and refinement of celestial navigation techniques, however, English seafaring capabilities also benefited from some more obvious, physical changes. In 1588, for example, on the eve of the Spanish Armada, a senior Spanish officer believed that the English had “many more long-range guns”. By the 1540s, medieval ironmaking techniques involving the blast furnace had gradually spread from Germany, to Normandy, and thence to the Weald of Sussex and Kent. Whereas in the first half of the sixteenth century England had typically imported three quarters of its iron from Spain, by 1590 it had not only quintupled its consumption of iron but was also almost entirely self-sufficient. And by allowing England to exploit its plentiful domestic deposits of iron, the blast furnace resulted in it producing many more cheap cannon.
Iron guns were in many ways worse for ships than those of bronze. They were heavier, prone to corrosion, and more likely to explode without warning. Bronze guns, by contrast, would first bulge and then split, but in any case tended to last. When the British captured Gorée off the coast of Senegal in 1758, they found a working English-made bronze cannon that dated from 1582. Yet iron was only 10-20% the price of bronze. Although the Royal Navy for decades continued to prefer bronze, cheap, medium-sized cannon of iron proliferated, becoming affordable to merchants, pirates, and privateers — a situation that was unique to England.
English ships were thus especially well-armed, allowing them to access new markets even when they sailed into hostile waters. They were soon some of the only merchants able to hold their own against the latest Mediterranean apex predator, whether it be the Spanish navy, Algeria-based corsairs, or Ottoman galleys. And they were able to insert themselves, sometimes violently, into the inter-oceanic trades — all despite the armed resistance of the Spanish and Portuguese, who had long monopolised those routes. In the 1560s, John Hawkins tried a few times to muscle in on the transatlantic Portuguese and Spanish trade in slaves. With backing from the monarch and her ministers, he captured Portuguese slave ships, raided and traded along the African coastline himself, and then sold slaves in the Spanish colonies of the Americas, sometimes having to attack those colonies before the local governor would allow them to trade. (The attempt was ultimately unsuccessful, as Hawkins’s privateering fleet was all but destroyed in 1568 and the English were not involved in the slave trade again for almost a century.)
The English hold over the hostile markets was only threatened during times of peace on the continent, when their ships’ defensiveness no longer gave them a special advantage. The Dutch usurped English dominance of the trade with Iberia and the Mediterranean, for example, during the Dutch Republic’s truce with Spain 1609-21. Their more efficient ships, especially for bulk commodities — the fluyt invented at Hoorn in the late 1580s — were cheaper to build, required fewer sailors, and were easier to handle. But these advantages only made them competitive when the risk of attack was low, as they were hardly armed. When wars resumed, the English had a chance to regain their position.
Finally, the English acquired a few further advantages when it came to ship design. Thanks to the shipwright Matthew Baker, who had been on the trial voyage Cabot dispatched to the Mediterranean, England experienced a revolution in using mathematics to design ships. Baker’s methods, seemingly developed in the 1560s, allowed him to more cheaply experiment with new forms, and by the 1570s these began to bear fruit. The old ocean-going carracks and galleons, with their high forecastles and aftercastles, became substantially sleeker. Taking inspiration from nature, Baker designed a streamlined, elongated hull modelled below the waterline upon a cod’s head with a mackerel tail. Above the waterline, too, he lowered the forecastle and set it further back, as well as flattening the aftercastle.
Starting in 1570 with his prototype the Foresight, and more fully developed in 1575-77 with the Revenge, these razed or “race-built” galleons gave the English some significant advantages. Drake even chose the Revenge as his flagship to battle the Spanish Armada in 1588, and to lead an ill-fated reprisal invasion of Portugal the following year. The higher castles of carracks and old-style galleons were suited to clearing an enemy’s decks with arrows and gunfire, as well as to defend against boarders. They were designed for combat at close quarters, in which height was an advantage. They were floating fortresses, their imposing height known to inspire terror. The race-built galleons, by contrast, by making the ship less top-heavy, could have longer and lower gundecks, with more of the ship’s displacement devoted to ordnance — especially useful when taking advantage of the cheaper but heavier cannon made of iron. Rather than killing an enemy ship’s sailors and soldiers, the race-built galleons were optimised for blasting through its hull. What they lost in “majesty and terror”, they made up for with overwhelming firepower. They aimed to sink.
March 19, 2021
Did Soviet Soldiers Ever Get Time Off? – WW2 – OOTF 021
World War Two
Published 18 Mar 2021Ever wonder if the Kriegsmarine saw any action in the Pacific Ocean? Or if the average Soviet soldier ever got a vacation from the most destructive conflict in the history of humanity? You can find out the answers in this episode of Out of the Foxholes!
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Lewis Braithwaite and Dennis Stepanov
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Dennis Stepanov and Lewis Braithwaite
Edited by: Miki Cackowski
Sound design: Marek Kamiński
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
Daniel WeissSources:
David Rumsey Map Collection, David Rumsey Map Center, Stanford Libraries
Bundesarchiv
Portrait of Robert Eyssen, courtesy of Gareth Collins
Komet schematics, courtesy of Rama https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
State Library of QueenslandSoundtracks from the Epidemic Sound:
Phoenix Tail – “At the Front”
Johannes Bornlof – “The Inspector 4”
Howard Harper-Barnes – “Prescient”
Jo Wandrini – “Puzzle Of Complexity”Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
March 17, 2021
Rebuilding the Royal Canadian Navy
I somehow missed this article by Sir Humphrey when he posted it a few weeks back. He’s looking at the Australian and Canadian governments’ respective decisions to use the British Type 26 design to replace their current anti-submarine fleets and considering some of the economic and military concerns that led to the decision.
In both cases there have been media articles in the last week over the programmes and concerns. In Canada, the challenge has been that the cost has grown to a total of $77bn for 15 escorts. There has been cost growth from an originally scheduled $14bn many years ago, and the first of class will not now be delivered until 2031. This has led to suggestions in some media quarters that Canada could do things faster and more cheaply if it simply bought an off the shelf foreign design now and got on with things.
An artist’s rendition of BAE’s Type 26 Global Combat Ship, which was selected as the Canadian Surface Combatant design in 2019, the most recent “largest single expenditure in Canadian government history” (as all major weapon systems purchases tend to be).
(BAE Systems, via Flickr)[…]
The issue now is that Canada will need to establish, almost from scratch, a frigate construction programme and workforce for a finite period of time without a clear plan of what follows on when the last hull is completed. At the same time it will need to run on ships that are becoming increasingly elderly – it is likely that most of the Halifax class will see more than 40 years of service, and some may approach their 50th birthdays before being replaced – something that will pose an increasing maintenance and resource challenge.
Could things be done more cheaply or quickly? Almost certainly yes, but only if you are willing to make massive compromises. It could be possible, for example, to look to licence build an existing design that is already in service. There are plenty of designs out there that could be licence built and brought into service in the next few years — probably at less cost than the T26 programme.
But while this may sound easy, its also a recipe for disaster. It’s easy to look at country X and say “they’re buying this ship for that much” and assume that Canada is getting a bad deal. But Country X is likely to have a very different set of requirements, and their design will reflect it.
For example, Canada needs a ship able to operate with NATO and 5 EYES as a fully integrated player – this adds cost to fit specific systems and equipment that is compatible. Canada will also want to fit bespoke systems to meet national needs – again this will require design changes, that come at a price. Bolting on all manner of different requirements that Canada needs to meet the unique operational circumstances adds price and complexity to the design.
While you probably could take an off the shelf design and build it now, it would be just that, an off the shelf design. It wouldn’t be optimised for local needs, and it wouldn’t have the right equipment, comms, meet local design standards, or be certified for use with national equipment.
You are then faced with two choices – either bring a cheap ship into service that is entirely unsuitable and not designed for your needs, but is a lot cheaper, or spend an enormous amount of money shifting the design to better reflect your needs. If you choose the latter, then suddenly you are adding cost and time in, and the 2031 date will slip even further.
If you choose the former, then you have to accept that the design is “as it comes” and will have minimal Canadian input – so limited industrial offsets, very little economic benefit, and the long-term support solutions will firmly be tied into the country of origin and not Canada. In other words, Canadian taxpayer dollars will be spent to support a foreign economy.
That last point is really the key. Canadian governments, in my lifetime at least, never look at the military requirement as the top priority and sometimes not even the second or third priority. The economic spin-offs, especially in those cases where the benefits can be allocated to marginal parliamentary constituencies, will be the top priority. As is always a talking point in the case of any major military hardware acquisition, this is going to be the “single largest expenditure in Canadian government history”. Just as the replacement of the RCAF’s aged CF-18 fighters will be the largest expenditure in its turn.
March 5, 2021
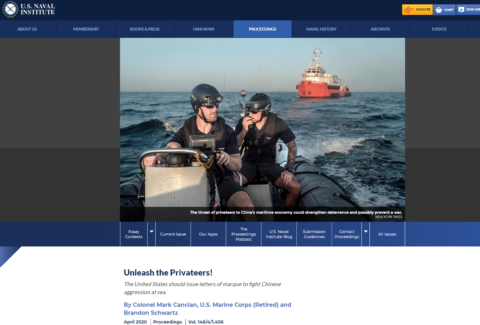
Privateering today?
In a recent post at Astral Codex Ten, Scott Alexander posted a link to an article in the US Naval Institute Proceedings putting forward arguments for the United States issuing modern day Letters of Marque. Today he posted a few reactions from his readers to the proposal:
On the article about privateers, local naval expert Bean writes:
It’s time for the standard disclaimer any time Proceedings comes up: Proceedings is intended as a forum for discussion of matters of interest to naval officers, and it is not peer reviewed. Often very not peer reviewed. Like in this case. Please don’t judge the USNI on the basis of this stuff. They do a lot of good work.
And yes, it is that stupid. First, privateering is probably illegal today. The US didn’t sign the 1856 Paris declaration outlawing it, but the ban is almost certainly considered customary international law today, and thus binding on the US, too. (International law is very weird.)
Second, it makes no sense. It was something that people did in an era when the ability of the state to do things was sharply constrained, and it was never all that profitable. These days, the government is a lot more effective, and if it wants to hunt Chinese commerce (never mind the issues about who owns the cargo, which is rather different in the days of worldwide communications and the shipping container) it will make auxiliary commerce raiders of its own. There’s definitely no need to have a DDG sit outside a Brazilian port waiting. Take any reasonable civilian ship (big yacht, fishing boat, tug, whatever) and fit it with a couple of 40mm guns and a boarding party. Have it do the waiting instead.
And our other defense expert, John Schilling, writes:
Modern naval weapons are too good at sinking ships, whereas privateering requires capturing ships intact to be profitable. For a trivial, and in this context uncontroversial, investment, China can equip their merchant fleet with defensive weapons that will sink any privateer, unless the privateer sinks them first.
– Privateers, being incapable of surviving a fight with real warships (especially modern ones), need to be able to hide from and if necessary outrun enemy warships. That’s a lot harder to manage in a world of radio, radar, maritime patrol aircraft, and satellites. Harder still if you insist on taking prizes, which will be Lojacked beyond your ability to clear at sea. Even in a hot war with the United State, China will probably be able to spare e.g. an H-6K for a day to sink the privateer that just sank one of China’s freighters, and that’s all it will take.
– The rest of the world regards privateering as flat-out illegal, so virtually all of the ports of the world will be closed to the privateers *and their prizes*. Operating in the South China Sea directly from Hawaii, without any intermediate bases (what’s left of Guam will have its hands full), is going to be logistically challenging to say the least. And the value of that prize ship you just took is greatly diminished if it can only be used in the US coastal trade, its cargo sold only on the US domestic market never to be reexported.
This is a stupid idea that keeps coming back every year or two because somebody read too many Napoleonic sea-adventure stories and thinks they’re the only one who read those stories so their clever “obscure” idea is something the rest of us haven’t heard and rejected a dozen times already.
There’s a problem in medicine where people think doctors are trustworthy experts. While this is often true, there are about a million doctors, and some tiny fraction of them are insane. The reasonable doctors mostly keep their mouths shut, but sometimes an insane doctor will endorse some sort of terrible alternative medicine, and then people will get excited: “A doctor endorsed it! It must be real!” The fact is, you can find doctors saying pretty much any bizarre thing — I hear some of them even have Substacks.
My thought when reading that article was “this sounds crazy … but wait! It’s written by a colonel and published by the US Naval Institute! That sounds just wacky enough to make a good link!”
Now I am concerned that colonels work the same way as doctors. I wonder what else is like this.
Colonels absolutely do work the same way as doctors, lawyers, and (especially) journalists — Michael Chrichton christened this the “Gell-Mann Amnesia Effect”.
The topic is as good an excuse as I’m likely to find to post Mark Knopfler’s “Privateering”:
“Privateering”
Yon’s my privateer
See how trim she lies
To every man a lucky hand
And every man a prize
I live to ride the ocean
The mighty world around
To take a little plunder
And to hear the cannon sound
To lay with pretty women
To drink Madeira wine
To hear the rollers thunder
On a shore that isn’t mine
Privateering we will go
Privateering, yo ho ho ho
Privateering we will go
Yo ho ho, yo ho ho
The people on your man o’ war
Are treated worse than scum
I’m no flogging captain
And by God I’ve sailed with some
Come with me to Barbary
We’ll ply there up and down
Not quite exactly
In the service of the Crown
To lay with pretty women
To drink Madeira wine
To hear the rollers thunder
On a shore that isn’t mine
Privateering we will go
Privateering, yo ho ho ho
Privateering we will go
Yo ho ho, yo ho ho
Look’ee there’s my privateer
She’s small but she can sting
Licensed to take prizes
With a letter from the King
I love the streets and taverns
Of a pretty foreign town
Tip my hat to the dark-eyed ladies
As we sally up and down
To lay with pretty women
To drink Madeira wine
To hear the rollers thunder
On a shore that isn’t mine
Privateering we will go
Privateering, yo ho ho ho
Privateering we will go
Yo ho ho, yo ho ho
Britannia needs her privateers
Each time she goes to war
Death to all her enemies
Though prizes matter more
Come with me to Barbary
We’ll ply there up and down
Not quite exactly
In the service of the Crown
To lay with pretty women
To drink Madeira wine
To hear the rollers thunder
On a shore that isn’t mine
Privateering we will go
Privateering, yo ho ho ho
Privateering we will go
Yo ho ho, yo ho ho
March 2, 2021
Warship purchasing is not for the faint-of-heart
Ted Campbell talks about the way the Royal Canadian Navy plans for warship purchases … and how the best-laid plans can be derailed by ignorant political advisors:

An artist’s rendition of BAE’s Type 26 Global Combat Ship, which was selected as the Canadian Surface Combatant design in 2019, the most recent “largest single expenditure in Canadian government history” (until the RCAF gets their replacement for the CF-18 Hornet).
(BAE Systems, via Flickr)
Once upon time,* about 25 to 30 years ago, in the mid 1990s, when I was the director of a small, very specialized team in National Defence Headquarters (NDHQ) in Ottawa, something like this happened: One of my colleague, who had a title like Director of Maritime Requirements or something similar said to one of his principle subordinates, “Look, now that the 280s (Canada had four Tribal Class destroyers with pennant numbers starting at 280, they were often just called ‘280s’) are finished their mid-life refit and now that the new frigates are entering service it is time to put a ‘placeholder’ in the DSP for their eventual replacements.” The DSP was (still is?) the Defence Services Programme, it is the internal document which sets out the long range spending plans (maybe hopes is a better word) for the Canadian Armed Forces.
Anyway, the Navy commander (the officer assigned to write the document, not the Commander of the Royal Canadian Navy who is nicknamed the Kraken (CRCN)) sat at his desk and consulted the most recently approved planning document which, as far as I can remember, called for a surface fleet of 25 combat vessels and four large support ships plus numerous minor war vessels (like minesweepers) and training vessels. The officer then prepared a memorandum for the joint planning staff which said that the Navy would need 25 new combat ships, to be procured between about 2015 and 2035, in five “batches” of five ships each** at a total cost of about $100 Billion, in 2025 dollars. He didn’t say much beyond that, actually, he was just intending to “reserve” some money a generation or so in the future. His memorandum sailed, smoothly, past his boss and the commodore but questions came from a very senior Air Force general: Where he asked, did the $100 Billion come from? That was an outrageous number, he said.
A meeting ensure where the Navy engineering people came and said, “$100 Billion is a very reasonable guesstimate. Our brand new frigate are costing $1 Billion each when they come down the slipway. They will each have cost the taxpayers two to three times that by the time we send them to be broken up thirty or forty years from now. Adding in the inevitable costs of new technology and inflation, which we know is higher for things like military ships and aircraft than it is for consumer goods, then a life-cycle cost of $4 Billion for each ship is very conservative. The admirals and generals huffed and puffed but they didn’t argue ~ they knew that the engineering branch insisted on using life cycle costing, even though no-one but them understood it, and they also knew that arguing with engineers is like mud-wrestling with pigs: everyone gets dirty but the pigs love it.
A decade later, when a new government was planning the National Shipbuilding Procurement Strategy, which was all about making the Canadian shipbuilding industry competitive and had very little to do with ships ~ except they would be the “product” for which the Government of Canada would pay top-dollar, the Navy was told it could have fewer ships, in two classes, and someone ~ NOT the military’s engineering branch ~ assigned a cost figure to the project which was, to be charitable, pulled out of some political/public relations staffer’s arse.
[…]
* The story is true, in general, but I was not directly involved in any of it. I learned about what happened from three main sources: 1. routine briefings that my bosses (directors-general and branch chiefs) gave, regularly, to we directors, dealing with what was going on in the HQ and in the big wide world; 2. periodic chats with my colleagues, after work on Friday afternoons, in the bar of the Officers’ Mess ~ many of us regarded 2. as a more reliable source of information than 1.; and 3. in the case of the story about the Navy engineers and the Air Force general, by a friend and colleague who was in the room.
** The idea, long before the National Shipbuilding Strategy, was to keep shipyards moderately busy on a continuous basis. The 25 ships would all be similar: the first “batch” of five would be identical, one to the other; the second “batch” would be very similar but with some improvements; the five ships of batch 3 would be similar to the ships from the second batch and those from batch 4 would be rather like their batch 3 sisters. Finally, the batch 5 ships would be product improved versions of batch 4 ~ they would still be “sisters” of the batch 1 ships, but not, in any way, twins. The idea was that about the time that the batch 5 ships were being delivered the first of the batch 1 ships would be getting ready for a mid-life refit (after 15 to 20 years of service) which would result in it being much more like the batch 5 ships … and so on.
February 18, 2021
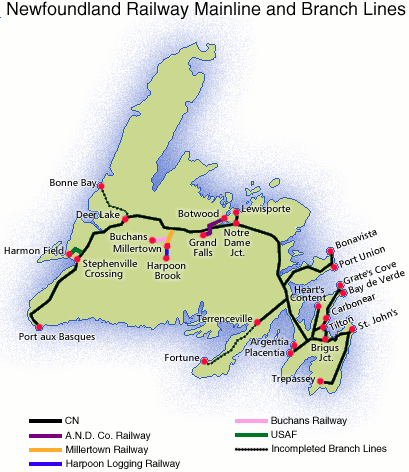
Fallen Flag — The Newfoundland Railway

Newfoundland played a pivotal role in World War II during the Battle of the Atlantic and as a staging point for ship convoys and aircraft movements. Construction of Allied bases and the associated movement of personnel resulted in a railway traffic surge. A British and Canadian airfield grew near the main line at Gander, and the United States also exploited Newfoundland’s relative proximity to Europe. The two largest American installations were a naval base at Argentia — site of the 1941 shipboard meeting between President Roosevelt and Prime Minister Churchill — and Harmon Field, an Air Force base on the west coast at Stephenville. Rail traffic was a barometer of wartime pressures; between 1941 and 1943, NR’s passenger count rose from 223,000 to 500,000; freight tonnage also doubled. So important was the line to American military interests that the U.S. government allocated $2 million of “lend-lease” funds for locomotive and car construction.
Newfoundland Railway’s Overland Limited (a.k.a. the “Newfie Bullet”) calls at Corner Brook in 1948, the year before CN took over.
Canadian National photo via Classic TrainsAlthough the war brought profits and a revitalized equipment roster, the railway was not immune from the conflict’s brutality. On October 14, 1942, the Port aux Basques–North Sydney (N.S.) ferry Caribou was torpedoed and sunk by a German submarine. Of 237 passengers and crew on board, 136 perished.
Canadian National control
Newfoundland’s 1949 entry into Canada saw responsibility for much of the transport infrastructure assumed by the Canadian government, whose Canadian National Railways was charged with the management and operation of the railway, as well as coastal steamship services and the ferry link to Nova Scotia. The federal government agreed to subsidize the operations. Despite wartime profits and some postwar rebounds, though, the railway had been and would continue to be a chronic money-loser.
Newfoundland Railway was exclusively steam-powered for all but the final seven months of its pre-Confederation existence, as GE 47-ton center-cab diesels 5000–5002 arrived in August 1948. The last new NR locomotives were class R-2-d Mikados 324–329, built by Montreal and delivered just weeks before Confederation. They became the youngest steam locomotives, by five years, on the entire CNR. In all, four 4-6-0s, a 2-8-0, 10 4-6-2s, and 30 2-8-2s were conveyed to CN.
[…]
Well into the 1960s, the railway provided the only land link spanning Newfoundland. When the first road across the island opened as part of the Trans-Canada Highway in late 1965, it triggered an irreversible shift of traffic off the railway. In the highway’s first 15 years, the percentage of island freight handled by train dropped by more than half. More than 24 hours — double the road time — was required for the St. John’s–Port aux Basques rail trip, and that was if the trains ran on time, a spotty prospect especially in winter.
Passengers benefitted from CN’s continued investment in rolling stock, although the non-air-conditioned fleet couldn’t provide mainland comfort levels. The principal pre-Confederation passenger train was the overnight Overland Limited. CN renamed it Caribou in 1950, a fitting tribute to the ferry lost in 1942. To most folks, though, the train was known from the war onward as the “Newfie Bullet,” a wry reference to its leisurely schedule (daily in summer, triweekly the rest of the year). Although CN buses replaced the “Bullet” in July 1969, mixed trains kept serving isolated mainline points and the Carbonear, Bonavista, and Argentia branches.
From the Wikipedia entry on the post-abandonment fate of the line:
The former Newfoundland Railway station in St. John’s now hosts the Railway Coastal Museum. Numerous towns across the island have preserved railway equipment on display.
With few exceptions, the roadbed now forms the T’Railway Provincial Park rail trail. Until 2005, the Trinity Loop Amusement Park operated a miniature train, one of the few remaining places on Newfoundland with tracks still in place. The park closed down and was abandoned in 2005 due to lack of interest. Since then, all of the buildings have been heavily vandalized and Hurricane Igor washed away part of the park, including a large section of the rail bed. Local railway fans have been pushing government to retain the park as an historic site but officials have expressed little interest.
Some rolling stock was converted to a narrower gauge of 914 mm (3 ft) and sold to the White Pass & Yukon Route (WP&YR) railway, which reopened for service in 1988. Gravel cars used by WP&YR are still painted in CN orange; unconfirmed information indicates that some Newfoundland passenger cars were converted into passenger cars of vintage appearance for WP&YR.
January 30, 2021
The Extraordinary Voyage of USS Marblehead
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 6 Jan 2021By May 1942, nearly half of the forty surface ships of the U.S. Asiatic fleet would be sunk, including the fleet’s largest vessel, the heavy cruiser USS Houston. But the improbable survival of one of the fleet’s vessels, the light cruiser USS Marblehead, is the stuff of legend. The extraordinary voyage of the Marblehead is history that deserves to be remembered.
This is original content based on research by The History Guy. Images in the Public Domain are carefully selected and provide illustration. As very few images of the actual event are available in the Public Domain, images of similar objects and events are used for illustration.
You can purchase the bow tie worn in this episode at The Tie Bar:
https://www.thetiebar.com/?utm_campai…All events are portrayed in historical context and for educational purposes. No images or content are primarily intended to shock and disgust. Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. Non censuram.
Find The History Guy at:
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TheHistoryGuy
Please send suggestions for future episodes: Suggestions@TheHistoryGuy.netThe History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered is the place to find short snippets of forgotten history from five to fifteen minutes long. If you like history too, this is the channel for you.
Awesome The History Guy merchandise is available at:
teespring.com/stores/the-history-guyScript by THG
#usnavy #thehistoryguy #WWII
December 17, 2020
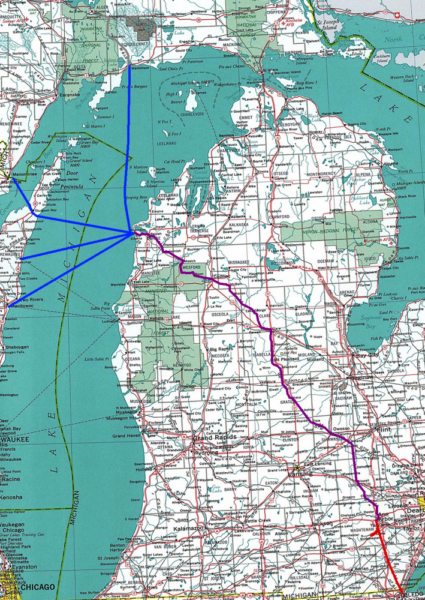
Fallen Flag — the Ann Arbor Railroad
This month’s Classic Trains featured fallen flag is the Michigan-based Ann Arbor Railroad which operated rail services from Toledo, Ohio to Elberta and Frankfort, Michigan, along with lake ferry service across Lake Michigan to Manitowoc and Kewaunee, Wisconsin and Menominee and Manistique in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. Robert I. Warrick provides an outline of the history of the line:
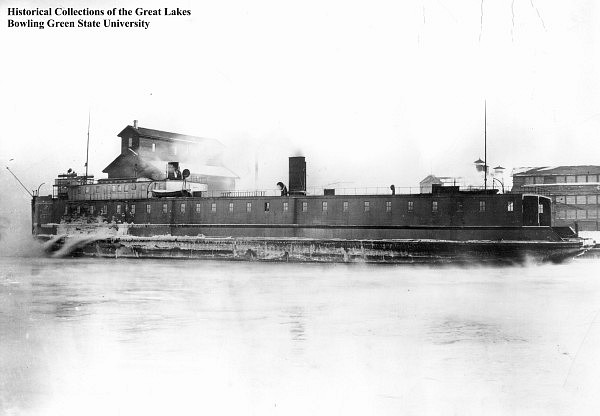

Ann Arbor No. 1, built in 1892 by Craig Shipbuilding Co. in Toledo, Ohio. She was destroyed in a fire on March 7, 1910 at Manitowoc, Wisconsin.
Photo from Bowling Green State University via Wikimedia Commons.
The Ann Arbor Railroad was as much a steamship line as a railroad. Built from Toledo, Ohio, northwest to Frankfort, Mich., it existed for one reason — to move freight in car ferries across Lake Michigan to bypass Chicago. From 1910 to 1968, “the Annie” operated 320 car ferry route-miles versus 292 miles of railroad. AA was at the forefront of car ferry design and innovation, from the first wooden-hulled vessels to the most advanced car ferry to ever sail Lake Michigan.
During the 1940s, up to six ferries made the round trip from Boat Landing, as AA called its yard in Elberta on the south side of Frankfort harbor, to two Wisconsin and two Michigan Upper Peninsula ports. The boats ran year-round on a tight schedule, timed to match with three pairs of scheduled Toledo freights, where AA interchanged with five trunk lines. Well-kept 2-8-2s powered those short, fast trains across AA’s rolling profile until 1950, when Alco FA2s took over.
[…]
The Eastern mergers of the 1960s ultimately doomed the old Ann Arbor. As planning for Penn Central went on, the Norfolk & Western merged with Wabash, Nickel Plate, and two smaller roads in 1964. N&W wanted no part of the Ann Arbor and its costly ferries, so AA was foisted off on DT&I, which was profitable by the 1960s.
With ICC approval, DT&I took over the Ann Arbor on August 31, 1963, and soon replaced the tired FA2s with 10 GP35s, riding on Alco trucks and painted in DT&I orange with large “Ann Arbor” lettering. DT&I’s GPs often mixed with the Annie’s.
DT&I had ferry Wabash refitted, changed her name to City of Green Bay, and loaned AA $2.5 million to rebuild Ann Arbor No. 7. The railroad renamed No. 7 Viking, lengthened it, installed four EMD 2,500 h.p. 567 diesels. But even with the bigger boats, capacity remained an issue as car sizes increased. AA was losing money. First the ferry route to Manistique, Mich. (and AA subsidiary Manistique & Lake Superior), was discontinued, then the one to Menominee, Mich.
Ann Arbor’s fate was sealed. A firm was hired to liquidate Pennsylvania Company assets, including AA and DT&I. Ann Arbor defaulted on the loan for the Viking on November 1, 1972, and filed for bankruptcy on October 15, 1973, leading to AA’s inclusion with other bankrupts in the Regional Rail Reorganization Act of 1973 that resulted in Conrail.
December 11, 2020
The Salvage of Pearl Harbor Pt 3 – The First and the Last
Drachinifel
Published 2 Dec 2020Today we look at the salvage efforts on the USS Shaw, first vessel salvaged from the remains of the attack on Pearl Harbor and the work on the last two vessels under the team’s care, the Utah and Oklahoma
Sources:
www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/B00C0JIXJO
https://www.history.navy.mil/our-coll…
www.amazon.co.uk/Pearl-Harbor-Fleet-Salvage-Appraisal/dp/0898755654
www.amazon.co.uk/Descent-into-Darkness-Harbour-Divers/dp/0891417451
Videos – US National Archives / US Department of DefenseFree naval photos and more – www.drachinifel.co.uk
Want to support the channel? – https://www.patreon.com/Drachinifel
Want a shirt/mug/hoodie – https://shop.spreadshirt.com/drachini…
Want a poster? – https://www.etsy.com/uk/shop/Drachinifel
Want to talk about ships? https://discord.gg/TYu88mt
Want to get some books? www.amazon.co.uk/shop/drachinifelDrydock
Episodes in podcast format – https://soundcloud.com/user-21912004
December 10, 2020
The Salvage of Pearl Harbor Pt 2 – Up She Rises!
Drachinifel
Published 18 Nov 2020Today we look at the salvage efforts on the three battleships outright sunk in the attack on Pearl Harbor that would be returned to service.
Sources:
www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/B00C0JIXJO
https://www.history.navy.mil/our-coll…
www.amazon.co.uk/Pearl-Harbor-Fleet-Salvage-Appraisal/dp/0898755654
www.amazon.co.uk/Descent-into-Darkness-Harbour-Divers/dp/0891417451
Videos – US National Archives / US Department of DefenseFree naval photos and more – www.drachinifel.co.uk
Want to support the channel? – https://www.patreon.com/Drachinifel
Want a shirt/mug/hoodie – https://shop.spreadshirt.com/drachini…
Want a poster? – https://www.etsy.com/uk/shop/Drachinifel
Want to talk about ships? https://discord.gg/TYu88mt
Want to get some books? www.amazon.co.uk/shop/drachinifelDrydock
Episodes in podcast format – https://soundcloud.com/user-21912004
December 9, 2020
The Salvage of Pearl Harbor Pt 1 – The Smoke Clears
Drachinifel
Published 11 Nov 2020Today we look at the start of the salvage efforts in the aftermath of the attack on Pearl Harbour.
Sources:
www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/B00C0JIXJO
https://www.history.navy.mil/our-coll…
www.amazon.co.uk/Pearl-Harbor-Fleet-Salvage-Appraisal/dp/0898755654
www.amazon.co.uk/Descent-into-Darkness-Harbour-Divers/dp/0891417451Free naval photos and more – www.drachinifel.co.uk
Want to support the channel? – https://www.patreon.com/Drachinifel
Want a shirt/mug/hoodie – https://shop.spreadshirt.com/drachini…
Want a poster? – https://www.etsy.com/uk/shop/Drachinifel
Want to talk about ships? https://discord.gg/TYu88mt
Want to get some books? www.amazon.co.uk/shop/drachinifelDrydock
Episodes in podcast format – https://soundcloud.com/user-21912004
December 7, 2020
E.01 – Enter Japan – Pearl Harbor – WW2 – 120 A – December 7, 1941
World War Two
Published 7 Dec 2020Powered by World of Warships – https://wo.ws/PearlHarbor – Register now to receive an exclusive bonus!
In this episode: Japan’s meticulous planning and preparation made it possible to surprise the Americans at Pearl Harbor. Alert on Oahu is largely nonexistent. It is the deep breath before the plunge.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Spartacus Olsson and Indy Neidell
Directed by: Wieke Kapteijns
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Produced by: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Co-Producers: Maria Kyhle and Francis van Berkel
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Set Design by: Astrid Deinhard
Graphic Design by: Mikolaj Uchman
Map Animations by: Daniel Haczyk and Eastory
Assistant Editors: Miki Cackowski, Daniel Weiss, Karolina Dołega
Still Colorizers: Adrien Fillon, Norman Stewart, Jaris Almazani, Daniel Weiss, Mikolaj Uchman, Carlos Ortega Pereira
Research by: Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Markus Linke, Wieke Kapteijns, Bastian Gaete, Lewis Braithwaite, Tim Smith, Ian Irungu
Sound Design by: Marek Kamiński
Dogfights by: Daniel Weiss, Bastian Gaete, Ian Sowden, Dennis StepanovVoices:
Mitsuo Fuchida – Daniel Grieb
Ada Peggy Olsson – Shani Neidell Beard
Iyōzō Fujita – Emi Celis
James Anderson – Emi Celis
Dorinda Stagner – Zora Johnson
Jack Kelley – Ryan Socash
James McClelland – Spartacus Olsson
Phil Rasmussen – Spartacus Olsson
Dan Wentrcek – Dennis Stepanov
Thompson Izawa – Samir Mechel
Robert Isacksen – Ian Sowden
Joseph K. Taussig Jr. – Tim Smith
James Cory – Ryan TeboFilm colorization by: Ricks Film Restoration
Naval Gameplay by: World of Warships
Archive material provided by: Reuters/ScreenoceanA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
1 hour ago (edited)
When we set out to do this crazy project we thought we wanted to try some really new things. As anyone knows that follows us regularly, our first and foremost goal is remembrance — to shine a light on our past and learn form our ancestors’ mistakes and achievements. We try our best to do that with a dedication to facts and details liberated from partisan, or ideological historiography. For this purpose, the attack on Pearl Harbor serves very well. It is a compact event over only a few hours that is spectacular in its nature, tragic in its effect, gripping in its drama, and has tremendous impact on WW2 on all fronts. It is also an event that is often simplified to the point of misunderstanding, has been woven into national mythology, and given rise to some pretty nutty conspiracy myths. Simply put: the Attack on Pearl Harbor is short enough, exciting enough, and misunderstood enough for us to do a limited series like this.But more than that we also wanted to try some new technical and narrative things. Since we started doing historical documentaries with the Great War in 2014 we have tried to be on the forefront of pioneering new ways of creating historiography for the modern media world. Narratively, we have dedicated ourselves to chronologies, which in historiography is nothing new, but it is new in the world of film documentaries (at least to the level we do it) — so we thought; “heck what if we go down to minute by minute for this” — well we did and it taught us an enormous amount about Pearl Harbor, but also about how we can write. We will get back to that in further comment on the series. As for technology, it truly is technology that enables our work, well any media — for us it is social media, affordable ways to capture film, global virtual remote working spaces, digital research opportunities, digital film archives, and so on.
Two areas we had not been able to venture into was recreation of scenes using computer graphics and colorization of moving images. Using a gaming engine to create animation is also nothing new, but usually very, very expensive because you have to first create the world, the assets and the characters for your recreation. But for Pearl Harbor, World of Warships https://worldofwarships.com and World of Warplanes https://worldofwarplanes.com opened an opportunity to do this on a new scale at a cost that is only a fraction of what it usually costs. Along the way we also got to know Ricks Film Restorations (https://bit.ly/ricksfilmresorations and https://www.youtube.com/user/Rick88888888) who use AI technology to enhance and colorize film footage. While both of these technologies are only at the beginning of their potential, we think the results are spectacular. More than anything it has enabled us to enhance the emotional and visual experience for this series to a level we never reached before. Last but not least it enabled us to use the financial contributions of the TimeGhost Army, and World of Warships to create five hours of content for less than 1/50th — only 2% — of what it would cost to do with traditional means.
creatingstuff
In the Name of the entire TimeGhost Team,
Astrid, Indy, Spartacus, and WiekeEpisode Guide:
This is a 10 episode limited series within our weekly coverage of WW2 — to see the immediate events leading up to this day watch episode 119 from December 5, https://youtu.be/DYUzmBuX-6Y. Some of the events covered briefly as they start on this day, such as the invasions in the West Pacific will be covered in more detail in the coming weeks, especially in episode 120K (the 11th episode this week).coming out on December 12.The playlist to get all these episodes in one go is here: https://bit.ly/Pearl-min-by-min
USS Pennsylvania and Pearl Harbor
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 22 Apr 2019USS Pennsylvania was in dry dock when the attack came at Pearl Harbor. The History Guy remembers part of her history that may have been forgotten.
This episode was originally posted December 7, 2017. It has been updated to correct some errors in the original, and new footage of USS Pennsylvania has been added.
This is original content based on research by The History Guy. Images in the Public Domain are carefully selected and provide illustration. As images of actual events are sometimes not available, images of similar objects and events are used for illustration.
All events are portrayed in historical context and for educational purposes. No images or content are primarily intended to shock and disgust. Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. Non censuram.
Find The History Guy at:
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TheHistoryGuy
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered is the place to find short snippets of forgotten history from five to fifteen minutes long. If you like history too, this is the channel for you.
Awesome The History Guy merchandise is available at:
https://teespring.com/stores/the-hist…Script by THG
#ushistory #thehistoryguy #usspennsylvania
December 6, 2020
Halifax: Canada’s Great War Casualty
Geographics
Published 14 Jul 2020This video is #sponsored by Squarespace.
Credits:
Host – Simon Whistler
Author – Ben Adelman
Producer – Jennifer Da Silva
Executive Producer – Shell HarrisBusiness inquiries to admin@toptenz.net
If you found this video interesting, you might also want to read my article on the Halifax Explosion here.