Well That Aged Well
Published 12 May 2021In this episode we take a look at the Roman Army, and its comanders. What made the Roman Army so efficent? Was it the practice? The motivation? Their courrage? Or was it more to it? Find out in this week’s episode of “Well That Aged Well”, With Erlend Hedegart.
(more…)
January 18, 2023
The Roman Army, With Adrian Goldsworthy
January 17, 2023
The Early Emperors, Part 11 – The Flavian Reconstruction
seangabb
Published 29 Dec 2022This is a video record of a lecture given by Sean Gabb, in which he discusses the three Flavian Emperors who ruled between 69 and 98 AD — Vespasian, Titus, and Domitian. He also discusses the Jewish Revolt and the eruption of Vesuvius.
The Roman Empire was the last and the greatest of the ancient empires. It is the origin from which springs the history of Western Europe and those nations that descend from Western Europe.
(more…)
Growing an Ancient Roman Garden
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 23 Aug 2022
January 12, 2023
The Early Emperors, Part 10 – The Year of the Four Emperors
seangabb
Published 27 Dec 2022This is a video record of a lecture given by Sean Gabb, in which he discusses the three Emperors who followed in swift succession between the fall of Nero and the accession of Vespasian — Galba, Otho, and Vitellius.
The Roman Empire was the last and the greatest of the ancient empires. It is the origin from which springs the history of Western Europe and those nations that descend from Western Europe.
(more…)
January 10, 2023
The Early Emperors, Part 9 – Nero: Can We Trust the Sources?
seangabb
Published 25 Dec 2022This is a video record of a lecture given by Sean Gabb, in which he discusses the reasons for the black reputation possessed by the Emperor Nero.
The Roman Empire was the last and the greatest of the ancient empires. It is the origin from which springs the history of Western Europe and those nations that descend from Western Europe.
(more…)
January 5, 2023
Roman Emperors, Part 8 – Nero: Life and Death
seangabb
Published 20 Dec 2022This is a video record of a lecture given by Sean Gabb, in which he discusses what we can know or suspect about the life of the Emperor Nero. Some criticism here of Tacitus as a reliable source.
The Roman Empire was the last and the greatest of the ancient empires. It is the origin from which springs the history of Western Europe and those nations that descend from Western Europe. It is the political entity within which the Christian faith was born, and the growth of the Church within the Empire, and its eventual establishment as the sole faith of the Empire, have left an indelible impression on all modern denominations. Its history, together with that of the Ancient Greeks and the Jews, is our history. To understand how the Empire emerged from a great though finally dysfunctional republic, and how it was consolidated by its early rulers, is partly how we much understand ourselves.
(more…)
December 24, 2022
History-Makers: Saint Nicholas to Santa Claus
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 23 Dec 2022Merry Sinterklaasfeest to all, and to all a good night.
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
(more…)
December 21, 2022
Tom Holland’s Dominion
Ed West expands on the review he wrote when Holland’s book was first published in 2019:
The Romans are the most “epic” figures in history, to use my young son’s favourite word, exerting a glamour and allure that no civilisation has successfully matched. This magnetism can also appear heightened by what followed, the illiterate bleakness of the early Middle Ages, and the fun-sucking religion that came with it. Many down the years have lamented the switch from the Rome of the Caesars to the Rome of the popes.
The young Tom Holland was one of them. Raised as an Anglican, the historian’s childhood fascination with dinosaurs evolved into one for the equally glamorous ancients. “Although I vaguely continued to believe in God,” he writes: “I found him infinitely less charismatic than the gods of the Greeks: Apollo, Athena, Dionysus. I liked the way that they did not lay down laws, or condemn other deities as demons; I liked their rock-star glamour. As a result, by the time I came to read Edward Gibbon and his great history of the decline and fall of the Roman Empire, I was more ready to accept his interpretation of the triumph of Christianity: that it had ushered in an ‘age of superstition and credulity’. My childhood instinct to see the biblical God as the po-faced enemy of liberty and fun was rationalised.”
This, indeed, is a widespread view. Since Gibbon wrote his great work in the late 18th century there has existed the popular idea that the Renaissance, with its return to classical values, and the Enlightenment, which saw the birth of reason over superstition, were a reaction to Christianity, which had in those thousand dark medieval years suppressed science and freedom.
Yet the truth and paradox, as Holland shows in this truly epic account of how Christianity came to shape the West, is that the western idea of secularism is itself a very Christian one. Liberalism was never a reaction to Christianity, it was a product, perhaps one might heresy; ditto Marxism, socialism and the various progressive creeds of the modern era, right up to the current Great Awokening with its focus on the sanctity of victimhood.
All our assumptions about progress, the rights of the individual, our horror of racism and sexual exploitation, even the acceptance of gay marriage, are the products of Christianity. They are not in themselves universal or “natural”, and to the Romans these ideas of human rights and dignity would have been incomprehensible, laughable even.
Holland made his name with thrilling popular histories set in the ancient world, yet the more he studied antiquity, the more alien it became to him. It wasn’t just that Spartans or Romans killed innocents in large numbers, but that they lacked even the suggestion that the weak might be worth pitying. “That my belief in God had faded over the course of my teenage years did not mean that I had ceased to be Christian,” he writes.
Cruelties such as the exposure of infants – especially female infants – were almost universally accepted in antiquity, except among one or two small German tribes and, at the other end of the empire, a monotheistic people in the eastern Mediterranean. Perhaps the obscenest horror, however, was the practice of crucifixion, a death so cruel that Roman writers barely touched on the subject. Indeed only “four detailed accounts of the process by which a man might be sentenced to the cross, and then suffer his punishment, have survived from antiquity. Remarkably, they all describe the same execution.”
This is the story of how on that one Friday in Judea the world was changed forever — with a moral revolution like nothing before or since.
December 14, 2022
QotD: The “tooth-to-tail ratio” in armies
The first issue is what in military parlance is called the “tooth to tail” ratio. This is the ratio of the number of actual combat troops (the “tooth”) to logistics and support personnel (the “tail”) in a fighting force. Note that these are individuals in the fighting force – the question of the supporting civilian economy is separate. The thing is, the tooth to tail ratio has tended to shift towards a longer tail over time, particular as warfare has become increasingly industrialized and technical.
The Roman legion, for instance, was essentially all tooth. While there was a designation for support troops, the immunes, so named because they were immune from having to do certain duties in camp, these fellows were still in the battle line when the legion fought. The immunes included engineers, catapult-operators, musicians, craftsmen, and other specialists. Of course legions were also followed around by civilian non-combatants – camp-followers, sutlers, etc. – but in the actual ranks, the “tail” was minimal.
You can see much the same in the organization of medieval “lances” – units formed around a single knight. The Burgundian “lance” of the late 1400s was composed of nine men, eight of which were combatants (the knight, a second horsemen, the coustillier, and then six support soldiers, three mounted and three on foot) and one, the page, was fully a non-combatant. A tooth-to-tail ratio of 8:1. That sort of “tooth-heavy” setup is common in pre-industrial armies.
The industrial revolution changes a lot, as warfare begins to revolve as much around mobilizing firepower, typically in the form of mass artillery firepower as in mobilizing men. We rarely in our fiction focus on artillery, but modern warfare – that is warfare since around 1900 – is dominated by artillery and other forms of [indirect] fires. Artillery, not tanks or machine guns, after all was the leading cause of combat death in both World Wars. Suddenly, instead of having each soldier carry perhaps 30-40kg of equipment and eat perhaps 1.5kg of food per day, the logistics concern is moving a 9-ton heavy field gun that might throw something like 14,000kg of shell per day during a barrage, for multiple days on end. Suddenly, you need a lot more personnel moving shells than you need firing artillery.
As armies motorized after WWI and especially after WWII, this got even worse, as a unit of motorized or mechanized infantry needed a small army of mechanics and logistics personnel handling spare parts in order to stay motorized. Consequently, tooth-to-tail ratios plummeted, inverted and then kept going. In the US Army in WWI, the ratio was 1:2.6 (note that we’ve flipped the pre-industrial ratio, that’s 2.6 non-combat troops for every front line combat solider), by WWII it was 1:4.3 and by 2005 it was 1:8.1. Now I should note there’s also a lot of variance here too, particularly during the Cold War, but the general trend has been for this figure to continue increasing as more complex, expensive and high-tech weaponry is added to warfare, because all of that new kit demands technicians and mechanics to maintain and supply it.
[NR: Early in WW2, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill frequently harassed his various North African generals for the disparity between the “ration strength” of their commands and the much-smaller number of combat troops deployed. If General Wavell had 250,000 drawing rations, Churchill (who last commanded troops in the field in mid-WW1) assumed that this meant close to 200,000 combat troops available to fight the Italians and (later) the Germans. This almost certainly contributed to the high wastage rate of British generals in the Western Desert.]
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday, April 22, 2022”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-04-22.
December 10, 2022
QotD: The Western Roman Empire – “decline and fall” or “change and continuity”?
So who are our [academic] combatants? To understand this, we have to lay out a bit of the “history of the history” – what is called historiography in technical parlance. Here I am also going to note the rather artificial but importance field distinction here between ancient (Mediterranean) history and medieval European history. As we’ll see, viewing this as the end of the Roman period gives quite a different impression than viewing it as the beginning of a new European Middle Ages. The two fields “connect” in Late Antiquity (the term for this transitional period, broadly the 4th to 8th centuries), but most programs and publications are either ancient or medieval and where scholars hail from can lead to different (not bad, different) perspectives.
With that out of the way, the old view, that of Edward Gibbon (1737-1794) and indeed largely the view of the sources themselves, was that the disintegration of the western half of the Roman polity was an unmitigated catastrophe, a view that held largely unchallenged into the last century; Gibbon’s great work, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire (1789) gives this school its name, “decline and fall“. While I am going at points to gesture to Gibbon’s thinking, we’re not going to debate him; he is the “old man” of our title. Gibbon himself largely exists only in historiographical footnotes and intellectual histories; he is not at this point seriously defended nor seriously attacked but discussed as the venerable, but now out of date, origin point for all of this bickering.
The real break with that view came with the work of Peter Brown, initially in his The World of Late Antiquity (1971) and more or less canonically in The Rise of Western Christendom (1st ed. 1996; 2nd ed. 2003, 3rd ed. 2013). The normal way to refer to the Peter Brown school of thought is “change and continuity” (in contrast to the traditional “decline and fall”), though I rather like James O’Donnell’s description of it as the Reformation in late antique studies.
Among medievalists this reformed view, which focuses on continuity of culture and institutions from late antiquity to the early Middle Ages, remains essentially the orthodoxy, to the point that, for instance, the very recent (and quite excellent) The Bright Ages: A New History of Medieval Europe (2021) can present this vision as an uncomplicated fact, describing the “so-called Fall of Rome” and noting that “there was never a moment in the next thousand years in which at least one European or Mediterranean ruler didn’t claim political legitimacy through a credible connection to the empire of the Romans” and that “the idea that Rome ‘fell’ on the other hand, relies upon a conception of homogeneity – of historical stasis … things changed. But things always change” (3-4, 12-3). As we’ll see, I don’t entirely disagree with those statements, but they are absolute to a degree that suggests there is no real challenge to the position. There have been a few cracks in this orthodoxy among medievalists, particularly the work of Robin Flemming (a revision, not a clear break, to be sure), to which we’ll return, but the cracks have been relatively few.
While some ancient historians also bought into this view, purchase there has always been uneven and seems, to me at least, now to be waning further. Instead, a process of what James O’Donnell describes as a “counter-reformation” (which he stoutly resists with his own The Ruin of the Roman Empire; O’Donnell is a declared reformer) is well underway, a response to the “change and continuity” narrative which seeks to update and defend the notion that there really was a fall of Rome and that it really was quite bad actually. This is not, I should note, an effort to revive Gibbon per se; it does not typically accept his understanding of the cause of this decline (and often characterizes exactly what is declining differently). Nevertheless, this position too is sometimes termed the “decline and fall” school. My own sense of the field is that while nearly all ancient historians will feel the need to concede at least some validity to the reformed “change and continuity” vision, that the counter-reformation school is the majority view among ancient historians at this point (in a way that is particularly evident in overview treatments like textbooks or the Cambridge Ancient History (second edition)). We’ll meet many of the core works of this revised “decline and fall” school as we go.
As O’Donnell noted in a 2005 review for the BMCR, the reformed school tends to be strongest in the study of the imperial east rather than the west (something that will make a lot of sense in a moment), and in religious and cultural history; the counter-reformation school is stronger in the west than the east and in military and political history, though as we’ll see, to that list must at this point now be added archaeology along with demographic and economic history, at which point the weight of fields tends to get more than a little lopsided.
Those are our two knights – the “change and continuity” knight and the “decline and fall” knight (and our old man Gibbon, long out of his dueling days). To this we must add the nitwit: a popular vision, held by functionally no modern scholars, which represents the Middle Ages in their entirety as a retreat from a position of progress during the Roman period which was only regained during the “Renaissance” (generally represented as a distinct period from the Middle Ages) which then proceeded into the upward trajectory of the early modern period. Intellectually, this vision traces back to what Renaissance thinkers thought about themselves and their own disdain for “medieval” scholastic thinking (that is, to be clear, the thinking of their older teachers), a late Medieval version of “this ain’t your daddy’s rock and roll!”
But almost every intellectual movement represents itself as a radical break with the past (including, amusingly, many of the scholastics! Let me tell you about Peter Abelard sometime); as historians we do not generally accept such claims uncritically at face value. For a long time, well into the 19th century, the Renaissance’s cultural cachet in Europe (and the cachet of the classical period where it drew its inspiration) shielded that Renaissance claim from critique; that patina now having worn thin, most scholars now reject it, positioning the Renaissance as a continuation (with variations on the theme) of the Middle Ages, a smooth transition rather than a hard break. At the same time, knowledge of developments within the Middle Ages have made the image of one unbroken “Dark Age” untenable and made clear that the “upswing” of the early modern period was already well underway in the later Middle Ages and in turn had its roots stretching even deeper into the period. It is also worth noting here, that the term “Dark Age” has to do with the survival of evidence, not living conditions: the age was not dark because it was grim, it was dark because we cannot see it as clearly.
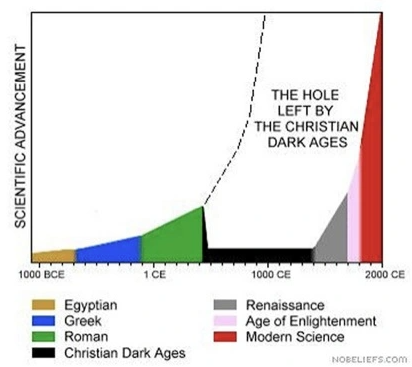
The popular version of this idea continues, however, to have a lot of sway in the popular conception of the Middle Ages, encouraged by popular culture that mistakes the excesses of the early modern period for “medieval” superstition and exaggerates the poverty of the medieval period (itself essentialized to its worst elements despite being approximately a millennia long), all summed up in this graph:
We are mostly going to just dunk relentlessly on this graph and yet we will not cover even half of the necessary dunking this graph demands. We may begin by noting that in its last century, the Roman Empire was Christian, a point apparently missed here.
While that sort of vision is not seriously debated by scholars, it needs to be addressed here too, in part because I suspect a lot of the energy behind the “change and continuity” position is in fact to counter some of the worst excesses of this thesis, which for simplicity, we’ll just refer to as “The Dung Ages” argument, but also because assessing how bad the fall of the Roman Empire in the West was demands that we consider how long-lasting any negative ramifications were.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Rome: Decline and Fall? Part I: Words”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-01-14.
December 2, 2022
QotD: Rome’s legions settle down to permanent fortresses
The end of the reign of Augustus (in 14AD) is a convenient marker for a shift in Roman strategic aims away from expansion and towards a “frontier maintenance”. The usual term for both the Roman frontier and the system of fortifications and garrisons which defended it is the limes (pronounced “lim-ees”), although this wasn’t the only word the Romans applied to it. I want to leave aside for a moment the endless, complex conversation about the degree to which the Romans can actually be said to have strategic aims, though for what it is worth I am one of those who contends that they did. We’re mostly interested here in Roman behavior on the frontiers, rather than their intent anyway.
What absolutely does begin happening during the reign of Augustus and subsequently is that the Roman legions, which had spent the previous three centuries on the move outside of Italy, begin to settle down more permanently on Rome’s new frontiers, particularly along the Rhine/Danube frontier facing Central and Eastern Europe and the Syrian frontier facing the Parthian Empire. That in turn meant that Roman legions (and their supporting auxiliary cohorts) now settled into permanent forts.
The forts themselves, at least in the first two centuries, provide a fairly remarkably example of institutional inertia. While legionary forts of this early period typically replaced the earthwork-and-stakes wall (the agger and vallum) with stone walls and towers and the tents of the camp with permanent barracks, the basic form of the fort: its playing-card shape, encircling defensive ditches (now very often two or three ditches in sequence) remain. Of particular note, these early imperial legionary forts generally still feature towers which do not project outward from the wall, a stone version of the observation towers of the old Roman marching camp. Precisely because these fortifications are in stone they are often very archaeologically visible and so we have a fairly good sense of Roman forts in this period. In short then, put in permanent positions, Roman armies first constructed permanent versions of their temporary marching camps.
And that broadly seems to fit with how the Romans expected to fight their wars on these frontiers. The general superiority of Roman arms in pitched battle (the fancy term here is “escalation dominance” – that escalating to large scale warfare favored the heavier Roman armies) meant that the Romans typically planned to meet enemy armies in battle, not sit back to withstand sieges (this was less true on Rome’s eastern frontier since the Parthians were peer competitors who could rumble with the Romans on more-or-less even terms; it is striking that the major centers in the East like Jerusalem or Antioch did not get rid of their city walls, whereas by contrast the breakdown of Roman order in the third century AD and subsequently leads to a flurry of wall-building in the west where it is clear many cities had neglected their defensive walls for quite a long time). Consequently, the legionary forts are more bases than fortresses and so their fortifications are still designed to resist sudden raids, not large-scale sieges.
They were also now designed to support much larger fortification systems, which now gives us a chance to talk about a different kind of fortification network: border walls. The most famous of these Roman walls of course is Hadrian’s Wall, a mostly (but not entirely) stone wall which cuts across northern England, built starting in 122. Hadrian’s Wall is unusual in being substantially made out of stone, but it was of-a-piece with various Roman frontier fortification systems. Crucially, the purpose of this wall (and this is a trait it shares with China’s Great Wall) was never to actually prevent movement over the border or to block large-scale assaults. Taking Hadrian’s wall, it was generally manned by something around three legions (notionally; often at least one of the legions in Britain was deployed further south); even with auxiliary troops nowhere near enough to actually manage a thick defense along the entire wall. Instead, the wall’s purpose is slowing down hostile groups and channeling non-hostile groups (merchants, migrants, traders, travelers) towards controlled points of entry (valuable especially because import/export taxes were a key source of state revenue), while also allowing the soldiers on the wall good observation positions to see these moving groups. You can tell the defense here wasn’t prohibitive in part because the main legionary fortresses aren’t generally on the wall, but rather further south, often substantially further south, which makes a lot of sense if the plan is to have enemies slowed (but not stopped) by the wall, while news of their approach outraces them to those legionary forts so that the legions can form up and meet those incursions in an open battle after they have breached the wall itself. Remember: the Romans expect (and get) a very, very high success rate in open battles, so it makes sense to try to force that kind of confrontation.
This emphasis on controlling and channeling, rather than prohibiting, entry is even more visible in the Roman frontier defenses in North Africa and on the Rhine/Danube frontier. In North Africa, the frontier defense system was structured around watch-posts and the fossatum Africae, a network of ditches (fossa) separating the province of Africa (mostly modern day Tunisia) from non-Roman territory to its south. It isn’t a single ditch, but rather a system of at least four major segments (and possibly more), with watch-towers and smaller forts in a line-of-sight network (so they can communicate); the ditch itself varies in width and depth but typically not much more than 6m wide and 3m deep. Such an obstruction is obviously not an prohibitive defense but the difficulty of crossing is going to tend to channel travelers and raids to the intentional crossings or alternately slow them down as they have to navigate the trench (a real problem here where raiders are likely to be mounted and so need to get their horses and/or camels across).
On the Rhine and the Danube, the defense of the limes, the Roman frontier, included a border wall (earthwork and wood, rather than stone like Hadrian’s wall), similarly supported by legions stationed to the rear, with road networks positioned; once again, the focus is on observing threats, slowing them down and channeling them so that the legions can engage them in the field. This is a system based around observe-channel-respond, rather than an effort to block advances completely.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part II: Romans Playing Cards”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-11-12.
November 24, 2022
QotD: Roman legionary fortified camps
The degree to which we should understand the Roman habit of constructing fortified marching camps every night as exceptional is actually itself an interesting question. Our sources disagree on the origins of the Roman fortified camp; Frontinus (Front. Strat 4.1.15) says that the Romans learned it from the Macedonians by way of Pyrrhus of Epirus but Plutarch (Plut. Pyrrhus 16.4) represents it the other way around; Livy, more reliable than either agrees with Frontinus that Pyrrhus is the origin point (Liv. 35.14.8) but also has Philip V, a capable Macedonian commander, stand in awe of Roman camps (Liv. 31.34.8). It’s clear there was something exceptional about the Roman camps because so many of our sources treat it as such (Liv. 31.34.8; Plb. 18.24; Josephus BJ 3.70-98). Certainly the Macedonians regularly fortified their camps (e.g. Plb. 18.24; Liv 32.5.11-13; Arr. Alex. 3.9.1, 4.29.1-3; Curtius 4.12.2-24, 5.5.1) though Carthaginian armies seem to have done this less often (e.g. Plb. 6.42.1-2 encamping on open ground is treated as a bold new strategy).
It is probably not the camps themselves, but their structure which was exceptional. Polybius claims Greeks “shirk the labor of entrenching” (Plb. 6.42.1-2) and notes that the stakes the Romans used to construct the wooden palisade wall of the camp are more densely placed and harder to remove (Plb. 18.18.5-18). The other clear difference Polybius notes is the order of Roman camps, that the Romans lay out their camp the same way wherever it is, whereas Greek and Macedonian practice was to conform the camp to the terrain (Plb. 6.42); the archaeology of Roman camps bears out the former whereas analysis of likely battlefield sites (like the Battle of the Aous) seem to bear out the latter.
In any case, the mostly standard layout of Roman marching camps (which in the event the Romans lay siege, become siege camps) enables us to talk about the Roman marching camp because as far as we can tell they were all quite similar (not merely because Polybius says this, but because the basic features of these camps really do seem to stay more or less constant.
The basic outline of the camp is a large rectangle with the corners rounded off, which has given the camps (and later forts derived from them) their nickname: “playing card” forts. The size and proportions of a fortified camp would depend on the number of legions, allies and auxiliaries present, from nearly square to having one side substantially longer than the other. This isn’t the place to get into the internal configuration of the camp, except to note that these camps seemed to have been standardized so that the layout was familiar to any soldier wherever they went, which must have aided in both building the camp (since issues of layout would become habit quickly) and packing it up again.
Now a fortified camp does not have the same defensive purpose as a walled city: the latter is intended to resist a siege, while a fortified camp is mostly intended to prevent an army from being surprised and to allow it the opportunity to either form for battle or safely refuse battle. That means the defenses are mostly about preventing stealthy approach, slowing down attackers and providing a modest advantage to defenders with a relative economy of cost and effort.
In the Roman case, for a completed defense, the outermost defense was the fossa or ditch; sources differ on the normal width and depth of the ditch (it must have differed based on local security conditions) but as a rule they were at least 3′ and 5′ wide and often significantly more than this (actual measured Roman defensive fossae are generally rather wider, typically with a 2:1 ratio of width to depth, as noted by Kate Gilliver. The earth excavated to make the fossa was then piled inside of it to make a raised earthwork rampart the Romans called the agger. Finally, on top of the agger, the Romans would place the valli (“stakes”) they carried to make the vallum. Vallum gives us our English word “wall” but more nearly means “palisade” or “rampart” (the Latin word for a stone wall is more often murus).
Polybius (18.18) notes that Greek camps often used stakes that hadn’t had the side branches removed and spaced them out a bit (perhaps a foot or so; too closely set for anyone to slip through); this sort of spaced out palisade is a common sort of anti-ambush defense and we know of similar village fortifications in pre- and early post-contact North America on the East coast, used to discourage raids. Obviously the downside is that when such stakes are spaced out, it only takes the removal of a few to generate a breach. The Roman vallum, by contrast, set the valli fixed close together with the branches interlaced and with the tips sharpened, making them difficult to climb or remove quickly.
The gateway obviously could not have the ditch cut across the entryway, so instead a second ditch, the titulum, was dug 60ft or so in front of the gate to prevent direct approach; the gate might also be reinforced with a secondary arc of earthworks, either internally or externally, called the clavicula; the goal of all of this extra protection was again not to prevent a determined attacker from reaching the gates, but rather to slow a surprise attack down to give the defender time to form up and respond.
And that’s what I want to highlight about the nature of the fortified Roman camp: this isn’t a defense meant to outlast a siege, but – as I hinted at last time – a defense meant to withstand a raid. At most a camp might need to withstand the enemy for a day or two, providing the army inside the opportunity to retreat during the night.
We actually have some evidence of similar sort of stake-wall protections in use on the East Coast of Native North America in the 16th century, which featured a circular stake wall with a “baffle gate” that prevented a direct approach and entrance. The warfare style of the region was heavily focused on raids rather than battles or sieges (though the former did happen) in what is sometimes termed the “cutting off way of war” (on this see W. Lee, “The Military Revolution of Native North America” in Empires and Indigines, ed. W. Lee (2011)). Interestingly, this form of Native American fortification seems to have been substantially disrupted by the arrival of steel axes for presumably exactly the reasons that Polybius discusses when thinking about Greek vs. Roman stake walls: pulling up a well-made (read: Roman) stake wall was quite difficult. However, with steel axes (imported from European traders), Native American raiding forces could quickly cut through a basic palisade. Interestingly, in the period that follows, Lee (op. cit.) notes a drift towards some of the same methods of fortification the Romans used: fortifications begin to square off, often combined a ditch with the palisade and eventually incorporated corner bastions projecting out of the wall (a feature Roman camps do not have, but later Roman forts eventually will, as we’ll see).
Roman field camps could be more elaborate than what I’ve described; camps often featured, for instance, observation towers. These would have been made of wood and seem to have chiefly been elevated posts for lookouts rather than firing positions, given that they sit behind the vallum rather than projecting out of it (meaning that it would be very difficult to shoot any enemy who actually made it to the vallum from the tower).
When a Roman army laid siege to a fortified settlement, the camp formed the “base” from which siege works were constructed (particularly circumvallation – making a wall around the enemy’s city to keep them in – and contravallation – making a wall around your siege position to keep other enemies out. We’ll discuss these terms in more depth a little later). Some of the most elaborate such works we have described are Caesar’s fortifications at the Siege of Alesia (52 BC; Caes. B.G. 7.72). There the Roman line consisted of an initial trench well beyond bow-shot range from his planned works in order to prevent the enemy from disrupting his soldiers with sudden attacks, then an agger and vallum constructed with a parapet to allow firing positions from atop the vallum, with observation towers every 80 feet and two ditches directly in front of the agger, making for three defensive ditches in total (be still Roel Konijnendijk‘s heart! – but seriously, the point he makes on those Insider “Expert Rates” videos about the importance of ditches are, as you can tell already, entirely accurate), which were reinforced with sharpened stakes faced outward. As Caesar expressly notes, these weren’t meant to be prohibitive defenses that would withstand any attack – wooden walls can be chopped or burned, after all – but rather to give him time to respond to any effort by the defenders to break out or by attackers to break in (he also contravallates, reproducing all of these defenses facing outward, as well).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part II: Romans Playing Cards”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-11-12.
November 17, 2022
QotD: The Dummies’ Guide to Meditations by Marcus Aurelius
Difficulty: Easy. You can beneficially read Meditations even if you know next to nothing. You’ll get more out of it the more you know, of course, but it’s the closest thing ancient philosophy had to a how-to manual.
Who: Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor in the mid-late 2nd century AD. The last of the “Five Good Emperors”, Marcus spent much of his time dealing with barbarian incursions and plague. There are some good biographies of the man, but Wiki covers the high points.
What: Because of the above, the Meditations were something like Marcus’s private self-help manual. He’s reminding himself to remain literally Stoic in the face of serious, seemingly unsolvable problems.
When: Late 2nd century AD. Greco-Roman philosophy was well-developed at this point; Stoicism was part of the classical tradition.
Where: In general, the European part of the Roman Empire. Specifically, on campaign against the barbarians – Marcus wrote a lot of the Meditations at the front.
Why: Because this man was the richest, most powerful individual in his world … and hated it. As a Stoic, he believed that virtue was its own — and, indeed, the only — reward, but as Roman Emperor he was forced to do un-virtuous things all day every day. It’s good instruction for how to live with yourself — how to be a man in a world that so often forces you to act like a snake.
Essential Background: Not much beyond the above.
Nice to have: The basics of Stoic doctrine. Specifically, their belief that “living virtuously” and “living according to nature” were basically synonymous, and that they were the only way to true happiness. A little Stoic epistemology, too — as their way of life depends on seeing the true nature of things, their standards for knowledge (what we’d call “justified true belief”) are extremely high. A statement like “pain is indifferent” is clear, and useful, on its own, but knowing the Stoic view of knowledge helps one appreciate just how prevalent the “indifferents” are, and how tough being truly indifferent is. Also nice to know: The wholesale adoption of Marcus by medieval Christians. There’s a very strong Stoic streak in Christianity’s first 1500 years; Marcus is always up there with the very best of the “virtuous pagans”.
None of these are necessary, though — you could lightly edit the Meditations (taking out the “thank you’s” at the start of Book One, explaining a few allusions) — and publish it today as a self-help manual. Also not necessary: Any real background in ancient philosophy. Back then, “philosophy” meant “a way of living”, not “a system for investigating the world”. Since Marcus is convinced of Stoicism’s truth, he doesn’t spend any time engaging the doctrines of other schools.
Severian, “Reading the Classics: An Illustration”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-02-14.
November 12, 2022
Long distance communication in the pre-modern era
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes considers why the telegraph took so long to be invented and describes some of the precursors that filled that niche over the centuries:
… I’ve also long wondered the same about telegraphs — not the electric ones, but all the other long-distance signalling systems that used mechanical arms, waved flags, and flashed lights, which suddenly only began to really take off in the eighteenth century, and especially in the 1790s.
What makes the non-electric telegraph all the more interesting is that in its most basic forms it actually was used all over the world since ancient times. Yet the more sophisticated versions kept on being invented and then forgotten. It’s an interesting case because it shows just how many of the budding systems of the 1790s really were long behind their time — many had actually already been invented before.
The oldest and most widely-used telegraph system for transmitting over very long distances was akin to Gondor’s lighting of the beacons, capable only of communicating a single, pre-agreed message (with flames often more visible at night, and smoke during the day). Such chains of beacons were known to the Mari kingdom of modern-day Syria in the eighteenth century BC, and to the Neo-Assyrian emperor Ashurbanipal in the seventh century BC. They feature in the Old Testament and the works of Herodotus, Aeschylus, and Thucydides, with archaeological finds hinting at even more. They remained popular well beyond the middle ages, for example being used in England in 1588 to warn of the arrival of the Spanish Armada. And they were seemingly invented independently all over the world. Throughout the sixteenth century, Spanish conquistadors again and again reported simple smoke signals being used by the peoples they invaded throughout the Americas.
But what we’re really interested in here are systems that could transmit more complex messages, some of which may have already been in use by as early as the fifth century BC. During the Peloponnesian War, a garrison at Plataea apparently managed to confuse the torch signals of the attacking Thebans by waving torches of their own — strongly suggesting that the Thebans were doing more than just sending single pre-agreed messages.
About a century later, Aeneas Tacticus also wrote of how ordinary fire signals could be augmented by using identical water clocks — essentially just pots with taps at the bottom — which would lose their water at the same rate and would have different messages assigned to different water levels. By waving torches to signal when to start and stop the water clocks (Ready? Yes. Now start … stop!), the communicator could choose from a variety of messages rather than being limited to one. A very similar system was reportedly used by the Carthaginians during their conquests of Sicily, to send messages all the way back to North Africa requesting different kinds of supplies and reinforcement, choosing from a range of predetermined signals like “transports”, “warships”, “money”.
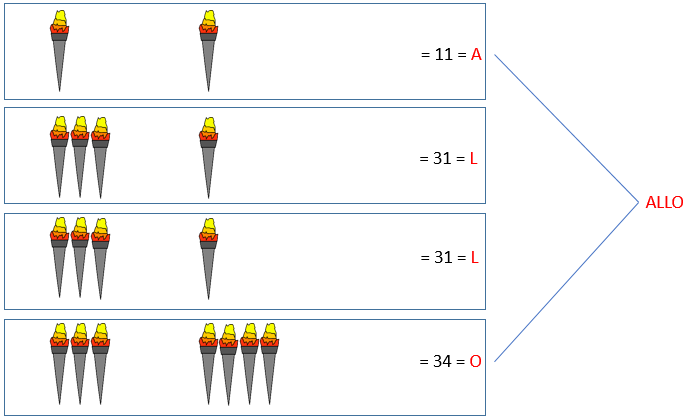
Diagram of a fire signal using the Polybius cipher.
Created by Jonathan Martineau via Wikimedia Commons.By the second century BC, a new method had appeared. We only know about it via Polybius, who claimed to have improved on an even older method that he attributed to a Cleoxenus and a Democleitus. The system that Polybius described allowed for the spelling out of more specific, detailed messages. It used ten torches, with five on the left and five on the right. The number of torches raised on the left indicated which row to consult on a pre-agreed tablet of letters, while the number of torches raised on the right indicated the column. The method used a lot of torches, which would have to be quite spread out to remain distinct over very long distances. So it must have been quite labour-intensive. But, crucially, it allowed for messages to be spelled out letter by letter, and quickly.
Three centuries later, the Romans were seemingly still using a much faster and simpler version of Polybius’s system, almost verging on a Morse-like code. The signalling area now had a left, right, and middle. But instead of signalling a letter by showing a certain number of torches in each field all at once, the senders waved the torches a certain number of times — up to eight times in each field, thereby dividing the alphabet into three chunks. One wave on the left thus signalled an A, twice on the left a B, once in the middle an I, twice in the middle a K, and so on.
By the height of the Roman Empire, fire signals had thus been adapted to rapidly transmit complex messages over long distances. But in the centuries that followed, these more sophisticated techniques seem to have disappeared. The technology appears to have regressed.
October 11, 2022
QotD: The debt we owe to the Carolingian Renaissance
The importance of the Carolingian Renaissance for text-preservation, by the by, is immediately relevant to anyone who has looked at almost any manuscript tradition: the absolute crushing ubiquity of Caroline minuscule, the standard writing form of the period, is just impossible to ignore (also, I love the heck out of Caroline minuscule because it is easy to both read and write – which is why it was so popular in this period; an unadorned, practical script – I love it; it’s the only medieval script I can write in with any meager proficiency). The sudden burst of book-copying tends to mean – for ancient works, at least, that if they survived to c. 830, then they probably survive to the present. Sponsored by Charlemagne and Louis the Pious, the scribes of the Carolingian period (mostly monks) rescued much of the Latin classical corpus we now have from oblivion. It is depressingly common to hear “hot-takes” or pop-culture references to how the “medievals” or the Church were supposedly responsible for destroying literature or ancient knowledge (this trope runs wild in Netflix’s recent Castlevania series, for instance) – the reverse is true. Without those 9th century monks, we’d probably have about as much Latin literature as we have Akkadian literature: not nothing, but far, far less. Say what you will about the medieval Church, you cannot blame the loss of the Greek or Roman tradition on them.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: A Trip Through Dhuoda of Uzès (Carolingian Values)”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-03-27.