On May 30th 1940, just after the war cabinet crisis & during the Dunkirk evacuation;
Winston Churchill was informed by the Canadian Prime Minister, Mackenzie King, of more dreadful news.
Roosevelt had no faith in Churchill nor Britain, and wanted Canada to give up on her.
Roosevelt thought that Britain would likely collapse, and Churchill could not be trusted to maintain her struggle.
Rather than appealing to Churchill’s pleas of aid — which were politically impossible then anyway — Roosevelt sought more drastic measures.
A delegation was summoned [from] Canada.
They requested Canada to pester Britain to have the Royal Navy sent across the Atlantic, before Britain’s seemingly-inevitable collapse.
Moreover, they wanted Canada to encourage the other British Dominions to get on board such a plan.
Mackenzie King was mortified. Writing in his diary,
“The United States was seeking to save itself at the expense of Britain. That it was an appeal to the selfishness of the Dominions at the expense of the British Isles. […] I instinctively revolted against such a thought. My reaction was that I would rather die than do aught to save ourselves or any part of this continent at the expense of Britain.”
On the 5th June 1940, Churchill wrote back to Mackenzie King,
“We must be careful not to let the Americans view too complacently prospect of a British collapse, out of which they would get the British Fleet and the guardianship of the British Empire, minus Great Britain. […]
Although President [Roosevelt] is our best friend, no practical help has been forthcoming from the United States as yet.”
Another example of the hell Churchill had to endure — which would have broken every lesser man.
Whilst the United States heroically came to aid Britain and her Empire, the initial relationship between the two great powers was different to what is commonly believed.
(The first key mover that swung Roosevelt into entrusting Churchill to continue the struggle — and as such aid would not be wasted on Britain — was when Churchill ordered the Royal Navy’s Force H to open fire and destroy the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kébir — after Admiral Gensoul had refused the very reasonable offers from Britain, despite Germany and Italy demanding the transference of the French Fleet as part of the armistices.)
Andreas Koreas, Twitter, 2024-12-27.
March 30, 2025
QotD: FDR, Mackenzie King and Churchill in 1940
March 19, 2025
The Korean War 039 – Kim Gets ROKrolled – March 18, 1951
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 18 Mar 2025Seoul falls to the South Koreans this week — the 4th time it’s changed hands since last June. There is no big celebration this time, though, since much of the city has been completely destroyed. This is just part of Operation Ripper, which advances all over to little enemy resistance, also taking the important town of Hongcheon.
Chapters
00:00 Intro
00:58 Recap
01:46 Soviet Intervention?
04:22 Operation Rugged
07:01 Task Force 77
09:36 South Korean Porters
11:02 MacArthur and McClellan
13:55 Summary
14:13 Conclusion
(more…)
March 18, 2025
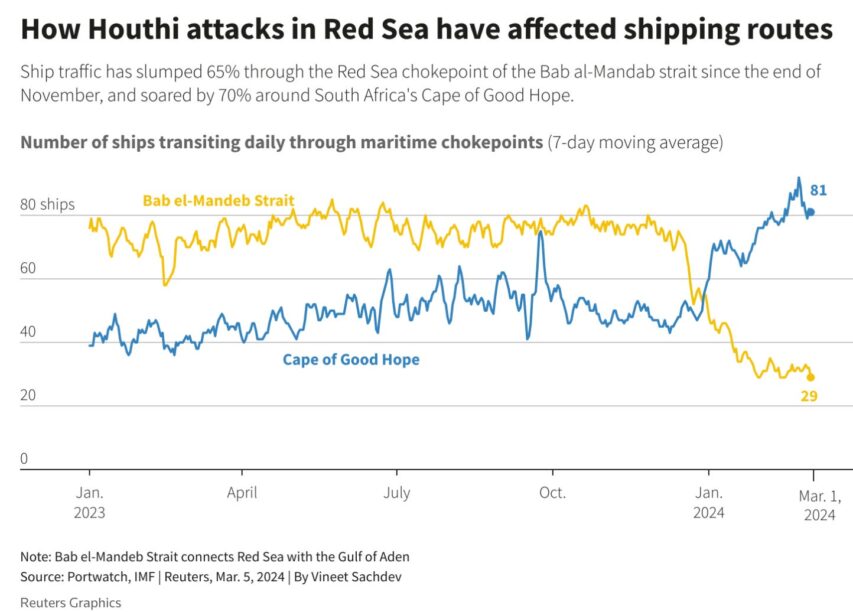
Getting rid of Houthi and the Blowfish
It has been alarming just how long the west — and especially the United States — have been willing to put up with Houthi attacks on shipping going through the Red Sea. President Trump has indicated that American patience has run out, as CDR Salamander discusses:

The Houthi Ansarullah “Al-Sarkha” banner. Arabic text:
الله أكبر (Allah is the greatest)
الموت لأمريكا (death to America)
الموت لإسرائيل (death to Israel)
اللعنة على اليهود (a curse upon the Jews)
النصر للإسلام (victory to Islam)
Image and explanatory text from Wikimedia Commons.
… in the almost 18 months since the Houthi rebels have been attacking Western shipping in the Red Sea, we have mostly been playing defense.
Why have we been playing defense? The Biden Administration, like the Obama Administration, was worm-ridden with Iranian accommodationalists. The Houthi, like Hamas and Hezbollah, are Iranian proxies.
After the murder, rape, slaughter, and kidnapping from Gaza into Israel on October 7th, 2023 by Iranian proxies, the Houthi started their campaign of support — as directed by Iran — by attacking shipping in the Red Sea.
It could not be ignored, but we never took the needed action. We did not even do half-measures. At best we did quarter-measures.
The attacks continued and our credibility on the world stage degraded in proportion to that.
As we have discussed often here, we have a few thousand years of dealing with piracy and bad-faith actors on the high seas. It has direct costs in commerce, treasure, and lives.
This cannot be allowed to continue.
Over the weekend, the new Trump Administration put down a marker. We seem to have ratcheted things up a bit. Not much available on open source, but over the weekend, CENTCOM put out a few things;
CENTCOM Forces Launch Large Scale Operation Against Iran-Backed Houthis in Yemen On March 15, U.S. Central Command initiated a series of operations consisting of precision strikes against Iran-backed Houthi targets across Yemen to defend American interests, deter enemies, and restore freedom of navigation.
[…]
Where is all this going? Well, let’s establish a few things first.
- Clearly what we were doing was not working.
- The Houthi are a 4th rate non-naval power. We like to tell everyone that, though we are the world’s second largest navy, we are the most capable. If we can’t keep the Houthi away from shipping through a major Sea Line of Communication, then why should anyone expect we could do more.
- Europe won’t/can’t help. They not only lack the capability to project power ashore against the Houthi to any reasonable measure, they lack the will.
- China does not care. It does not impact them. They benefit from this chaos against the West.
- Russia thinks this is wonderful.
- Iran can’t believe we are letting this go on. The Houthi are the last significant proxy, so they will do all they can to keep them going.
The lines are fairly clear right now. Not much room to maneuver. Looks like we will be at this for awhile. More extended range time.
March 13, 2025
Leadership of HMCS Harry DeWolf take a TOUR of HMCS Haida National Historic Site, Parks Canada
Royal Canadian Navy / Marine Royale Canadienne
Published 10 Nov 2024Canada’s “most fightingest ship” served in our Navy for 20 years between 1943 and 1963. The last Tribal Class Destroyer in the world, it and its company persevered through the Second World War, Korean War and Cold War.
The ceremonial flagship of our Navy, HMCS Haida was saved from the scrapyards and now rests in Hamilton as a museum ship, a Parks Canada National Historic Site.
One of HMCS Haida‘s Captains was the Naval hero Harry DeWolf — the namesake of the Harry DeWolf Class of ships. The grandson of a Veteran who served on the ship recently took the leadership of HMCS Harry DeWolf for a tour after arriving alongside, showing the stark differences between the newest vessels of our fleet and this vintage destroyer showing the many differences between life in the Navy then and now.
#CanadaRemembers #HelpLeadFight
March 6, 2025
HMCS Bonaventure – The Pride of Canada’s Fleet
Skynea History
Published 22 Oct 2024For today’s video, we’ll be looking at the last of Canada’s aircraft carriers. Not typically a navy you associate with that kind of ship, but the Canadians actually operated three during the Cold War.
The third, HMCS Bonaventure, is an interesting one. A small ship, that operated aircraft at the very edge of her capability. And routinely baffled American pilots in the process.
Yet, she was also a ship that came to an end before her time. Decommissioned and scrapped, right after an expensive (and extensive) mid-life overhaul. In what is generally seen as a bad political move, more than anything to do with her capabilities.
(more…)
March 4, 2025
FDR – behind closed doors – was as bad as Trump while the Dunkirk evacuation was going on
Winston Churchill became prime minister of Britain the same day the Germans launched their attack against France and the Low Countries in May, 1940. The situation went from bad to appalling in very short order as the vaunted French army’s high command crumbled under the stress (even if the soldiers fought bravely in most cases). The British Expeditionary Force retreated with the French mobile forces toward the English Channel, eventually evacuating as many troops as they could from the port of Dunkirk. During this time, Churchill was appealing to the American President Franklin D. Roosevelt for whatever aid he could send.
Postwar histories tended to portray FDR as both benevolent and helpful toward Churchill in this stressful period, but behind closed doors FDR was far less a future ally, as Andreas Koureas explained on Twitter:

More than a year after FDR’s attempt to pry Canada and the Royal Navy away from a “dying” Britain, he and Churchill met onboard HMS Prince of Wales, in Placentia Bay, Newfoundland, during the Atlantic Charter Conference. President Franklin D. Roosevelt (left) and Prime Minister Winston Churchill are seated in the foreground. Standing directly behind them are Admiral Ernest J. King, USN; General George C. Marshall, U.S. Army; General Sir John Dill, British Army; Admiral Harold R. Stark, USN; and Admiral Sir Dudley Pound, RN. At far left is Harry Hopkins, talking with W. Averell Harriman.
US Naval Historical Center Photograph #: NH 67209 via Wikimedia Commons.
Ironically, the truth is that in 1940, Roosevelt — behind closed doors — behaved worse than Trump.
On the 20th May 1940, after multiple failed pleas for aid, Churchill wrote to Roosevelt that:
“If members of the present administration were finished and others came in to parley amid the ruins, you must not be blind to the fact that the sole remaining bargaining counter with Germany would be the fleet, and if this country was left by the United States to its fate no one would have the right to blame those then responsible if they made the best terms they could for the surviving inhabitants. Excuse me, Mr. President, putting this nightmare bluntly.”
Roosevelt’s refusal for aid was understandable given the political situation in America. As he told Churchill earlier that month, it wasn’t “wise for that suggestion to be made to the Congress at this moment”.
However, what he did after the 20th May telegram wasn’t.
Not bothering to even reply to Churchill’s warnings, Roosevelt instead sought to get Canada to give up on Britain.
As Roosevelt thought that Britain would likely collapse, and Churchill could not be trusted to maintain the struggle, he summoned a delegation for Canada.
The aim was to get Canada to pester Britain to have the Royal Navy sent across the Atlantic, before Britain’s seemingly-inevitable collapse.
Furthermore, to ensure this, the Americans wanted Canada to encourage the other British Dominions to get on board such a plan, and likewise gang up against Britain.
You can see Mackenzie King’s (PM of Canada) disbelief and horror in his diary,
“The United States was seeking to save itself at the expense of Britain. That it was an appeal to the selfishness of the Dominions at the expense of the British Isles. […] I instinctively revolted against such a thought. My reaction was that I would rather die than do aught to save ourselves or any part of this continent at the expense of Britain.”
King telegrammed Churchill on the 30th May that this was the closed-door political situation across the Atlantic.
Bear in mind, Roosevelt was trying to instigate this during the Dunkirk evacuations.
How Churchill didn’t break knowing the one ally he needed in his darkest hour thought he’d fail, I have no idea.
On the 5th June 1940, Churchill wrote back to Mackenzie King,
“We must be careful not to let the Americans view too complacently prospect of a British collapse, out of which they would get the British Fleet and the guardianship of the British Empire, minus Great Britain. […] Although President [Roosevelt] is our best friend, no practical help has been forthcoming from the United States as yet.”
(The first key mover that swung Roosevelt into entrusting Churchill to continue the struggle — and as such aid would not be wasted on Britain — was when Churchill ordered the Royal Navy’s Force H to open fire and destroy the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kébir — after Admiral Gensoul had refused the very reasonable offers from Britain, despite Germany and Italy demanding the transference of the French Fleet as part of the armistices.)
February 23, 2025
Portuguese Navy Lugers: Model m/910 from DWM and Mauser
Forgotten Weapons
Published 2 Nov 2024Following Portuguese Army adoption in 1908, the Portuguese Navy adopted the Luger in 1909 as the m/910. The pattern they chose was a “new model” Luger in 9x19mm, with a 100mm / 4″ barrel. A total of 650 were ordered in late 1909 and delivered between 1910 and 1912. The guns had Portuguese-language safety and extractor markings (“Seguranca” and “Carregada“) and included grip safeties. They were in a dedicated serial number range of 1 to 650. The first 350 were delivered under the reign of Portuguese King Manuel II and had crown-over-anchor chamber crests. With the establishment of a Republic in Portugal, that marking was changed to “R.P.” over an anchor, which was used on the remaining guns (351-650).
In the mid 1930s, the Navy ordered another 156 m/910 Luger pistols, this time from the Mauser company. These had the same Portuguese markings, but without any special crest — just blank chambers. They were numbered in Mauser’s export/commercial serial number range, and are in the “v” block of numbers. A few more very small orders were placed in 1941 and 1942, but these were filled with basically straight German P08 pistols.
(more…)
February 17, 2025
QotD: Decisive factors in the Roman victory over the Seleucids
Zooming out even further, why Roman victory in the Roman-Seleucid War? I think there are a few clear factors here.
Ironically for a post covering land battles, the most important factor may be naval: Rome’s superior naval resources (and better naval allies), which gave the Romans an enormous operational advantage against Antiochus. In the initial phase, the Romans could get more troops to Greece than the king could, while further on, Roman naval supremacy allowed Roman armies to operate in Anatolia in force (while Antiochus, even had he won in Greece, had no hope of operating in Italy). Neutralizing Antiochus’ navy both opened up options for the Romans and closed down options for Antiochus, setting the conditions for Roman victory. It would have also neutered any Roman defeat. If Antiochus wins at Magnesia, he cannot then immediately go on the offensive, after all: he has merely bought perhaps a year or two of time to rebuild his navy and try to contest the Aegean again. Given the astounding naval mobilizations Rome had shown itself capable of in the third century, one cannot imagine Antiochus was likely to win that contest.
Meanwhile, the Romans had better allies, in part as a consequence of the Romans being better at getting allies. The Romans benefit substantially from allied Achaean, Pergamese and Rhodian ships and troops, as well as support from the now-humbled Philip V of Macedon and even supplies and auxiliaries from Numidia and Carthage. Alliance-management is a fairly consistent Roman strength and it shows here. It certainly seems to help that Roman protestations that they had little interest in a permanent presence in Greece seem to have been somewhat true; Rome won’t set up a permanent provincia in Macedonia until 146 (though the Romans do expect their influence to predominate before then). By contrast, Antiochus III, clearly bent on rebuilding Alexander’s empire, was a more obvious threat to the long-term independence and autonomy of Greek states like the Pergamum or Rhodes.
Finally, there is the remarkable Seleucid glass jaw. The Romans, after all, sustained a defeat very much like Magnesia against Hannibal in 216 (the Battle of Cannae) and kept fighting. By contrast, Antiochus is forced into a humiliating peace after Magnesia, in which he cedes all of Anatolia, gives up any kind of navy and is forced to pay a crippling financial indemnity which will fatally undermine the reign of his successor and son Seleucus IV (leading to his assassination in 175, leading to yet further Seleucid weakness). Part of this glass jaw may have been political: after Magnesia, Antiochus’ own aristocrats seem pretty well done with their king’s adventurism against Rome.
But at the same time, some of it was clearly military. Antiochus didn’t have a second army to fall back on and Magnesia represented essentially a peak “all-call” Seleucid mobilization. A similar defeat at Raphia had forced a similarly unfavorable peace earlier in his reign, after all. Part of the problem, I would argue, is that the Seleucids needed their army for more than just war: they needed it to enforce taxation and tribute on their own recalcitrant subjects. As a result, no Seleucid king could afford to “go for broke” the way the Roman Republic could, nor could the Seleucids ever fully mobilize the massive population of their realm. The very nature of the Hellenistic kingdom’s ethnic hierarchy made fully tapping the potential resources of the kingdom impossible.
As a result, while Antiochus III was not an incompetent general, he ruled a deceptively weak giant. Massive revenues were offset by equally massive security obligations and the Seleucids seem to have been perenially cash strapped (with a nasty habit of looting temples to make up for it). The very nature of the Seleucid Empire – like the Ptolemaic one – as an ethnic empire where Macedonians ruled and non-Macedonians were ruled kept Antiochus from being able to fully mobilize his subjects. It may also explain why so many of those light infantry auxiliaries seem to have run off without much of a fight. Eumenes and his Pergamese troops fought for their independence, the Romans for the greater glory of Rome and the socii for their own status and loot within the Roman system, but what could Antiochus offer a subjected Carian or Cilician except a paycheck and a future of continued subjugation? That’s not much to die for.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Phalanx’s Twilight, Legion’s Triumph, Part IVb: Antiochus III”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-04-05.
February 16, 2025
Bismarck’s Final Battle – The Bismarck Part 4
World War Two
Published 15 Feb 2025It is the end for the Bismarck; crippled by airstrikes, there is no hope of salvation. As the British battleships close in, Admiral Gunter Lutjens gives a final Sieg Heil, readies his guns, and prepares to meet his destiny.
(more…)
February 10, 2025
The Swordfish Strike! – The Bismarck Part 3
World War Two
Published 9 Feb 2025Reeling from the loss of HMS Hood, the Royal Navy chases Bismarck across the Atlantic Ocean. Battleships and search planes comb the vast expanses of water. Finally, they spot the German behemoth. It’s time to unleash the Swordfish!
(more…)
February 2, 2025
HMS Hood – Death in 17 Mins – The Bismarck Part 2
World War Two
Published 1 Feb 2025On May 24, 1941, the Kriegsmarine‘s mighty battleship Bismarck goes head to head with the Royal Navy’s HMS Hood. Seventeen minutes later, just one of the steel titans is left afloat and 1,400 men are dead.
Special thanks goes to the HMS Hood Association, to learn more about HMS hood visit hmshood.org.uk
(more…)
January 27, 2025
The Bismarck‘s First Adventure – The Bismarck Part 1
World War Two
Published 26 Jan 2025At 02:00 on May 19, 1941, Germany’s most powerful battleship ever sets sail. Bismarck will sail out into the North Atlantic, evade the Royal Navy and tear apart Britain’s Atlantic convoys. At least that’s the plan … pretty soon things start to go wrong.
(more…)
January 4, 2025
Winning WW2’s Most Important Battle – Battle of the Atlantic
Historigraph
Published 15 Aug 2024The Second World War featured many important land battles on a colossal scale. They involved hundreds of thousands of participants, ranged across hundreds of miles and inflicted the most terrible destruction. But none of them were as long-running, as vast or as crucial to allied victory as that fought at sea in the Atlantic, where for four years Allied navies and civilian sailors fought a life or death struggle against Germany’s U-boats. This is the story of how it was fought, and how it was won.
00:00 – WW2’s most important battle
00:45 – The U-boat menace in the early years
08:53 – The massacre off the eastern seaboard
13:12 – American ship printer go brrrrrrrrr
19:31 – The Allies gain the upper hand
21:49 – Black May: the convoy battles of 1943
24:41 – The most important victory of WW2
(more…)
December 16, 2024
The Price of Victory by N.A.M. Rodger
In The Critic, Phil Weir reviews the final volume in N.A.M. Rodger’s three-book study of the history of the Royal Navy:
This October a major scholarly achievement was realised with the publication of The Price of Victory, the third and final instalment of N.A.M. Rodger’s great trilogy on the naval history of Britain from 660 AD to 1945. It has been an odyssey, albeit one that to complete took more than three times longer than Homer’s hero took to journey home.
The first volume, Safeguard of the Sea, was published back in 1997, some six years after Rodger had left his job as Assistant Keeper of the Public Records at the then Public Records Office to join the National Maritime Museum. Having moved to Exeter University, he completed the second volume, Command of the Ocean, covering the period from 1649 to 1815, in 2004.
Mindful of the fates of others who have attempted grand, multi-volume naval histories of Britain, Nicholas Rodger, now aged 74, was known to quip that one of his key aims was to become the first historian to live to see it completed. What he describes as “an exciting episode of brain surgery” delayed the completion of the final volume for several years, and left achieving this a closer-run thing than was — one suspects — entirely comfortable.
To the immense relief of all, Rodger recovered to complete his great work, and it has, emphatically, been well worth the wait. The Price of Victory is, like its predecessors, a most substantial work in both physical and scholarly senses.
At the outset of his task, Rodger aimed to create “not a self-contained ‘company history’ of the Royal Navy, but a survey of the contribution which naval warfare with all its associated activities has made to national history”. In doing so, he sought to link naval warfare “to political, social, economic, diplomatic, administrative, agricultural, medical, religious and other histories which will never be complete until the naval component of them is understood”.
He has succeeded handsomely, firmly entwining naval and naval-related matters into the core fabric of the history of the British Isles. The Price of Victory is a worthy conclusion to an epic series that will both stand in its own right and, as he hopes, serve as a baseline for future scholarly endeavours.
The vast, polyglot erudition underpinning Rodger’s prose wears no disguise. Yet, for all its great length and the density of knowledge each page imparts, The Price of Victory is, like its two preceding volumes, a lively read, leavened with the author’s dry wit.
December 7, 2024
Aftermath: December 8
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 8 Dec 2021December 7, 1941 is remembered as the date that will live in infamy, but that term was spoken by President Franklin Roosevelt on December 8th. Nowhere was the weight of history more obvious than in the territory of Hawaii.
(more…)