Tsar Vlad launched his short, victorious war a full year ago, expecting to have the troops home by spring if not sooner. It hasn’t worked out to his timetable at all. Ukraine still stands, although it’s taken one hell of a battering in the process and drawn in more and more vocal support in the west, which has belatedly been followed by actual military supplies and equipment to replace those expended holding back the Russian forces. CDR Salamander follows up his predictions from last year on how things looked to him at that moment in time:
On the day the war started I made 7-points. Let’s review them and see how I did back on 24 FEB 22.
1. The remaining delusions about the post-Cold War security arrangements in Europe should be firmly buried. History is back and she has her Festivus pole front and center. She has some issues with us, and we’re going to hear about it.
This continues to get firmer and displayed in stark relief. All the “offsets” and “transformations” and “war is new” snake oil sold the last few decades really should not be allowed to have any public space besides to say, “I was wrong.” Rest assured, that won’t stop them — but the issues we raised over the almost 18-yrs of this blog and 14-yrs of the Midrats Podcast remain true. From the shallow magazines to the fact you never have enough large caliber guns to no war is short … we — and a lot of other people tut-tut’d for years — were correct.
2. NATO has a German problem. While all the “right people” will not shut up about how wonderful former Chancellor Angela Merkle was, people need to be very clear eyed about what a complete disaster she and the German political class have been over the last two decades. They have starved what should be continental European NATO’s most potent military into irrelevance. Her disastrous feel-good, ethno-masochistic immigration policy weakened European cohesion and fed the worst parts of European political subcultures. Yes, she made a lot of well meaning Germans feel good about themselves, but it was a sugar-high that rotted the teeth and poisoned the national metabolism. While willing to defend Europe to the last Pole and Germany to the last American, she decided to preen in her neo-pagan EuroGreen superiority onomastic politics by ditching clean nuclear power and through the complete corruption of her elite, shacked herself to Russian energy oligarchs and thus the Kremlin. Germany needs to fix herself, and NATO needs to work around her and punish her until she starts to behave like a constructive 21st Century security partner.
Germany has made great progress, but is being dragged kicking and screaming in to the 21st Century.
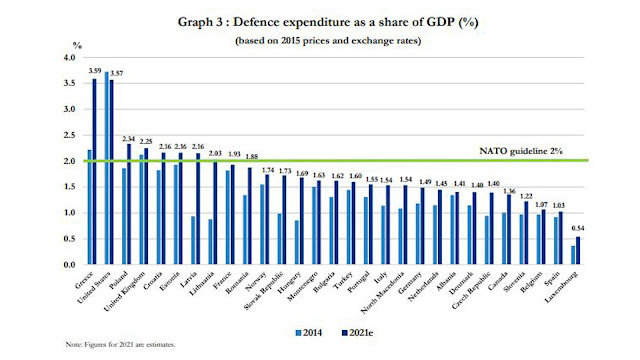
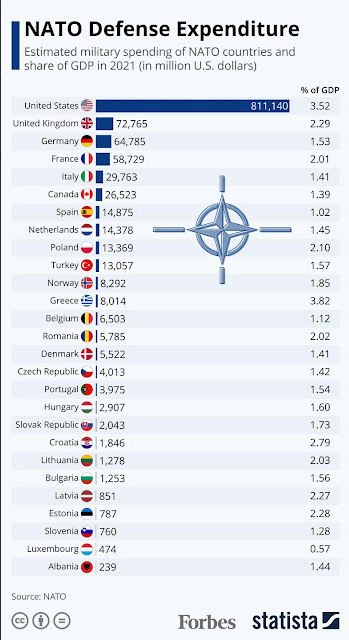
3. As our friend Jerry Hendrix pointed out yesterday, the moral leaders in NATO right now are the Baltic Republics and I would add Visegrad nations. You can throw Romania in there too. France will go hot and cold as she fights her desire to do the right thing for European security while at the same time nurse her 1,000 year old drive to be the premier leader of Western Europe. Serious but weaker nations will lean on a reluctant USA and limited United Kingdom … simply because — to be frank — much of the rest of the alliance is not that capable.
I think this graph tells that story well;
The front-line nations are putting their money where their existential threat is.
4. In line with #1 above, it is time for Finland at least, and probably Sweden, to join NATO. They both have a long and bloody history with the Russians and should see clearly what time it is.
Another check.
5. Ukraine waited too long to rearm. Weakened and distracted by a corrupt elite, the good parts of her nation could not get ready fast enough. After the first Russo-Ukraine war of 2014 she should have modeled the armed neutrality of Switzerland with a civilian populace trained and armed to the teeth. As we’ve discussed here before with the former Soviet republics and Warsaw Pact nations, every village needs a few ATGM militia teams trained to slow any advance through their patch of land. If Ukraine can, in whole or part, survive without vassalhood, perhaps they could get there. They can only get there if they build a nation people are willing to fight and die for.
Everyone is rediscovering the utility of a good military-industrial complex that can quickly grow to scale. Amazing what the green-eye-shade accounts forced those who actually are supposed to study war to believe.
A few days ago, Dominic Sandbrook explained that the Ukraine-Russia conflict “is not complicated”:
A year ago, as Vladimir Putin launched his so-called “special military operation” to seize the Ukrainian capital, kill Volodymyr Zelenskyy and wipe much of the latter’s country from the map of Europe, who’d have imagined that the third week of February 2023 would begin with Joe Biden strolling around the streets of Kyiv in sunglasses? For that matter, who would have predicted that Mr Zelenskyy, only recently returned from his own trip to London, would be at his side — still the president of a free country, and still very much alive?
Sometimes it’s nice to be wrong. Like many, probably most Western observers, I held out little hope for Ukraine once the drums of war began to beat in earnest. A couple of days after Mr Putin’s brutal invasion began, I wrote a bullish essay looking back at Ukraine’s history of suffering and resilience. But even as I was agonising over my prose, the bleak news continued to pour in. “Now, while I have been writing, Russian tanks are rolling into the suburbs,” I wrote at one stage. Did I think they would be driven back? I didn’t. “Kyiv will rise again,” I wrote at the end. Stirring words, or so I hoped. But the person I was really trying to persuade was myself, and I didn’t succeed.
In truth, I underestimated the Ukrainian people’s resilience, their courage, their love of country. And I was wrong, too, about the Western alliance. After more than a decade of drift and inaction, from the shameful failure to respond to the seizure of Crimea to the near-criminal indifference to the suffering in Syria, I doubted whether any major Western leader would make more than a token protest about the first full-scale European invasion since the Forties. I never expected to see Finland and Sweden jump off the fence and apply for Nato membership. Nor did I imagine that Joe Biden would be so unswerving in his commitment, or so generous with US military aid. Above all, I never anticipated that Kyiv would hold out, that Kharkiv would stand or that Kherson would be retaken. As I say, it’s nice to be wrong.
It’s often said that the war in Ukraine feels like a throwback, returning us to an age when nationalistic strongmen nursed atavistic dreams of conquest, sending thousands of men to die so that they might scratch new frontiers into the soil of Europe. For all the drones and social media gimmicks, the fighting certainly feels old-fashioned: reading David Patrikarakos’s harrowing dispatch from the front line in Bakhmut, it’s impossible not to think of Passchendaele or Verdun. But for a child of the Seventies, perhaps the most old-fashioned thing of all is the spectacle of a genuinely clear-cut conflict, an unambiguous clash of right and wrong, that feels closer in spirit to the struggle against Hitler’s Germany than to most of the wars in my lifetime.
Andrew Sullivan is convinced that the war is just, but worries whether it is prudent — and he calls it not Ukraine’s but “the West’s defensive war against Russia”:
It is right and just to defend a sovereign country from attack by a much larger neighbor; to fight back against an occupying force committing war crimes on a massive scale; to oppose the logic of dictatorships and defend the foundations of democracy; to uphold a post-Cold War international order which forbids the redrawing of borders by force; to unite democratic countries in Europe against a resurgence of imperial Russia; to defang and defeat a poisonous chauvinism that despises modern freedoms for women and gay people.
It is indeed right and just. But is it prudent?
That’s the question I’m still grappling with, in a week which saw the conflict deepen and the two sides entrench their positions further. President Biden’s trip to Kyiv and his speech in Poland have heightened the stakes, turning this into a more obvious proxy war between the United States and Russia … edging gingerly but relentlessly toward something more direct.
He’s all in now: declaring that Ukraine “must triumph” and that Russia cannot win a war that the Russian leader deems existential. NATO armaments are pouring into Ukraine at an accelerating rate. The training of Ukrainian troops is happening across the Continent. Germany is sending tanks. Pressure is building on Britain to send fighter jets.
The US is ratcheting up arms production as fast as it can, while seriously depleting our own Stinger surface-to-air missiles, 155mm howitzers and ammunition, and Javelin anti-tank missile systems. These are good times for arms producers:
The Army is planning a 500% increase in artillery shell production, from 15,000 a month to 70,000, according to Army acquisition chief Doug Bush … and intends to double the production of Javelin anti-tank missiles, make roughly 33% more Guided Multiple Launch Rocket Systems surface-to-surface medium-range missiles a year, and produce each month a minimum of 60 Stinger anti-aircraft missiles — which were “almost not in production at all”, according to Bush.
When Ukraine’s effective military is made up almost entirely of NATO equipment, and trained by NATO forces, there surely comes a point at which claiming NATO is not actually at war with Russia gets fuzzy.