World War Two and Spartacus Olsson
Published 21 Feb 2026In Q4 1933 Hitler pivots Nazi Germany from internal takeover to outward defiance. The London Economic Conference collapses and the tariff truce unravels, Hitler withdraws from the Disarmament Conference and the League of Nations — then stages the November 12 plebiscite and one‑party Reichstag election to claim the nation stands behind him. As Goebbels tightens propaganda and press control through the Editors’ Law (Schriftleitergesetz) and daily directives, the Winter Relief campaign turns “charity” into social pressure and Volksgemeinschaft theater. In December, Reichsbank president Hjalmar Schacht hardens the transfer moratorium to conserve foreign currency for raw materials and rearmament. Using contemporary voices, this episode shows how isolation, manipulation, and “unity” accelerate Europe toward a pre‑war era.
(more…)
February 22, 2026
How to Use a Tariff War to Disrupt the World – Death of Democracy 04 – Q4 1933
April 20, 2025
The formal end of the League of Nations, 18 April, 1946
Norman Stewart reposted the text of an article in the Louisville, Kentucky Courier-Journal of 19 April, 1946 to mark the demise of the League of Nations:

Building A of the Palace of Nations in Geneva, now an office of the United Nations.
Photo by Mourad Ben Abdallah via Wikimedia Commons.
League of Nations dies, willing its assets to U.N.
GENEVA (AP, April 18) – The League of Nations, created to preserve peace after a world cataclysm, expired tonight and willed to the United Nations its physical assets in the hope that the new organization might succeed where the League had failed.
It had lived 26 years.
Delegates from 34 nations, outnumbered by spectators in the galleries, witnessed the death of first major peace organization of the 20th century.
Quietly, the delegates answered “Yes” to a roll call on a motion providing that “with effect from the day following the close of the present session of the Assembly, the League of Nations shall cease to exist except for the sole purpose of the liquidation of its affairs”.
Last session ends
At 5:43 p.m., Carl J. Hambro of Norway, president of the Assembly, pounded his gavel and solemnly announced: “I declare the 21st and last session of the General Assembly of the League of Nations closed”.
Thus ended the life of the peace organization conceived largely by President Wilson, but never joined by the United States.
Its legal existence dated from the entry into force of the Treaty of Versailles on January 10, 1920.
The nostalgic formalities of terminating the League were interrupted only with a problem that is the heritage of the century’s second great peace effort – the United Nations.
Egyptian objects
Mahmoud Mohamed Aldarwiche, the Egyptian delegate, abstained from voting on a resolution that pointed out that present League members with mandated territories have declared they will continue to administer these countries as mandates until they are placed under trusteeship of the United Nations.
“It is the view of my government,” said Aldarwiche, “that mandates have terminated with the dissolution of the League of Nations, and that insofar as Palestine is concerned there should be no question of putting it under trusteeship.”
Egypt feels, he added, that Palestine has reached a stage “where it should no longer continue under mandate of trusteeship. Her development is not behind that of Syria, Lebanon, Iraq or Transjordan, who have won independence”.
Treaties turned over
Hambro told Aldarwiche the United Nations probably would discuss the matter in September.
One of the League’s final acts was to turn over to the United Nations thousands of treaty texts.
In physical assets the United Nations will inherit property valued at $11,700,000. These include the League palace, other real estate and the League’s stock of paper, furniture, typewriters and similar equipment.
The League confirmed Sean Lester of Ireland as secretary-general as from 1940 and Seymour Jacklin of South Africa as treasurer from 1944. They will continue to serve until the last of the League’s affairs are liquidated.
April 14, 2025
QotD: Pax Americana replaces Pax Britannica
Britain […] inherited responsibility for a century of the “Pax Britannica” by the simple expedient of being the strongest economy standing after the Napoleonic Wars. (The United States – the only potentially economically healthy rival post the devestation of Europe – having shot itself in the foot by joining in briefly on Napoleon’s “anti-British coalition” movement in 1812, and having its trade smashed and most of its ports and the capital reduced to smoking ruins as a result. Bad timing.)
The British government spent most of the next century being dragged – reluctantly – into being arbitrators of conflicts they wanted nothing to do with. Finishing with being stuck with the Great War, and then responsibility for some of the most hopeless basket-case states handed over to “Mandate Powers” by the Versailles peace … as one British minister presciently pointed out, no one wanted Palestine, and it would be nothing but a disaster for whoever gets stuck with it … (Fortunately for the US, their Congress repudiated Wilson’s ridiculous League of Nations before the plan to lumber the US with the Mandate for places like Georgia – the Russian bit on the Black Sea that is! – could be put through.)
It is unsurprising that the British taxpayer spent the next 50 years trying to get out of international police-keeping obligations. With the sole exception of reluctantly agreeing to fight against the expansionary dictatorships in World War Two, British taxpayers voted for disarmament and de-colonisation whenever they could. (Abandoning some states – particularly in Africa – that might eventually have developed into safe and secure states, way before they were ready for independence … much to the cost of world peace and security since …)
The United States has had a similar experience more recently. Having inherited responsibility for maybe 50 years of the “Pax Americana” by the simple expedient of being the strongest economy standing after the Second World War. (Their only potential rival being the British Commonwealth of Nations — who between them had 5 of the next 10 biggest and healthiest post-war economies — being more than happy to let the dumb Americans have a go at being world policemen for a time, and see how they liked being blamed by everyone else for absolutely everything.)
The Americans discovered pretty quickly that the things they had been complaining about the British doing for the last 200 years were exactly what they had now signed up for, and finding even quicker that their taxpayers simply weren’t willing to carry the can, and take the blame, for very long at all.
Arguably the US’s fun with being world policeman was already pretty much over after Korea, and certainly after Vietnam. It is notable that the first Gulf War was NOT paid for by the US taxpayer … the US troops turned up but only if Saudi Arabia and Europe paid for them to do so (and preferably with a British Division on one flank, Australian warships on the other, and NATO fighters overhead …) none of this “we will carry the can and our taxpayers will just cope” crap for post-Vietnam American taxpayers.
Nigel Davies, “Types of Empires: Security, Conquest, and Trade”, rethinking history, 2020-05-02.
April 8, 2025
The Broken Promise of Free Palestine – W2W 19 – 1948 Q1
TimeGhost History
Published 6 Apr 2025By 1948, Britain’s conflicting promises in Palestine have created a powder keg ready to explode. Contradictory pledges made to Arabs and Zionists during WWI set the stage for rising tensions, violent uprisings, and ultimately civil war. As Britain prepares to withdraw and the UN votes for partition, violence escalates, and the hope for a peaceful, free Palestine shatters into chaos. How did the broken promises lead to such tragedy?
(more…)
January 24, 2025
Was WW1 Pointless? – War Goals Of Every Major Nation
The Great War
Published 13 Sept 2024The First World War is often seen as futile and pointless. Millions of men fought and died for years, but no one was satisfied with the outcome, which did not bring a lasting peace. But that is not how governments and many people saw the war as it was being fought. So what did the countries fighting actually want to achieve? In other words, what was the purpose of the First World War?
(more…)
August 17, 2024
“The notion of a pre-existing Palestinian state is a modern fabrication that ignores the region’s actual history”
Debunking some of the common talking points about the Arab-Israeli conflicts down to the present day:
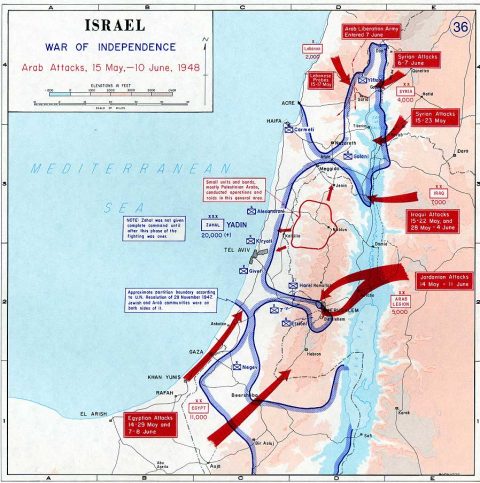
Arab attacks in May and June 1948.
United States Military Academy Atlas, Link.
Before Israel declared independence in 1948, the region now known as Israel, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip was part of the British Mandate for Palestine, which was established by the League of Nations after the fall of the Ottoman Empire in the First World War.
Under Ottoman rule, the area was divided into various administrative districts, with no distinct political entity known as “Palestine”. The concept of a Palestinian national identity emerged in the 20th century, largely in response to the Zionist movement and increased Jewish immigration in the area.
However, there was never a Palestinian state, flag or anthem. The notion of a pre-existing Palestinian state is a modern fabrication that ignores the region’s actual history.
The modern State of Israel’s legitimacy is rooted in international law and global recognition. On Nov. 29, 1947, the United Nations General Assembly passed Resolution 181, known as the “Partition Plan”, proposing two states — one Jewish and one Arab.
The Jewish community accepted the plan, demonstrating a willingness to compromise for peace. However, the Arab states rejected it, refusing to recognize any Jewish state, and instead launched a military assault on Israel following its declaration of independence on May 14, 1948.
Another pervasive myth is the “Nakba” or “catastrophe”, narrative, which claims that Palestinians were forcibly expelled by Israel in 1948. This version omits the critical context that it was the Arab nations that invaded Israel, causing many Arabs to be expelled or flee their homes.
Rather than absorbing the displaced population, the surrounding Arab countries kept them in refugee camps, using them as pawns to pressure Israel. Organizations like UNRWA perpetuated this situation, keeping Palestinians in limbo rather than encouraging their integration into their host countries. This contrasts sharply with how other refugee populations have been handled, where integration and resettlement are the norm.
The land referred to as “Palestine” has always been inherently Jewish. The Jewish people have maintained a continuous presence there for thousands of years, long before Islam or the Arab conquests.
May 9, 2024
How the First World War Created the Middle East Conflicts
The Great War
Published Dec 8, 2023The modern Middle East is a region troubled by war, terrorism, weak and failed states, and civil unrest. But how did it get this way? The map of today’s Middle East was mostly drawn after the First World War, and the war that planted many of the seeds of conflict that still plague Israel, Palestine, Iraq, Syria and even Iran today.
(more…)
April 16, 2024
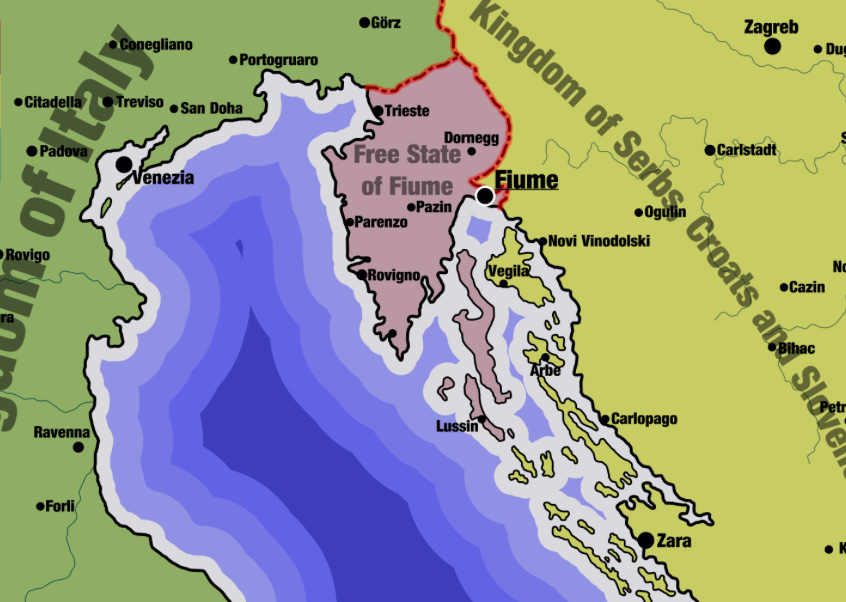
Gabriele D’Annunzio’s Impresa – the 1919 occupation of Fiume
Ned Donovan on the turbulent history of the Adriatic port of Fiume (today the Croatian city of Rijeka) after the end of the First World War:
Fiume was a port on the Adriatic coast with several thousand residents, almost half of whom were ethnic Italians that had been under Austro-Hungarian rule for several hundred years after it once having been a Venetian trade port. By some quirk, Fiume was missed in the Treaty of London, probably because it had never been envisioned by the Allies that the Austro-Hungarian Empire would ever truly disintegrate and the rump of it that would remain required a sea port in some form. The city’s other residents were ethnically Serbian and Croatian, who knew the city as Rijeka (as you will find it named on a map today). All of this complexity meant that the fate of Fiume became a major topic of controversy during the Versailles Peace Conference. President Woodrow Wilson had become so unsure of what to do that he proposed the place become a free city and the headquarters of the nascent League of Nations, under the jurisdiction of no country.
By September 1919 there was still no conclusion as to the fate of Fiume. Events had overtaken the place and through the Treaty of St Germain, the Austro-Hungarian Empire had been dissolved after the abdication of the final Habsburg Emperor Charles I. Once again, Fiume had not been mentioned in the treaty and the country it had been set aside for no longer existed. The city’s fate was still at play.
Enter Gabriele D’Annunzio, an aristocrat from Abruzzo on the eastern coast of Italy. Born in 1863, he was a handsome and intelligent child and was nurtured by his family to be exceptional, with a predictable side effect of immense selfishness. As a teenager, he had begun to dabble in poetry and it was praised by authors unaware of his age. At university he began to be associated with Italian irredentism, a philosophy that yearned for all ethnic Italians to live in one country – by retaking places under foreign rule like Corsica, Malta, Dalmatia and even Nice.
[…]
The Italian government’s lack of interest [in Fiume] was unacceptable to D’Annunzio and he made clear he would take action to prevent it becoming part of Yugoslavia by default. With his fame and pedigree he was able to quickly assemble a small private force of ex-soldiers, who he quickly took to calling his “legionaries”. In September 1919 after the Treaty of St Germain was signed, his small legion of a few hundred marched from near Venice to Fiume in what they called the Impresa – the Enterprise. By the time he had reached Fiume, the “army” numbered in the thousands, the vanguard crying “Fiume or Death” with D’Annunzio at its head in a red Fiat.
The only thing that stood in his way was the garrison of the Entente, soldiers who had been given orders to prevent D’Annunzio’s invasion by any means necessary. But amongst the garrison’s leaders were many [Italian officers] sympathetic to D’Annunzio’s vision, some even artists themselves and before long most of the defenders had deserted to join the poet’s army. On the 12th September 1919, Gabriele D’Annunzio proclaimed that he had annexed Fiume to the Kingdom of Italy as the “Regency of Carnaro” – of which he was the Regent. The Italian government was thoroughly unimpressed and refused to recognise their newest purported land, demanding the plotters give up. Instead, D’Annunzio took matters into his own hands and set up a government and designed a flag (to the right).
The citizens of what had been a relatively unimportant port quickly found themselves in the midst of one of the 20th Century’s strangest experiments. D’Annunzio instituted a constitution that combined cutting-edge philosophical ideas of the time with a curious government structure that saw the country divided into nine corporations to represent key planks of industry like seafarers, lawyers, civil servants, and farmers. There was a 10th corporation that existed only symbolically and represented who D’Annunzio called the “Supermen” and was reserved largely for him and his fellow poets.
These corporations selected members for a state council, which was joined by “The Council of the Best” and made up of local councillors elected under universal suffrage. Together these institutions were instructed to carry out a radical agenda that sought an ideal society of industry and creativity. From all over the world, famous intellectuals and oddities migrated to Fiume. One of D’Annunzio’s closest advisers was the Italian pilot Guido Keller, who was named the new country’s first “Secretary of Action” – the first action he took was to institute nationwide yoga classes which he sometimes led in the nude and encouraged all to join. When not teaching yoga, Keller would often sleep in a tree in Fiume with his semi-tame pet eagle and at least one romantic partner.
If citizens weren’t interested in yoga, they could take up karate taught by the Japanese poet Harukichi Shimoi, who had translated Dante’s works into Japanese. Shimoi, who quickly became known to the government of Fiume as “Comrade Samurai” was a keen believer in Fiume’s vision and saw it as the closest the modern world had come to putting into practice the old Japanese art of Bushido.
The whole thing would have felt like a fever dream to an outsider. If a tourist was to visit the city, they would have found foreign spies from across the world checking into hotels and rubbing shoulders with members of the Irish republican movement while others did copious amounts of cocaine, another national pastime in Fiume. The most fashionable residents of Fiume carried little gold containers of the powder, and D’Annunzio himself was said to have a voracious habit for it. Sex was everywhere one turned and the city had seen a huge inward migration of prostitutes and pimps within days of D’Annunzio’s arrival. Almost every day was a festival, and it was an odd evening if the harbour of Fiume did not see dozens of fireworks burst above it, watched on by D’Annunzio’s uniformed paramilitaries.
D’Annunzio himself lived in a palace overlooking the city, Osbert Sitwell describes walking up a steep hill to a Renaissance-style square palazzo which inside was filled with plaster flowerpots the poet had installed and planted with palms and cacti. D’Annunzio would cloister himself in his rooms for 18 hours a day and without food. Immaculate guards hid amongst the shrubs to ensure he would not be disturbed. In D’Annunzio’s study, facing the sea, he sat with statutes of saints and with French windows onto the state balcony. When he wanted to interact with his people he would wait for a crowd to form over some issue, walk to the balcony and then ask what they wanted.
June 28, 2023
The Treaty of Versailles: 100 Years Later
Gresham College
Published 4 Jun 2019The Treaty of Versailles was signed in June 1919. Did the treaty lead to the outbreak of World War II? Was the attempt to creat a new world order a failure?
A lecture by Margaret MacMillan, University of Toronto
04 June 2019 6pm (UK time)
https://www.gresham.ac.uk/lectures-an…A century has passed since the Treaty of Versailles was signed on 28 June 1919. After WWI the treaty imposed peace terms which have remained the subject of controversy ever since. It also attempted to set up a new international order to ensure that there would never again be such a destructive war as that of 1914-18. Professor MacMillan, a specialist in British imperial history and the international history of the 19th and 20th centuries, will consider if the treaty led to the outbreak of the Second World War and whether the attempt to create a new world order was a failure.
(more…)
November 13, 2021
Creation of Israel
The Cold War
Published 1 Jun 2019Our series on the history of the Cold War period continues with a documentary on the creation of Israel, Zionist movement, reactions and diplomatic maneuvers of other states and the build-up to first Arab-Israeli war
Consider supporting us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thecoldwar
October 29, 2021
QotD: Another proof of Parkinson’s “Law of the Custom-Built Headquarters Building”
The organisation [the League of Nations] lingered on and, with a final irony, it was now that it assumed the outward shape that is generally associated with it. The Palace of Nations [Wiki], begun in 1929, was finished in 1936, just in time to become a mausoleum. Here at last were the necessary offices, 700 of them, and the fitting conference rooms for the words that no longer meant anything. There was a floor of Finnish granite, walls and pillars faced with Swedish marble, enigmatic and forbidding murals, depicting Technical Progress, Medical Progress, Social Progress, the Abolition of War, and so on, by the Catalan artist Jose Maria Sert. Under their sombre painted sermons, the Assemblies still met and passed their resolutions; everyone was still very busy. But underneath it all the mainspring was broken.
John Terraine, The Mighty Continent, 1974, quoted by Brian Micklethwait, 2021-07-20.
September 2, 2021
Road to WWII: A Basic Causal Analysis
Thersites the Historian
Published 19 Nov 2019This video is a primer for undergraduates in broad history survey courses that will hopefully help make sense of the interwar years between World War I and World War II.
Patreon link: https://www.patreon.com/thersites
PayPal link: paypal.me/thersites
Twitter link: https://twitter.com/ThersitesAthens
Minds.com link: https://www.minds.com/ThersitestheHis…
Steemit/dtube link: https://steemit.com/@thersites/feed
BitChute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/jbyg…
Backup Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUrD…
August 22, 2021
QotD: Woodrow Wilson, wrong on many things, but quite right on this one thing
Woodrow Wilson was wrong about many things, but he was a veritable hedgehog about One Big Thing: the principle of national self-determination. When it came to his dream of the League of Nations, Wilson was a utopian romantic; but on the question of how to draw national political boundaries, he was a Founding Father of what may be called National Realism.
National Realism comprehends and respects the perhaps tragic, but nevertheless undeniable, fact that most people are deeply attached to collective identities and aspirations. It accepts as both natural and important that psychological well-being would be rooted in a terroir, a set of traditions or other mythologies about who people are and where they come from, that can serve as a source of meaning and self-understanding, as well as social cohesion. It acknowledges that nationalism is a fixture of modern social and political reality.
The idea that a self-described people should have the right to determine its own collective destiny was once considered progressive. Nineteenth-century liberal nationalists like Giuseppe Mazzini in Italy and Ernest Renan in France saw in the nation-state the fullest political expression of peoplehood, a true source of law and legitimacy, a celebration of diversity, and a font of culture, art, and human flourishing. The idea of national self-determination also resonated with the American Founding and with the Declaration of Independence, which proclaimed that governments derive their powers from the consent of the governed and found in Natural Law the right for one people to “dissolve the political bands which have connected it with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature’s God entitle them.” For good or ill, the French Revolution had awakened modern ethnic self-awareness among European peoples, and ever since, nationalism has been the most robust political force in international affairs. Nationalism is a property of modern nation states, the same way that gravity is a property of physical matter. It is unwise to underestimate its power.
Diversity is now, supposedly, the primus inter pares of our political values. But ethnic and racial diversity, in all its colorful pageantry, is traditionally associated with empires, not republics. Diversity brings to mind Barbara Tuchman’s description of Queen Victoria’s Diamond Jubilee, with its splendid processions of Royal Nigerian Constabulary, Borneo Dyak Police, turbaned and bearded Lancers of Khapurthala and Badnagar, Zaptichs from Cyprus with their tasseled fezzes and black-maned ponies, Houssas from the Gold Coast, Chinese from Hong Kong, and Malays from Singapore, all paying homage to the great monarch. Imperial Rome was an equally spectacular kaleidoscope of nations and religions. By contrast, republican Rome was merely, austerely, Roman.
As a good Progressive, Wilson understood that modern democratic government is incompatible with multi-ethnic empire. But it took the cataclysmic breakdown of the Old World empires in the meat-grinder of World War I to bring the idea of national self-determination into political focus. It would be wise to remember that that civilization-shattering conflict was blamed in large part on the lack of congruence between state and ethnic boundaries. Most of Wilson’s famous Fourteen Points, outlined 101 years ago this month, were dedicated to correcting this discrepancy on the basis of national self-determination.
E.M. Oblomov, “The Case for National Realism: Diversity is the hallmark of empires, not democracies”, City Journal, 2019-01-02.
July 1, 2021
Woodrow Wilson, Isolationism, and the Birth of the Charleston | B2W:ZEITGEIST! I E.20 Harvest 1923
TimeGhost History
Published 30 Jun 2021Wilson won the Nobel Peace Prize for crafting the League of Nations at Versailles, but even he couldn’t bring America out of its isolationism. This season he pours out his disappointment in his first-ever radio address. Optimism still reigns in the world of popular culture though, this season the Charleston is born.
(more…)
June 24, 2021
First Arab-Israeli War 1948 – Political Background – COLD WAR
The Cold War
Published 31 Aug 2019Our series on the history of the Cold War period continues with a documentary explaining the political background of the First Arab-Israeli War of 1948.
To learn about the military events of this conflict, go to the Kings and Generals channel
Consider supporting us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thecoldwar