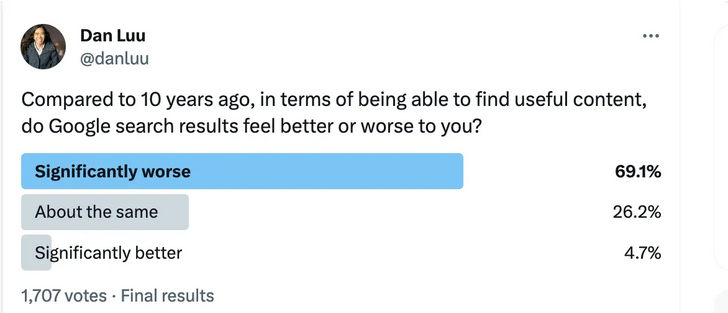
Ted Gioia used to be a techno-optimist, eagerly looking forward to ever-improving online experiences. He, like so many of us, has reluctantly come to the conclusion that those hopes are fading out of sight:
I once loved new technology. I lived in the heart of Silicon Valley for 25 years, and was bursting with enthusiasm for its free-wheeling mission to transform the world — and have some fun along the way.
When the Worldwide Web made its debut, I thought I’d found Nirvana. It was like tech was turning everything into a game.
But look at me now. When I hear the phrase “web platform” I reach for my gun.
Where did it go wrong? Did I just get old and embittered? Or did something change in the tech world?
Let me share a story that might help us decide.
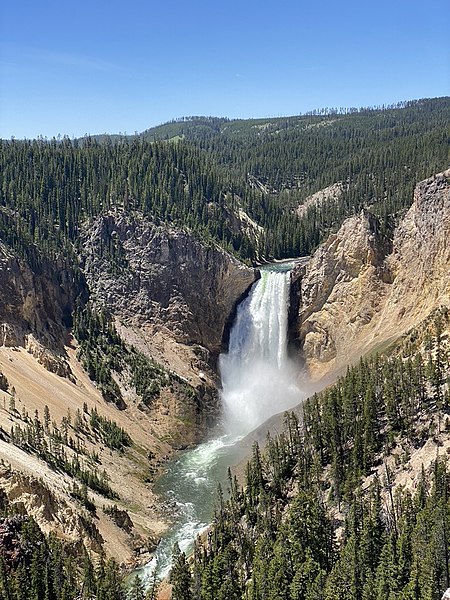
This is a story about the birth of the search engine.
There were no commercial search engines back in 1993. But a Stanford student named David Filo compiled a list of his 200 favorite websites.
His buddy Jerry Yang helped turn this into an online list. They called it “Jerry’s Guide to the Worldwide Web”. Filo and Yang added new websites every day to their list — and classified them according to categories.
This turned into Yahoo.
Here’s my favorite part of the story: These two students didn’t even know they were running a business.
They did it for fun. They did it out of love. They did it because it was cool. “We wanted to avoid doing our dissertations”, Yang later explained.
But a venture capitalist named Mike Moritz heard about Filo and Yang, and tracked them down. The founders of Yahoo were living in total squalor in a trailer littered with stale food and pizza boxes, strewed alongside sleeping bags and overheating computers. A phone rang constantly — but nobody bothered to pick it up.
Moritz was dismayed by this dorm-room-gone-wild ambiance, but he was impressed with the students’ web searching technology. So he asked them the obvious question: How much did they plan to charge users?
Filo and Yang had no answer for this. They wanted to give their tech away for free.
Yahoo wasn’t even selling ads back then. It wasn’t tracking users and selling their private information. It didn’t even have a bank account.
But it was a community and had millions of users.
That was a word you heard frequently in Silicon Valley in the early days. People didn’t build web platforms — they formed online communities.
It was a FUN community. People enjoyed being a member. Even the absurd name Yahoo was part of the game — although early investors hated it.
Yang’s job title was “Chief Yahoo”. Filo’s position was “Cheap Yahoo”.
Investors always hate those kinds of things.
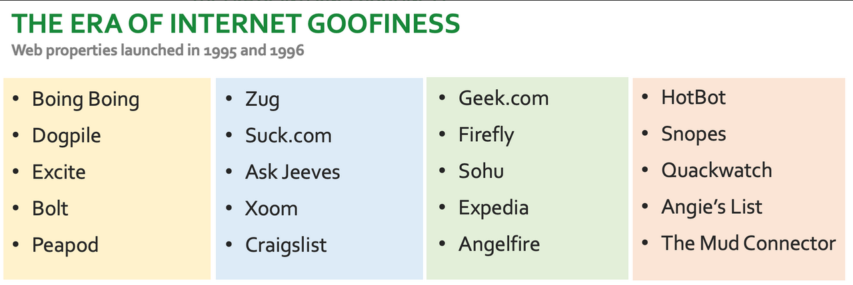
But a new web business, back then, was expected to have a silly name. Here are some of the websites launched in the mid-1990s.
Moritz wanted to turn Yahoo into a business. And the founders realized that their fun community was growing faster than they could handle in their down-and-out trailer. So they sold out 25% of Yahoo for $1 million.