The extent of active disinterest to ongoing criminal activity in British towns and cities over a period of several years passes belief. The fear of being accused of racism metastasized to the extent that the authorities may even have colluded with criminals to hide the crimes to preserve politicians’ and senior bureaucrats’ careers. It’s now broken through the conspiracy of silence to being actively discussed in British media and even on the floor of the House of Commons. Even the Prime Minister may have to answer for past actions (or inactions):
It’s very easy to judge the past, particularly when you’re on the “right side of history”. What supreme confidence it must take to assume that all previous generations had got it so wrong, and that humanity was simply waiting for you to turn up and set them straight.
And yet isn’t it curious that so many who like to judge the values and behaviour of people in the past are also rarely willing to turn that critical eye on other cultures that exist today? According to the principle of cultural relativism, all societies and ways of life are equal. So we must not assert that we are morally better to a culture that permits the genital mutilation of children or that denies women an education, but we may assume that we are highly superior to the Ancient Greeks.
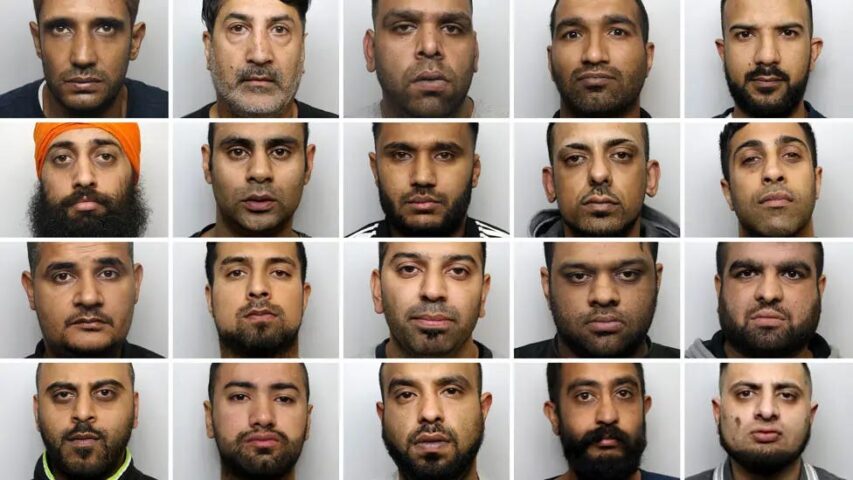
This debate has become particularly relevant with the recent explosion of interest in the rape gangs scandal. A report by Professor Alexis Jay in 2022 determined that more than 1,400 young girls were raped and abused in the period between 1997 and 2013 by what became known as the “grooming gangs”, so called because of the manipulative tactics that were employed to gain the victims’ trust. These groups comprised mostly of men of Pakistani heritage, which led many authorities to overlook the severity of the crimes.
Consider this example from a speech delivered by Andrew Norfolk, reporter for the Times. When police discovered a 13-year-old girl, drunk and mostly naked in the company of seven Pakistani men, they arrested her and failed to question any of the adults.
Police have admitted that such failures to investigate were largely down to a desire to avoid allegations of racism. The Jay report noted that several members of local council staff “described their nervousness about identifying the ethnic origins of perpetrators for fear of being thought as racist; others remembered clear direction from their managers not to do so”. Politicians and media commentators were more concerned with maintaining the fantasy that multiculturalism has been a success, rather than taking seriously their obligation to safeguard children. When Julie Bindel — the first journalist to investigate the grooming gangs — tried to publish her findings, she faced resistance ‘because some editors feared an accusation of racism’.
The Labour government has shown itself incapable of making amends. Jess Phillips has rejected a request for a public inquiry into child sexual exploitation in Oldham. And Keir Starmer has stated that anyone interested in a full-scale inquiry into these failings is jumping “on a bandwagon of the far right”.
This acute form of tone-deafness would, in any sound political climate, be cause for immediate resignation. While it is true that racists will be quick to weaponise the criminal behaviour of a minority, there is nothing remotely “far right” in taking an interest in the wellbeing of children and wishing to see those who abuse them held to account. But Starmer is a banshee of a prime minister; he makes a terrible noise but is completely lacking in substance.
Something may change with the release this week of crime league tables according to nationality. Up until now, there has been tremendous political resistance to releasing such statistics, with police in many European countries not recording such details at all in order to preserve the daydream of multiculturalism. And yet those that do keep such records have revealed a clear trend. Data from the Danish government, for instance, has shown that although non-Western immigrants constitute only 9% of the population, they account for 25% of convictions for violent crime. According to the Telegraph, in Sweden immigrants are “three times more likely to be registered as a suspect for assault than the native population – which grows to four times for robbery, and five times for rape”.
By happenstance, I posted this to social media the other day, which seems apposite: