The values composing civilization and the values required to protect it are normally at war. Civilization values sophistication, but in an armed force sophistication is a millstone.
The Athenian commanders before Salamis, it is reported, talked of art and of the Acropolis, in sight of the Persian fleet. Beside their own campfires, the Greek hoplites chewed garlic and joked about girls.
Without its tough spearmen, Hellenic culture would have had nothing to give the world. It would not have lasted long enough. When Greek culture became so sophisticated that its common men would no longer fight to the death, as at Thermopylae, but became devious and clever, a horde of Roman farm boys overran them.
The time came when the descendants of Macedonians who had slaughtered Asians till they could no longer lift their arms went pale and sick at the sight of the havoc wrought by the Roman gladius Hispanicus as it carved its way toward Hellas.
The Eighth Army, put to the fire and blooded, rose from its own ashes in a killing mood. They went north, and as they went they destroyed Chinese and what was left of the towns and cities of Korea. They did not grow sick at the sight of blood.
By 7 March they stood on the Han. They went through Seoul, and reduced it block by block. When they were finished, the massive railway station had no roof, and thousands of buildings were pocked by tank fire. Of Seoul’s original more than a million souls, less than two hundred thousand still lived in the ruins. In many of the lesser cities of Korea, built of wood and wattle, only the foundation, and the vault, of the old Japanese bank remained.
The people of Chosun, not Americans or Chinese, continued to lose the war.
At the end of March the Eighth Army was across the parallel.
General Ridgway wrote, “The American flag never flew over a prouder, tougher, more spirited and more competent fighting force than was Eighth Army as it drove north …”
Ridgway had no great interest in real estate. He did not strike for cities and towns, but to kill Chinese. The Eighth Army killed them, by the thousands, as its infantry drove them from the hills and as its air caught them fleeing in the valleys.
By April 1951, the Eighth Army had again proved Erwin Rommel’s assertion that American troops knew less but learned faster than any fighting men he had opposed. The Chinese seemed not to learn at all, as they repeated Chipyong-ni again and again.
Americans had learned, and learned well. The tragedy of American arms, however, is that having an imperfect sense of history Americans sometimes forget as quickly as they learn.
T.R. Fehrenbach, This Kind of War: A Study in Unpreparedness, 1963.
February 11, 2024
QotD: Learning and re-learning the bloody art of war
February 10, 2024
QotD: When Manchuria became Manchukuo
Back around the turn of the 20th century, the Russians decided to build a railroad across Siberia, the better to (among other things) supply their spiffy new naval base at Port Arthur, on the strategic Liaodong Peninsula (linking up with their Chinese Eastern Railway). This pissed off the Japanese, who claimed the Peninsula by right of conquest in the First Sino-Japanese War. Unpleasantness ensued.
Further unpleasantness ensued in the wake of World War I, when both Imperial Russia and Republican China collapsed. The Japanese had a big railroad project of their own going in the Kwantung Leased Territory, which was threatened by the chaos. Moreover, the big Japanese railroad project had grown — as Japanese industrial concerns tend to do — into a ginormous, all-encompassing combine known as Mantetsu.
So far, so recondite, I suppose, but stop me if this part sounds familiar: Mantetsu was so big, and so shady, that it was all but impossible to tell where “the guys running Mantetsu” ended and “the Japanese government” began. And it gets better: Thanks to the Japanese Empire’s distinctive (to put it mildly, and kindly) administrative structure, it was equally hard to tell where “the Japanese government” ended and “the Japanese military” began. Even better — by which I mean much, much worse, but again feel free to stop me when this sounds familiar — “the Japanese military” was itself composed of several wildly different, mutually hostile chains of command, all competing with each other for political power, economic access, and glory. Best of all — by which, again, I mean worst — since Mantetsu was so big, and so wired-in to every level of the Japanese government, it basically got its own army, which was effectively separate even from the Army High Command back in Tokyo.
Here again, the granular details are insanely complex, and I’m not qualified to walk you through them, but the upshot is: Thanks to all of the above, plus the active enmity of the rapidly-rearming Soviet Union and the rapidly-accelerating chaos of the Warlord Period in China, Japan’s foreign policy ended up being dictated by the Kwantung Army, with almost no reference to even the High Command, let alone the civilian politicians, back in Tokyo. A particular warlord giving the Mantetsu Board of Directors — or, you know, whoever — grief? No problem — boom! Oh, that didn’t solve the problem, and now the politicians are dragging their feet? Might as well blow up a different part of your own railway, seize a whole bunch of territory on that flimsy pretext, and set up a puppet government to give you cover …
I don’t expect y’all to follow all the links right away, so trust me on this: Nobody involved in any of that stuff ranked higher than colonel. Indeed, the guy most “responsible” — if that’s really the word — for all of this stuff was a staff pogue, also a colonel, named Kanji Ishiwara. He and another staff pogue, Seishiro Itagaki, who was head of the Kwantung Army’s intelligence section, orchestrated the Japanese invasion of China, and while it’s oversimplifying things a bit too much to say those two clowns started World War II in the Pacific, I’m not stopping you from saying it.
From there, events took on a logic of their own. The rest of the Army was soon committed to the war in North China, which rapidly became the war in all the rest of China. The Navy, not wanting to let the Army hog all the glory, had gotten in on the war a few years prior to the Marco Polo Bridge, and soon enough they were causing all kinds of international grief on their own account. Put simply, but not unfairly, you had the Navy chasing the Army, and the Army chasing itself, all across China, with the civilian politicians lagging way behind in the rear, desperately trying to catch up, or even just figure out what the hell was going on …
Severian, “Lessons from Manchuria”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-04-21.
January 12, 2024
QotD: Rome’s Italic “allies”
The Roman Republic spent its first two and a half centuries (or so) expanding fitfully through peninsular Italy (that is, Italy south of the Po River Valley, not including Sicily). This isn’t the place for a full discussion of the slow process of expanding Roman control (which wouldn’t be entirely completed until 272 with the surrender of Tarentum). The consensus position on the process is that it was one in which Rome exploited local rivalries to champion one side or the other making an ally of the one by intervening and the other by defeating and subjecting them (this view underlies the excellent M.P. Fronda, Between Rome and Carthage: Southern Italy During the Second Punic War (2010); E.T. Salmon, The Making of Roman Italy (1982) remains a valuable introduction to the topic). More recently, N. Terranato, The Early Roman Expansion into Italy (2019) has argued for something more based on horizontal elite networks and diplomacy, though this remains decidedly a minority opinion (I myself am rather closer to the consensus position, though Terranato has a point about the role of elite negotiation in the process).
The simple (and perhaps now increasingly dated) way I explain this to my students is that Rome follows the Goku Model of Imperialism: I beat you, therefore we are now friends. Defeated communities in Italy (the system is different outside of Italy) are made to join Rome’s alliance network as socii (“allies”), do not have tribute imposed on them, but must supply their soldiers to fight with Rome when Rome is at war, which is always.
It actually doesn’t matter for us how this expansion was accomplished; rather we’re interested in the sort of order the Romans set up when they did expand. The basic blueprint for how Rome interacted with the Italians may have emerged as early as 493 with the Foedus Cassianum, a peace treaty which ended a war between Rome and [the] Latin League (an alliance of ethnically Latin cities in Latium). To simplify quite a lot, the Roman “deal” with the communities of Italy which one by one came under Roman power went as follows:
- All subject communities in Italy became socii (“allies”). This was true if Rome actually intervened to help you as your ally, or if Rome intervened against you and conquered your community.
- The socii retained substantial internal autonomy (they kept their own laws, religions, language and customs), but could have no foreign policy except their alliance with Rome.
- Whenever Rome went to war, the socii were required to send soldiers to assist Rome’s armies; the number of socii in Rome’s armies ranged from around half to perhaps as much as two thirds at some points (though the socii outnumbered the Romans in Italy about 3-to-1 in 225, so the Romans made more strenuous manpower demands on themselves than their allies).
- Rome didn’t impose tribute on the socii, though the socii bore the cost of raising and paying their detachments of troops in war (except for food, which the Romans paid for, Plb. 6.39.14).
- Rome goes to war every year.
- No, seriously. Every. Year. From 509 to 31BC, the only exception was 241-235. That’s it. Six years of peace in 478 years of republic. The socii do not seem to have minded very much; they seem to have generally been as bellicose as the Romans and anyway …
- The spoils of Roman victory were split between Rome and the socii. Consequently, as one scholar memorably put it, the Roman alliance was akin to, “a criminal operation which compensates its victims by enrolling them in the gang and inviting them to share to proceeds of future robberies” (T. Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome (1995)).
- The alliance system included a ladder of potential relationships with Rome which the Romans might offer to loyal allies.
Now this isn’t a place for a long discussion of the Roman alliance system in Italy (that place is in the book I am writing), so I want us to focus more narrowly on the bolded points here and how they add up to significant changes in who counted as “Roman” over time. But I should note here that while I am calling this a Roman “alliance system” (because the Romans call these fellows socii, allies) this was by no means an equal arrangement: Rome declared the wars, commanded the armies and set the quotas for military service. The “allies” were thus allies in name only, but in practice subjects; nevertheless the Roman insistence on calling them allies and retaining the polite fiction that they were junior partners rather than subject communities, by doing things like sharing the loot and glory of victory, was a major contributor to Roman success (as we’ll see).
First, the Roman alliance system was split into what were essentially tiers of status. At the top were Roman citizens optimo iure (“full rights”, literally “with the best right”) often referred to on a community basis as civitas cum suffragio (“citizenship with the vote”). These were folks with the full benefits of Roman citizenship and the innermost core of the Roman polity, who could vote and (in theory, though for people of modest means, only in theory) run for office. Next were citizens non optimo iure, often referred to as having civitas sine suffragio (“citizenship without the vote”); they had all of the rights of Roman citizens except for political participation in Rome. This was almost always because they lived in communities well outside the city of Rome with their own local government (where they could vote); we’ll talk about how you get those communities in a second. That said, citizens without the vote still had the right to hold property in Roman territory and conduct business with the full protection of a Roman citizen (ius commercii) and the right to contract legal marriages with Roman citizens (ius conubii). They could do everything except for vote or run for offices in Rome itself.
Next down on the list were socii (allies) of Latin status (note this is a legal status and is entirely disconnected from Latin ethnicity; by the end of this post, Rome is going to be block-granting Latin status to Gauls in Cisalpine Gaul, for instance). Allies of Latin status got the benefits of the ius commercii, as well as the ability to move from one community with Latin status to another without losing their status. Unlike the citizens without the vote, they didn’t automatically get the right to contract legal marriages with Roman citizens, but in some cases the Romans granted that right to either individuals or entire communities (scholars differ on exactly how frequently those with Latin status would have conubium with Roman citizens; the traditional view is that this was a standard perk of Latin status, but see Roselaar, op. cit.). That said, the advantages of this status were considerable – particularly the ability to conduct business under Roman law rather than what the Romans called the “ius gentium” (“law of peoples”) which governed relations with foreigners (peregrini in Roman legal terms) and were less favorable (although free foreigners in Rome had somewhat better protections, on the whole, than free foreigners – like metics – in a Greek polis).
Finally, you had the socii who lacked these bells and whistles. That said, because their communities were allies of Rome in Italy (this system is not exported overseas), they were immune to tribute, Roman magistrates couldn’t make war on them and Roman armies would protect them in war – so they were still better off than a community that was purely of peregrini (or a community within one of Rome’s provinces; Italy was not a province, to be clear).
The key to this system is that socii who stayed loyal to Rome and dutifully supplied troops could be “upgraded” for their service, though in at least some cases, we know that socii opted not to accept Roman citizenship but instead chose to keep their status as their own community (the famous example of this were the allied soldiers of Praenesti, who refused Roman citizenship in 211, Liv. 23.20.2). Consequently, whole communities might inch closer to becoming Romans as a consequence of long service as Rome’s “allies” (most of whom, we must stress, were at one point or another, Rome’s Italian enemies who had been defeated and incorporated into Rome’s Italian alliance system).
But I mentioned spoils and everyone loves loot. When Rome beat you, in the moment after you lost, but before the Goku Model of Imperialism kicked in and you became friends, the Romans took your stuff. This might mean they very literally sacked your town and carried off objects of value, but it also – and for us more importantly – meant that the Romans seized land. That land would be added to the ager Romanus (the body of land in Italy held by Rome directly rather than belonging to one of Rome’s allies). But of course that land might be very far away from Rome which posed a problem – Rome was, after all, effectively a city-state; the whole point of having the socii-system is that Rome lacked both the means and the desire to directly govern far away communities. But the Romans didn’t want this land to stay vacant – they need the land to be full of farmers liable for conscription into Rome’s armies (there was a minimum property requirement for military service because you needed to be able to buy your own weapons so they had to be freeholding farmers, not enslaved workers). By the by, you can actually understand most of Rome’s decisions inside Italy if you just assume that the main objective of Roman aristocrats is to get bigger armies so they can win bigger battles and so burnish their political credentials back in Rome – that, and not general altruism (of which the Romans had fairly little), was the reason for Rome’s relatively generous alliance system.
The solution was for Rome to essentially plant little Mini-Me versions of itself on that newly taken land. This had some major advantages: first, it put farmers on that land who would be liable for conscription (typically placing them in carefully measured farming plots through a process known as centuriation), either as socii or as Roman citizens (typically without the vote). Second, it planted a loyal community in recently conquered territory which could act as a position of Roman control; notably, no Latin colony of this sort rebelled against Rome during the Second Punic War when Hannibal tried to get as many of the socii to cast off the Romans as he could.
What is important for what we are doing here is to note that the socii seem to have been permitted to contribute to the initial groups settling in these colonies and that these colonies were much more tightly tied to Rome, often having conubium – that right of intermarriage again – with Roman citizens. The consequence of this is that, by the late third century (when Rome is going to fight Carthage) the ager Romanus – the territory of Rome itself – comprises a big chunk of central Italy […] but the people who lived there as Roman citizens (with and without the vote) were not simply descendants of that initial Roman citizen body, but also a mix of people descended from communities of socii throughout Italy.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Queen’s Latin or Who Were the Romans, Part II: Citizens and Allies”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-06-25.
January 7, 2024
QotD: The US Army between 1945 and 1950
One aftermath of the Korean War has been the passionate attempt in some military quarters to prove the softness and decadence of American society as a whole, because in the first six months of that war there were wholesale failures. It has been a pervasive and persuasive argument, and it has raised its own counterargument, equally passionate.
The trouble is, different men live by different myths.
There are men who would have a society pointed wholly to fighting and resistance to Communism, and this would be a very different society from the one Americans now enjoy. It might succeed on the battlefield, but its other failures can be predicted.
But the infantry battlefield also cannot be remade to the order of the prevailing midcentury opinion of American sociologists.
The recommendations of the so-called Doolittle Board of 1945-1946, which destroyed so much of the will — if not the actual power — of the military traditionalists, and left them bitter, and confused as to how to act, was based on experience in World War II. In that war, as in all others, millions of civilians were fitted arbitrarily into a military pattern already centuries old. It had once fitted Western society; it now coincided with American customs and thinking no longer.
What the Doolittle Board tried to do, in small measure, was to bring the professional Army back into the new society. What it could not do, in 1946, was to gauge the future.
By 1947 the United States Army had returned, in large measure, to the pattern it had known prior to 1939. The new teen-agers who now joined it were much the same stripe of men who had joined in the old days. They were not intellectuals, they were not completely fired with patriotism, or motivated by the draft; nor was an aroused public, eager to win a war, breathing down their necks.
A great many of them signed up for three squares and a sack.
Over several thousand years of history, man has found a way to make soldiers out of this kind of man, as he comes, basically unformed, to the colors. It is a way with great stresses and great strains. It cannot be said it is wholly good. Regimentation is not good, completely, for any man.
But no successful army has been able to avoid it. It is an unpleasant necessity, seemingly likely to go on forever, as long as men fight in fields and mud.
One thing should be made clear.
The Army could have fought World War III, just as it could have fought World War II, under the new rules. During 1941-1945 the average age of the United States soldier was in the late twenties, and the ranks were seasoned with maturity from every rank of life, as well as intelligence.
In World War III, or any war with national emotional support, this would have again been true. Soldiers would have brought their motivation with them, firmed by understanding and maturity.
The Army could have fought World War III in 1950, but it could not fight Korea.
T.R. Fehrenbach, This Kind of War: A Study in Unpreparedness, 1963.
December 31, 2023
The British army in Northern Ireland, 1966-1975
Patrick Mercer reviews Huw Bennett’s Uncivil War: The British Army and the Troubles, 1966-1975 for The Critic:
Seen from today’s perspective, the litany of campaigns Britain fought between the World Wars seems unimportant. Yet disasters such as the Jallianwala Bagh massacre in Amritsar in April 1919, and the depredations of the Auxiliaries or Black and Tans in Ireland at much the same time, imperilled imperial strategy. [Richard Dannatt & Robert Lyman’s] Victory to Defeat underlines the actions of relatively small numbers of troops which threatened to unhinge whole campaigns. It makes the perfect counterpoint to Huw Bennett’s Uncivil War, which covers the opening years of the crisis in Northern Ireland in meticulous detail.
Bennett looks at operations in Northern Ireland only up until 1975 — arguably the most intense period — with a promise of further volumes to follow. This is the first, comprehensive attempt to deal in parallel with the political aspects of the campaign as well as the purely military ones. Although densely written, Uncivil War gives a very readable account of the first of three decades of conflict which dominated the everyday life of most of the combat arms of the Army. It now seems ironic, though, that Ulster was always treated as something of a sideshow when compared with the “real soldiering” of deterring the Soviets in Germany.
Central to Bennett’s book is the debacle of “Bloody Sunday” in January 1972, when paratroopers ran amok in Londonderry at a point of the campaign when the IRA was exhausted and finding it almost impossible to recruit. Politically, there might have been a breakthrough; militarily the terrorists were teetering on collapse, but one black sheep unit and the ham-fisted response by the chain of command galvanised the IRA. With a rifle’s crack, they guaranteed bloodshed for years to come.
If ever a victory was turned into defeat in modern times, this was it. Bennett pulls no punches in pointing that out. The interesting contrast with Lyman and Dannatt’s work is that no matter how much had been learnt from the Second World War, the doctrine that emerged could only be tested by blank firing exercises in Germany. Whilst the highly unlikely possibility of a war in Europe was constantly analysed, very little strategic thinking was put into the grinding, long-term campaign in Ulster that was actually killing people.
Certainly there were political initiatives and the intelligence machinery was constantly evolving, but the many battalions and regiments who were charged with everyday deterrence and occasional attrition wandered the streets with little imagination or flair, often only seeming to provide targets for the terrorists. If war against the Soviets was remote, bombs, snipers and ambushes in Ulster were certain. By contrast, the Field Service Pocket Book (India) of 1930 laid out clear advice and principles for operations on the North-West Frontier. In Ulster, we just blundered on.
If the lessons of 1918 were neglected, those that led to victory in 1945 were carefully studied, although any coherent tactical doctrine took until the 1980s to be published. Perversely, the operations that followed both world wars were much the same: small, far-flung, post-imperial scuffles which owed little to “conventional” fighting. Indeed, it might be argued that the real lessons that the Army needed to heed after 1945 were not those of a European war, but those which might have prepared it for long years in Northern Ireland or the former colonies.
December 29, 2023
QotD: The Hanoverian “reverse takeover of the British monarchy by the Germans”
Why, though, did Germans feel such a special affinity with “die Königin“? The most obvious reason is that the Royal Family is, to a great extent, of German extraction. The connections go back more than a thousand years to the Anglo-Saxons, but in modern times they begin with George I and the House of Hanover. This reverse takeover of the British monarchy by the Germans transformed the institution in countless ways. They may be summarised in four words: music, the military, the constitution and Christmas.
Music was a language that united the English and the Germans. The key figure was, of course, Handel — the first and pre-eminent but by no means the last Anglo-German composer. Born in Halle, Georg Friedrich Händel had briefly been George I’s Kapellmeister in Hanover yet had already established himself in England before the Prince Elector of Hanover inherited the British throne in 1714.
In London — then in the process of overtaking Paris and Amsterdam to become the commercial capital of Europe — he discovered hitherto undreamt-of possibilities. There he founded three opera companies, for which he supplied more than 40 operas, and adapted a baroque Italian art form, the oratorio, to suit English Protestant tastes.
His coronation music, such as the anthem, “Zadok the Priest”, imbued the Hanoverian dynasty with a new and splendid kind of sacral majesty. But he also added to its lustre by providing the musical accompaniment for new kinds of public entertainment, such as his Music for the Royal Fireworks: 12,000 people came to the first performance.
Along with music, the Germans brought a focus on military life. Whereas for the British Isles, the Civil War and the subsequent conflicts in Scotland and Ireland had been something of an aberration, war was second nature to German princes. Among them, George II was not unusual in leading his men into battle, although he was the last British monarch to do so.
Still, the legacy of such Teutonic martial prowess was visible in the late Queen’s obsequies: uniforms and decorations, pomp and circumstance, accompanied by funeral marches composed by a German, Ludwig van Beethoven. Ironically, the German state now avoids any public spectacle that could be construed as militaristic, yet most Germans harbour boundless admiration for the way that the British monarchy enlists the ceremonial genius of the armed services.
Even more important was the German contribution to the uniquely British creation of constitutional monarchy.
Each successive dynasty has left its mark on the monarchy’s evolution: from the Anglo-Saxons and Normans (the common law) to the Plantagenets (Magna Carta and Parliament) and Tudors (the Reformation). Only the Stuarts failed this test, at least until 1688. Even after the Glorious Revolution, the Bill of Rights and other laws that conferred statutory control over the royal prerogative, the constitutional settlement still hung in the balance when Queen Anne, the last Stuart ruler, died in 1714.
Coming from a region dominated by the theory and practice of absolute monarchy, the Hanoverians had no choice but to adapt immediately and seamlessly to the realities of politics in Britain, where their role was strictly limited. Robert Walpole and the long Whig ascendancy, during which the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty embedded itself irrevocably, could not have taken place without the acquiescence and active support of the new dynasty.
George III has been accused of attempting to reverse this process. The charge is unjust. Rather, as Andrew Roberts demonstrates in his new biography, he was “a monarch who understood his extensive rights and duties under the constitution”. He still had the right to refuse royal assent to parliamentary bills, but in half a century he never once exercised his veto (the last monarch to do so was the Stuart, Queen Anne in 1708).
At a time when enlightened despotism was de rigueur on the Continent, the Hanoverians were content to participate in an unprecedented constitutional experiment in their newly acquired United Kingdom. It was neither the first Brexit, nor the last, but it happened courtesy of a Royal Family that was still very German.
Daniel Johnson, “Why Germany mourned our Queen”, The Critic, 2022-10-30.
November 30, 2023
Men and Morale: Canadian Army Training in the Second World War
WW2TV
Published 1 Feb 2023Men and Morale: Canadian Army Training in the Second World War
Part of Canadian Week on WW2TV With Megan HamiltonThe Canadian Army of the Second World War spent more time preparing and training their citizen soldiers then they did in sustained action. This chiefly took place across Canada and in the United Kingdom. Adequate training functioned as a cradle for collective action, morale, empowerment, self-confidence, and, ultimately, success in battle. Yet, due to a number of factors, a sufficient standard of training was not always achieved by all.
There were limits to the Canadian Army’s ability to control the morale of its men as it created a vast organization from scratch. Training camp experiences varied, influenced by factors such as food, weather, comfort, group cohesion, leadership, skill level, discipline, social activities, and interactions with local civilians. In fact, it required a constant negotiation between camp leadership and the rank and file. Drawing from her research on both the Canadian and wider Commonwealth armies, Megan’s presentation will explain why soldiers’ morale in training was a difficult, yet vital, balancing act.
Originally from Vernon, British Columbia, Megan Hamilton is a social and military historian of the 20th century. She has an Honours Bachelor of Arts degree from Wilfrid Laurier University and a Master of Arts degree from the University of Waterloo. Her federally-funded master’s research focused on the Canadian experience of the Second World War, specifically the Vernon Military Camp. Megan’s work has been published by a number of platforms and in 2022 she won the Tri-University History Program’s top essay prize for master’s students.
She is currently located in London, England, where she has begun a fully-funded PhD at King’s College London and the Imperial War Museum, supervised by Dr. Jonathan Fennell. Her dissertation is a study of Second World War army training across the Commonwealth.
(more…)
November 16, 2023
The US military may need to find a modern-day Patroclus
John Carter explains why the sudden swerve in US military recruitment from all-diverse-all-the-time to an ad that might have been created in the 1960s … and why it still won’t help:
Sing, o muse, of the wrath of Achilles, son of Peleus, that brought countless ills upon the Achaeans …
Thus opens the foundational epic of European civilization.
Achilles is angry because his woman, Briseis, has been appropriated by Agamemnon, the leader of the Greeks. He expresses this discontent by going on strike. While the rest of the Greek army fights and dies outside the walls of Troy, Achilles lounges in his tent, content to sit out the combat until Agamemnon comes to his senses and returns his war bride. If Achilles were simply any other warm body with a spear, this wouldn’t be such a big deal, but he is Achilles – the greatest warrior of the Heroic Age. Without him, the Greeks are at a severe disadvantage. Achilles’ petulance is therefore a problem for Agamemnon.
The lesson is hardly a subtle one. Kings and generals need to keep their soldiers happy. They especially need to keep their best soldiers happy. If they don’t – for instance, by taking their women from them – morale will suffer, and they may well find themselves without the crucial support of their warriors when it most matters.
Washington seems to have missed that lesson, and now, they’re paying the price.
For the last decade they have been relentlessly and mercilessly whipping American whites: defaming them as racists, mocking their intelligence and manliness, tearing down their statues, erasing the names of their ancestral heroes, replacing their fictional archetypes with diverse doppelgangers in the media, disadvantaging them in education and employment, demanding that they attend racial struggle sessions. The list of outrages and humiliations is long and all too familiar, permeating as it does every one of our institutions.
But now, the Empire of Lies faces a problem.
War has returned to the world. History, its rumoured demise notwithstanding, once again stalks the land. Russia mauls the Ukraine; Israel is beset with enemies; the Empire’s influence in Africa frays by the day; China salivates over Taiwan.
Meanwhile the American domestic economy, long since hollowed out by the extractive rent-seeking of financial parasites, lurches from one crisis to the next. The Great Satan remains powerful, for the present, but the young bucks can scent that the silverback is not what he used to be. Their provocations increase in daring and intensity. If they aren’t slapped down, their boldness will only increase.
The criminal regime that has insinuated itself into the halls of American power is running against a clock. They must have a war to cover the slow collapse of their fake economy. They must have a war to prevent rival regimes from displacing their American golem. But their golem is crumbling. Therefore they must have a war sooner rather than later, because with every moment of delay America becomes weaker, while China and Russia become stronger.
Their problem is that no one wants to fight for them.
The core warrior population of America has always been the Scots-Irish of the Appalachian regions, the good ol’ boys of the South, and the farm boys of the Midwest. Hillbillies and rednecks, in other words. Many families from these areas have multi-generational traditions of service. Dad served in Vietnam, Grampa in WWII, Great-Grandpa in the Great War, and Great-Grandpa’s Pappy fought under Lee in the War of Northern Aggression.
These are precisely the white populations that have been singled out for the most unrelenting and vicious racial abuse over the last several decades. They are the one group that it’s okay to defame in the media, depicted as ignorant, bigoted, backwards, and inbred. The people running Hollywood seem to have a special disgust for them. For generations they have born this with a sort of stoic good cheer, accepting their role as the heel in the great kayfabe of American political drama even as they shouldered a disproportionate burden of blood, tears, and sweat in America’s imperial wars.
The events of the last two decades seem to have put an end to that. It wasn’t just the psychotic frenzy of race communism that gripped the regime’s mind, although that certainly played a factor as the military has hardly been immune to it. Who wants to serve in an armed forces that has thrown meritocracy in the trash to make sure the commissioned ranks include as many strong black lesbians as possible, that spends more time making sure the enlisted ranks understand the nuances of pronoun usage and the finer points of critical race theory than training for war? Demoralizing as all that has been, the absolutely pointless debacle of the Neocon Forever War in the Middle East has played at least as large a role.
QotD: Infantry soldiers in the age of pike and shot
The pike and the musket shifted the center of warfare away from aristocrats on horses towards aristocrats commanding large bodies of non-aristocratic infantry. But, as comes out quite clearly in their writing, those aristocrats were quite confident that the up-jumped peasants in their infantry lacked any in-born courage at all. Instead, they assumed (in their prejudice) that such soldiers would require relentless synchronized drilling in order to render the complex sequence of actions to reload a musket absolutely mechanical. As Lee points out [in Waging War], this training approach wasn’t necessary – other contemporary societies adapted to gunpowder just fine without it – but was a product of the values and prejudices of the European aristocracy of the 1500 and 1600s.
Such soldiers were, in their ideal, to quickly but mechanically reload their weapons, respond to orders and shift formation more or less oblivious to the battle around them. Indeed, uniforms for these soldiers came to favor high, starched collars precisely to limit their field of vision. This is not the man who, in Tyrtaeus’ words (elsewhere in his corpus), “bites on his lip and stands against the foe” but rather a human who, in the perfect form, was so mechanical in motions and habits that their courage or lack thereof, their awareness of the battlefield or lack thereof, didn’t matter at all. But at least, the [Classical] Greek might think, at least such men still ought not quail under fire but instead stood tall in the face of it.
After all, as late as the Second World War, it was thought that good British officers ought not duck or take cover under fire, in order to demonstrate and model good coolness under fire for their soldiers. The impression I get from talking to recent combat veterans (admittedly, American ones rather than British, since I live in the United States) is that an officer who behaved in that same way on today’s battlefield would be thought reckless (or stupid), not brave. Instead, the modern image of courage under fire is the soldier moving fast, staying low, moving to and through cover whenever possible – recklessness is discouraged precisely because it might put a comrade in danger.
Instead, the courage that is valued in many of today’s armies is the courage to stay calm and make cool, rational decisions. It is, to borrow the first line in Rudyard Kipling’s “If-“, “If you can keep your head when all about you/Are losing theirs and blaming it on you.” Which is not at all what was expected of the 17th century infantryman, whose officers trusted him to make nearly no decisions at all! But, as we’ve discussed, the modern system of combat demands that lots of decisions be devolved down further and further in the command hierarchy, with senior officers giving subordinates (often down to NCOs) the freedom to alter plans on the fly at the local level so long as they are following the general mission instructions (a system often referred to by its German term, auftragstaktik).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Universal Warrior, Part IIa: The Many Faces of Battle”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-02-05.
November 14, 2023
“Like all Luttwak stories, this is probably false but totally believable”
In the latest book review from Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, John Psmith considers Edward Luttwak’s fascinating and controversial The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, a book I quite enjoyed reading although I think his much later The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire one of his best books.
In one of the dozens of notorious interviews of Edward Luttwak that float around the internet, he’s asked how he chose the topic for his PhD dissertation. His answer is that one day at university he had a humiliating social encounter. Immediately afterwards, somebody pounced on him and asked what his dissertation was about anyway. He hadn’t even started thinking about what his topic would be, but he obviously couldn’t say that, and so instead he puffed himself up and made something up on the spot, and he did so by saying the most grandiloquent series of words one at a time like a large language model feverishly choosing the next token to maximize self importance: “The … GRAND … Strategy … … OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE!!” His interlocutor was sufficiently awed and impressed, but then he had to write the damn thing. Like all Luttwak stories, this is probably false but totally believable.1
But I’m very glad he wrote that thesis, because it was later turned into the wonderful book I’m reviewing. Now, one of the ways that the Psmiths subvert traditional gender roles is that it’s Jane, not I, who thinks about the Roman Empire every day. But this is only pretending to be a book about the Roman Empire. It’s really a book about “grand strategy” — how states can efficiently allocate scarce military, diplomatic, and financial resources to counter a variety of internal and external threats. It’s true that the examples are mainly drawn from four centuries of Roman history — starting with the Julio-Claudian dynasty and ending with the Empire losing control of Italy and Western Europe — but the analysis, and the lessons, are abstract enough that they transcend that particular context.
Luttwak believes that the state is a kind of machine for turning arable land into military power via taxation and conscription. A state that wants to maximize its survival odds can do so in three ways: (1) it can increase its “inputs”, by bringing a larger quantity of arable land under its control (so long as it avoids a commensurate increase in the threats it faces); (2) It can increase the efficiency of the machine, by extracting more grain and more labor from the people it rules, or by undertaking internal reforms to reduce the amount of potential that’s bled away by corruption and decadence; or (3) It can use its military as effectively as possible, doing more with less, killing many birds with one stone or setting up situations where a small allocation of force can tie down much larger opponents.
This third option is more or less what Luttwak means by “grand strategy,” and I think it may be the key that ties together all of Luttwak’s writing and thought. What do a book about the ancient world and a book about Cold War era coups have in common? They’re both about doing more with less, economizing force by wielding it with overwhelming brutality and efficiency. Luttwak’s coldly arithmetic view of the state is reminiscent of nothing so much as James C. Scott’s view of the world,2 but Luttwak is on the opposite team. Scott is an anarchist, Luttwak is a hard-boiled realist, and moreover he’s one with a deep aesthetic appreciation for power and violence, especially when used elegantly, like a scalpel, such that they have effects far out of proportion with their quantity.3
The history of Rome that Luttwak wants to tell is not the history of its cultural or civilizational achievements, but rather the history of how these people were so incredibly good at economizing on violence that they were able to waste a huge portion of their military and economic potential on civil wars, but still keep the lights on and the barbarians at bay. “Grand strategy” is how they accomplished that, but the strategy changed as the threats evolved and as the internal condition of the empire deteriorated. Luttwak delineates three distinct epochs — the founding of the empire under the Julio-Claudian dynasty, the rationalization of frontiers under the Antonine emperors, and the Crisis of the Third Century — and argues that each of the three featured a fundamentally different overall strategic posture on the part of Rome.
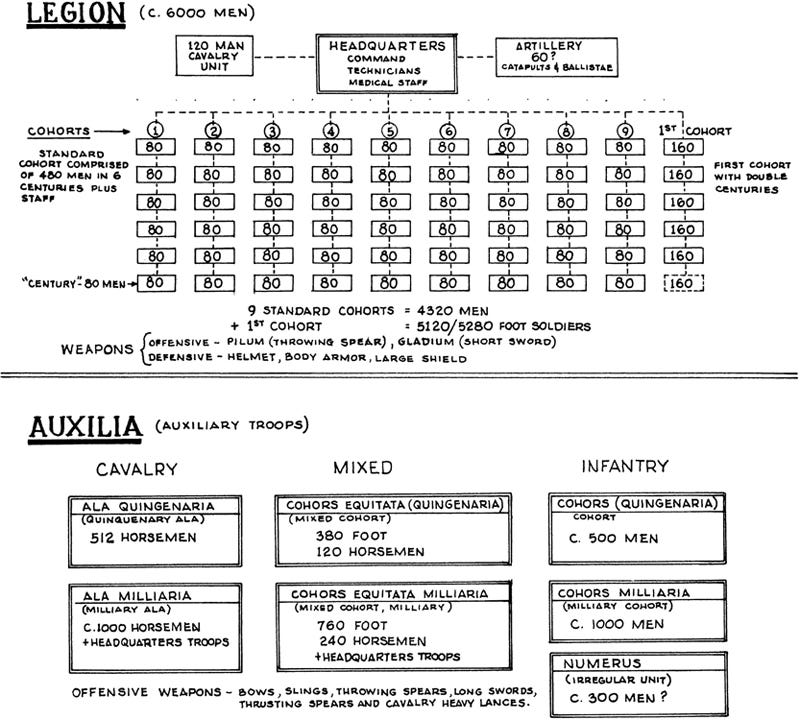
But before we get into all of that, I suppose we ought to talk about the legions. When people think of Roman military power, they usually think of the heavily-armed guys with red cloaks and horsehair plumes on their helmets. But of course they only made up a small fraction of the Roman military. We know that this has to be true because ancient armies, as much as modern armies, relied on combined-arms for their success. A legionary was a very scary kind of soldier, combining the roles of heavy infantry and combat engineer, but an army made up entirely of heavy infantry would be shredded by an opposing force of horse archers, for instance. So the Romans brought many other kinds of troops to bear: skirmishers, slingers, archers, light infantry, cavalry of their own (including mounted archers, light cavalry, and lancers with primitive barding that are a clear precursor of Medieval knights). And … almost to a man, all of these other forces were non-Roman.4 They were either mercenaries, or allied barbarians, or auxiliaries. As a kid in ancient history class I just accepted this as a fact, but reflect on it for a second and it seems very weird. This whole arrangement caused the Romans no end of trouble, so why did they do it that way?
Take the Luttwak pill and it all becomes clear: the Romans went all-in on legionaries as a way of economizing on force. The only people Rome could absolutely rely on were her citizens. The definition of a “real” Roman changed over time — at first it was only inhabitants of the city of Rome itself, later it was expanded to the surrounding countryside, and finally to all of Italy. But at every point it was a tiny fraction of the total population of the empire. Of that tiny fraction, some even smaller fraction are available to be trained as soldiers and to bear arms. What do you want those guys to be doing? The Roman answer is that you want them to be legionaries, because legionaries are not general-purpose soldiers, they’re specialists, and their specialties are: (1) besieging enemy cities, and (2) battles of attrition and annihilation.
1. Evidence that it’s false, he tells a completely different story in a different interview!
“I chose the subject because no theme in contemporary strategy was anywhere as interesting as the simple question of how Rome defended its territories (and added to them, now and then). Also, I did not want to waste my days reading the stultified & chaotically duplicative literature of ‘political science’ in which Strategy is imprisoned, when I could read instead in the often elegant, multi-lingual literature of Roman imperial studies.”
2. The zoomed-out, autistic alien robot anthropologist nature of this analysis also reminds me a bit of Vaclav Smil.
3. Wouldn’t the most elegant use of power be its deployment in such a way that it doesn’t really have to be used at all? In fact this is the main theme of Luttwak’s most recent book, The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire, a sort of sequel to this one. In the same interview as in the first footnote, Luttwak summarizes the argument of that book: Byzantine strategy was based on:
“a single, paradoxical, principle: do everything possible to raise, equip and train the best possible army and navy, and then … do everything possible to use them as little as possible … every alternative was to be tried to avoid, or at least minimize the destructive ‘attrition’ combat of main forces. Instead, potential enemies were to be dissuaded, bribed, subverted, weakened by getting others to attack them, sidetracked into other ventures; if enemy forces attacked nonetheless, they were to be contained and delayed by skirmishing, feints and demonstrations while the search went on for other powers near or far willing to attack or at least threaten the enemy power; if enemy attacks persisted nonetheless, they were to be met by countering maneuvers designed to exhaust them rather than the destructive combat of main forces, the very last resort. It was not only the precious trained manpower of the empire that this strategy wanted to conserve, but also the enemy’s … because today’s enemy could become tomorrow’s ally.
4. This isn’t quite true in every period. For instance during the Punic Wars, the Romans fielded “equites“, native Roman cavalry of their own, but it fell out of fashion pretty quickly thereafter.
November 11, 2023
In memoriam
A simple recognition of some of our family members who served in the First and Second World Wars:
The Great War
 Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)- Private Archibald Turner Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, mortally wounded 25 September, 1915 at Loos, age 27
(Elizabeth’s great uncle) - Private David Buller, Highland Light Infantry, died 21 October, 1915 at Loos, age 35
(Elizabeth’s great grandfather) - Private Harold Edgar Brand, East Yorkshire Regiment. died 4 June, 1917 at Tournai.
(My first cousin, three times removed) - Private Walter Porteous, Durham Light Infantry, died 4 October, 1917 at Passchendaele, age 18
(my great uncle, who had married the day before he left for the front and never returned) - Corporal John Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, wounded 2 September, 1914 (shortly before the First Battle of the Aisne), wounded again 29 June, 1918, lived through the war.
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)
The Second World War
- Flying Officer Richard Porteous, Royal Air Force, survived the defeat in Malaya, was evacuated to India and lived through the war
(my great uncle) - Able Seaman John Penman, Royal Navy, served in the Defensively Equipped Merchant fleet on the Atlantic convoys, the Murmansk Run (he may have been on a ship in convoy PQ-17, as we know he spent a winter in Russia) and other convoy routes, was involved in firefighting and rescue efforts during the Bombay Docks explosion in 1944, lived through the war
(Elizabeth’s father) - Private Archie Black (commissioned after the war and retired as a Major), Gordon Highlanders, captured during the fall of Singapore (aged 15) and survived a Japanese POW camp (he had begun to write an autobiography shortly before he died)
(Elizabeth’s uncle) - Elizabeth Buller, “Lumberjill” in the Women’s Timber Corps, an offshoot of the Women’s Land Army in Scotland through the war.
(Elizabeth’s mother) - Trooper Leslie Taplan Russon, 3rd Royal Tank Regiment, died at Tobruk, 19 December, 1942 (aged 23).
Leslie was my father’s first cousin, once removed (and therefore my first cousin, twice removed).
My maternal grandfather, Matthew Kendrew Thornton, was in a reserved occupation during the war as a plater working at Smith’s Docks in Middlesbrough. The original design for the famous Flower-class corvettes came from Smith’s Docks and 16 of the 196 built in the UK during the war (more were built in Canada). My great-grandmother was an enthusiastic ARP warden through the war (she reportedly enjoyed enforcing blackout compliance in the neighbourhood using the rattle and whistle that came with the job).
For the curious, the Commonwealth War Graves Commission the Royal British Legion, and the Library and Archives Canada WW1 and WW2 records site provide search engines you can use to look up your family name. The RBL’s Every One Remembered site shows you everyone who died in the Great War in British or Empire service (Canadians, Australians, New Zealanders, South Africans and other Imperial countries). The CWGC site also includes those who died in the Second World War. Library and Archives Canada allows searches of the Canadian Expeditionary Force and the Royal Newfoundland Regiment for all who served during WW1, and including those who volunteered for the CEF but were not accepted.
In Flanders fields the poppies blow
Between the crosses row on row,
That mark our place; and in the sky
The larks, still bravely singing, fly
Scarce heard amid the guns below.We are the Dead. Short days ago
We lived, felt dawn, saw sunset glow,
Loved and were loved, and now we lie
In Flanders fields.Take up our quarrel with the foe:
To you from failing hands we throw
The torch; be yours to hold it high.
If ye break faith with us who die
We shall not sleep, though poppies grow
In Flanders fields.Lieutenant Colonel John McCrae, MD Canadian Army Medical Corps (1872-1918)
Here is Mark Knopfler’s wonderful song “Remembrance Day” from his Get Lucky album, set to a slideshow of British and Canadian images from World War I through to more recent conflicts put together by Bob Oldfield:
November 9, 2023
Defending a stateless society: the Estonian way
David Friedman responded to a criticism of his views from Brad DeLong. Unfortunately, the criticism was written about a decade before David saw it, so he posted his response on his own Substack instead:
English version of the Estonian Defence League’s home page as of 2023-11-08.
https://www.kaitseliit.ee/en
Back in 2013 I came across a piece by Brad DeLong critical of my views. It argued that there were good reasons why anarcho-capitalist ideas did not appear until the nineteenth century, reasons illustrated by how badly a stateless society had worked in the Highlands of Scotland in the 17th century. I wrote a response and posted it to his blog, then waited for it to appear.
I eventually discovered what I should have realized earlier — that his post had been made nine years earlier. It is not surprising that my comment did not appear. The issues are no less interesting now than they were then, so here is my response:
Your argument rejecting a stateless order on the evidence of the Scottish Highlands is no more convincing than would be a similar argument claiming that Nazi Germany or Pol Pot’s Cambodia shows how bad a society where law is enforced by the state must be. The existence of societies without state law enforcement that work badly — I do not know enough about the Scottish Highlands to judge how accurate your account is — is no more evidence against anarchy than the existence of societies with state law enforcement that work badly is against the alternative to anarchy.
To make your case, you have to show that societies without state law enforcement have consistently worked worse than otherwise similar societies with it. For a little evidence against that claim I offer the contrast between Iceland and Norway in the tenth and eleventh centuries or northern Somalia pre-1960 when, despite some intervention by the British, it was in essence a stateless society, and the situation in the same areas after the British and Italians set up the nation of Somalia, imposing a nation state on a stateless society. You can find short accounts of both those cases, as well as references and a more general discussion of historical feud societies, in my Legal Systems Very Different From Ours. A late draft is webbed.
So far as the claim that the idea of societies where law enforcement is private is a recent invention, that is almost the opposite of the truth. The nation state as we know it today is a relatively recent development. For historical evidence, I recommend Seeing Like a State by James Scott, who offers a perceptive account of the ways in which societies had to be changed in order that states could rule them.
As best I can tell, most existing legal systems developed out of systems where law enforcement was private — whether, as you would presumably argue, improving on those systems or not is hard to tell. That is clearly true of, at least, Anglo-American common law, Jewish law and Islamic law, and I think Roman law as well. For details again see my book.
In which context, I am curious as to whether you regard yourself as a believer in the Whig theory of history, which views it as a story of continual progress, implying that “institutions A were replaced by institutions B” can be taken as clear evidence of the superiority of the latter.
And From the Real World
In chapter 56 of the third edition of The Machinery of Freedom I discussed how a stateless society might defend against an aggressive state, which I regard as the hardest problem for such a society. One of the possibilities I raise is having people voluntarily train and equip themselves for warfare for the fun (and patriotism) of it, as people now engage in paintball, medieval combat in the Society for Creative Anachronism, and various other military hobbies.
A correspondent sent me a real world example of that approach — the Estonian Defense League, civilian volunteers trained in the skills of insurgency. They refer to it as “military sport”. Competitions almost every week.
Estonia’s army of 6000 would not have much chance against a Russian invasion but the Estonians believe, with the examples of Iraq and Afghanistan in mind, that a large number of trained and armed insurgents could make an invasion expensive. The underlying principle, reflected in a Poul Anderson science fiction story1 and one of my small collection of economics jokes,2 is that to stop someone from doing something you do not have to make it impossible, just unprofitable. You can leverage his rationality.
Estonia has a population of 1.3 million. The league has 16,000 volunteers. Scale the number up to the population of the U.S. and you get a militia of about four million, roughly twice the manpower of the U.S. armed forces, active and reserve combined. The League is considered within the area of government of the Ministry of Defense, which presumably provides its weaponry; in an anarchist equivalent the volunteers would have to provide their own or get them by voluntary donation. But the largest cost, the labor, would be free.
Switzerland has a much larger military, staffed by universal compulsory service, but there are also private military associations that conduct voluntary training in between required military drills. Members pay a small fee that helps fund the association and use their issued arms and equipment for the drills.
1. The story is “Margin of Profit“. I discuss it in an essay for a work in progress, a book or web page containing works of short literature with interesting economics in them.
2. Two men encountered a hungry bear. One turned to run. “It’s hopeless,” the other told him, “you can’t outrun a bear.” “No,” he replied, “But I might be able to outrun you.”
QotD: The end of the “spoils system” and the professionalization of the bureaucracy
… There was, however, one last check on the power of faction: The bureaucracy.
I know, that seems weird, but unless you’ve really studied this stuff — it’s not taught in most high school or even college classes, for some mysterious reason — you probably don’t know that the civil service used to be entirely patronage-based. Our two most famous literary customs inspectors, for instance (Hawthorne and Melville), got their jobs through political connections, and that’s the way it worked for everyone — every time the other party won an election, most of the bureaucrats got turfed out, to be replaced by loyal party men. Trust me: very few of the names on this list would ring much of a bell even to field specialists, but they were big political cheeses in their day; Postmaster General was a plum federal post that was often handed to loyal Party men as a reward for a lifetime of faithful service. And so on down the line, including your local postmaster.
It took until 1883 to finally kill of this last vestige of federalism, but the Pendleton Act did it. Here again, this isn’t taught in school for some mysterious reason, but the political class took a very different lesson from the Civil War than the hoi polloi. While for the proles the Civil War was presented as a triumph of the common man, the elite understood that it was training, logistics, bureaucratization, professionalism that won the war for the Union. The Republicans made a big show of putting up U.S. Grant as “the Galena Tanner” in their campaign rhetoric but Grant had been a bankrupt tanner, and indeed a conspicuous failure at everything except war … and even there, his record was carefully doctored to present an image of a bumbling amateur suddenly being struck by inspiration, when in fact Grant was a West Pointer with an impressive combat record in the Mexican War. Now is not the time or place to discuss the merits, or not, of various Civil War figures, so just go with me on this: Pretty much all the big name generals on both sides of the war were presented to the public as talented gentleman amateurs, and it was heavily insinuated that the ones they couldn’t so portray — McClellan, and especially Robert E. Lee — lost because they were too hidebound, too “professional”.
The reality is almost the complete opposite — yeah, Stonewall Jackson ended the Mexican War as a mere captain (no mean feat in The Old Army, but whatever), but he had a tremendous combat record, and was so much of a military professional that he actually taught at a military academy. This is not to say there weren’t naive geniuses in the Civil War — see e.g. Nathan Bedford Forrest — but the Civil War, like all wars since the invention of the arquebus, was won by hardcore, long-service, well-trained professionals. A naive genius like Forrest might’ve been a better tactician, mano-a-mano and in a vacuum, than a West Point professional like Custer — then again, maybe not — but wars aren’t fought in vacuums. They’re fought on battlefields, and they’re won by supply weenies and staff pogues.
[…]
They took that experience with them into politics, and so it’s no surprise that the Federal government of the Gilded Age, though tiny by our standards, grew into such a leviathan in so short a time. Again, I’m just going to have to ask you to trust me on this, since for some reason it never gets covered in school, but back in the later 19th century words like “efficiency” really meant something to the political class. All those politician-generals (and politician-colonels and politician-majors and all the rest down at the local level) expected the State to function like the Army — that is to say, as a self-enclosed world where efficiency not only counts, but triumphs. An amateur civil service can’t do that, and so the days of the political sinecure had to end.
Severian, “Real Federalism Has Never Been Tried”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-03.
November 5, 2023
Military “institutional racism” and the Expert Infantry Badge
Chris Bray on a recent article in which a USAF Colonel lectures other “white colonels” about institutional racism in America’s military services:
Thoughts about the Air Force colonel who delivers sanctimonious lectures about institutional racism to his fellow “white colonels”.
In you’re an infantry soldier in the US Army, you can distinguish yourself by earning an Expert Infantry Badge. To do that, you have to qualify as an expert with the rifle, then complete a series of skills tests like “set headspace and timing on a caliber .50 machine gun” and “operate as a station in a radio net with SINCGARS radio single channel”. Then, finally, you have to complete a 12-mile road march. You can read the standards for that event here: carry a rifle and magazines, wear a helmet at all times, carry a rucksack weighing at least 35 pounds, and so on. When the person with the stopwatch says that three hours have elapsed, you’re either standing behind the finish line or in front of it; you either earn the EIB or you don’t.
The test isn’t subjective — the judges don’t award you style points. If you crawl across the finish line in a pool of blood and urine, sobbing for mommy, but you do it in less than three hours, and you still have your rucksack and your rifle and everything else at the end, you get the EIB.
Nor is it weighted. If you’re a fourth-generation VMI graduate with a fine old family name that can be found on the rolls of the Mayflower Society, you get the EIB if you cross the finish line on time. If you’re an E-2 who grew up in a trailer park and barely made it out of high school and doesn’t remember the names of all your so-called stepdads, you get the EIB if you cross the finish line on time. Officers and enlisted work to exactly the same standard. The credential comes from the task, full stop. This fact is the core of every credential you can earn in the military: If you’re authorized to wear the Parachutist Badge, you went to Fort Benning, or whatever they call it now, and jumped out of the plane five times without missing the ground. You did the thing. Doing the thing is who you are, in a growing list of things.
As a set of organizations built on task competence, for plainly measurable tasks that can’t be faked or fudged, the armed forces have been America’s first meritocracy. The first black West Point graduate was commissioned in 1877; the first black Medal of Honor recipient was born into slavery. Even in the segregated military, credentials obtained through task competence bore weight, as the court-martial of Jackie Robinson suggests with its outcome: In 1944, in Texas, a black officer was correct to harshly demand respect from a white enlisted soldier.
If you’ve served in the military, you’ve seen this. In my first posting as an infantryman, my company commander, first sergeant, platoon sergeant, and squad leader were black, a fact that I never heard anyone even mention. Rank, profession, and authority come from doing, without socioeconomic or racial chutes or ladders: If you can fly the plane, you’re a pilot. Up to the boundaries of the flag ranks, politics and identity don’t matter. (Regarding those flag ranks, see the late David Hackworth’s discussion of “perfumed princes”.)
And so the descent of the American military into the performative politics of DEI and equity and Robin DiAngelo books just blindly shits on the core value of the American military, which is that you get the rank and the status for what you do, full stop.
QotD: The Auftragstaktik principle of the Third Reich
[The Nazis], being Social Darwinists to the core, applied the military principle of Auftragstaktik to civilian life. “Mission-oriented” tactics means that the overall commanders leave as much as possible to the on-the-spot commanders, be they officers or noncoms, on the theory that properly-trained leaders will have a much better understanding of what needs to be done, and how to do it, than some general back at HQ. It’s the main reason the Wehrmacht could keep fighting so well, for so long, in the face of overwhelming opposition — tasks that would fall to an American company, or a Russian regiment, were often undertaken by a Wehrmacht platoon under the command of a senior corporal.
Obviously civilian life isn’t as goal-directed as the military in wartime, but a similar principle applied — given a vague set of generalized objectives from the top (Kershaw’s famous “working towards the Führer” thesis), everyone at every level was encouraged to move the ball downfield as he saw fit … with the added twist that, in the absence of a clearly defined, military-style chain of command, the various “subordinates” would ruthlessly battle it out with each other, Darwin-style, for bureaucratic supremacy.
Thus the Nazis’ infamous plate-of-spaghetti org charts. I’m not an expert, but I’m pretty sure there were more than a few guys who held wildly different ranks in various different organizations simultaneously. He might be a mere patrolman in the Order Police, but an officer in the SS, a noncom in the SA (you could be in both, at least in the early days), and so forth. I wouldn’t be surprised if there was more than one guy who technically reported to himself, somewhere deep in the bowels of the RHSA [Reich Security Main Office]. You could spend a lifetime trying to sort this stuff out …
Severian, “The Crisis of the Third Decade”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-03-18.