… I’m baffled by this idea — seemingly everywhere in modern marketing — that they can somehow annoy you into buying their products. Music streaming services like Spotify are all but unlistenable because of it — not only do you get four ads every three songs, but three of the four ads ask “Want a break from the ads? Join premium!!” Or … you know … I could just go back to listening to tunes the old fashioned way. Humanity’s Greatest Genius, when he lays off that shtick for a minute, actually has some good riffs on this. We all must learn to deprogram ourselves from the Cult of Free. If they’re giving away the product, then you are the product. Much like a college degree, “free” tech is actually negative equity — you’re actually worse off for doing it.
It has gotten so bad lately that they don’t just barrage you with ads, they’re now starting to force-feed you content. I used to have Amazon Music — the free one, of course — because it was a good way to listen to The Z Man’s podcasts and my classical library during my commute. I’d download albums to my phone, switch to “offline” mode, and listen that way. Which Amazon obviously considers no good, because they pushed out some “car mode” bullshit that now automatically turns your wifi on, then starts blasting hip hop at you. And that’s not all! A few weeks back, while trying to figure out a way to turn the damn thing off, I noticed that it now has a “your playlist” feature, based on “your” music … which is, of course, the same force-fed rap shit I’ve been trying so desperately to avoid. It has decided that not only shall I listen to Young Jeezy, Big Weezy, and MC Funetik Spelyn, I will also like it, to such a degree that they will start force-feeding me other shit based on my “likes”.
Yeah. Uninstalled. Fuck you, Bezos. I’ve got a CD player. And when Microsoft decides that I’m not listening to the right music on that, and uninstalls the driver, I’ve got a tape deck. And when that breaks, I will sing to myself as I go down the highway. 99 bottles of beer on the wall, motherfucker, just like bus trips back in Boy Scouts. Enough is enough.
Severian, “Mailbag / Grab Bag”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-06-18.
September 23, 2021
QotD: The problem with “free” tech stuff
August 31, 2021
QotD: “It’s not news, it’s irritainment”
“Did you watch the news last night?”
“Yeah, I watched [Tucker Carlson/Rachel Maddow].”
Except that’s not the news. That’s an editorial program where a person gets performatively angry about their opinion of selected bits of news so that you get angry about it along with them … righteously angry enough to sit through an hour’s worth of commercials.
It’s not news, it’s irritainment.
Tamara Keel, “It makes me so mad!”, View From The Porch, 2021-05-25.
July 24, 2021
QotD: Demolishing the Tim Hortons myth
I’m here to help. This is a safe place, Canada. I want to see you get through this. Which is why I need you to listen to me closely. These words will be painful, but it’s important you hear them:
Tim Hortons is not a defining national institution. Rather, it is a chain of thousands of doughnut shops, several of which have working toilets.
Tim Hortons is not an indispensable part of the Canadian experience. Rather, it is a place that sells a breakfast sandwich that tastes like a dishcloth soaked in egg yolk and left out overnight on top of a radiator.
Tim Hortons is not an anti-Starbucks choice that makes you a more relatable politician or a more authentic Canadian. Rather, it is a great place to buy a muffin if you’ve always wondered what it would be like to eat blueberry air.
There is no shame in having been caught up in the Hortons hype. It happens. Just last week, a columnist in the Toronto Star likened Tim Hortons to a precious vase that’s about to be juggled by its new owner, a monkey. (I was so irate at this irresponsible journalism that I wrote a letter demanding the Star issue a retraction. Everyone knows monkeys juggle only coconuts.)
Meanwhile, the NDP’s Peggy Nash — who, by all accounts, is an actual person and not a fictional construct of The Onion — gravely warned of the potential consequences of the Tim Hortons brand “falling into foreign hands.”
Yes, imagine the consequences. Maybe these madcap foreign owners will go so far as to alter the sandwiches so they taste like … something. Preferably like sandwich, but, at this point, most of us have stopped being picky.
Am I getting through to you, Canada? While we’re on the topic of hard truths, there is something else that needs to be said.
Canada, you sure do like your double-double — or, as it is by law referred to in news reports, the “beloved double-double.” But here’s a newsflash for you: If you drink your coffee with two creams and two sugars, the quality of the coffee itself is of little consequence. You might as well pour a mug of instant coffee or sip the urine of a house cat mixed with a clump of dirt from your golf spikes. It’s all basically the same thing once you bombard it with sweet and dairy. You’re really just wasting your …
I see from your reaction that I’ve crossed a line. I hereby withdraw my defamatory comments about the double-double and kindly ask that you return that handful of my chest hair.
Scott Feschuk, “Okay, Canada: It’s time for the hard truth about Tim Hortons”, Macleans, 2014-09-14.
July 18, 2021
July 6, 2021
GALAXY QUEST – WTF Happened To This Movie?
JoBlo Videos
Published 7 Feb 2020Hollywood has had its fair share of historically troubled productions. Whether it was casting changes, actor deaths, fired directors, in-production rewrites, constant delays, budget cuts or studio edits, these films had every intention to be a blockbuster, but were beset with unforeseen disasters. Sometimes huge hits, sometimes box office bombs.
In our latest episode we explore the 1999 surprise hit GALAXY QUEST, which had a long road to making it to the big screen. Starring Tim Allen, Sigourney Weaver, Alan Rickman, Sam Rockwell, Tony Shalhoub, Daryl Mitchell, Enrico Colantoni, Justin Long and Missi Pyle, this riff on Star Trek, directed by Dean Parisot, eventually got over its hurdles and made a galactic splash at the box office. Now, if we could just get that sequel …
For more MOVIE NEWS, visit: http://www.joblo.com
#GalaxyQuest #TimAllen #WTFHappenedToThisMovie
March 17, 2021
The long-gone economic framework of print newspapers
In The Line, Peter Menzies explains the economic underpinnings of the newspaper world back in the “good old days” before first radio, then TV, and finally the internet took all the profits out of their model:

“Newspaper Boxes” by Randy Landicho is licensed under CC BY 2.0
We will hear a lot in the months ahead about who’s making money from news, so let’s get something straight: Even in the profit-soaked heyday of Canadian newspapers, no one made money from news.
That all ended about 100 years ago when radio — and then television — began delivering it for free.
Oh sure, the occasional ongoing news story would inspire people to buy more newspapers. But in my 30 years in that business the only event that did so in any significant way was the death and funeral of Princess Diana. Even then, after the extra cost of newsprint and distribution, the financial return was insignificant.
But mythologies die hard. People in newsrooms believed news made money — and apparently some still do — even when year after year, surveys of readers showed that there were lots of other things that sold and sustained newspapers.
Some people bought them because they were looking for a job. For others, it was a house, a plumber, a companion, a pet, a car or, really, almost anything else you can think of that might be needed. Classified pages were every town and city’s marketplace. That’s where you found stuff you had to get and bought an ad when you had something to sell or tell people about. It was where you announced the births of your babies, the graduations, engagements and weddings of your children and the deaths of your parents. The lives of communities were recorded in the classified pages of their newspapers.
After a glance at the headlines, many other readers’ first and sometimes only stops were the horoscope, comics, crossword (an error there generated far more calls than a rogue columnist ever could) and other pleasant distractions. For still more, it was the stocks listings, sports scores or recipes to which they were primarily drawn.
There were movie and entertainment listings — even a TV guide so you’d know where and when to find Seinfeld. On Thursdays, you might buy a paper just for the Canadian Tire flyer. On weekends, specialty sections discussed books and told tales of travel adventures well-supported by the latest deals advertised by travel agencies. Housing developers pitched their latest home designs in special real estate sections. And there were magazines. Honestly, there were.
It’s been literal decades since we last subscribed to a print newspaper, and nearly as long since I picked one up from a news stand. My mother is the last person I recall still depending on buying a physical newspaper — she only stopped buying a Saturday Toronto Star in the last year or so — but that was mainly for the TV listings. Back when I still occasionally travelled on business (also more than a decade ago, now), it was a nostalgic treat to find a copy of USA Today at the door of my hotel room in the morning.
February 11, 2021
Tom Brady’s Super Bowl success has outlasted many titans of corporate America
Despite the headline, this isn’t really about the NFL, Tom Brady or the S*per B*wl, it’s about a key factor in free market economies: creative destruction.

“Blockbuster store closing sale” by Consumerist Dot Com is licensed under CC BY 2.0
Consider some of the names that bought Super Bowl airtime during Brady’s first rodeo in January 2002: AOL, Blockbuster, Radio Shack, Circuit City, CompUSA, Sears, Yahoo, VoiceStream Wireless, and Gateway Computers.
The Titans of Yesterday
Notice a theme? That list features some companies we saw in Captain Marvel, the 2019 hit movie that nailed 90s nostalgia and reminded us how fast the world had changed. Like when Blockbuster Video stores were still a thing.
For those who may not recall, when Brady was winning his first Super Bowl, Blockbuster was approaching its peak. In 2004, it operated 9,094 stores and employed some 84,300 people. The company was pulling in $6 billion in revenue annually and looked invincible. Today, a single Blockbuster store remains open — in the world.
Remember RadioShack? Once upon a time, it seemed as if you could find one of their brick-and-mortar stores in every corner of the USA. Not anymore. In 2015, RadioShack filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, in large part because of those many store locations, which cannibalized revenues.
Sears, one of the historic giants of retail, managed to make it to 2018 before announcing its bankruptcy. Its stores continue to close so fast, it’s hard to tell how many remain in operation. (The best guess is about 60.)
It’s sometimes difficult to remember that the titans of industry aren’t always the same companies from year to year, and the sector-dominating company today might well be begging for a bailout (or demanding protection from uppity new competitors) only a few years down the way.
Some might see the collapse of Blockbuster, Sears and company as a sign of something terribly wrong with our economic system. After all, Blockbuster alone paid rent at tens of thousands of properties and employed tens of thousands of workers. Sears was the largest American retailer (by far) for decades.
Watching the companies we once shopped at flounder and fail can be surprising, jarring even. But a closer look shows this cycle is not unusual and is actually the sign of a healthy market economy, not a dysfunctional one. What may seem like pure destruction actually clears the way for economic innovation and renewal. “Creative destruction” is how the economist Joseph Schumpeter (1880-1950) characterized business failure in a free market.
As economist Mark Perry points out, companies on top have a very hard time staying on top. Perry, a scholar at the American Enterprise institute and a professor of economics at the University of Michigan’s Flint campus, compared the 1955 Fortune 500 companies to the 2019 Fortune 500. He found that just 52 were still on the list six decades later.
I spent most of my working career in the software business, and many of the companies I’ve worked for over the years aren’t in business any more (my first job out of school was with Northern Telecom … remember them?). Software is a particularly fast-cycling industry, but it’s true of the economy as a whole at a slightly more sedate pace.
February 9, 2021
Tampa Bay quarterback Tom Brady – “What’s not to hate?”
I did watch the S*per B*wl on Sunday, although as the Canadian broadcast carefully replaces almost all of the expensive, creative, one-off ads with exactly the same ads the network showed all through the rest of the season, I watched it on my computer, and kept my mute button handy to silence the roughly 2/3rds of the broadcast that wasn’t actually football-related. (Although I’ve read many people commenting that the “special” ads aren’t as good as they used to be, I watch so little TV that I’m hardly qualified to judge personally.) In Monday’s NP Platformed newsletter, Colby Cosh used the old “there’s two kinds of people” device to talk about Tom Brady:
You can easily have an opinion about Brady, and you probably do, even if you’ve never watched a whole football game. But I have no way of predicting what that opinion is. Do you see him as a cheerful, intelligent family man who has transcended his natural limitations through hard work and study? Or is he just the jammiest SOB who ever lived? There was definitely something cruel in watching the immobile Brady dismantle the Chiefs of Patrick Mahomes, a passer equipped with physical gifts whose possibility was inconceivable before he broke into the league.
That’s probably part of how Brady has driven such a fault into North American bedrock. If there were a stat representing handsomeness-to-physical-impressiveness ratio, he would dominate the NFL. When you see photos of young Brady, who famously dropped to the sixth round of the draft, you no longer wonder how he dropped so far but why he was taken at all. Did the scouts fall in love, as they are known to do, with the “good face”?
Ancient Brady is young Brady with less mobility and accuracy. Mostly, like a relief pitcher with nothing but a fastball, he just darts the ball very efficiently at nearby targets. (Trading New England’s targets for Tampa Bay’s was, obviously, shrewd to the point of genius.) He is becoming as specialized, as optimized for one function, as a punter. But in his case the function seems to be “winning Super Bowls,” and we can’t attribute one iota of that to innate gifts denied to ordinary mortals. What’s not to hate?
Speaking of the ads, I do think the Babylon Bee got it exactly right here:
As a comment at Ace of Spades H.Q. related, the S*per B*wl has lost a lot of its cultural capital over the last few years:
49 — I work at a somewhat woke company. While talking about some projects we were working on the new guy asked me “hey why isn’t anyone talking about the superbowl?” and I remembered that even last year everyone was talking about the superbowl none stop the monday after.
Well you’ve finally done it lefties you’ve killed the NFL.
Posted by: 18-1
I tuned out the halftime show, even though the performer was kinda-sorta a local boy (born in Toronto), and I was a bit nonplussed with the visuals (I had the whole thing muted, natch). James Lileks found the show to be oddly reminiscent of 70’s SciFi movies:
The halftime show had a strange 70s sci-fi aesthetic; for some reason I kept thinking of The Black Hole and Logan’s Run. The most interesting part was picking out the buildings in the New York skyline arrayed in neon. Ah, it’s the AT&T Building, Philip Johnson’s famous po-mo Chippendale tower! And that would be the Met Life tower, which is actually the base for a much-larger tower unbuilt after the Crash of ’29. Hey, everyone, let’s pause this elaborate routine and destroy its momentum so I can wax pedantic!
Then there were all those dancers in masks, looking like victims of surgery in an old movie where a gangster got plastic surgery. A way of incorporating the pandemic zeitgeist, right? Last year: EMPOWERMENT AND SEX AND SEX EMPOWERMENT! This year: faceless people moving in mass to choreographed steps, then dissolving into random panic. There was something wrong about it, like some dank gas blown up through a fissure, filling balloons that looked like the humans who populate the shadows of a nightmare.
Previous years, the Super Bowl event was pure excess — mad, crass, exuberant, American overdrive, American overkill, a mix of skill and brute force. Something about this one felt desperate and shellshocked. I suppose I’m reading too much into it. But I don’t think we need fever dreams and worried-looking buskers in empty fields, at this point. It would be nice just to have some Clydesdales again.
I saw on another site (sorry, forgotten where I noticed it) that the bandages were an in-joke for The Weeknd’s fans, who’d been teased with several social media posts about him recovering from some sort of mysterious plastic surgery procedure leading up to the performance.
October 29, 2020
How to fix the CBC
… aside from cutting off the massive subsidies from the federal government, which would be my preferred solution if “nuke it from orbit” isn’t a viable choice. Let it sink or swim as a purely private media entity — I’d be betting on the “sink”, personally because they don’t currently have to compete thanks to their funding from the feds and are not noted for their quick adaptation skills. However, Peter Menzies isn’t quite as anti-CBC as I am:
In a recent piece here at The Line, I lamented the current status of the CBC. That’s easy enough to do, but it’s fair to ask what can actually be done to fix it. These ideas don’t provide all the answers but, implemented with conviction and speed, here’s where to start. Because there are some things that can be done, and relatively quickly, to revitalize the institution: the CBC may well be hell-bent on its own destructive dualism but clarifying its role and purifying its soul are still possible by getting it out of the advertising business and turning it into a proper public media.
Right now, the CBC is neither fish nor fowl. Sometimes, as with radio, it is a popular public broadcaster. At others, with its television channels, it fancies itself a commercial broadcaster, albeit a publicly-funded and relatively unpopular one. It plows both of those personalities into its commercial online operations and supplements them with reportage of the kind traditionally associated with newspapers. Like a creature of mythology, it shape-shifts through all of these roles as best suits its needs and moods.
On top of that, its OMG obsession with Trump’s America has drawn it far away from its content mandate to ensure Canadians learn about each other wherever they live in this vast and beautiful country. While its performance indicates otherwise, CBC’s purpose is not to secure a large audience share in the GTA or, in French, in Montreal, in order to earn more revenue. Nor is CBC News Network’s mandate to compete with CNN. The Corp’s raison d’etre, as defined in legislation, is to tell Canadians each other’s stories — even if the GTA and Montreal don’t care.
The only way to purify the CBC then, is to ban it — once and for all — from collecting advertising revenue from domestic consumption of its product. As its radio operations are already advertising-free this means no more ads on its TV or websites. Done. Finished.
September 20, 2020
The CBC’s latest bit of “mission creep”
At The Line, Jen Gerson wonders what the hell the CBC thinks it’s doing with this move:
Let us take a moment to leverage a little credibility under the CBC’s ass.
What the fuck is the CBC playing at, here? The corporation receives a cool $1 billion in public funding per year and it’s using taxpayer funds to, yet again, horn into the revenue streams of private communications outlets. No one — literally not a single Canadian taxpayer who isn’t already employed by the CBC — wants to throw money at a public broadcaster so that it can: “Help Canada’s strongest brands shape and share inspiring stories across our platforms and across the country.” Vomit.
No one asked for a taxpayer-funded advertising firm, you goddamn loons.
This is yet another classic example of one of the most dysfunctional habits of the MotherCorp: mission creep. A massive and rudderless operation unfettered from the practical limitations of profit-seeking has proven itself unable to restrain its own boneheaded impulses.
We, at The Line, can hear the pitiable defences already: “Oh, but they’re already underfunded. Of course they need to, uh, use their incredible taxpayer-funded competitive advantage to eat into the dwindling revenue streams of failing private media outlets just to survive!”
No. No. No they do not.
When faced with a dysfunctional hydra-headed cultural behemoth that is demonstrably incapable of keeping its mandate in its pants, the first impulse should not be to shovel ever-more taxpayer funds into the ever-widening maw. The CBC could respond to *cough* “inadequate funding” by narrowing its scope and focus to the things that make it most necessary to the Canadian public that it serves — radio, news, documentary, serving regions and topics that the private sector cannot adequately penetrate. Instead it goes off and does weird shit like this, and CBC Comedy, and CBC Music.
CBC. Guys.
You cannot be everything to everyone. You shouldn’t be everything to everyone. Canadians are not well served by a monopolistic government-funded one-stop #content communications shop. Figure out what you do best and stick to it. Focus on supplementing — rather than crushing — private-sector journalism. Maybe even consider ways to support private-sector start ups and independents, especially in local markets. “Revenue generation” is not the place where a public broadcaster should demonstrate self-defeating, industry-following innovation.
August 12, 2020
QotD: The circle of recycled life
1. Somewhere in this great land, a concerned and responsible corporation is having their twice-weekly colorful and compelling advertising supplement printed on 100% recycled paper.
2. As soon as they are completed millions of these colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements are shipped by truck to the various regional receiving centers of the U.S. Post Office.
3. From those centers, any number of allocated pallets of these colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements are broken out, put on U.S. Post Office trucks and delivered to local postal carrier destinations inside northern California.
4. My personal Paradise postal carrier and hundreds of others report for work at local postal carrier centers throughout northern California and load up their vans with enough of these colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements to deliver one or more to each and every house on their route.
5. My very polite personal Paradise postal carrier parks her van at the end of my block and loads her sack with these colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements.
6. She comes up my walk, up the porch stairs, and deposits my full share of these colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements into my mailbox with a clang every day between one and three in the afternoon.
7. Hearing the clang I sigh and wend my weary way to the front door and open my mailbox and pluck out said colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements.
8. With a heavier sigh I go back in, trudge through my house, out my back door to the alley, and place the colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements into my Recycling bin with the rest of the week’s mound.
9. Tomorrow the huge, lumbering Paradise Waste Management Recycling garbage truck will stop and empty my Recycling bin into its maw and haul all the colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements off to the Chico California Recycling and Brand New Mountain of Garbage center.
10. The collected colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements will then be shipped, by truck, to the center for turning recyclable paper into … recycled paper which will then be used by a concerned and responsible corporation for their twice-weekly colorful and compelling advertising supplements printed on 100% recycled paper.
Wash. Rinse. Repeat. Next year, as sure as spring brings septic system failures to Paradise, postage will increase because the U.S. Postal Colorful and compelling 100% recyclable advertising supplements “Service” will need more money to keep The Recycled Circle of life going.
Gerard VanderLeun, “The Circle of Recycled Life”, American Digest, 2018-06-01.
July 16, 2020
QotD: The young Herbert Hoover
Herbert Hoover was born in 1874 to poor parents in the tiny Quaker farming community of West Branch, Iowa. His father was a blacksmith, his mother a schoolteacher. His childhood was strict. Magazines and novels were banned; acceptable reading material included the Bible and Prohibitionist pamphlets. His hobby was collecting oddly shaped sticks.
His father died when he is 6, his mother when he is 10. The orphaned Hoover and his two siblings are shuttled from relative to relative. He spends one summer on the Osage Indian Reservation in Oklahoma, living with an uncle who worked for the Department of Indian Affairs. Another year passes on a pig farm with his Uncle Allen. In 1885, he is more permanently adopted by his Uncle John, a doctor and businessman helping found a Quaker colony in Oregon. Hoover’s various guardians are dutiful but distant; they never abuse or neglect him, but treat him more as an extra pair of hands around the house than as someone to be loved and cherished. Hoover reciprocates in kind, doing what is expected of him but excelling neither in school nor anywhere else.
In his early teens, Hoover gets his first job, as an office boy at a local real estate company. He loves it! He has spent his whole life doing chores for no pay, and working for pay is so much better! He has spent his whole life sullenly following orders, and now he’s expected to be proactive and figure things out for himself! Hoover the mediocre student and all-around unexceptional kid does a complete 180 and accepts Capitalism as the father he never had.
His first task is to write some newspaper ads for Oregon real estate. He writes brilliant ads, ads that draw people to Oregon from every corner of the country. But he learns some out-of-towners read his ads, come to town, stay at hotels, and are intercepted by competitors before they negotiate with his company. Of his own initiative, he rents several houses around town and turns them into boarding houses for out-of-towners coming to buy real estate, then doesn’t tell his competitors where they are. Then he marks up rent on the boarding houses and makes a tidy profit on the side. Everything he does is like this. When an especially acrimonious board meeting threatens to split the company, a quick-thinking Hoover sneaks out and turns off the gas to the building, plunging the meeting into darknes. Everyone else has to adjourn, the extra time gives cooler heads a change to prevail, and the company is saved. Everything he does is like this.
(on the other hand, he has zero friends and only one acquaintance his own age, who later describes him to biographers as “about as much excitement as a china egg”.)
Hoover meets all sorts of people passing through the Oregon frontier. One is a mining engineer. He regales young Herbert with his stories of traveling through the mountains, opening up new sources of minerals to feed the voracious appetite of Progress. This is the age of steamships, skyscrapers, and railroads, and to the young idealistic Hoover, engineering has an irresistible romance. He wants to leave home and go to college. But he worries a poor frontier boy like him would never fit in at Harvard or Yale. He gets a tip – a new, tuition-free university might be opening in Palo Alto, California. If he heads down right away, he might make it in time for the entrance exam. Hoover fails the entrance exam, but the new university is short on students and decides to take him anyway.
Herbert Hoover is the first student at Stanford. Not just a member of the first graduating class. Literally the first student. He arrives at the dorms two months early to get a head start on various money-making schemes, including distributing newspapers, delivering laundry, tending livestock, and helping other students register. He would later sell some of these businesses to other students and start more, operating a constant churn of enterprises throughout his college career. His academics remain mediocre, and he continues to have few friends – until he tries out for the football team in sophomore year. He has zero athletic talent and fails miserably, but the coach (whose eye for talent apparently transcends athletics) spots potential in Hoover and asks him to come on as team manager. In this role, Hoover is an unqualified success. He turns the team’s debt into a surplus, and starts the Big Game – a UC Berkeley vs. Stanford football match played on Thanksgiving which remains a beloved Stanford football tradition.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Hoover”, Slate Star Codex, 2020-03-17.
May 13, 2020
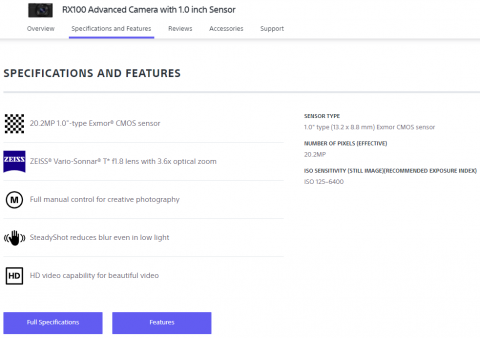
Okay, I’ll be careful not to call this “deceptive advertising” in future
At View from the Porch, Tam explains why digital camera terminology sometimes seems to be deliberately deceptive:
The disconnect comes when you run into the “luxury” or “enthusiast” end of the compact camera market, where the physical size of the 1″ sensor in cameras like Sony’s RX100 line or the Canon PowerShot G7/G9 is touted as a selling point.
Because the sensor itself is not physically an inch in any dimension. For that matter, a tiny 1/2.5″ sensor isn’t two fifths of an inch in any dimension either.
Small CCD/CMOS video sensors are labeled based on the size of video tube they replace. These tubes had a rectilinear imaging surface inside the cylindrical glass vacuum tube. Inside a 1″ tube would be an imaging surface measuring 16mm diagonally, or a little less. When solid state sensors started replacing tubes forty years ago, they were labeled according to the tube they’d replace.
So to this day, a sensor 16mm (or a bit less) diagonally is still called a 1″ sensor.
For that matter, “35mm” film is only 35mm if you measure from edge-to-edge, sprocket holes and all. “Full Frame/35mm” sensors are only about 29mm diagonally; there aren’t any digital sprocket holes.
Just like we still “dial” and “hang up” our cell phones, even though phones with dials and handsets that you hang on the wall are a vanishing memory, digital imaging technology is still named after the analog technologies it supplanted.
January 1, 2020
QotD: “Bin End” sales
I was amused this week to see to see a sign outside my local Wine Rack store which read “Sawmill Creek Bin End Sale.” Bin end usually means the last few bottles or cases of the lot. For a wine that arrives in Canada by the boatload, “bin end” sounds a bit far fetched. Then again, “Tanker End Sale” doesn’t sound quite as dignified.
Richard Best, The Frugal Oenophile Newsletter, 2005-07-13.