Ideological revolutions follow a predictable pattern. At some point, you see what the Bolsheviks called “the Revolt of the Left SR’s.” “SR” stands for “socialist revolutionaries”, so their “left” was, of course, radical by all but Bolshevik standards. Nonetheless, they actually meant it when they said they were for “soviet power”, the “soviets” in this case being “assemblies made up of actual workers, not limpwristed eggheads like Lenin whose fathers were minor nobility”.
As Solzhenitsyn explained it, in the early days of the Bolshevik revolution, these SRs were part of a coalition government with the Bolsheviks. As such, they had to be given a certain amount of jobs in the ministries, including the justice ministry. They actually believed that stuff about The Workers, so they weren’t ready to send people to Siberia for twenty, thirty, forty years like Lenin demanded. They broke with Lenin (over other issues as well, obviously), the Bolsheviks crushed them, and once the Bolsheviks had power over all the ministries, there’s your gulag archipelago. Same as it ever was.
The Nazis had their “Left SR’s”, too. These were the Strasserites, led by brothers Otto and Gregor, the guys who put the “Socialist” in “National Socialism”. The Night of the Long Knives was a purge against both “left” and “right” — though Röhm and his butt boys get all the press, one of the Strasser brothers got his, too. That’s German efficiency for you!
And then there was the original Terror, in France, and even before that we had ours, too — the Whiskey Rebellion and Shays’ Rebellion aren’t usually taught as ideological (they’re usually not taught at all, of course), but they were. We’ve had two revolutions (before this week), in fact, and in both cases you had those pesky “we really believe this shit!” types causing all kinds of problems for the revolutionary government — see, for example, those state governors who made Jeff’s life hell in Richmond, objecting to the nationalization of their state militias on the grounds that the Confederacy is actually, you know, a confederacy, and that drafts and war production boards and taxes in kind and all the rest are exactly the kind of tyranny you’d expect from Abe’s gang in Washington …
Severian, “Speaking of Purges…”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-01-08.
June 13, 2023
QotD: The purge of the Socialist Revolutionaries
June 12, 2023
It’s an insult to Chuck Barris and The Gong Show to compare it to the Justin Trudeau Show
In the weekly dispatch from The Line, the editors defend the honour of the original Gong Show and say that it’s not fair or right to compare that relatively staid and dignified TV show to the Canadian government’s performance art on the foreign interference file:
When the news broke late Friday afternoon that David Johnston was resigning from his position as special rapporteur on Chinese interference, the general reaction across the chattering class was a variable admixture of amusement and scorn. There’s probably a German word for it, but the security and intelligence expert Wesley Wark captured the tone of it with the headline on his Substack post, which said, simply: “Gong Show“.
We’re somewhat inclined to concur with Wark, except the three-ring train wreck that has marked Johnston’s time as Justin Trudeau’s moral merkin has been so disastrous that we think apologies are due to Chuck Barris, in light of the relative sobriety of his famous game show.
Reporters at the Globe and Mail and Global News started breaking stories about Chinese interference in Canadian elections a few months back, based largely on leaks from inside the Canadian intelligence apparatus. Almost immediately it was clear that the Liberals had a major problem on their hands, one that was going to require levels of transparency, good judgment and political even-handedness that this government has manifestly failed to achieve during its almost eight years in power.
Yet when Trudeau announced that he was going to appoint an “eminent Canadian” as “special rapporteur” to do an investigation and report back to the government with recommendations for how it should tackle the issue, we gave a collective groan here at The Line. Given the endless similar tasking of retired Supremes passim, it was clear that the pool from which Trudeau was going to fish his eminent personage was very shallow, and pretty well-drained. Indeed, at least one of us here was willing to bet large sums that it would be David Johnston.
What do we make of all this? Here’s the situation as we see it, in bullet form for brevity’s sake:
- Johnston should never have been offered the position of special rapporteur
- Having been offered the job of special rapporteur, Johnston should never have accepted it
And that is basically it. But given that Trudeau had the poor judgment to ask him, and Johnston had the poor judgment to accept, we think everything that has happened since was pretty much inevitable. We couldn’t have guessed at all the details of how this would have played out, especially the delicious elements beginning with the decision to hire Navigator to provide strategic advice (to manage what, exactly?), the revelation that Navigator had also provided strategic advice to Han Dong (who, recall, Johnston more or less exonerated), the firing of Navigator and the involvement of Don Guy and Brian Topp … this is really just gongs piled upon gongs piled upon gongs.
But the overall trajectory of Johnston’s time as special rapporteur? If you had told us ahead of time that this was more or less how things would go, we wouldn’t have been much surprised. Why? Because we live in Canada. And this is how Canada’s governing class behaves. It is a small, incestuous, highly conflicted and enormously self-satisfied group of people that is so isolated from the rest of the country they don’t even realize how isolated they are.
Honestly. What in heaven’s name gave Trudeau the idea that it would be smart to ask a former governor general to help launder his government’s reputation? And why on Earth did Johnston think it was a good idea to accept? Forget the Navigator stuff, this turkey was never going to fly. Johnston’s report was not accepted as the wise counsel of a wise man; instead it was seen as a partisan favour by a conflicted confidant. Sure, Johnston was subject to some pretty unfair attacks from the opposition, but what did he think was going to happen? Has he paid any attention over the last decade? But pride is a form of stubborness, and even after parliament voted for him to go, Johnston insisted he would stay on to finish his work. Until, on Friday afternoon, he decided he would not.
We’re not going to speculate about why Johnston finally pulled the chute. We’d like to think that the former GG in him thought it best to obey the will of the House of Commons. We rather hope it had nothing to do with some pointed (and unanswered) questions put to Johnston’s office by the Globe and Mail, asking whether Navigator had been given a heads-up on Johnston’s conclusions on the Dong file.
Maybe it doesn’t matter. As Paul Wells put it in a recent column, Trudeau sought to “outsource his credibility by subcontracting his judgment,” where credibility was supposed to flow from Johnston to Trudeau. Instead, and we would say, inevitably, the flow went in the opposite direction. If the prime minister had any credibility to lead the country on this issue, he wouldn’t need a special rapporteur in the first place. The fact that Trudeau felt the need to appoint one is a tacit admission that he knows he doesn’t have the trust of the people.
And that is the real problem here. The Johnston saga has ended where it was always going to, with a once-honorable man’s reputation in tatters and the problem he was brought in to address still unresolved. David Johnston has resigned, as he must have. In our view, that’s one resignation too few.
Why Modern Movies Suck – The Strong Female Character
The Critical Drinker
Published 10 Jun 2023One of the most tiresome tropes of the past ten years in moviemaking is the “Strong Female Character”. Not women who are smart, capable, well written and complex, but bland, boring, superficially “strong” characters designed to pander to simplistic ideals of female empowerment.
(more…)
“The more recent four or five years at Indigo have been a disastrophe”
In the latest SHuSH newsletter, Ken Whyte outlines the rise and fall of Canada’s biggest bookstore chain that stopped trying to be a bookstore chain and now appears to be looking for a new identity to assume in the wake of several board resignations and the announced resignation of Heather Reisman, the founder and public face of the chain:

“Indigo Books and Music” by Open Grid Scheduler / Grid Engine is licensed under CC0 1.0
Indigo opened its first bookstore in Burlington in 1997 and quickly expanded across the country in competition with the Chapters chain, which it bought in 2001. Heather’s husband, Gerry Schwartz, provided much of the financing in these years. Gerry is the controlling shareholder of Onex, a private equity firm that now has about $50 billion in assets under management.
Influential in Ottawa, the Schwartz-Reismans managed to convince the federal government to approve Indigo’s purchase of Chapters and also keep the US book chain Borders from moving north into Canada — a double play that cleared the field of meaningful competition and wouldn’t have happened in a country with serious antitrust enforcement.
Heather, as Indigo CEO, cast herself as the queen of Canadian literature, making personal selections of books to her customers, hosting book launches, interviewing celebrity authors, etc.
From a financial perspective, Indigo took about five years to get rolling after the Chapters acquisition. It looked steady through the late aughts and into the teens when Amazon showed up in force. Indigo’s share price caved. Unable to convince Ottawa to push Amazon back across the border, Heather adopted a new strategy, backing out of books and recasting Indigo as a general merchandiser selling cheeseboards, candles, blankets, and a lot of other crap to thirtyish women. “We built a wonderful connection with our customers in the book business,” she famously said. “Then, organically, certain products became less relevant and others were opportunities.” This charmed investors, if not the book community, and Indigo’s share price hit a high of $20 a share in 2018. By then, books, as a share of revenue, had fallen from 80 percent of revenue to below 60 percent (they are now 46 percent).
The more recent four or five years at Indigo have been a disastrophe. With its eighty-eight superstores and eighty-five small-format stores, the company lost $37 million in 2019, $185 million in 2020, and $57 million in 2021. Things looked somewhat better in 2022 with a $3 million profit, but its first three quarters of 2023 (Indigo has a March 28 year-end) resulted in an $8 million loss and its fourth quarter featured one of the most spectacular cyberhacks in Canadian commercial history. The company’s website was breached and its employment records held for ransom, resulting in a ten-day blackout for all of the company’s payment systems and a month-long outage in online sales. The share price is now $2.00 or one tenth the 2018 high.
ANALYSIS AND IRRESPONSIBLE SPECULATION
Given everything Indigo has been through over the last several years, and especially the last several months, it’s not surprising that Heather wants to pack it in. She’s seventy-four and super wealthy. There’s nothing but a desperately hard slog ahead for her money-losing company. Why stay?
Still, this has the feel of something that blew up at a board meeting, or in advance of a board meeting. It’s highly irregular for a company to lose almost half its directors in a single day. If these changes had been approached in conventional fashion, there would have been more in the way of messaging and positioning, especially regarding Heather. For all intents and purposes, she is Indigo. It wouldn’t exist without her. They ought to be throwing her a retirement parade and presenting her with a golden cheeseboard. Instead, all she’s getting, for now, are a few cliches in a terse press release.
It’s also weird that this all happened days before we get the company’s year-end results (they were out by this time last year). My guess is that the board got a preview, that the picture is ugly, that there are big changes afoot, and that the directors were nudged out as the start of a major retrenchment or given the option of sticking around for a bloodbath and chose instead to exit.
How to make a Wall Shelf | Episode 3
Paul Sellers
Published 27 Jan 2023This is truly an action-packed episode, with so much teaching on various techniques passed down through the years but mostly lost to upcoming generations. From saw stop-cuts to planing and shaping with spokeshaves, planes, rasps, and files, we include many strategies for you to learn from.
From these final fitting and shaping stages, we walk you through the glue-up phase so that every joint seats perfectly, because there is more to clamping a project than just tightening the screw thread and hoping for the best. We want the project to be dead square when the glue is dry, and clamps can indeed clamp a project out of square.
Our way is the proven way used by centuries of crafting artisans.
——————–
(more…)
QotD: Cities in the pre-modern era
This week and next, we’re going to look at an issue not of battles, but of settings: pre-modern cities – particularly the trope of the city, town or castle set out all alone in the middle of empty spaces. Why does the city or castle-town set amidst a sea of grass feel so off? And what should that terrain look like – especially in how it is shaped by the human activity taking place in a town’s hinterland. This is less of a military history topic (though we’ll see that factors in), and more of an economic history one. If that’s your jam – stay tuned, there will be more. If it’s not – don’t worry, we won’t abandon military topics either.
I find myself interested in pre-modern economies and militaries in roughly equal measure (in part because both are such crucial elements of state or societal success or failure). One of the reasons is that they are so interconnected: how military force is raised, supplied, maintained and projected is deeply dependent on how the underlying economy (which supplies the men, food, weapons and money) is structured and organized. And military institution and activities often play an important role in shaping economic structures in turn. So even if you are just here for the clashing of swords, remember: every sword must be forged, and every swordsman must be fed.
(Additional aside: I am assuming a west-of-the-Indus set of cereals: grain, barley and millet chiefly. Specifically, I am not going to bring in rice cultivation – the irrigation demands and density of rice farming changes a lot (the same is also true, in the opposite direction, to agriculture based around sorghum or yams). Most (western) fantasy and historic dramas are not set in rice-planting regions (and many East Asian works seem to have a much better grasp on where rice fields go and need no correction), so I’m going to leave rice out for now. I’m honestly not qualified to speak on it anyway – it is too different from my own area of research focus, which is on a Mediterranean agricultural mix (wheat, barely, olives, grapes), and I haven’t had the chance to read up on it sufficiently).
Lonely Cities
There’s a certain look that castles and cities in either historical dramas or fantasy settings set in the ancient or medieval world seem to have: the great walls of the city or castle rise up, majestically, from a vast, empty sea of grassland. […] These “lonely cities” are everywhere in fantasy and historical drama. I think we all know something is off here: cities and other large population centers do not simply pop up in the middle of open fields of grass, generally speaking. So if this shouldn’t all be grassland, what should be here? Who should be here?
What is a City For?
I think we need to start by thinking about why pre-modern towns and cities exist and what their economic role is. I’ll keep this relatively brief for now, because this is a topic I’m sure we’ll return to in the future. As modern people, we are used to the main roles cities play in the modern world, some of which are shared by pre-modern cities, and some of which are not. Modern cities are huge production centers, containing in them both the majority of the labor and the majority of the productive power of a society; this is very much not true of pre-modern cities – most people and most production still takes place in the countryside, because most people are farmers and most production is agricultural. Production happens in pre-modern cities, but it comes nowhere close to dominating the economy.
The role of infrastructure is also different. We are also used to cities as the center-point lynch-pins of infrastructure networks – roads, rail, sea routes, fiber-optic cable, etc. That isn’t false when applied to pre-modern cities, but it is much less true, if just because modern infrastructure is so much more powerful than its pre-modern precursors. Modern infrastructure is also a lot more exclusive: a man with a cart might visit a village where the road does not go, but a train or a truck cannot. The Phoenician traders of the early iron age could pull their trade ships up on the beach in places where there was no port; do not try this with a modern container ship. Infrastructure is largely a result of cities, not their original purpose or cause.
So what are the core functions of a pre-modern city? I see five key functions:
- Administrative Center. This is probably the oldest purpose cities have served: as a focal point for political and religious authorities. With limited communications technology, it makes sense to keep that leadership in one place, creating a hub of people who control a disproportionate amount of resources, which leads to
- Defensive/Military Center. Once you have all of those important people and resources (read: stockpiled food) in one place, it makes sense to focus defenses on that point. It also makes sense to keep – or form up – the army where most of the resources and leaders are. People, in turn, tend to want to live close to the defenses, which leads to
- Market Center. Putting a lot of people and resources in one place makes the city a natural point for trade – the more buyers and sellers in one place, the more likely you are to find the buyer or seller you want. As a market, the city experiences “network” effects: each person living there makes the city more attractive for others. Still, it is important to note: the town is a market hub for the countryside, where most people still live. Which only now leads to
- Production Center. But not big industrial production like modern cities. Instead it is the small, niche production – the sort of things you only buy once-in-a-while or only the rich buy – that get focused into cities. Blacksmiths making tools, producers of fine-ware and goods for export, that sort of thing. These products and producers need big markets or deep pockets to make end meet. The majority of the core needs of most people (things like food, shelter and clothes) are still produced by the peasants, for the peasants, where they live, in the country. Still, you want to produce goods made for sale rather than personal use near the market, and maybe sell them abroad, which leads to
- Infrastructure Center. With so much goods and communications moving to and from the city, it starts making sense for the state to build dedicated transit infrastructure (roads, ports, artificial harbors). This infrastructure almost always begins as administrative/military infrastructure, but still gets used to economic ends. Nevertheless, this comes relatively late – things like the Persian Royal Road (6th/5th century BC) and the earliest Roman roads (late 4th century BC) come late in most urban development.
Of course, all of these functions depend, in part, on the city as a concentration of people. but what I want to stress – before we move on to our main topic – is that in all of these functions the pre-modern city effectively serves the countryside, because that is still where most people are and where most production (and the most important production – food) is. The administration in the city is administering the countryside – usually by gathering and redistributing surplus agricultural production (from the countryside!). The defenses in the city are meant to defend the production of the countryside and the people of the countryside (when they flee to it). The people using the market – at least until the city grows very large – are mostly coming in from the country (this is why most medieval and ancient markets are only open on certain days – for the Romans, this was the “ninth day”, the Nundinae – customers have to transit into town, so you want everyone there on the same day).
(An aside: I have framed this as the city serving the economic needs of the countryside, but it is equally valid to see the city as the exploiter of the countryside. The narrative above can easily be read as one in which the religious, political and military elite use their power to violently extract surplus agricultural production, which in turn gives rise to a city that is essentially a parasite (this is Max Weber’s model for a “consumer city”) that contributes little but siphons off the production of the countryside. The study of ancient and medieval cities is still very much embroiled in a debate between those who see cities as filling a valuable economic function and those who see them as fundamentally exploitative and rent-seeking; I fall among the former, but the latter do have some very valid points about how harshly and exploitatively cities (and city elites) could treat their hinterlands.)
Consequently, the place and role of almost every kind of population center (city, town or castle-town) is dictated by how it relates to the countryside around it (the city’s hinterland; the Greeks called this the city’s khora (χώρα)).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Lonely City, Part I: The Ideal City”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-07-12.
June 11, 2023
Rewriting the well-worn story of how the steam engine was invented
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes pushes back against the story we’ve been telling for over 200 years about how the steam engine came to be:
The standard pre-history of the steam engine goes a little like this:
- There were a few basic steam-using devices designed by the ancients, like Hero of Alexandria’s spinning aeolipile, which are often regarded as essentially toys.
- Fast forward to the 1640s and Evangelista Torricelli, one of Galileo’s disciples, demonstrates that vacuums are possible and the atmosphere has a weight.
- The city leader of Magdeburg, Otto von Guericke, c.1650 creates vacuums using a mechanical air pump, and is soon using atmospheric pressure to lift extraordinary weights. This sets off a spate of experimentation by the likes of Robert Boyle, Robert Hooke, Christiaan Huygens, and Denis Papin, to create vacuums under pistons.
- As a result of the new science of vacuums, by the 1690s and 1700s the mysterious Thomas Savery and especially the Devon-based ironmonger Thomas Newcomen are able to develop the first commercially practical engines using atmospheric pressure. Steam engine development continued from there.
This is the narrative that had become set in the 1820s, if not earlier, and has been repeated with many of the same names and dates by book after book after book ever since. It’s a narrative that I have even repeated myself.
But, as I only recently discovered, atmospheric pressure and vacuums were actually being exploited long before Torricelli was even born, by people who believed that vacuums were impossible and had no concept of atmospheric pressure. Devices very much like Savery’s, which exploited both the pushing force of expanding hot steam and the sucking effect of condensing it with cold — what we now know to be caused by atmospheric pressure — were being developed far earlier.
I began to give a more accurate account of the development of the atmospheric engine in a detailed three-part series on why the steam engine wasn’t invented earlier (see parts I, II, III, which give more detail and the references). But I haven’t put it all together in one easily digestible place, and since writing I’ve continued to discover even more. So here’s a rough sketch summarising what really happened, based on everything I’ve found so far […]
The development of the atmospheric engine was thus significantly longer and more complicated than the traditional narrative suggests. Far from being an invention that appeared from out of the blue, unlocked by the latest scientific advancements, it started to take shape from decades and centuries of experiments and marginal improvements from a whole host of inventors, active in many different countries. It’s a pattern that I’ve seen again and again and again: if an invention appears to be from out of the blue, chances are that you just haven’t seen the full story. Progress does not come in leaps. It is the product of dozens or even hundreds of accumulated, marginal steps.
The Invasion of Normandy begins! – WW2 – Week 250 – June 10, 1944
World War Two
Published 10 Jun 2023The Allies’ gigantic amphibious invasion of France begins and by the end of the week they’ve carved out a decent-sized beachhead. Meanwhile in Italy the Allied advance takes Rome. The Soviets are launching new attacks of their own — now against the Finns, and the Japanese at Kohima … have just plain had enough.
(more…)
Minimum alcohol pricing fails utterly in reducing “problem” drinking, but it’s aces for padding the state’s coffers
Christopher Snowden counts coup on Scotland’s utterly failed “minimum pricing model” for alcohol which has cost Scots additional hundreds of millions of pounds for no discernable improvement in any measurable:
This study was published yesterday and got no attention whatsoever from the media despite it being written by a team in Sheffield who used to get blanket coverage for their every pronouncement. What changed? Well, they used to produce models showing that minimum alcohol pricing would work and now they’ve produced a study showing that their model didn’t work.
The results above suggest the introduction of MUP in Scotland did not lead to a decline in the proportion of adult drinkers consuming alcohol at harmful levels. It also did not lead to any change in the types of alcoholic beverage consumed by this group, their drinking patterns, the extent to which they consumed alcohol while on their own or the prevalence of harmful drinking in key subgroups.
Oof! So much for the “exquisitely targeted” policy of minimum pricing being an “almost perfect alcohol policy because it targets cheap booze bought by very heavy drinkers“.
After building your entire reputation on modelling minimum pricing, it must have been painful for them to write this …
… the lack of evidence for a decline in the prevalence of harmful drinking arising from MUP is contrary to model-based evidence that informed the introduction of the policy.
Hey-ho. I guess the model was garbage, as I said from the start. Never mind. It’s only cost drinkers in Scotland a few hundred million pounds. Will the Supreme Court be taking another look at that court case that was won off the back of an incorrect model?
The lack of change in the prevalence of harmful drinking may arise for several reasons. First, people drinking at harmful levels may be less responsive to price changes than lighter drinkers.
You don’t say! If only someone had mentioned this earlier!
Previous qualitative research and studies of purchasing behaviour among people with alcohol dependence (i.e. a group that comprises approximately 20% of those drinking harmfully in the United Kingdom and thus 1% of the overall population) supports this view. However, the very large price increases imposed by MUP on people drinking harmfully, their inability to switch to cheaper products and clear evidence of successful policy implementation and compliance, mean their price responsiveness would need to be extremely low to negate any impact on consumption.
But it is extremely low! I explained this over a decade ago when I took the model to task for making the plainly daft assumption that heavy drinkers are more price sensitive than moderate drinkers. I wrote:
“The model assumes that minimum pricing will have more effect on the consumption patterns of heavy drinkers than on moderate drinkers because heavy drinkers are more price-sensitive. This is a convenient belief since it is heavy drinkers who cause and suffer the most alcohol-related harm, but can we really assume that someone with an alcohol dependency is more likely to be deterred by price rises than a more casual consumer? The SAPM model says that they are, and yet there is ample evidence to support the common sense view that heavy drinkers and alcoholics are less price-sensitive than the general population (eg. Gallet, 2007; Wagenaar, 2009). Indeed, research has shown that price elasticity for the heaviest drinkers is ‘not significantly different from zero’ — they will, in other words, purchase alcohol at almost any cost.”
You don’t need an encyclopaedic knowledge of the price elasticity literature to work this out. For most people, it falls under the umbrella of the bleeding obvious. Here we are 11 years later and the penny still hasn’t quite dropped at Sheffield, but we’re getting closer.
Ask Ian: Why So Few Reproduction Historic Guns?
Forgotten Weapons
Published 22 Feb 2023From Paul on Patreon:
“I’ve always thought there were a lot of older guns that deserve to be reproduced, many of which could be really simple to manufacture. PSA is planning the release of their StG44 repro which is exciting. But why don’t we see this sort of thing more often. I suppose not everyone in the firearms community is going to want this sort of thing, but I think there are a lot of guns that would sell well enough to justify their reproduction.”Fundamentally, we don’t see more reproduction firearms because they are actually a lot harder and more expensive to make than people would think, and the market for them is smaller than people would think. Re-engineering old firearms for new production is a really substantial project, and the original data required rarely exists. The guns must be cheap enough and reliable enough to attract modern buyers, which will often require compromises on authenticity — which immediately reduces the already-small pool of potential buyers.
(more…)
QotD: The revolt against “meritocracy”
As with almost every one of these crusades the left goes on, it ain’t what they’re saying it is. And those of us on the right(ish) who think that it’s all part of a master plan to destroy society so the great communist utopia appears automagically aren’t precisely right. I mean, most people on the left would welcome collapse, because, yes, they believe a communist matriarchy is ONLY waiting for the “oppressors” who create capitalism and patriarchy to vanish (oblivious to the fact that “capitalism” is trading, which seems to be a natural condition of the human monkey and not eradicable by any regime real or imaginary; and that “patriarchy” doesn’t exist in the west.) But that’s not the point, because they don’t think they’re bringing about collapse. They think they’re fighting injustice.
When we say “merit” and “meritocracy” they think we’re using “code words” to say “white males”. There are reasons for this, besides the fact that the left is heavily into Manichaean thought systems that go something like: identify problem — find a person who MIGHT be responsible for/benefits from the system as it exists — assume that if that person were removed, the problem would be gone. See, French Revolution.
The initial confusion on the left arises from the fact that they might never, in fact, have witnessed meritocracy in their dealings or those of people around them.
This is because, as part of the long march, and to secure absolute control of all fields and institutions, the left has a mythology (the Manichaean thing again) that anyone who disagrees with them is evil. And of course, you don’t hire evil people.
The problem with that type of hiring is that you’re NOT hiring the best. And most people know they’re not the best. And hire someone less bright than they are. This in four generations takes you to the level of management/operation that takes monarchies twenty generations of inbreeding to achieve.
Right now, in everything but the hard sciences and STEM (and they’ve gotten into some of those, and can’t always be routed around.) the people in power would consider pouring piss out of a boot with the instructions written on the sole a feat of unachievable genius.
Most of them are so vacuous they don’t even know they’re incompetent. Or, like Michelle Obama in her essay on why everyone was mean to her at Harvard, they assume everyone else is just as incompetent.
The reason they get hired, stay hired and continue to get push/accolades/power is that they have the “right picture in head” by which you should understand “the left picture in head”. They view the world exactly as they were taught to view it by their Marxist teachers and professors. Reality is Manichean, and if there is any issue at all, you find the person who might be causing it (hint, usually you find the person who is a heretic to the left, even if in a minor thing) and you attack that person. If the person is not immediately obvious, you look for deviationism or examples of hidden thought crime.
It’s appalling, and in a society with no protection for the individual, it fills mass graves, but it is the way their minds — for lack of a better term — operate. They’ve been trained to operate that way. Not to look at human nature, or the conditions in the world, or even the limits of engineering and materials (what’s holding us back on batteries, for instance. They prefer to think oil executives, personally, are holding back the all-electric solar cars we should already have.) No. “Find the culprit” “Eliminate him/her” “Everything is beautiful in the garden”. Seen in this light, the Green Nude Heel makes “perfect sense”. And is a genius work in scope. Which is why she got all upset at criticism and thought that it only meant people wanted her to find all the little subculprits and work out all the details of the pogroms necessary to make it work. Not getting that people were saying “Not in this world, not with these humans, not in this REALITY”.
Sarah Hoyt, “Just Deserts”, According to Hoyt, 2019-06-06.
June 10, 2023
Do you also dream of apocalypse?
John Psmith certainly does, as he explains before plunging into a review of a book on Chinese warfare between 300 and 900 AD:
I have a secret confession to make. Late at night, when Mrs. Psmith and the Psmithlets are all tucked away in their beds, I like to stay up in my study and fantasize about … the end of the world. But not just any end of the world, because most apocalypses are very boring. For example: “AI unleashes killer nanobots that turn everybody into paperclips.” Yawn. How dull. Where’s the drama in that? No, like all disordered fantasies, mine are fun, and ever-so-conveniently constructed to push the bounds of plausibility while still being technically possible. I’m mostly fantasizing about apocalypses where almost everybody dies, but where one dashing and well-prepared man with pluck and determination and a giant pile of book reviews can restore an island of order and civilization. Hey come on, it could happen!
Most apocalypses would be awful — we would all die instantly, or else we would all die slowly and painfully, but somewhere perfectly balanced in the middle are the apocalypses that would be very exciting, and those are the emotional driver that lead me to engage in a mild degree of prepping. Now like all potential addicts, I have some hard and fast rules, clear lines that prevent me from spending all my family’s savings on refurbishing an old missile silo. My main rule is that any prepping I do has to have a dual use in some less exciting but more likely scenario.
So I store a lot of water in my basement because, look the US government tells me it could be useful in the event of a regional or local disaster. We have emergency bags pre-packed that include a list of rendezvous locations a day’s walk from our house because, hey, there are all kinds of reasons we might need that, okay? I own this tool so I can shut off my gas in the event of an earthquake and totally not because it looks handy for bludgeoning feral packs of marauders, so stop judging me. I have precious metals buried in the ground in a secret location because, uhhh … it’s good to have a tail-risk hedge in your portfolio, all right? What’s that? Why is there ammo in there too? Look, a good portfolio should be anti-fragile …
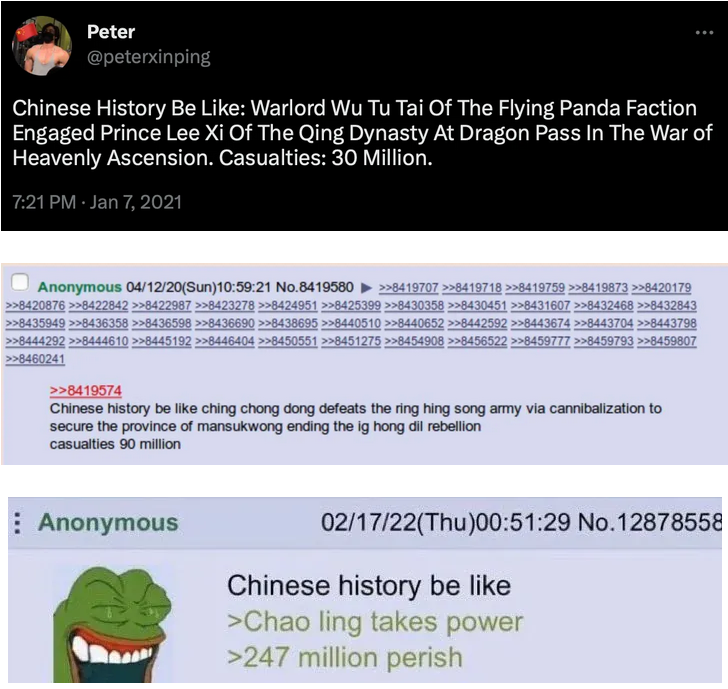
I think all of this is why I like Chinese history so much, because it’s just way crazier, bloodier, and more apocalyptic than the history of most other places. In Western Europe civilization collapsed once (okay fine, twice (okay, fine, three times)), and we’re still ruminating over it and working through this unending cultural psychodrama like some civilization-scale therapy addict. Meanwhile, in China, civilization collapsing is like Tuesday. The history of China is an endless cycle of mini-apocalypses in which the entire political, economic and moral order gets razed to the ground and Mad Max conditions prevail for a few decades or centuries, until somebody gathers enough power in his hands to establish a new dynasty and all is peaceful and harmonious under heaven. A few hundred years later, that new regime grows tired and old, the Mandate of Heaven slips away, and the cycle repeats.
Feeding a Greek Hoplite – Ancient Rations
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 6 Jun 2023
(more…)
Remember the Freedom Convoy of 2022?
The media worked very hard to demonize the grassroots protests that coalesced into the Canadian Freedom Convoy in early 2022, and they’ve continued to push the notion that either the movement was an utter failure or that it was a maple-flavoured January 6 “insurrection” righteously suppressed by our beloved Dear Leader and his stormtroops. Someone using the handle “Kulak” wants to remind you that the convoy wasn’t a failure and in fact was the catalyst for great changes both in Canada and around the world:

A screenshot from a YouTube video showing the protest in front of Parliament in Ottawa on 30 January, 2022.
Photo via Wikimedia Commons.
I keep encountering this misconception from people who don’t follow Canadian politics …
That somehow the Trucker convoy was defeated.
The Freedom Convoy was the most wildly immediately successful protest in Canadian history, maybe WORLD history.
People remember Trudeau’s crackdown, old ladies having their skulls cracked with batons, Disabled indigenous grandmothers trampled by police horses, Bank accounts frozen and public employees investigated for mere donations …
And there’s a big reason people remember this … It was dramatic, and the media and the regime certainly wanted you to think resistance was futile …
What people don’t remember is what happened in the immediate aftermath: The government caved on absolutely everything within a week for the most important things, and then a month or so for the rest.
First off there was the massive political shift that happened as the convoy was occurring:
Jason Kenny, the pro-lockdown Premiere of Alberta (Canada’s most conservative province) was forced to announce his resignation, and Alberta immediately lifted all its lockdown impositions.
Erin O’Toole the pro-lockdown leader of the Conservative Party was likewise forced to resign, his temporary replacement Candice Bergen (not to be mistaken with the actress) being a longtime rival opposed to lockdowns, and his main rival who replaced her after intra-party elections was Pierre Poilievre, the politician after Maxime Bernier who was quickest to embrace the Truckers and their cry for freedom.
As the convoy was ongoing Trudeau invoked the Emergencies Act (the Act which replaced the War Measures Act for invoking Martial Law) … Now these grant the government almost unlimited powers, famously the War Measures Act was invoked by Trudeau’s Father to detain Quebeckers and raid hundreds of homes without warrants during the FLQ separatist crisis of 1972 … the catch is that while the follow on Emergencies Act can be invoked by a Prime Minister Parliament has to sign off on the act’s continued use within one week.
Well skulls were cracked, accounts frozen, and as the week passed things came down to the deadline … On the very last night … Trudeau managed to get sign-off (without the Conservative opposition) from the House of Commons, but it had to go to the Upper House, the Canadian Senate.
NOW. The Canadian Senate is a shameful institution.
It’s like the British House of Lords but without the nobility.
A Senate seat is a lifetime appointment, by the Prime Minister … and that’s it. Little to no review, no democratic input, and this is supposed to be equivalent or superior to our elected House of Commons …
Naturally the go-to use of the Senate is as a spoils system for cronies. Do some shameful favour for a Prime Minister, raise a lot of money for the party, be politically connected to a provincial gov the PM wants to buy off … get a Senate seat.
One of the longest-standing political agreements in Canada is how badly the Senate needs to be abolished … but can’t be because Quebec is nominally overrepresented in the Senate, and abolishing it would cause a constitutional crisis.
H/T to Donna Laframboise for the link.
George MacDonald Fraser – Quartered Safe Out Here
We Have Ways of Making You Talk
Published 16 Jan 2023Merry Christmas from “We Have Ways of Making You Talk”. Over the next 12 days Al and James are reading extracts from some of their favourite books about the Second World War. Today Al is reading from Quartered Safe Out Here, by George MacDonald Fraser.
(more…)