Amy Eileen Hamm reports on how the British Columbia College of Nurses and Midwives (BCCNM) acted on its concern that not enough complaints against their members were being lodged by First Nations people:
As regular readers of Quillette will know, many Canadian institutions have fervently adopted the cause of “decolonization” — a vaguely defined term that one university describes as the dismantling of “assumed Euro-western disciplinary constructs and traditions”. This can mean anything from abolishing musical scales (which “perpetuate and solidify the hegemony of [the] Euro-American repertoire”); to reimagining our scientific understanding of sunlight, so as to correct “the reproduction of colonialism” that has infected “physics and higher physics education”; to assailing the gender binary through a “decolonizing act of resistance”.
That’s the theory, anyway. In practice, institutional efforts at “decolonization” generally translate into affirmative-action hiring programs and policies to mandate symbolic (generally empty) gestures such as land acknowledgements. They’ve also created a cash cow for “specialist” administrators and third-party consultants in what is now known as the “equity, diversity, inclusion, and decolonization” sector. The premise is that decolonization is so difficult and complex that it can only be overseen by said (highly paid) professionals.
My own professional sector, nursing, provides a useful case study. In British Columbia, where I live and work, nurses are licenced by the British Columbia College of Nurses & Midwives (BCCNM), whose offices are located “on unceded Coast Salish territory, represented today by the Musquea?m, Squamish and Tsleil-Waututh Nations.” In other words, Vancouver.
If a patient feels that he or she has experienced “incompetent, unethical, or impaired nursing or midwifery practice”, he or she can complain to the BCCNM through its complaints portal. It’s not a complicated process. You send an email describing what the nurse allegedly did, when the incident occurred, and whether there were any witnesses. If you’ve already complained to someone else, you’re supposed to note that as well, along with your suggestions for resolving the complaint. That’s it.
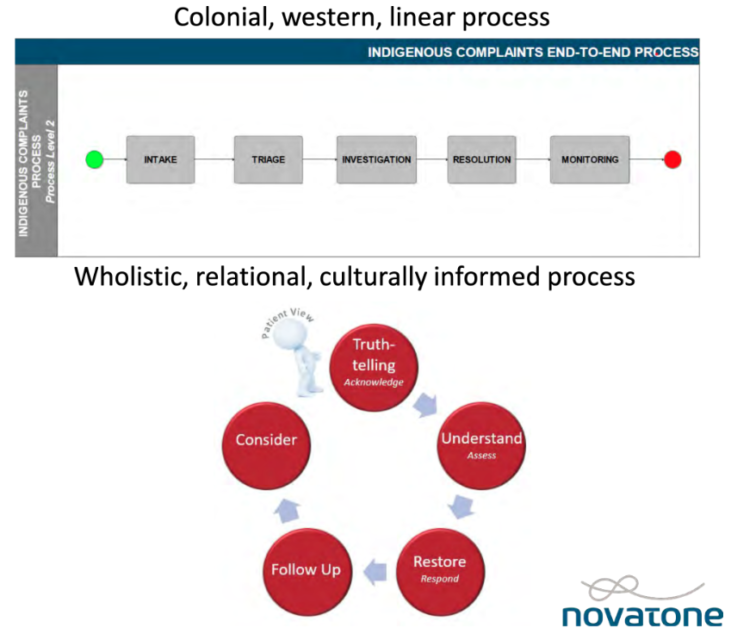
But apparently, this process is just too onerous — and even dangerous — for Indigenous people. And so the BCCNM has paid C$97,000 to a self-described “boutique business process management firm” called Novatone, which has duly produced a lengthy report on how to “make the BCCNM complaints process safer for Indigenous Peoples.” The same title — mantra might be a better word — appears at the top of all 50 pages: Looking Back to Look Forward: How Indigenous ways of being, knowing, and doing must inform the BCCNM feedback process and reflect the principles of cultural safety, cultural humility, and anti-racism.
(For the benefit of those outside Canada, the mystical-sounding phrase, “ways of knowing”, along with its “being” and “doing” variants, has now entered the official idiom as a means to signify the unfalsifiable shaman-like intuitions that supposedly guide the consciousness of Indigenous people throughout every facet of their existence — including, apparently, complaining about the care they receive from nurses.)