Ever met a pro athlete? How about a fighter pilot, or a trauma surgeon? I’ve met a fair amount of all of them, and unless they’re on their very best behavior they all tend to come off as raging assholes. And they get worse the higher up the success ladder they go — the pro athletes I’ve met were mostly in the minors, and though they were big-league assholes they were nothing compared to the few genuine “you see them every night on Sports Center” guys I met. Same way with fighter pilots — I never met an astronaut, but I had buddies at NASA back in the days who met lots, and they told me that even other fighter jocks consider astronauts to be world-class assholes …
The truth is, they’re not — or, at least, they’re no more so than the rest of the population. It’s just that they have jobs where total, utter, profoundly narcissistic self-confidence is a must. It’s what keeps them alive, in the pilots’ case at least, and it’s what keeps you alive if, God forbid, you should ever need the trauma surgeon. Same way with the sportsballers. I can say with 100% metaphysical certainty that there are better basketball players than Michael Jordan, better hitters than Mike Trout, better passers than Tom Brady, out there. There are undoubtedly lots of them, if by “better” you mean “possessed of more raw physical talent at the neuronal level”. What those guys don’t have, but Jordan, Brady, Trout et al do have, is the mental wherewithal to handle failure.
Everyone knows of someone like Billy Beane, the Moneyball guy. So good at football that he was recruited to replace John Elway (!!) at Stanford, but who chose to play baseball instead … and became one of the all-time busts. He had all the talent in the world, but his head wasn’t on straight. Not to put too fine a point on it, he doubted himself. He got to Double A (or wherever) and faced a pitcher who mystified him. Which made him think “Maybe I’m not as good as I think I am?” … and from that moment, he was toast as a professional athlete. Contrast this to the case of Mike Piazza, the consensus greatest offensive catcher of all time. A 27th round draftee, only picked up as a favor to a family friend, etc. Beane was a “better” athlete, but Piazza had a better head. Striking out didn’t make him doubt himself; it made him angry, and that’s why Piazza’s in the Hall of Fame and Beane is a legendary bust.
The problem though, for us normal folks, is that the affect in all cases is pretty much the same … and it’s really hard to turn off, which is why so many pro athletes (fighter jocks, surgeons, etc.) who are actually nice guys come off as assholes. It’s hard to turn off … but as it turns out, it’s pretty easy to turn ON, and that’s in effect what Game teaches.
Severian, “Mental Middlemen II: Sex and the City and Self-Confidence”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-06.
March 11, 2024
QotD: The profound asshole-ishness of the “best of the best”
March 10, 2024
QotD: Sustainability
I would argue that financial stability has everything to do with environmental sustainability (though I will admit that this comparison is a bit hard since environmentalists seem to bend over backwards to NOT define “sustainability” very precisely). In fact, I think that sustainability is baked right into the heart of capitalism.
The reason for this comes back to the magic of prices. Of all the amazing, wondrous things we celebrate in the world, prices may be the most overlooked. Just think of it: with no governing structure or top down ruling board, a single number encapsulates everything most everyone in the world knows about a particular product: both its utility and relative scarcity, both now and as anticipated in the future. It is a consensus derived voluntarily between millions of people who never meet with each other and likely never communicate with each other.
It is amazing to me that people who talk so much about their concern for scarcity tend to be the same folks who ignore prices and even eschew markets and capitalism. But in prices we have a number that gives us a single metric telling us the world’s consensus on the current and future scarcity of any commodity.
We do know that prices can miss some things. Perhaps most relevant today, they can fail to include the cost of emissions (ground, water, air) associated with that commodities extraction, refining and processing, and use. But compared to the effort of trying to create some alternate structure for managing product scarcity, this is a relatively simple problem to fix (simple technically, but not necessarily politically). Estimates of these pollution costs can be added as a tax (e.g. a carbon tax on fossil fuels to take into account climate effects of CO2 emissions) and prices will continue to work their magic but with these new factors added.
Warren Meyer, “Sustainability Is Baked Right Into the Heart of Capitalism”, Coyote Blog, 2019-10-10.
March 9, 2024
Salt – mundane, boring … and utterly essential
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes looks at the importance of salt in history:
There was a product in the seventeenth century that was universally considered a necessity as important as grain and fuel. Controlling the source of this product was one of the first priorities for many a military campaign, and sometimes even a motivation for starting a war. Improvements to the preparation and uses of this product would have increased population size and would have had a general and noticeable impact on people’s living standards. And this product underwent dramatic changes in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, becoming an obsession for many inventors and industrialists, while seemingly not featuring in many estimates of historical economic output or growth at all.
The product is salt.
Making salt does not seem, at first glance, all that interesting as an industry. Even ninety years ago, when salt was proportionately a much larger industry in terms of employment, consumption, and economic output, the author of a book on the history salt-making noted how a friend had advised keeping the word salt out of the title, “for people won’t believe it can ever have been important”.1 The bestselling Salt: A World History by Mark Kurlansky, published over twenty years ago, actively leaned into the idea that salt was boring, becoming so popular because it created such a surprisingly compelling narrative around an article that most people consider commonplace. (Kurlansky, it turns out, is behind essentially all of those one-word titles on the seemingly prosaic: cod, milk, paper, and even oysters).
But salt used to be important in a way that’s almost impossible to fully appreciate today.
Try to consider what life was like just a few hundred years ago, when food and drink alone accounted for 75-85% of the typical household’s spending — compared to just 10-15%, in much of the developed world today, and under 50% in all but a handful of even the very poorest countries. Anything that improved food and drink, even a little bit, was thus a very big deal. This might be said for all sorts of things — sugar, spices, herbs, new cooking methods — but salt was more like a general-purpose technology: something that enhances the natural flavours of all and any foods. Using salt, and using it well, is what makes all the difference to cooking, whether that’s judging the perfect amount for pasta water, or remembering to massage it into the turkey the night before Christmas. As chef Samin Nosrat puts it, “salt has a greater impact on flavour than any other ingredient. Learn to use it well, and food will taste good”. Or to quote the anonymous 1612 author of A Theological and Philosophical Treatise of the Nature and Goodness of Salt, salt is that which “gives all things their own true taste and perfect relish”. Salt is not just salty, like sugar is sweet or lemon is sour. Salt is the universal flavour enhancer, or as our 1612 author put it, “the seasoner of all things”.
Making food taste better was thus an especially big deal for people’s living standards, but I’ve never seen any attempt to chart salt’s historical effects on them. To put it in unsentimental economic terms, better access to salt effectively increased the productivity of agriculture — adding salt improved the eventual value of farmers’ and fishers’ produce — at a time when agriculture made up the vast majority of economic activity and employment. Before 1600, agriculture alone employed about two thirds of the English workforce, not to mention the millers, butchers, bakers, brewers and assorted others who transformed seeds into sustenance. Any improvements to the treatment or processing of food and drink would have been hugely significant — something difficult to fathom when agriculture accounts for barely 1% of economic activity in most developed economies today. (Where are all the innovative bakers in our history books?! They existed, but have been largely forgotten.)
And so far we’ve only mentioned salt’s direct effects on the tongue. It also increased the efficiency of agriculture by making food last longer. Properly salted flesh and fish could last for many months, sometimes even years. Salting reduced food waste — again consider just how much bigger a deal this used to be — and extended the range at which food could be transported, providing a whole host of other advantages. Salted provisions allowed sailors to cross oceans, cities to outlast sieges, and armies to go on longer campaigns. Salt’s preservative properties bordered on the necromantic: “it delivers dead bodies from corruption, and as a second soul enters into them and preserves them … from putrefaction, as the soul did when they were alive”.2
Because of salt’s preservative properties, many believed that salt had a crucial connection with life itself. The fluids associated with life — blood, sweat and tears — are all salty. And nowhere seemed to be more teeming with life as the open ocean. At a time when many believed in the spontaneous generation of many animals from inanimate matter, like mice from wheat or maggots from meat, this seemed a more convincing point. No house was said to generate as many rats as a ship passing over the salty sea, while no ship was said to have more rats than one whose cargo was salt.3 Salt seemed to have a kind of multiplying effect on life: something that could be applied not only to seasoning and preserving food, but to growing it.
Livestock, for example, were often fed salt: in Poland, thanks to the Wieliczka salt mines, great stones of salt lay all through the streets of Krakow and the surrounding villages so that “the cattle, passing to and fro, lick of those salt-stones”.4 Cheshire in north-west England, with salt springs at Nantwich, Middlewich and Northwich, has been known for at least half a millennium for its cheese: salt was an essential dietary supplement for the milch cows, also making it (less famously) one of the major production centres for England’s butter, too. In 1790s Bengal, where the East India Company monopolised salt and thereby suppressed its supply, one of the company’s own officials commented on the major effect this had on the region’s agricultural output: “I know nothing in which the rural economy of this country appears more defective than in the care and breed of cattle destined for tillage. Were the people able to give them a proper quantity of salt, they would … probably acquire greater strength and a larger size.”5 And to anyone keeping pigeons, great lumps of baked salt were placed in dovecotes to attract them and keep them coming back, while the dung of salt-eating pigeons, chickens, and other kept birds were considered excellent fertilisers.6
1. Edward Hughes, Studies in Administration and Finance 1558 – 1825, with Special Reference to the History of Salt Taxation in England (Manchester University Press, 1934), p.2
2. Anon., Theological and philosophical treatise of the nature and goodness of salt (1612), p.12
3. Blaise de Vigenère (trans. Edward Stephens), A Discovrse of Fire and Salt, discovering many secret mysteries, as well philosophical, as theological (1649), p.161
4. “A relation, concerning the Sal-Gemme-Mines in Poland”, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 5, 61 (July 1670), p.2001
5. Quoted in H. R. C. Wright, “Reforms in the Bengal Salt Monopoly, 1786-95”, Studies in Romanticism 1, no. 3 (1962), p.151
6. Gervase Markam, Markhams farwell to husbandry or, The inriching of all sorts of barren and sterill grounds in our kingdome (1620), p.22
March 8, 2024
A fresh look at the PUA “bible”
In UnHerd, Kat Rosenfield considers the original pick-up artist bible, The Game by Neil Strauss, in light of more than a decade of changes in how moderns approach relationships with the opposite sex:
A decade letter, I’m struck by the astonishing prescriptiveness of this line: the notion that any sexual encounter preceded by flirtation, negotiation, or indeed any assessment of a suitor’s desirability should be understood as “less-than-ideal” — and that any man who seeks to make himself desirable to an as-yet-uncertain woman is doing something inherently sleazy. Granted, the anti-Game backlash began in the form of reasonable scrutiny of controversial seduction techniques like “negging” (a slightly backhanded compliment deployed for the sake of flirtation).
But since then it has morphed into something much stranger: the idea that anything a man does to impress a woman, from basic grooming to speaking in complete sentences, should be viewed with suspicion. Behind this is the same low-trust mindset that leads women to treat every date as a hunt for the red flags that reveal her suitor as a secret monster. If he compliments you? That’s lovebombing, which means he’s an abuser. If he doesn’t compliment you, that’s withholding, which also means he’s an abuser. Other alleged “red flags” include oversharing, undersharing, paying for the date, not paying for the date, being too eager, being five minutes late, and drinking water — or worse, drinking water through a straw.
Today, the turn against pick-up artistry can be understood at least in part as a reaction against some of its more prominent contemporary practitioners, including men such as Andrew Tate, who makes Mystery look like a catch by comparison. But it is also no doubt an outgrowth of a culture in which male sexuality has effectively been characterised as inherently predatory, while female sexuality is seen as virtually non-existent. The question that seduction manuals once aimed to answer — “how do I, a shy young man, successfully and confidently approach women?” — is now, in itself, a red flag, one likely to provoke anything from squawking indignation to abject horror to bystanders wondering if they ought to call the police. That you are even thinking of approaching women just goes to show what a troglodyte you really are. What do women want? The contemporary answer appears to be: to be left alone, forever, until they die — or to meet someone in a safe and sanitised way, via dating app … although even that option is increasingly positioned as inherently dangerous.
Meanwhile, I was surprised upon revisiting The Game to realise that the strategies contained within the book are not just useful but mostly in keeping with more traditional dating and courtship advice, from “peacocking” (wearing something eye-catching or unusual that can act as a conversation starter), to passing “shit tests” (responding with humour and confidence when a woman teases you). Even the much-derided negging wasn’t originally designed with the goal of insulting or belittling women, but rather to teach men how to talk to them without fawning and drooling all over the place. In the end, the message of The Game is more or less identical to the one in popular women’s dating guides, like The Rules or He’s Just Not That Into You: that confidence is sexy, and naked desperation is a turnoff.
And while this may just be a function of one too many viewings of the BBC’s Pride & Prejudice (featuring Mr Darcy, a man in possession of £50,000 a year and an absolutely legendary negging game), I wonder if the aim of seduction guides is, paradoxically, to restore our confidence in the tension, the mystery, and the playfulness of courtship in the age of the casual hookup. Even as we rightly rejoice in the fact that society no longer stigmatises women for desiring and pursuing sex, there is surely still something to be said for subtlety — and just because we aren’t consigned to the role of the passive damsel, dropping a handkerchief on the ground in the hope that the right man will pick it up, that doesn’t mean every woman wants to be horny on main. It’s not just that announcing your desire through a megaphone can seem uncouth; it’s also a lot less exciting than the dance of lingering glances, double entendres, and simmering chemistry that characterises a mutually-desired seduction in the making. Certain people might deride this brand of sexual encounter as “less-than-ideal” for its political incorrectness, but it’s wildly popular — in novels, in films, and in the fantasies of individual women — for a reason.
Meanwhile, the contemporary dating landscape is one in which the sheer fun of dating, courtship, and, yes, falling into bed together has been largely back-burnered in favour of something at once formal and immensely self-serious. In a world of handwringing over sexual consent — in which a man just talking to a woman at a coffeeshop can trigger an emergency response protocol — the stakes of sex itself come to seem unimaginably high, a breakneck gamble where one wrong move will result in a lifetime of trauma (or, if you’re a guy, a lifetime on a list of shitty men). Add to this the proliferation of dating apps, which makes the entire romantic enterprise feel more like a job search than a playground, and the whole thing begins to seem not just fraught but inherently adversarial — a negotiation between two parties whose interests are completely at odds, who cannot trust each other, and where there’s a very real risk of terrible and irreparable harm.
March 7, 2024
The WPATH to danger … for children and teens
Andrew Doyle outlines the exposure of internal communications from the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) showing some extremely concerning things about the organization and the political agenda of many of its members:
The ideological march through the medical institutions was rapid and unexpected. In recent years, we have seen leading paediatric specialists asserting that children who say they are “in the wrong body” must have their feelings immediately affirmed. We have been told that if a boy claims to be a girl, or vice versa, they must be believed and fast-tracked onto a pathway to medicalisation: first puberty blockers, then cross-sex hormones, and in some cases irreversible surgery.
This worldwide medical scandal has disproportionately impacted gay, autistic, and gender non-conforming children. Where clinicians should have been looking out for the interests of the vulnerable, they have been encouraging them to proceed with experimental treatments. Few people would have imagined that mutilating children to ensure they better conform to gendered stereotypes would one day be considered progressive. But here we are.
Much of the responsibility must lie in the hands of WPATH (World Professional Association for Transgender Health), a US-based organisation established in 1979 that is recognised as the leading global authority in this area. WPATH has pushed for the normalisation of the “gender-affirming” approach, and its “Standards of Care” have formed the basis of policies throughout the western world, including in the NHS.
But in an explosive series of leaked files, the credibility of WPATH might now be irreparably shattered. Whistleblowers have provided author and journalist Michael Shellenberger with videos and messages from the WPATH internal chat system which suggest that the health professionals involved in recommending “gender-affirming” healthcare are aware that it is not scientifically or medically sound. A full report has been written by journalist Mia Hughes for the Environmental Progress think-tank. The title is as chilling as its contents: The WPATH Files: Pseudoscientific Surgical and Hormonal Experiments on Children, Adolescents, and Vulnerable Adults.
Some of the leaked internal messages are astonishing in their disregard for basic medical and ethical standards. For all that paediatric gender specialists have publicly stated that there is a consensus in favour of the “affirmative” model, that it is evidence-based, and that it is safer than a psychotherapeutic alternative, their private conversations would seem to suggest otherwise.
There are messages in the WPATH Files proving that surgeons and therapists are aware that a significant proportion of young people referred to gender clinicians suffer from mental health problems. Some specialists associated with WPATH are proceeding with treatment even for those who cannot realistically consent to it. After all, how could a pre-pubescent or even adolescent child fully grasp the concepts of lifelong sterility and the loss of sexual function? As one author of the WPATH “Standards of Care” acknowledges in a leaked message:
[It is] out of their developmental range to understand the extent to which some of these medical interventions are impacting them. They’ll say they understand, but then they’ll say something else that makes you think, oh, they didn’t really understand that they are going to have facial hair.
Or what about the endocrinologist who admits that “we’re often explaining these sorts of things to people who haven’t even had biology in high school yet”? And these are the very patients who have been approved for potentially irreversible procedures.
March 6, 2024
March 5, 2024
The National Microbiology Laboratory scandal in brief
Tristin Hopper rounds up some of the eye-opening details of the security breach at Winnipeg’s National Microbiology Lab which certainly looks like a factor in the Wuhan Coronavirus pandemic story:
Whether or not COVID-19 started as an accidental lab leak, the pandemic just so happens to have originated in the same neighbourhood as the Wuhan Institute of Virology, home to a coronavirus laboratory with a known history of lax security protocols.
For that reason alone it’s a major scandal that Canada’s own high-security biolab was employing two scientists – married couple Xiangguo Qiu and Keding Cheng – who according to CSIS exhibited a reckless disregard of lab security and the protection of confidential information. Now, tack on the fact that both Cheng and Qiu are suspected of prolonged unauthorized contact with the Chinese government.
This week, Health Canada bowed to opposition pressure and published an illuminating package of more than 600 official documents detailing CSIS’s evidence against the couple, as well as internal emails from the Winnipeg-based National Microbiology Laboratory where they worked. The highlights are below.
The lab is surprisingly casual about shipping planet-altering pathogens
One of the main accusations against Qiu is that she sent lab samples to China, the U.S. and the U.K. without proper authorization. Around this same time, she also sent highly virulent Ebola samples to the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
[…]
Cheng was accused of breaking virtually every cyber-security law in the book
If Qiu’s signature offence was sending out lab materials without proper authorization, Cheng’s was that he routinely ignored even the most basic protocols about computer security.
[…]
Throughout, both were in constant (unauthorized) touch with China
The CSIS reports don’t necessarily frame Qiu and Cheng as traitors.
[…]
The pair kept changing their story after being presented with smoking gun evidence, according to CSIS
Some of the documents’ more cinematic passages are when CSIS agents describe lengthy interrogations in which the pair were confronted about their alleged breaches of Canadian national security.
February 28, 2024
QotD: When the rules in the dating market all changed
So far we’ve only been talking about guys, but the gals went through their own version of the same process way back in the days. Indeed, it’s because the girls changed that the guys got into PUA in the first place.
Under the old dispensation, back before the Clinton Era (1988-2001), everyone acknowledged that there were a lot of users and abusers, douchebags and parasites and losers, out there in the world. That being the case, simply being an all-around ok guy with a steady job — what the PUAs came to term “beta providers” — was, in itself, a pretty solid resume in the dating market. “Just be yourself” was every guy’s dad’s advice when it came to dating, and back then it was pretty solid, since it was assumed that the decent job etc. flowed from being a decent human being. And since every girl’s mom was telling her complementary things, the system worked … until it didn’t, and you can date the change precisely: June 6, 1998, the premiere of the HBO series Sex and the City.
[…] Everyone has met one of those “one of the guys”-type girls. They’re great fun, and while you know what I mean when I say they’re not necessarily marriage material as-is, you therefore also know what I mean when I say they really are what feminists all claim to be: Strong, confident women. They are what they are, and they know it, take it or leave it.
The problem is, most women — and, it goes without saying, all feminists — aren’t “strong, confident women”, in the same way the vast majority of guys aren’t naturally “alpha males”. That’s the dialectic I’ve been trying to get at in this series of posts. Sex and the City, as much as every episode needs to be burned and the ashes shot into deep space, was just the manifestation of a long-developing process. Thanks to all that “self-esteem” shit that started in the Seventies, sometime in the Clinton Era a critical mass of young women decided that what they needed was to be “strong” and “self-confident”. But they didn’t know how to do that, because the people telling them this were fat lesbian college professors. Then HBO, sensing a valuable market niche, got into the act …
Sex and the City […] is the gayest show in the history of television. Carrie and the Gals don’t act like women; they act the way women think men act — which is to say, they act like gay men. Recall that the late 1990s also saw an explosion of female “comedians”, whose one “joke” was some version of “I got my period today, but damn, I still crave dick.” (Sex and the City, you’ll recall, was pitched as a comedy). And that’s a serious problem, because as every straight guy has said at least once in his life, being gay would be fabulous if not for the “sex with guys” part. I mean, how awesome would it be (every young man thinks), if you could reorient your whole life around your crotch?
Severian, “Mental Middlemen III: SATC”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-06.
February 26, 2024
QotD: Lockdown rebuttal
First, lockdowns were neither prudent nor essential. It’s not as if government officials considered the collateral damage to be inflicted on the economy, society, and health – not all health problems are caused by covid – by the lockdowns and then rationally concluded that the benefits of locking down outweighed these costs. No. The collateral damages were ignored. As the New York Times‘s Joe Nocera and Vanity Fair‘s Bethany McLean – authors of the just-released The Big Fail – write, “But there was never any science behind lockdowns – not a single study had ever been undertaken to measure their efficacy in stopping a pandemic. When you got right down to it, lockdowns were little more than a giant experiment.”1 In no universe is such a policy prudent.
Nor were lockdowns “essential”. As Nocera and McLean note,
… the weight of the evidence seems to be with those who say that lockdowns did not save many lives. By our count, there are at least 50 studies that come to the same conclusion. After The Big Fail went to press, The Lancet published a study comparing the COVID infection rate and death rate in the 50 states. It concluded that “SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 deaths disproportionately clustered in U.S. states with lower mean years of education, higher poverty rates, limited access to quality health care, and less interpersonal trust – the trust that people report having in one another.” These sociological factors appear to have made a bigger difference than lockdowns (which were “associated with a statistically significant and meaningfully large reduction in the cumulative infection rate, but not the cumulative death rate”.)
Second, the lockdowns were, contra Mr. Orrell’s claim, utterly unprecedented. Isolating individuals known to be infected, such as Typhoid Mary, is a categorically different measure than locking down whole societies. Such lockdowns were never used until China locked Wuhan down in early 2020. Here again are Nocera and McLean: “On April 8, 2020, the Chinese government lifted its lockdown of Wuhan. It had lasted 76 days – two and a half months during which no one was allowed to leave this industrial city of 11 million people, or even leave their homes. Until the Chinese government deployed this tactic, a strict batten-down-the-hatches approach had never been used before to combat a pandemic. Yes, for centuries infected people had been quarantined in their homes, where they would either recover or die. But that was very different from locking down an entire city; the World Health Organization called it ‘unprecedented in public health history’.”
It’s jarring to encounter in an essay that features many excellent arguments – as Mr. Orrell’s does – such irrational and utterly uninformed claims as Mr. Orrell offers about lockdowns.
Donald J. Boudreaux, responding to an article by Brent Orrell in Law & Liberty, 2023-10-31.
1. “COVID Lockdowns Were a Giant Experiment. It Was a Failure.” Intelligencer, October 30, 2023.
February 21, 2024
“College attendance is our society’s only meaningful initiation ritual, and it thus assumes an existential importance that renders it near-impossible to replace until an alternative is found”
Johann Kurtz believes the modern university’s survival despite its increasingly irrational and counterproductive actions can be explained as the last modern example of an initiation ritual:
Our understanding of the college system is incomplete. Until we correct this, we won’t be able to fix or replace the system.
First, consider a paradox: college attendance remains near all-time highs [Link], yet the majority of Americans no longer believe it is worth the cost [Link].
The college system seems irrationally resistant to declining value. We must therefore ask: is there an important non-rational reason for college attendance which we have failed to acknowledge?
I believe the answer is “Yes”. College attendance is our society’s only meaningful initiation ritual, and it thus assumes an existential importance that renders it near-impossible to replace until an alternative is found.
Our culture is historically anomalous in lacking explicit initiation rituals.
Mircea Eliade, the great religious historian of the 20th-century, defined initiation rituals as “a body of rites and oral teachings whose purpose is to produce a decisive alteration in the religious and social status of the person to be initiated“.
In philosophical terms, initiation is equivalent to a basic change in existential condition; the novice emerges from his ordeal endowed with a totally different being from that which he possessed before his initiation; he has become another.
— Mircea Eliade, Rites and Symbols of Initiation: The Mysteries of Birth and Rebirth
In Europe, fully expressed initiation rituals were common until the end of the Middle Ages, and in the wider world, until the end of the First World War. Now, they only persist in the West in the sacramental practices of devout Christians (baptism, confirmation, and so forth).
Once, however, these practices were of tremendous importance to us, as Eliade makes clear:
To gain the right to be admitted among adults, the adolescent has to pass through a series of initiatory ordeals: it is by virtue of these rites, and of the revelations that they entail, that he will be recognized as a responsible member of the society. Initiation introduces the candidate into the human community and into the world of spiritual and cultural values. He learns not only the behavior patterns, the techniques, and the institutions of adults but also the sacred myths and traditions of the tribe, the names of the gods and the history of their works …
In the absence of local community rituals, the universities are a natural site for their replacement. These have always been religious sites, although the nature and expression of this religion has transmuted over time.
H/T to Bruce Gudmundsson at Extra Muros for the link and his additional comments:
This hypothesis accords with the argument, made often in this blog, that education and schooling are two very different things. At the same time, it suggests that one of the definitive purposes of Extra Muros, the encouragement of young people to eschew the conventional college experience in favor of a combination of practical pursuits and systematic self-tuition, may be a fool’s errand. After all, if four (or five or six) years of drinking second-rate beer from red plastic cups does for the office-bound folk of North America what fear-filled rites of passage do for members of the bone-in-the-nose set, then I might well be sailing against the wind.
Upon second thought, I find hope in the possibility that the parasite (or, to be more precise, the cancer) promoted by d’Angelo, Kendi, and company will soon deal the coup de grâce to its mortally-wounded host.
The coming-of-age ordeals of warrior tribes demand that boys who would be men prove possession of such martial virtues as courage and self-command. The rites-of-passage of the modern middle classes, however, require that postulants demonstrate a mixture of conformity, conscientiousness, and, to a diminishing degree, intelligence. (Readers familiar with the oeuvre of economist Bryan Caplan will recognize the source of this troika. However, it is worth noting that, while Professor Caplan will occasionally tip his hat in the direction of the campus-based building of basic brain-power, he devotes far more attention to the collegiate cultivation of the two components of Sitzfleisch.)1
The cult of Marx, Mao, and Marcuse demands complete compliance, not only with its basic tenets, but also with any changes in the party line that, from time to time, may occur. (I am old enough to remember the days when campus commies of the caucasian persuasion could don dashikis without facing charges of “cultural appropriation”.) Thus, those who sit at the feet of the acolytes of critical theory learn an art of great value to people who wish to thrive in a large organization, that of discarding the old hat, and putting on the new one, at just the right time. (Think, if you will, of the mid-level employees of the McDonalds Corporation, who, over the course of the last four decades, were obliged to alter their opinion of the McRib sandwich more often than they changed the oil in their cars.)
1. Bryan Caplan, The Case Against Education: Why the Education System is a Waste of Time and Money (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2018), pages 9-21.
February 16, 2024
QotD: The PUA (Pick-up artist)
If you’ve read The Game […] you can’t help being struck by how expensive all this must be, both in time and money. Mystery, the first PUA guru who kicked the whole “community” off by offering classes, charged something like $1-5000 for a week-long class — serious money back then, and that’s before you consider that guys were flying in from all over the country, indeed from all over the world, to take them. That aside, consider what it would take to hit at least three Sunset Strip clubs a night, three nights a week. I’m well past my bar-hopping days, but when I was in grad school, the “trendy” clubs in College Town charged $10-20 just in cover …
This was two decades or more ago, and College Town was in Podunkville. Imagine what they’re charging to get into the hot nightspots on the Sunset Strip. I bet just getting into the clubs costs these aspiring PUAs a couple hundred bucks, every week, for months. Then there’s all the other stuff Strauss said he did to transform himself into “Style” — laser-whitening his teeth, tanning beds, classes on elocution and posture, a whole new (and ever-changing) wardrobe, surfing. I can’t even begin to calculate it, but at one point he and three other PUAs are living in a Hollywood Hills mansion that once belonged to one of the Rat Pack — monthly rent, $50K. Then throw in the fact that all of this takes a tremendous amount of time, and consider the toll that must take on your body. I hit the sauce pretty hard back in my day, and one of the reasons I stopped was that the hangovers really started hurting — one night of bar-hopping now, and I’d be bedridden for days. I’m getting exhausted just typing this, and do you see what I mean?
And all this without getting a single girl. I think everyone here has been in at least one relationship, so we know that no matter how casual you keep it, bare-bones relationship management, even of pump-and-dumps, takes a fairish bit of time (so I’ve heard, anyway). I might be misremembering, but at one point Strauss claims he was managing something like four or five more or less long-term hookups simultaneously. I don’t think there are enough hours in the day …
Much better, then, to just say you’re a PUA. To do it Tyler Durden style, in other words. I’m pretty sure you could sell the illusion of yourself as a hardcore PUA with one not-too-expensive night on the town. Just dress up like one of these goobers, hit up one bar, and take selfies with a bunch of girls, making sure to alter the shot angles enough that no one can tell you’re in the same bar the whole time. Post one or two stories of your conquests a week, and you could portray yourself as some kind of pickup master in no time at all.
Of course, that’s if you want to consciously fake it. I have no idea what “Tyler Durden” was doing, not being a sociopath myself, but as Strauss tells it, his disciples got snookered into it. They really did want to learn how to pick up girls, but since dressing up like a PUA and talking about getting girls is much easier than actually getting girls, a night on the town with those guys ended up being an endless series of “approaches”. Again, it’s how you define “effective”, and Strauss lets the cat out of the bag a bit when he informs us of the PUA’s weird lingo for “closing”. There’s the “f-close”, of course, which should be obvious, but there’s also the “kiss close” and even the “phone number close” … and both of those count as complete successes.
Severian, “Mental Middlemen”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-05.
February 9, 2024
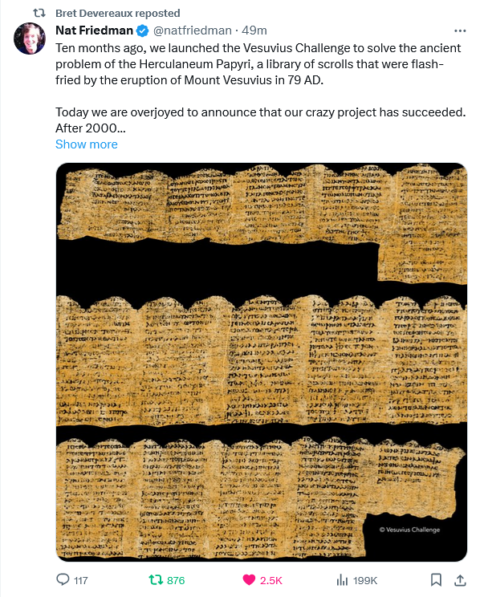
The (so-far limited) ability to read the Herculaneum Papyri may vastly increase our knowledge about the Roman world
Colby Cosh on the achievement of the three young researchers who were awarded the Vesuvius Challenge prize earlier this month, and what it might mean for classicists and other academics:
On Monday morning, Farritor and two other young Vesuvius Challenge notables, Youssef Nader and Julian Schillinger, were announced as winners of the grand prize. Nader and Schillinger had, like Farritor, already won Vesuvius Challenge prizes for smaller technical discoveries, and Nader had in fact been a mere heartbeat behind Farritor in producing the same “porphyras” from the same scan. After Farritor nabbed his US$40,000 “first letters” prize, the three decided to combine their efforts to net the big fish.
The result is a text that represents about five per cent of one of the thousands of scrolls recovered — and there may be more not yet recovered — from the Villa of the Papyri. The enormous villa was owned by an unknown Roman notable, but there are clues that one of its librarians was the Epicurean philosopher Philodemus of Gadara, who lived from around 110 to 35 BC. Until his identity was connected with the library, Philodemus did not receive too much attention even from classicists. But the Vesuvius Challenge efforts have now yielded fragments of what has to be an Epicurean text — one which discusses the delights of music and food, and condemns an unnamed adversary, possibly a Stoic, for failing to give a philosophical account of sensual pleasure.
The recovery of dozens more of the works of Philodemus would be — one might now say “will be” — a world-changing event for the classics. We know Philodemus was close to Calpurnius Piso (101-43 BC), the father-in-law of Julius Caesar and a likely owner of the doomed villa. He almost certainly had a front-row seat for the prelude to the end of the Roman Republic. We know he wrote works on religion, on natural philosophy and on history: even his thoughts on music and poetry would be of marked interest.
But nobody knows what else, what copies of older works, may be lurking in Philodemus’s library. At this moment antiquarians know the titles of dozens of lost plays by Aeschylus and Sophocles and Euripides and Aristophanes; we are missing major works of Aristotle and Euclid and Archimedes and Eratosthenes. We know that Sulla wrote his memoirs and that Cato the Elder wrote a seven-book history of Rome. Any of these old writings, or others of equal significance, may materialize suddenly out of oblivion now, thanks to the Vesuvius Challenge. It’s an impressive triumph for the idea of prize-giving as an approach to solving scientific problems, and the news release from the challenge offers a discussion of what the funding team got right and where the project will go next.