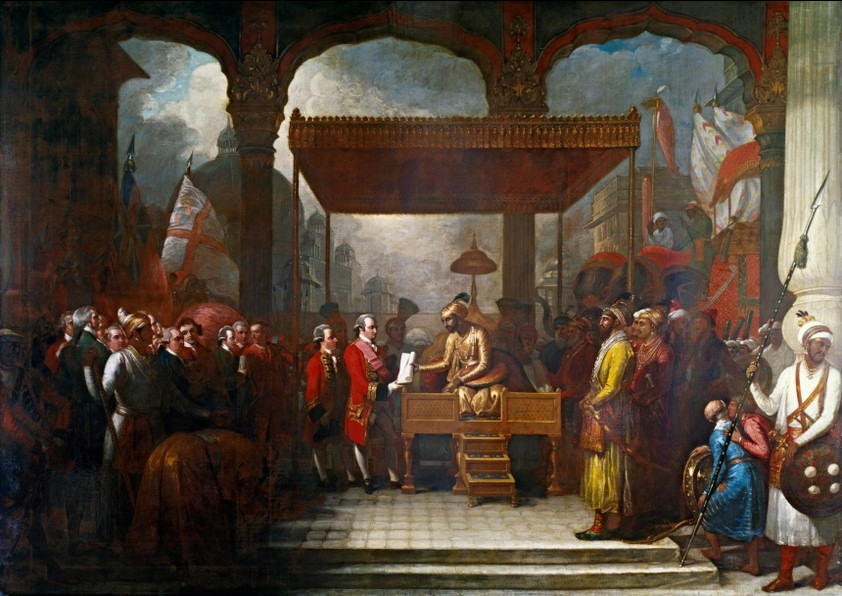
Fraser Myers explains why the much-remarked-upon British crime statistics showing huge increases in hate crimes are much more a statistical artifact than a true reflection of the state of British society:
Allegedly, England and Wales are in the grip of a “surge” in homophobic and transphobic hate crime. “The rate of LGBT hate crime per capita rose by 144 per cent between 2013-14 and 2017-18”, it reports. Hate-crime hotspots like South Yorkshire and Hampshire experienced even larger surges, it claims, with police-recorded crimes rising by 376 per cent and 189 per cent in the same period, respectively.
To make matters worse, according to LBGT campaigners, this rise in hate crime doesn’t even capture the true extent of the hatred out there. Taz Edwards-White, alliance manager at equalities and diversity organisation Metro, told the Guardian that the hate-crime figures were likely to be “the tip of the iceberg”. She and other campaigners say this rise could be down to the rise of right-wing populism.
The truth is rather different. Every year for the past five years, the release of police-recorded data on hate crime has been accompanied by panicked media reports of a hate-crime surge. But as last year’s Home Office report made abundantly clear, large increases “are due to the improvements made by the police in their identification and recording of hate-crime offences and more people coming forward to report these crimes rather than a genuine increase” (emphasis mine).
What’s more, there is a good reason why the “surge” identified by the Guardian takes off in 2013-2014. 2014 was the year the College of Policing released its Hate Crime Operational Guidance [PDF], which is still used to this day. This guidance actually demands that the numbers increase. “Targets that see success as reducing hate crime are not appropriate”, it says. As part of the drive to record more crime, there has been a slew of public-information campaigns and regular exhortations from police for the public to report hateful incidents, particularly in the wake of major political events like the EU referendum and the 2017 terror attacks.
Police-recorded data has other problems, too. Police are obliged to record not only criminal actions but also all non-crime hate incidents. A non-crime hate incident is literally any event that is perceived by the victim or any other person to be motivated by hostility towards a so-called protected characteristic. The key word here is perceived. As the Operational Guidance makes clear: “The victim does not have to justify or provide evidence of their belief, and police officers or staff should not directly challenge this perception. Evidence of the hostility is not required for an incident or crime to be recorded as a hate crime or hate incidents.”