One that continues to baffle me is the indefatigable enthusiasm of some fans for explaining to others that Barrayaran neo-feudalism is a terrible system of government, as if their fellow readers couldn’t figure that out for themselves. It seems to rest on an a-historical understanding, or simply a lack of understanding, of feudalism, a system that died out in our world five hundred years ago, to be replaced by geographically based national states. (Well, four hundred years ago, in Japan.) From the passion these readers bring to the table, one would gather they imagine insidious card-carrying Feudalists are dire threat to the lifeblood of our nation. I’m not sure I should tell them about the SCA.
Portrayal is not promulgation, people.
That said, I’ve spent thirty years learning that no writer, be they ever so clear and plain, can control how readers read, or misread, their texts. Reading is a dance, not a march. If some readers step on one’s feet, well, it’s still better than sitting by the wall … Usually.
Lois McMaster Bujold, “Lois McMaster Bujold on Fanzines, Cover Art, and the Best Vorkosigan Planet”, Tor.com, 2017-11-02.
March 23, 2022
QotD: Fansplaining that feudalism is bad
March 7, 2022
QotD: Historical fiction and fantasy works usually leave out the vast majority of the people who did all the work
… there is a tendency when popular culture represents the past to erase not merely the farmers, but most of the commons generally. Castles seem to be filled with a few servants, a whole bunch of knights and lords and perhaps, if we are lucky, a single blacksmith that somehow makes all of their tools.
But the actual human landscape of the pre-modern period was defined – in agrarian societies, at least – by vast numbers of farms and farmers. Their work proceeded on this cyclical basis, from plowing to sowing to weeding to harvesting and threshing to storage and then back again. Religious observances and social festivals were in turn organized around that calendar (it is not an accident how many Holy Days and big festivals seem to cluster around the harvest season in late Autumn/early Winter, or in Spring). The uneven labor demands of this cycle (intense in plowing and reaping, but easier in between) in turn also provided for the background hum of much early urban life, where the “cities” were for the most part just large towns surrounded by farmland (where often the folks living in the cities might work farmland just outside of the gates). People looked forward to festivals and events organized along the agricultural calendar, to the opportunities a good harvest might provide them to do things like get married or expand their farms. The human drama that defines our lives was no less real for the men and women who toiled in the fields or the farmhouses.
And of course all of this activity was necessary to support literally any other kind of activity.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Bread, How Did They Make It? Part III: Actually Farming”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-08-06.
February 7, 2022
History Summarized: Vikings
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 14 Jul 2017Huge thanks to our friend Shad at Shadiversity! Check out his channel for historical weaponry and much more: https://www.youtube.com/user/shadmbrooks
Grab your swords and hop in your longboats, because it’s time to learn a thing or two about the Vikings!
This video was produced with assistance from the Boston University Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program.
Thanks to patron Karl Erik L Hoftaniska for suggesting this topic!
PATREON: www.patreon.com/user?u=4664797
MERCH LINKS:
Shirts – https://overlysarcasticproducts.threa…
All the other stuff – http://www.cafepress.com/OverlySarcas…Find us on Twitter @OSPYouTube!
From the comments:
Finn Chitwood
4 years ago
In the words of a brilliant Icelandic magazine: “Viking was a seasonal, temporary occupation, not an ethnicity.”
January 3, 2022
How did the Greeks and Romans count Years?
toldinstone
Published 31 Dec 2021The AD/CE system we use to date the year was introduced — more or less by accident — during the Middle Ages. Before its invention, the classical world used a wide range of dating systems.
Please consider supporting this channel on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/toldinstoneIf you liked this video, you might also enjoy my book Naked Statues, Fat Gladiators, and War Elephants: Frequently Asked Questions about the Ancient Greeks and Romans:
https://www.amazon.com/Naked-Statues-…
If you’re so inclined, you can follow me elsewhere on the web:
https://www.reddit.com/r/AskHistorian…
https://www.instagram.com/toldinstone/
https://www.goodreads.com/author/show…Chapters:
0:00 Introduction
0:51 Ancient Greek Calendars
1:42 Counting by Olympiads
2:22 The Seleucid Era
2:56 Consular Dating
3:26 Ab Urbe Condita
4:28 Indictions
4:56 Christian Chronology
5:40 Anno Domini
7:00 Conclusion
December 29, 2021
A history of and my first go at MEDIEVAL TENNIS
Lindybeige
Published 28 Sep 2021Thanks to Audible for sponsoring this video. New Audible members get a 30-day free trial. Visit http://audible.com/lindybeige or text “lindybeige” to 500 500 to try Audible today.
Tennis is a very old sport, going back at least to the 1200s. Here I try my hand at it for the very first (but not last) time, and talk about the history of it a bit.
Many thanks to Jesmond Dene Real Tennis Club (https://www.jdrtc.co.uk) where this was shot.
Editing this took a LONG time. We had three cameras recording at the same time, and synching the footage up took an age. The sound consisted mainly of echoing footsteps and ball bounces, and the fact that the main microphone kept glitching did not help (you will notice some of the patches to the sound using other mics, but most I made fairly smooth).
Court map by Atethnekos at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Anne Boleyn picture by English school – https://thetudortravelguide.com/2019/…, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Support me on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/Lindybeige
Buy the music – the music played at the end of my videos is now available here: https://lindybeige.bandcamp.com/track…
Buy tat (merch):
https://outloudmerch.com/collections/…Lindybeige: a channel of archaeology, ancient and medieval warfare, rants, swing dance, travelogues, evolution, and whatever else occurs to me to make.
▼ Follow me…
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Lindybeige I may have some drivel to contribute to the Twittersphere, plus you get notice of uploads.
My website:
http://www.LloydianAspects.co.uk
December 23, 2021
Cheshire and Durham in the English Parliament
In his end-of-the-year Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes looks at two of the historic counties of England that lacked Parliamentary representation until surprisingly late dates:
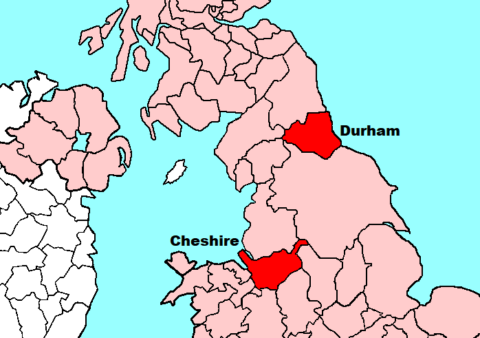
Cheshire and Durham (post-medieval boundaries: English county boundaries have varied wildly over the centuries).
Base map by Hogweard at Wikimedia Commons.
England, compared to other parts of Europe, is often said to have been remarkably centralised early on. France, for example, in the late eighteenth century had some thirteen or so regional parliaments, while Britain just had the one. Scotland’s separate parliament was famously dissolved in 1707, with the official union of Scotland with England. Wales gained representation at the English parliament at Westminster from 1536. So far so expected.
But less well-known is that the county of Cheshire — some of it now disappeared under Greater Manchester — used to have an entirely separate parliament of its own, and was not represented at Westminster until 1543. Arguably, it has about as much historical claim to a national assembly today as Wales. Rule of Cheshire was even, very briefly, included among the various titles of the monarch. Richard II, as well as being king of England, was in 1397-99 also styled “Prince of Chester”. He drew his personal bodyguard from among the men of Cheshire too. So whatever happened to Cheshire nationalism?
On a related note: the mantra “no taxation without representation” looms large in the history of American independence. But parts of England itself had gone unrepresented for decades too. County Durham, traditionally ruled by its prince-bishop, was not represented by any MPs in the House of Commons at all until 1654. And as it only gained representation under the revolutionary Protectorate, this was undone upon the restoration of the monarchy in 1660. The county would not be represented again until 1675.
Why? One might argue that the bishop of Durham, who sat in the House of Lords, could be considered its parliamentary representative. But he was not elected, and most importantly had little say over the matter of parliamentary taxation, which was controlled by the Commons. Before 1603 this was not much of an issue, as county Durham was exempt from various taxes because it was near the hostile Scottish border. But the accession of James VI of Scotland to become king of England meant that the hostile border suddenly disappeared. County Durham thus became subject to parliamentary taxation without having any say over those taxes at all — a situation that they then had to bear for over sixty years! Where were the Durham revolutionaries?
November 27, 2021
Making a Medieval TART DE BRY (Brie Tart) | Brie: The King of Cheese
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 28 Apr 2020This Tart de Bry, or Brie Tart, comes from The Forme of Cury and was served at the table of King Richard II (1367 – 1400). Its flavor is nearly as rich as the history of the cheese that goes into it, and in this episode I will explore both.
Help Support the Channel with Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/tastinghistory
Follow Tasting History with Max Miller:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tastinghist…
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TastingHistory1Episodes mentioned in this video:
Medieval Cheesecake (for tart dough) – https://youtu.be/GCCJ2Qpr1nM
Medieval Cheese (for straining cheese) – https://youtu.be/vlQZ3NPnoLk
Rapé Fig Spread: https://youtu.be/_o7Oq-OjKu8LINK TO INGREDIENTS & TOOLS**
SAFFRON THREADS – https://amzn.to/2yTwoPS
PIE SHIELD – https://amzn.to/2YeTnjh
TART TIN – https://amzn.to/2yPbUrCLINK TO SOURCE:
The Forme of Cury: https://amzn.to/31frAAy**Amazon offers a small commission on products sold through their affiliate links, so each purchase made from this link, whether this product or another, will help to support this channel with no additional cost to you.
TART DE BRY
RECIPE (1390 – The Forme of Cury)
Take a crust ynch depe in a trape. Take yolkes of ayren rawe and chese ruayn and medle it and the yolkes together. And do thereto powdor gynger, sugar, safron and salt. Do it in a trape, bake it, and serve it forth.MODERN RECIPE (Based on Lorna J Sass’s adaptation from To The King’s Taste – https://amzn.to/3bNg2XE)
INGREDIENTS
– 1 pound of Brie cheese, the younger the better
– 6 egg yolks
– ⅛ tsp saffron (about 10 threads ground up)
– ¾ tsp light brown sugar or more if you want a sweeter tart.
– ⅜ teaspoon powdered ginger
– A pinch of salt
– A sprinkle of nutmeg or cinnamon (optional)METHOD
1. Preheat the oven to 425°F / 220°C.
2. Roll out your tart dough to about an ⅛ inch thick and line your tin. Add pie weights and set in the oven to blind bake for 10 minutes. Remove the crust and remove the pie weights. If the bottom of the crust is not fully cooked, return it to the oven without the weights for 5 minutes. Once out of the oven, press down the bottom of the crust if it has risen. Allow crust to cool completely and reduce the oven temperature to 350°F / 175°C.
3. Remove the rind from the brie saving some to the side. Then cut the brie into small pieces and place in a blender with the egg yolks. Blend together. Then add the saffron, brown sugar, ginger, and salt and blend to combine.
4. Place a bit of the rind on the bottom of the tart and add the cheese mixture and smooth the top. If you are using cinnamon or nutmeg, sprinkle a bit on top now.
5. Bake at 350°F / 175°C for 30 to 40 minutes or until the top is set and begins to brown. Serve warm or at room temperature.SOURCES
The Forme of Cury – By Samuel Pegge – https://amzn.to/3cXBycA
To The King’s Taste – Lorna J. Sass – https://amzn.to/3bNg2XE
The Course of History: 10 Meals that Changed the World – https://amzn.to/2yWuIoL
Brie Cheese History – https://www.thespruceeats.com/history…PHOTOS
Abbaye Notre-Dame-de-Jouarre – Fredlesles CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…)
By J. Chéreau – Musée de la Révolution française, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
A carriage underside has broken sending the occupants flying Wellcome / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…)
Blue Stilton – Coyau / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0
Limberger Cheese – Original photo by John Sullivan
Gruyere – © Rolf Krahl / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…)
Stracchino – Cvezzoli / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…)
Brie cheese with fresh thyme on black background – Marco Verch / CC BY-SA 2.0 (https://flickr.com/photos/160866001@N…)#brie #cheese #medieval #medievalfood #tastinghistory #medievalrecipes
November 25, 2021
History of Venice: Rise to Glory
Epic History TV
Published 14 Dec 2018Listen to or download the music HERE: smarturl.it/epichistoryvenice
Music by https://www.musicdesigngroup.comThanks to Elias Tsiantas for the 3D Venetian galley footage
Thanks to Miłek Jakubiec for the Battle of Marignano imageSupport the channel & get exclusive previews at Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/epichistorytvWant to learn more? We recommend A History of Venice by the late John Julius Norwich, a great popular historian on all things Mediterranean (as an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases): http://geni.us/7q71zx
#EpicHistoryTV #HistoryofVenice
October 31, 2021
Soul Cakes & Trick-or-Treating
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 30 Oct 2020Help Support the Channel with Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/tastinghistory
Follow Tasting History here:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tastinghist…
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TastingHistory1
Reddit: r/TastingHistoryLINKS TO INGREDIENTS & EQUIPMENT**
Canon EOS M50 Camera: https://amzn.to/3amjvwu
Canon EF 50mm Lens: https://amzn.to/3iCrkB8
Currants: https://amzn.to/2T3qItA
Nutmeg: https://amzn.to/2IGDlcb
Clove: https://amzn.to/3dyNWRP
Mace: https://amzn.to/31j625h
Saffron: https://amzn.to/3560pbP
KitchenAid Stand Mixer: https://amzn.to/37hsboALINKS TO SOURCES**
The Customs and Traditions of Wales by Trefor Owen: https://amzn.to/37gi6bt
The Book of Hallowe’en by Ruth Eda Kelley: https://amzn.to/3dDb41i
Trick or Treat: A History of Halloween by Lisa Morton: https://amzn.to/348t0xQ**Amazon offers a small commission on products sold through their affiliate links, so each purchase made from this link, whether this product or another, will help to support this channel with no additional cost to you.
Editor: WarwicSN – https://www.youtube.com/WarwicSN
SOUL CAKES
ORIGINAL 16TH CENTURY RECIPE (From Elinor Fettiplace’s Receipt Book)
To make Cakes
Take flower & sugar & nutmeg & cloves & mace & sweet butter & sack & a little ale barm, beat your spice & put in your butter & your sack, cold, then work it well all together & make it in little cakes & so bake them, if you will you may put in some saffron into them or fruit.MODERN RECIPE
INGREDIENTS
– ½ Cup Lukewarm Ale (Below 100°F/38°C)
– 1 Teaspoon Yeast
– 3 Cups (360g) Flour
– ½ Cup (100g) Sugar
– 4 Tablespoons Butter Softened
– ½ Teaspoon Salt (if you’re using unsalted butter)
– ¼ Teaspoon Nutmeg
– ¼ Teaspoon Clove
– ¼ Teaspoon Mace
– ⅓ Cup Sack or Sherry
– 1/4 Teaspoon Saffron Threads (optional)
– 3/4 Cup Dried Fruit, plus more for decoration. (Optional)
– 1 Egg for Egg Wash (Optional)METHOD
1. Create an “ale barm” by mixing the yeast with the lukewarm ale and letting sit for 10 minutes. If you are using saffron, mix that into the sherry and let steep.
2. In a large bowl, mix the flour, sugar, salt, nutmeg, clove, and mace together. Add the yeasted ale and work it in. Then work in the softened butter and the sack with saffron along with any fruit you are using. Mix until everything the dough comes together, then knead for 5 – 12 minutes. The longer you knead, the more bread-like the cakes will be, but the more they will rise.
3. Allow dough to rise for 1 hour (it will likely not double in size), then punch the dough down and form into small cakes. Cover and allow the cakes to rise for another 20 minutes while you preheat the oven to 400°F/200°C.
4. When the cakes have puffed up, add the optional egg wash and/or additional fruit, or form a cross on the top of each cake using the back of a knife (do not cut the cross in). Then back fro 20 minutes. When baked, allow to cool before serving.#tastinghistory #halloween #soulcakes
October 22, 2021
QotD: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in the ancient (or medieval) world
PTSD is more than feeling bad about being in a war, or grief at the loss of a buddy. Here are the diagnostic guidelines. Note how a diagnosis requires one intrusion symptom (involuntary and instrusive memories, dreams, flashbacks, marked physiological reactions) and persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma and two negative alterations in cognition and mood associated with the trauma and two marked alterations in arousal and reactivity associated with the trauma. A lot of the examples being cited in the comments do not come anywhere near meeting that criteria. As I read and understand that, an individual who is voluntarily recounting the trauma – much less re-exposing themselves to it by going out to fight again – without significant reactions (read the guidelines – these are really very significant reactions) doesn’t fit the criteria. They may well have another form of mental wound, mind you; grief, fear, loss, guilt and so on are all very real things. But they do not, by our current medical definition, have this wound. Specificity here is necessary because we aren’t asking a question about grief or loss or guilt – feelings which all humans feel at one point or another – but about a very specific mental wound that combat (or other trauma) may inflict.)
That is often not the impression that you would get from a quick google search (though it does seem to be the general consensus of the range of ancient military historians I know) and that goes back to arguments ex silentio. A quick google search will turn up any number of articles written by folks who are generally not professional historians declaring that PTSD was an observed phenomenon in the deep past, citing the same small handful of debatable examples. But one thing you learn very rapidly as a historian is that if you go into a large evidence-base looking for something, you will find it.
That’s not a species of research positivity – it’s a warning about confirmation bias, especially if you do not establish a standard of proof before your investigation. It is all too easy to define down your definition of “proof” until the general noise of the source-base looks like proof. In this case, we have to ask – before we go looking – what would evidence of PTSD in ancient societies (I’m going to start there because it is where I am best informed) look like?
Well, ancient societies engaged in a lot of warfare. Among the citizenry – the sort of fellows who write to us and are written about in our sources – combat experience was almost ubiquitous. That only really changes as we get into the Roman Empire, as violence levels both decline generally and are pushed to the frontier via a professional army. The percentage of veterans in the citizen population (again, citizen here is an important caveat, but then those fellows basically are our primary source base) probably equaled that of the WWI generation in Britain or France, except all the time (there’s a point in the Second Punic War where the Roman censors went through the entire rolls, checking to see how many had managed to avoid military service and found only a few thousand in a citizen body of c. 150,000 adult males). So what ought we expect from our sources? We should expect to see signs of PTSD everywhere. It should be absolutely pervasive in a source-base produced almost entirely by, for and about combat veterans, in societies where military mortality exceeded modern rates by a robust margin.
And it simply isn’t there. There is one very frequently cited account in Herodotus (Hdt. 6.117) of a man named Epizelos experiencing what is generally understood as “conversion disorder” (which used to be badly labeled “hysterical blindness”) in combat. Without being wounded he went blind at a sudden terror in battle and never recovered his sight. Herodotus terms it a θῶμα – a “wonder” or “marvel”, a word that explicitly implies the strange uncommonness of the tale. Herodotus is concerned enough about how exceptional this sounds that he is quick not to vouch for its veracity – he brackets the story (beginning and end) noting that it was what he was told (by someone else) that Epizelos used to say happened to him. In short, this was uncommon enough that Herodotus distances himself from it, so as not to be thought as a teller of tall-tales (though Herodotus is, in fact, a teller of tall tales).
This one example – cited endlessly and breathlessly in internet articles – is remarkable not because it is typical, but because it is apparently very unusual (also, it is my understanding – with the necessary caveat that I am not an expert – that while conversion disorder is a consequence of emotional trauma, it is not clear that it is associated with PTSD more generally). Meanwhile, in the war literature of the Romans, in their poetry (including that by folks like Horace, who fought in quite terrible battles), in the military literature of the Greeks, in the reflections of Xenophon (both on his campaigns and his commands), in the body of Greek lyric poetry … all of it – nothing. It is simply not there – not as a concern that such a condition might befall someone, nor a report that it had done so. Nothing. The lacuna baffled me for years.
My impression is that the medieval literature looks much the same: a few scattered passages that, if you squint hard enough, might be PTSD set against a vast backdrop of nothing in a society where literature was dominated by the war-fighting class. More examples than in the classical corpus (but then the medieval corpus is much larger; oddly, the examples I’ve seen all seem to concern crusading particularly), but nothing close to what we would expect given a literary tradition absolutely dominated by military aristocrats and their (often clerical) families. I call this my impression, because the medieval corpus is both much larger and I have read much less of it; but if there is a hidden reservoir of accounts showing clear symptoms of PTSD, I have not found it yet. I was always struck that – despite the fact that monastic life was often a destination for medieval military aristocrats troubled by their life of violence – none of the monastic rules I have read (admittedly, not all of them), which often have guidelines for abbots to deal with difficult monks, have had anything about how to deal with the symptoms of PTSD.
Now that’s not to say there isn’t grief at loss, mind you! The lamentations of defeat, the sorrow of losing a loved one (even in victory), the misery of war – that you find in the ancient texts in abundance. It occupies literary topoi, it is depicted in artwork, it gets entire tragedies to stretch out in, it is addressed by great big political speeches, it sits at the cornerstone of the Iliad‘s narrative (one reason, no doubt, that the Iliad remains a useful text for soldiers working through their experiences). But the persistent symptoms of PTSD, no. I haven’t been able to find one “flashback” or combat-memory related dissociative episode in ancient literature. You might argue that they simply weren’t recorded, but that strikes me as unlikely in societies where other forms of war-damage were so fiercely valorized and which would have often seen – as with Epizalos – such symptoms as divine omens. There should be dozens and dozens of them. These are societies with active medical literature, after all!
I think the evidence strongly suggests that ancient combatants did not experience PTSD as we do now. The problem is that the evidence of silence leads us with few tools with which to answer why. One answer might be that it existed and they do not tell us – because it was considered shameful or cowardly, perhaps. Except that they do tell us about other cowardly or shameful things. And the loss and damage of war – death, captivity, refugees, wounds, the lot of it – are prominent motifs in Greek, Roman and European Medieval literature. War is not uniformly white-washed in these texts – not every medieval writer is Bertran. We can’t rule out some lacuna in the tradition, but given just how many wails and moans of grief and loss there are in the corpus it seems profoundly unlikely. I think we have to assume that it isn’t in the sources because they did not experience it or at least did not recognize the experience of it.
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-04-24.
October 9, 2021
The incredible growth of London after 1550
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes considers some alternative explanations for London’s spectacular growth beginning in the reign of Queen Elizabeth I:
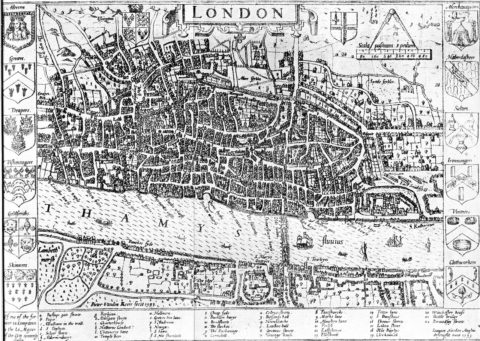
John Norden’s map of London in 1593. There is only one bridge across the Thames, but parts of Southwark on the south bank of the river have been developed.
Wikimedia Commons.
As regular readers will know, I’ve lately been obsessed with England’s various economic transformations between 1550 and 1650 — the dramatic eightfold growth of London, in particular, and the fall in the proportion of workers engaged in agriculture despite the growth of the overall population.
As I’ve argued before, I think that the original stimulus for many of these changes was the increased trading range of English overseas merchants. Thanks to advances in navigational techniques, they were able to find new markets and higher prices for their exports, particularly in the Mediterranean and then farter afield. And they were able to buy England’s imports much more cheaply, by going directly to their source. Although the total value of imports rose dramatically — by 150% in just 1600-38 — the value of exports seems to have risen by even more, as there’s plenty of evidence to suggest that for most of the period England had a trade surplus. The supply of money increased, even though Britain had no major gold or silver mines of its own.
The growing commerce was the major spur to London’s growth, with English merchants spending their profits in the city, and ever-cheaper and more varied luxury imports enticing the nobility from their country estates. Altogether, the concentration of people and wealth in London must have resulted in all sorts of spill-over effects to further drive its growth. After the initial push from overseas trade, I suspect that by the late seventeenth century the city was large enough that it was running on its own steam.
But on twitter, economic historian Joe Francis offered a slightly different narrative. Although he agrees that a change to overseas trade was the prime mover, he suggests that the trade itself was too small as a proportion of the economy to account for much of London’s growth. I disagree, for various reasons that I won’t go into now, but Joe brought to my attention various changes on the monetary side. Inspired by the work of Nuno Palma, he suspects that it was not the trade per se, but the fact of an export surplus that was doing the heavy lifting, by increasing the country’s money supply.
An increased money supply should have facilitated England’s internal trades, reducing their costs, and allowing for greater regional specialisation. Joe essentially thinks that I’ve got the mechanism slightly back to front: instead of London’s growing demands having reshaped the countryside, he contends that the specialisation of the entire country is what allowed for the better allocation of economic resources and workers to where they were most productive — a process from which a large city like London quite naturally then emerged.
I have some doubts about whether this process could really have been led from the countryside. The regional specialisation that we see in agriculture, for example, only really starts to become obvious from the 1600s onwards, by which stage London’s population had already begun to balloon from a puny 50,000 in 1550, to 200,000 and rising. I also haven’t found much evidence of other internal trade costs falling. Internal transportation — by packhorse, river, or down the coast — doesn’t seem to have become all that more efficient. Roads and waggon services don’t show much sign of improvement until the eighteenth century, and not many rivers were made more navigable before the mid-seventeenth century either. This is not to say that England’s internal trade didn’t increase. It certainly did, as London sucked in food and fuel in ever larger quantities, and from farther and farther afield. But it still looks like this was led by London demand, rather than by falling costs elsewhere.
Besides, the influxes of bullion from abroad would have all been channelled through London first, along with most of the country’s trade. To the extent that monetisation made a difference to the costs of trade then, this would have made a difference first in the city, before emanating out to its main suppliers, and then outwards. I thus see the Palma narrative as potentially complementary to my own.
October 4, 2021
History Summarized: Sicily
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 1 Oct 2021The plot twist of Medieval Italian History is that the main event was happening in the South — In the centuries before the Renaissance, Sicily and southern Italy were sporting one of the most spectacular cultures in the world, combining the greatest hits of Mediterranean history in one place. It’s way cool, you guys.
SOURCES & Further Reading: Sicily: An Island at the Crossroads of History by John Julius Norwich, The Great Cities in History by John Julius Norwich, Great Courses Lectures “Muslims in the Court Of Roger II – 1130” from Turning Points in Middle Eastern History by Eamonn Gerron and “Renaissance Italy’s Princes and Rivals” from Renaissance: The Transformation of the West by Jennifer McNabb
This video’s topic was requested by our patron Salvatore Corasaniti. Thank you for supporting our channel!
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
PODCAST: https://overlysarcasticpodcast.transi…
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/osp
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
From the comments:
Overly Sarcastic Productions
2 days ago
I can’t even begin to describe how much Ancient Sicily Content™ I had to cut for time.
Fear not, Magna Graecia will get the spotlight it deserves in another video.
-B
September 20, 2021
History-Makers: Maimonides
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 17 Sep 2021“From Moses to Moses, there was none like Moses.” Jump into 1100s Cordoba & Cairo as we take a look at the life of one of the Medieval world’s most boundary-breaking History-Makers: Moses Maimonides!
SOURCES & Further Reading: Great Courses lectures “Jewish Scholar in Cairo: Moses Maimonides” from The History and Achievements of the Islamic Golden Age by Eamonn Gearon and “Maimonides and Jewish Law” from Great Minds of the Medieval World by Dorsey Armstrong. Britannica “Maimonides” https://www.britannica.com/biography/…, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy “Maimonides” https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/ma…, The Guide For The Perplexed, Mishne Torah and Commentary on the Mishnah by Maimonides
Special thanks to Yellow/LudoHistory for his assistance in checking over my script. You can check out his livestreams playing historically-inspired videogames over at https://www.twitch.tv/ludohistory
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
PODCAST: https://overlysarcasticpodcast.transi…
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/osp
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
September 15, 2021
Hansa – Northern Silk Road – Economic History
Kings and Generals
Pubished 14 Sep 2021Use our code
KINGSANDGENERALS10and link: https://bit.ly/3mACCeg to get 10% off (save up to $47!) your own authentic Japanese subscription box from Bokksu! Don’t miss out on this amazing snack-journey through Japan!Kings and Generals animated historical documentary series on medieval history and economic history continues with a video on Hansa, also known as the Hanseatic League, which played a crucial role in the European trade in the late medieval, becoming known as the Northern Silk Road and dominating Baltic and North Sea trade for centuries.
Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/KingsandGenerals or Paypal: http://paypal.me/kingsandgenerals. We are grateful to our patrons and sponsors, who made this video possible: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1o…
The video was made by Michael Merc https://bit.ly/340tcO2 while the script was researched and written by Matt Hollis. 2d art and animation – amicus verus (https://www.artstation.com/amicus_verus). Narration by Officially Devin (https://www.youtube.com/user/OfficiallyDevin)
✔ Merch store ► https://teespring.com/stores/kingsand…
✔ Podcast ► http://www.kingsandgenerals.net/podcast/
✔ Twitter ► https://twitter.com/KingsGenerals
✔ Instagram ► http://www.instagram.com/Kings_GeneralsProduction Music courtesy of Epidemic Sound: http://www.epidemicsound.com
#Documentary #Hansa #EconomicHistory
This video was sponsored by Bokksu
September 8, 2021
500 Year-Old Pizza VS Today
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 25 May 2021Help Support the Channel with Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/tastinghistory
Tasting History Merchandise: crowdmade.com/collections/tastinghistoryFollow Tasting History here:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tastinghist…
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TastingHistory1
Tiktok: TastingHistory
Reddit: r/TastingHistory
Discord: https://discord.gg/d7nbEpyTasting History’s Amazon Wish List: https://amzn.to/3i0mwGt
LINKS TO INGREDIENTS & EQUIPMENT**
Sony Alpha 7C Camera: https://amzn.to/2MQbNTK
Sigma 24-70mm f/2.8 Lens: https://amzn.to/35tjyoW
10 inch removable bottom pan: https://amzn.to/3f8ZZI0
Rose Water: https://amzn.to/3oL0xqILINKS TO SOURCES**
Scappi Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o4Ymv…
Tomato Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=beBQg…
Pizza – A Global History by Carol Helstosky: https://amzn.to/3bHFPCQ**Some of the links and other products that appear on this video are from companies which Tasting History will earn an affiliate commission or referral bonus. Each purchase made from these links will help to support this channel with no additional cost to you. The content in this video is accurate as of the posting date. Some of the offers mentioned may no longer be available.
Subtitles: Jose Mendoza
PHOTO CREDITS
Stuffed pizza from Giordano’s: By TNVWBOY – https://www.flickr.com/photos/tnvwboy…, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Lombardi’s Pizza: By Beyond My Ken – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Sushi Pizza: Quinn Dombrowski from Berkeley, USA, CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…, via Wikimedia Commons
Pizza Bagels: Mike Mozart https://www.flickr.com/photos/jeepers…MUSIC CREDITS
“Bushwick Tarentella” – Thatched Villagers by Kevin MacLeod is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…
Source: http://incompetech.com/music/royalty-…
Artist: http://incompetech.com/#tastinghistory #pizza













