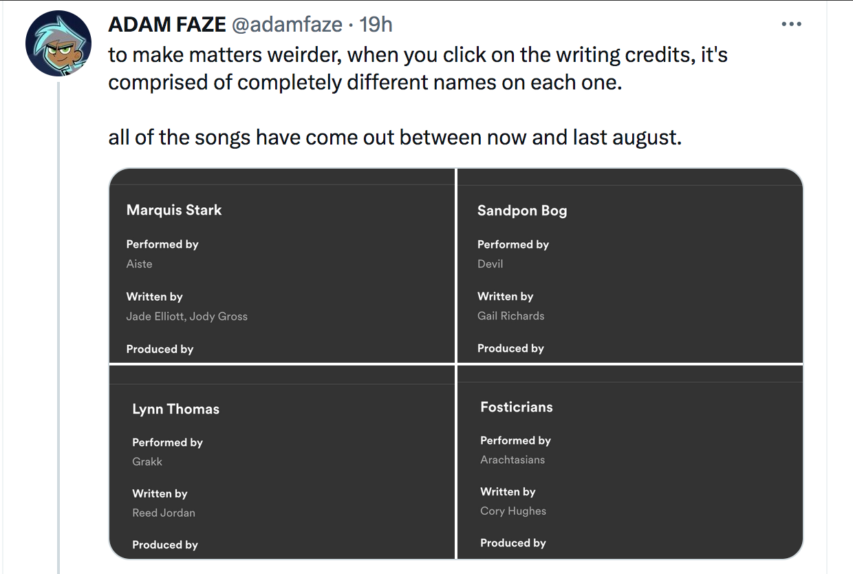
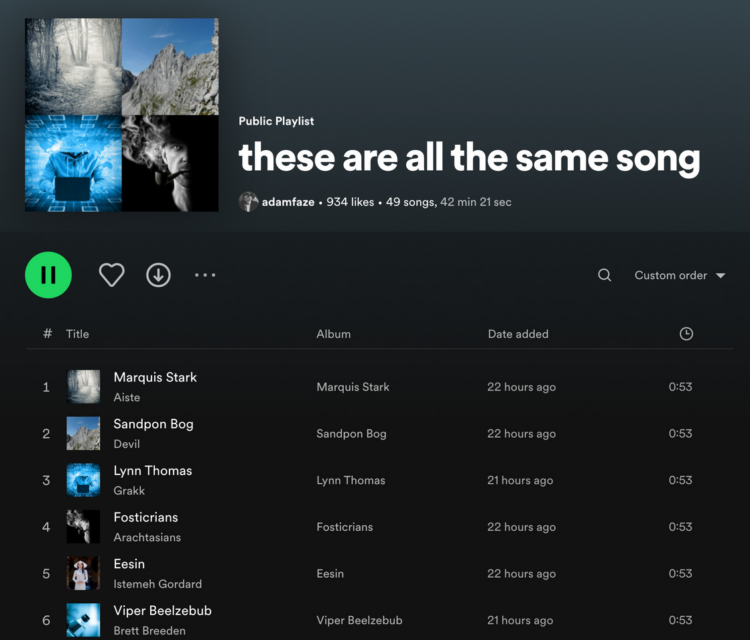
At Wrong Side of History, Ed West linked to this post by Gurwinder on the TikTok threat to western civilization:

For thousands of years, humans sought to subjugate their enemies by inflicting pain, misery, and terror. They did this because these were the most paralyzing emotions they could consistently evoke; all it took was the slash of a sword or pull of a trigger.
But as our understanding of psychology has developed, so it has become easier to evoke other emotions in complete strangers. Advances in the understanding of positive reinforcement, driven mostly by people trying to get us to click on links, have now made it possible to consistently give people on the other side of the world dopamine hits at scale.
As such, pleasure is now a weapon; a way to incapacitate an enemy as surely as does pain. And the first pleasure-weapon of mass destruction may just be a little app on your phone called TikTok.
[…]
Other platforms, like Facebook and Twitter, use recommendation algorithms as features to enhance the core product. With TikTok, the recommendation algorithm is the core product. You don’t need to form a social network or list your interests for the platform to begin tailoring content to your desires, you just start watching, skipping any videos that don’t immediately draw your interest. Tiktok uses a proprietary algorithm, known simply as the For You algorithm, that uses machine learning to build a personality profile of you by training itself on your watch habits (and possibly your facial expressions.) Since a TikTok video is generally much shorter than, say, a YouTube video, the algorithm acquires training data from you at a much faster rate, allowing it to quickly zero in on you.
The result is a system that’s unsurpassed at figuring you out. And once it’s figured you out, it can then show you what it needs to in order to addict you.
Since the For You algorithm favors only the most instantly mesmerizing content, its constructive videos — such as “how to” guides and field journalism — tend to be relegated to the fringes in favor of tasty but malignant junk info. Many of the most popular TikTokers, such as Charli D’Amelio, Bella Poarch, and Addison Rae, do little more than vapidly dance and lip-sync.
Individually, such videos are harmless, but the algorithm doesn’t intend to show you just one. When it receives the signal that it’s got your attention, it doubles down on whatever it did to get it. This allows it to feed your obsessions, showing you hypnotic content again and again, reinforcing its imprint on your brain. This content can include promotion of self-harm and eating disorders, and uncritical encouragement of sex-reassignment surgery. There’s evidence that watching such content can cause mass psychogenic illness: researchers recently identified a new phenomenon where otherwise healthy young girls who watched clips of Tourette’s sufferers developed Tourette’s-like tics.
A more common way TikTok promotes irrational behavior is with viral trends and “challenges”, where people engage in a specific act of idiocy in the hope it’ll make them TikTok-famous. Acts include licking toilets, snorting suntan lotion, eating chicken cooked in NyQuil, and stealing cars. One challenge, known as “devious licks”, encourages kids to vandalize property, while the “blackout challenge”, in which kids purposefully choke themselves with household items, has even led to several deaths, including a little girl a few days ago.
The Chinese government — not wishing this kind of insanity spreading among their own people — have ensured that it’s only foreigners getting the full TikTok experience:
Last month FBI Director Chris Wray warned that TikTok is controlled by a Chinese government that could “use it for influence operations”. So how likely is it that one such influence operation might include addicting young Westerners to mind-numbing content to create a generation of nincompoops?
The first indication that the Chinese Communist Party is aware of TikTok’s malign influence on kids is that it’s forbidden access of the app to Chinese kids. The American tech ethicist Tristan Harris pointed out that the Chinese version of TikTok, Douyin, is a “spinach” version where kids don’t see twerkers and toilet-lickers but science experiments and educational videos. Furthermore, Douyin is only accessible to kids for 40 minutes per day, and it cannot be accessed between 10pm and 6am.
Has the CCP enforced such rules to protect its people from what it intends to inflict on the West? When one examines the philosophical doctrines behind the rules, it becomes clear that the CCP doesn’t just believe that apps like TikTok make people stupid, but that they destroy civilizations.