Anang
Published 6 May 2012If you want to read more about WW2 leadership, read Andrew Roberts Masters & Commanders.
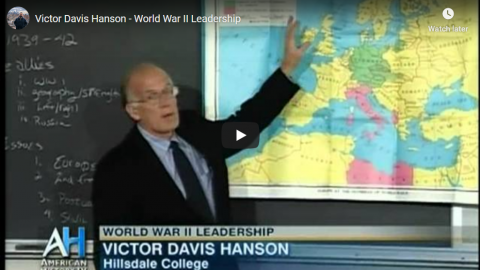
Victor Hanson, a professor emeritus of Classics at California State University, Fresno, lectured to a history class on Masters and Commanders at Hillsdale College. In this fall seminar in classical and military history Professor Hanson examined how leaders, both civilian officials and generals on the battlefield, conducted themselves in wartime. That day’s class focused on Franklin D. Roosevelt and Winston Churchill and how those very different American and British leaders learned to work together to defeat Nazi Germany.
Original link: http://www.c-spanvideo.org/program/29…
January 8, 2020
Victor Davis Hanson – World War II Leadership
December 29, 2019
Winter is coming, peace is not – the frozen fronts – WW2 – 070 – December 28, 1940
World War Two
Published 28 Dec 2019Italy finds itself in a dire position in Albania as Christmas is celebrated in a war-torn Europe and fighting continues in China.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
– Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
– Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
– Adrien Fillon – https://www.instagram.com/adrien.colo…Sources:
– IWM: CH 251, A12882, FL 1905, A 1732, H 6285, D 717Soundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
– “March Of The Brave 4” – Rannar Sillard
– “March Of The Brave 9” – Rannar Sillard
– “Walk With Legends” – Bonnie Grace
– “The End Of The World 2” – Håkan Eriksson
– “March Of The Brave 10” – Rannar Sillard
– “Easy Target” – Rannar Sillard
– “Guilty Shadows 4” – Andreas Jamsheree
– “Deviation In Time” – Johannes BornlofArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
December 18, 2019
Adolf Hitler’s First Steps In Politics – The Foundation Of The Nazi Party I THE GREAT WAR 1919
The Great War
Published 17 Dec 2019Get a free audiobook and 2 Audible Originals with a 30-day trial: http://audible.com/greatwar or text
greatwarto 500 500.Like many former soldiers, lance corporal Adolf Hitler was disillusioned with the new German Republic after the Armistice in 1918. Like man of his country men he was also in dire need of a job. The Bavarian Army provided an opportunity and soon young Adolf Hitler found himself in the ranks of an obscure political party in Munich: The German Workers’ Party.
» SUPPORT THE CHANNEL
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thegreatwar
Merchandise: https://shop.spreadshirt.de/thegreatwar/» SOURCES
Dietrich Eckart, Bolshevism from Moses to Lenin.
Gottfried Feder, Brechung der Zinsknechtschaft 1919.
Fest, Joachim C.: Hitler. Eine Biographie, 1973.
Heiden, Konrad: Adolf Hitler: Das Zeitalter der Verantwortungslosigkeit. Ein Mann gegen Europa, 2016.
Ulrich, Volker: Adolf Hitler. Band 1: Die Jahre des Aufstiegs 1889-1939. 2013.
Fest, Joachim C: The face of the Third Reich: Portraits of the Nazi Leadership. 1999
Program of the German Workers’ Party, 1920 (http://germanhistorydocs.ghi-dc.org/s…)
Jeremy Noakes and Geoffrey Pridham, eds., Nazism 1919-1945, Vol. 1, The Rise to Power 1919-1934. Exeter: University of Exeter Press, 1998, pp. 12-14.»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Toni Steller
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Phillip Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Daniel Kogosov (https://www.patreon.com/Zalezsky)
Research by: Markus Linke
Fact checking: Florian WittigChannel Design: Alexander Clark
Original Logo: David van StepholdA Mediakraft Networks Original Channel
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2019
December 12, 2019
The Few Who Opposed Hitler – German Resistance in 1940 – WW2 – War Against Humanity 006
World War Two
Published 11 Dec 2019Where all German faithful Nazis? Not by a stretch, but a resounding majority approved of the Nazis, especially before the war, and again after the victory in France. Anyone that actively opposed Hitler and his gang were not only risking their life, but faced an uphill battle against public opinion. And yet … some people did.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Spartacus Olsson
Written by: Spartacus Olsson and Joram Appel
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Joram Appel and Spartacus Olsson
Edited by: Mikołaj Cackowski
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
Cassowary Colorizations – https://www.flickr.com/photos/cassowa…
Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
Norman Stewart – https://oldtimesincolor.blogspot.com/Sources:
Archive of I. M. Bondarenko
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
5 hours ago
This is the first episode of five War Against Humanity videos that will focus on Resistance in 1940. In this episode we look at Germany, then France, after that the Benelux countries and Scandinavia, then Poland and finally China. The first two episodes will come out before Christmas and the next will follow at the beginning of the new year. These episodes are all introductions to a recurring coverage of the war behind the lines. Resistance and collaboration with the occupying enemy was an essential component of WW2, but because it was clandestine, often private enterprises, the records are less detailed than the ones of the official war machines of the belligerents. Thus, resistance is not always as easy to organize on a weekly time line. Therefore we will return irregularly to the events behind each frontline to look at the developments over a somewhat longer timespan. We will do our best to follow the individuals who played a central part in the events and machinations. We hope that in this way we can give you more insight into WW2 events that are often overlooked, or covered in a less cohesive way.
December 8, 2019
The Road to Moscow – German Invasion Plans – WW2 – 067 – December 7, 1940
World War Two
Published 7 Dec 2019Wilhelm Canaris once again disturbs Hitlers plans to drag Spain into the war, as the Germans finalize their plan for the Invasion of the Soviet Union which is scheduled for the summer of 1941. Meanwhile, the Greek counter-offensive into Albania loses steam and the Pope objects to the German T-4 euthanasia program.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Mikołaj Cackowski
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
– Cassowary Colorizations
– Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/Sources:
Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
USHMM, photograph number 60468
IWM (HU 76031)Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
2 days ago (edited)
YouTube has age-restricted our Blitz Spirit WW2 video and had REMOVED our Between Two Wars episode on the Holodomor (1932-02). We received a warning, which means that next time this happens we will be banned from publishing content for one week. They state that our “content was removed due to a violation of our Community Guidelines,” on account of publishing “violent of graphic content”, explaining that “Violent or gory content intended to shock or disgust viewers, or content encouraging others to commit violent acts, is not allowed on YouTube.”EDIT: After pushing our appeal, YouTube has reinstated the episode and it’s back up. The Blitz video is still age-restricted.
Needless to say, we were shocked and disgusted by this action and legitimisation. Though it’s back up [here], this still shows how much our independence depends on our Patreon supporters. Without them, we would have been long gone. So please consider supporting our effort and help us spread vital knowledge about our world’s history, albeit hard to swallow or confronting. Don’t let YouTube decide what will be a part of our public memory! You can support us on https://patreon.com/timeghosthistory or https://timeghost.tv.
Cheers,
Joram
December 5, 2019
QotD: [Literal] Health Nazis
[T]he Nazis’ focus on the threats that risky habits pose to “public health” makes perfect sense in light of their collectivist ideology. “Brother national socialist,” said one bit of Nazi propaganda, “do you know that your Führer is against smoking and thinks that every German is responsible to the whole people for all his deeds and missions, and does not have the right to damage his body with drugs?”
Smith adds: “Clearly there were considerable links between the promotion of particular lifestyles and the racial hygiene movement. Tobacco and alcohol were seen as ‘genetic poisons,’ leading to degeneration of the German people.”
The point, I hasten to add, is not that today’s “public health” paternalists are Nazis. I am not suggesting that everyone who hates smoking is just like Hitler. But there is an unmistakable totalitarian logic to the notion that the government has a responsibility to promote “public health” by preventing us from engaging in activities that might lead to disease or injury. The implication is that we all have a duty to the collective to be as healthy as we can be, an idea the Nazis embraced but one that Americans ought to find troubling.
Jacob Sullum, “So What If Hitler Was an Anti-Smoker?”, Reason Hit and Run, 2004-12-17.
December 3, 2019
Czechoslovakia – the Last Bastion of Democracy | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1935 Part 1 of 4
TimeGhost History
Published 2 Dec 2019Czechoslovakia is holding on to democracy by a thread. It even looks like they might be able to integrate the German Czechoslovakians, but Hitler’s rise to power changes everything.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Francis van Berkel
Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Francis van Berkel and Rune Væver Hartvig
Edited by: Daniel Weiss and Wieke Kapteijns
Sound design: Marek KamińskiA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
TimeGhost History
2 days ago
The year is 1935 CE. Central Europe is entirely dominated by Authoritarians and Fascists. Well not entirely! One small country of indomitable Czechs and Slovaks still holds out for democracy. And life is not easy for the German Nazis who garrison the towns and villages in Bohemia and Moravia…One thing in this episode might go unnoticed. It is how important it is to note that the term Sudeten German has only become widespread after WWI. It shows us how the delicate balance of ethnic groups had been upset after the Great War.
Before 1918, these same people felt comfortable called themselves Bohemian or Moravian. On the other side of the border that now divides Czechoslovakia from Germany, Austria, Poland and Hungary Czech and Slovak speakers felt comfortable calling themselves for instance Carpathian, Silesian, or Bavarian. In only 17 years this regional sense of unity has now been eradicated. It’s really easy to fall into the trap of the identity rhetoric of the time. To say that “Well, what did you expect? You forced people to be part of a country that wasn’t theirs” it’s an easy explanation for all of this conflict.
Well as we have often pointed out it wasn’t that simple. Fanned by identity politics on all sides, the borders have become fevering soars that are spreading infection into all of Europe. It is a disease that now threatens to develop into sepsis for the whole European continent. And think of this; borders are nothing but lines on maps, things invented arbitrarily in people’s minds… isn’t it remarkable how we as a species can invent our own demise?
November 3, 2019
Mussolini plays Hitler like a Fiddle – The Invasion of Greece – WW2 – 062 – November 2, 1940
World War Two
Published 2 Nov 2019A new front opens up in Greece as the Italians invade, while the Battle of Britain seems to come to an end.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: EastoryColorisations by Norman Stewart and Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Sources:
– IWM: HU 76031, E 15223, E 450, E 6661, A 22111
– killer by Arthur Shlain from the Noun Project
– National Portrait Gallery, London
– Torpedo body icon by Blaise Sewell from the Noun Project
– FDR Presidential Library & MuseumEastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
3 days ago (edited)
This week covers about two major events with effects that will ripple through the remainder of the war. Actually, both have been attributed by historians for being “the one event” that caused the war to end as it did. You’ll have to stick around to find out how and when that will be though. Though I can tell you one thing now. History is rarely that simple. If you like our series and want to enable us to cover the complex web of events, locations, individuals and techniques that changed the outcome of the war, please consider supporting us on https://www.patreon.com/timeghosthistory or on our own website at https://timeghost.tv. If you would like to make a one-time contribution, you can do so via PayPal to (paypal@timeghost.tv).
Cheers, Joram
November 1, 2019
Why All Germans Were Nazis – How Hitler Created the Third Reich | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1934 Part 1 of 4
TimeGhost History
Published 31 Oct 2019After Hitler seized power in Germany in January 1933, he rapidly transformed the Democratic Weimar Republic into a repressive, totalitarian and racist state. In 1934, Germany became Nazi Germany.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Subscribe to our World War Two series: https://www.youtube.com/c/worldwartwo…
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Spartacus Olsson and Francis van Berkel
Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Francis van Berkel and Spartacus Olsson
Edited by: Wieke Kapteijns
Sound design: Marek KamińskiImage sources: Bundesarchiv, Bundesarchiv, Bild 102-15282A / Georg Pahl, Heinz Bergschicker Deutsche Chronik 1933-1945 – Ein Zeitbild der faschistischen Diktatur
Icons from the Noun Project: Police by IconTrack, soldier by Simon Child, police man by Gregor Cresnar, hello by Universal Icons.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
Spartacus Olsson
2 hours ago
Now, this episode explains the measures that the Nazis used to gain control over the German people. It is not an attempt to justify, or be apologetic of the responsibility for the horrors committed during the Nazi regime. But it is also not a blanket condemnation of Germans. What happened in Germany starting in 1933 should serve us all as a warning to what can happen when you let loose authoritarian power, normalize lies as an acceptable part of political discourse, and make mainstream the disregard of basic human values. We should all think of that although the Nazis were especially efficient in their implementation of an authoritarian system, they are by far not the only ones that have succeeded in seducing whole a nation into blind hatred and acceptance of the suffering and death of others to forward an ideology. We should remember that freedom and democracy is essential, but also that words matters. The beginning of oppression starts with an endless stream of lies that confuse public discourse to the point that facts don’t matter anymore and truth becomes fiction. This video shows us what can happen next. Our mantra as a channel is to focus on the facts, not our opinions, not our ‘truth’ — just the facts m’am — and that is what we have presented here, for better or worse.
October 27, 2019
Hitler is Disappointed by his Allies – WW2 – 061 – October 26, 1940
World War Two
Published 26 Oct 2019Hitler finds out that not everyone is ready to do his bidding. Much to the frustration of Hitler, Franco, Petain and Mussolini all have their reasons to take the high road.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Karolina Dołęga
Map animations: EastoryColorisations by Norman Stewart and Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Sources: Biplane by Hea Poh Lin from the Noun Project
Eastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
October 22, 2019
QotD: The Soviet contribution to defeating Hitler
Stalin emerged from the second world war as its most successful warlord, head of a nation whose contribution to the destruction of Nazism had won worldwide admiration. Although the leaders of the western states quickly understood the threat posed by the new Soviet Empire to freedom and democracy, many of their citizens did not.
Between 1941 and 1945 so much praise had been heaped upon Uncle Joe, the defenders of Stalingrad, heroic factory workers of the Volga and suchlike, that thereafter it proved a hard task to disabuse many people of their illusions about Mother Russia. They were not wrong in believing that hundreds of thousands of young British and American men were alive in 1945 because Red soldiers had done more than their rightful share of dying.
Any examination of the Bolshevik revolution and its legacy must linger on the Great Patriotic War, because that victory remains the only indisputable and durable achievement the rulers of Russia can boast since 1917, save the invention of some remarkable weapons systems and spacecraft.
Max Hastings, “The centenary of the Russian revolution should be mourned, not celebrated”, The Spectator, 2016-12-10.
October 20, 2019
QotD: Why Orwell wrote Nineteen Eighty-Four
Many thanks for your letter. You ask whether totalitarianism, leader-worship etc. are really on the up-grade and instance the fact that they are not apparently growing in this country and the USA.I must say I believe, or fear, that taking the world as a whole these things are on the increase. Hitler, no doubt, will soon disappear, but only at the expense of strengthening (a) Stalin, (b) the Anglo-American millionaires and (c) all sorts of petty führers of the type of de Gaulle. All the national movements everywhere, even those that originate in resistance to German domination, seem to take non-democratic forms, to group themselves round some superhuman führer (Hitler, Stalin, Salazar, Franco, Gandhi, De Valera are all varying examples) and to adopt the theory that the end justifies the means. Everywhere the world movement seems to be in the direction of centralised economies which can be made to “work” in an economic sense but which are not democratically organised and which tend to establish a caste system. With this go the horrors of emotional nationalism and a tendency to disbelieve in the existence of objective truth because all the facts have to fit in with the words and prophecies of some infallible führer. Already history has in a sense ceased to exist, ie. there is no such thing as a history of our own times which could be universally accepted, and the exact sciences are endangered as soon as military necessity ceases to keep people up to the mark. Hitler can say that the Jews started the war, and if he survives that will become official history. He can’t say that two and two are five, because for the purposes of, say, ballistics they have to make four. But if the sort of world that I am afraid of arrives, a world of two or three great superstates which are unable to conquer one another, two and two could become five if the führer wished it. That, so far as I can see, is the direction in which we are actually moving, though, of course, the process is reversible.
As to the comparative immunity of Britain and the USA. Whatever the pacifists etc. may say, we have not gone totalitarian yet and this is a very hopeful symptom. I believe very deeply, as I explained in my book The Lion and the Unicorn, in the English people and in their capacity to centralise their economy without destroying freedom in doing so. But one must remember that Britain and the USA haven’t been really tried, they haven’t known defeat or severe suffering, and there are some bad symptoms to balance the good ones. To begin with there is the general indifference to the decay of democracy. Do you realise, for instance, that no one in England under 26 now has a vote and that so far as one can see the great mass of people of that age don’t give a damn for this? Secondly there is the fact that the intellectuals are more totalitarian in outlook than the common people. On the whole the English intelligentsia have opposed Hitler, but only at the price of accepting Stalin. Most of them are perfectly ready for dictatorial methods, secret police, systematic falsification of history etc. so long as they feel that it is on “our” side. Indeed the statement that we haven’t a Fascist movement in England largely means that the young, at this moment, look for their führer elsewhere. One can’t be sure that that won’t change, nor can one be sure that the common people won’t think ten years hence as the intellectuals do now. I hope they won’t, I even trust they won’t, but if so it will be at the cost of a struggle. If one simply proclaims that all is for the best and doesn’t point to the sinister symptoms, one is merely helping to bring totalitarianism nearer.
You also ask, if I think the world tendency is towards Fascism, why do I support the war. It is a choice of evils — I fancy nearly every war is that. I know enough of British imperialism not to like it, but I would support it against Nazism or Japanese imperialism, as the lesser evil. Similarly I would support the USSR against Germany because I think the USSR cannot altogether escape its past and retains enough of the original ideas of the Revolution to make it a more hopeful phenomenon than Nazi Germany. I think, and have thought ever since the war began, in 1936 or thereabouts, that our cause is the better, but we have to keep on making it the better, which involves constant criticism.
George Orwell, responding to a letter from Noel Willmett, 1944-05-18.
October 12, 2019
Göring, the Stoned Nazi Nut – Doped WW2 Leaders Part 1
World War Two
Published 10 Oct 2019Hermann Göring was one of the most powerful leaders of the Third Reich. He was also a drug addict with some serious problems and a remarkable lifestyle.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Joram Appel
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Research by: Joram Appel
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: EastoryColorisations by Norman Stewart and Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Eastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.Sources:
Klimbim Colorizations – https://klimbim2014.wordpress.com/A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
31 minutes ago (edited)
Though this episode is mostly about the lifestyle of Hermann Göring, we will certainly get back to his more serious impact on the Nazi party, Germany and World War Two. For those of you who are new here, we are following World War Two Week by Week, in which we do pay a lot of attention to all those smaller but still significant events. If you would like to watch the series, make sure to subscribe and to click here to start watching from episode one: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3-A1gVm9T0A&list=PLsIk0qF0R1j4Y2QxGw33vYu3t70CAPV7XCheers,
The TimeGhost team.
October 11, 2019
Germany Never Elected Hitler | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1933 Part 1 of 3
TimeGhost History
Published 10 Oct 2019Hitlers rise to power, also known as the Machtergreifung, was riddled with physical and mental manipulation, political games and an exploitation of the Democratic system. This episode follows the events leading up to the Nazi takeover of Germany.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Spartacus Olsson
Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Spartacus Olsson
Edited by: Daniel Weiss
Sound design: Iryna Dulkaimage source:
Deutsche BundesarchivA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
Spartacus Olsson
18 minutes ago
Hi, for those of you that don’t know me yet, I’m the lead author of this series and the author of this episode. Now, as you will, or have just seen, this episode covers an event of earth-shattering magnitude in human history. An event that is often misunderstood and glossed over. The reason for that is not that there is anything controversial, or stupendously new with what we’re documenting here. The simple fact is that its just too detailed and too complicated to cover in general history studies, especially in secondary school. The level we get into here is usually only covered in specialized lectures at college or university level. Tons and tons of books have been written on the topic and yet, many misconceptions remain. It was my goal to dispel some of the many misunderstandings that abound about how Hitler finally seized power. One of the chief myths is that Hitler was elected. As the video shows, that is not what happened. So you might ask yourself; how come the vast majority of Germans finally rallied behind him? Because they did, there’s no question. But you see, that happens after he seizes power and it will be the topic of our next episode on Germany that covers the Nazi consolidation of power.It was also my goal to cast some more light on a topic that has been weaponized in political debate in recent years: the level of Socialism in the German National Socialist Worker’s Party. I hope that I have laid the latter one to rest, but I fear that the comment section will still be full of politically biased nonsense on this topic. It’s quite tiring for our community managers to answer that misrepresenting alt-right trope over and over again. And we won’t stop you from posting it, even if it’s nonsense. Instead we will try to patiently answer, but think fifteen times about posting ‘Nazis were Socialists, duh!’ or “Dude, Nazis are left-wing, duh!’ out of respect for us. What we will not tolerate is that you post links to any of the clown videos by non-historians that try to perpetuate that myth. We are a team of actual historians. We have no interest in ‘pinning’ Naziism on anyone. We also have no interest in ‘pinning’ Socialism on anyone. Nor should you, if you have any interest whatsoever in understanding history. Revolutionary Socialism, Communism, Fascism and Nazism have all brought down a lot of suffering on humanity – if we are supporters of freedom and democracy we need to learn from that. Throwing them all in one bucket and dumping it on our perceived political opponents is not learning, it’s obfuscation, confusion, and destruction of education. So respect humanity, respect history and don’t take part in that kind of nonsense.
October 6, 2019
Hitler and the Art of the Deal – WW2 – 058 – October 5 1940
World War Two
Published 5 Oct 2019Hitler is trying to get new Axis Powers on board in his fight against Britain, promising them all huge territorial gains.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: EastoryColorisations by Norman Stewart and Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Eastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.Sources:
– IWM: A 220
– Photos of Herbert Morrison and John Anderson by Yousuf Karsh, Dutch National Archives
– National Library of Australia
– Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
– Colorized portrait of Mao Zedong by Olga Shirnina, aka Klimbim
– Flag of Spain by SanchoPanzaXXI on Wikimedia CommonsA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.