World War Two
Published 20 Mar 2025December 1930 plunges Germany deeper into chaos. Nazis and Communists join forces against Chancellor Brüning’s emergency decrees, while a shocking court decision boosts Hitler’s power. Violent riots erupt over the film All Quiet on the Western Front, and police uncover a terrifying communist bomb plot aimed at sparking civil war. With extremism rising, is Weimar democracy heading for disaster?
(more…)
March 22, 2025
How One Movie Drove Hitler’s Men Crazy – Rise of Hitler 12, December 1930
March 17, 2025
My Big Fat Greek Civil War – W2W 12 – 1947 Q2
TimeGhost History
Published 16 Mar 2025As Europe emerges from WWII, Greece plunges into chaos. Political polarization, revenge killings, and failed diplomacy ignite a bitter civil war, turning former allies into deadly foes. From communist partisans regrouping in the mountains, to royalists asserting brutal dominance, the battle lines are drawn. Could Greece become the first major flashpoint in the Cold War, threatening peace across the Balkans and beyond?
(more…)
March 8, 2025
Murder in the Name of Democracy – War Against Humanity 002
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 7 Mar 2025The battles on the Korean peninsula started long before 1950. Today Sparty looks back at the uprising and insurgency on Jeju Island in 1948, the threat of Communist revolt, and the harsh reaction of the Korean government. This really was the war before the war.
(more…)
February 27, 2025
QotD: The ANC, the Inkatha Freedom Party, and the Zulus during Apartheid
… one underappreciated fact is that [South Africa] was handed over to Leninists. Before reading this book, I think I had in the back of my mind some vague sense, probably absorbed from racist Twitter accounts, that Nelson Mandela had some sort of communist affiliation, but the reality is so much worse than I’d imagined and very curiously unpublicized. Mandela’s African National Congress was a straightforwardly revolutionary communist party during their decades of exile, with leaders constantly flying to the Soviet Union and to East Germany to be wined and dined, and to get lessons on governance from the Stasi.
Those lessons were enthusiastically put into practice — the ANC set up a network of death camps in Angola at which traitors and enemies and just plain inconvenient people were worked or tortured to death. They also founded a paramilitary terrorist army called uMkhonto we Sizwe (MK) that waged a brutal dirty war, supposedly against the apartheid government but actually against anybody they didn’t like. The vast majority of the victims of MK were black people who happened not to support the ANC, especially Zulus in their tribal homeland in what’s now KwaZulu-Natal province, who were subjected to regular massacres in the 80s and early 90s.
The ANC and the MK had a special hatred for the Zulus. In part, because the ANC’s leadership was disproportionately Xhosa, and their ancestors had suffered during King Shaka’s wars of expansion in the 19th century. But this ancient ethnic grudge wasn’t the fundamental problem, and indeed it was later papered over. The real problem was that the Zulus dared to engage in political organization outside the ANC and its subsidiary, the South African Communist Party (SACP). The preferred Zulu political vehicle was the Inkatha Freedom Party (IFP), which was associated with the Zulu monarchy and the traditional amakhosi (chieftains). This made it an independent base of power within black South Africa, and a competing claim on the loyalty of Zulu citizens. The ANC considered this situation unacceptable.
Like many avowedly communist organizations, the ANC was allergic to political competition of any sort. Internally, the party practiced an especially harsh form of democratic centralism — most policy decisions were made by a tiny and incestuous central committee, and members were expected to be totally submissive in the face of party discipline. This extended even to the point of party permission being necessary for senior members to marry. Externally, the party had an entitled attitude common to successful revolutionary organizations from North Korea to Albania — they were the incarnation of the aspirations of the South African people and the vanguard of their brilliant future, so all other political organizations were ipso facto illegitimate. Can you guess what happened when these people were handed power?
John Psmith, “REVIEW: South Africa’s Brave New World, by R.W. Johnson”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2023-03-20.
February 21, 2025
Berlin ’45: City of Spies
World War Two
Published 20 Feb 2025In 1945, Berlin is a city in ruins — but for the world’s spies, it’s a goldmine. As the Soviets, Americans, British, and French carve up the capital, they scramble to seize Nazi secrets, recruit informants, and outmaneuver each other in an intelligence war that will define the Cold War. From stolen blueprints to fabricated reports, Berlin becomes the world’s first battleground of espionage.
(more…)
February 17, 2025
France Starts the Vietnam War – W2W 005
TimeGhost History
Published 16 Feb 2025In 1946, tensions in Indochina explode into full-scale war. As France struggles to reclaim its empire, Ho Chi Minh’s Viet Minh fight for independence, setting the stage for a brutal conflict that will shape the next three decades. With international powers pulling the strings, Vietnam becomes the first battleground of the post-war era’s colonial struggles.
(more…)
February 4, 2025
QotD: The American political spectrum
I tend to think of the American political spectrum as broadly dividing into six major groups (political “tribes” we might say), arranged very roughly from left to right, though I must note that there are serious differences within tribes as much as between them. Going left-to-right, there is first (1) The Left, who are the sort of left-leaning folks who get upset if you call them liberals and are committed to more aggressive forms of socialism that envision and end to or massive curtailment of things like markets. Your actual Marxists go here. Then moving right there are (2) Progressives, who are generally committed to liberalism as a philosophy, but favor large-scale government intervention inside that framework to reshape society (“progressivism”), which they believe can be reshaped for the better. Bernie Sanders, Elizabeth Warren and AOC go here; some of these folks will call themselves social democrats, evoking the form of this ideology in Europe. Then you have (3) Left-Liberals (“Social Liberals”), who have the same ideological components as the progressives (progressivism+liberalism), but with an inversion of the emphasis, where the individual liberty claim of liberalism is the dominant strain over the society-reshaping goals of progressivism. This is where the mainstream and especially moderate wings of the Democratic party sits.
Then on the right you have (4) Right-liberals (“Classical liberals”), who share liberalism with groups (2) and (3) but reject (or at least substantially challenge) the idea that society can be “engineered” with positive results. This group largely left the Republican party between 2016 and the present (though some were already libertarians). Notably, (3) and (4) in the United States tend to share hawkish anti-authoritarian, anti-communist foreign policy views; this is where the foreign policy “blob” lives. To their right are (5) Traditionalist Conservatives. Because the United States was founded as a liberal country, they tend to still hold some liberal views (and respond well to liberal, “freedom-centered” framing) but their main ideological commitment is generally conservative in its literal meaning of being traditionalist, desiring things to not change or to recover that which has changed and there is a willingness to compromise on liberalism in the pursuit of that. This, I’d argue, is where the core of the Republican Party currently exists. Finally, you have (6) Right-Authoritarians, who come in various forms based on the authority they believe ought to structure society, e.g. populist authoritarians are fascists, whereas Catholic religious authoritarians are integralists and so on. But the core idea here is that there exists an authority, be it the “national will” (invariably channeled by an individual charismatic leader and often herrenvolk in nature) or tradition or the church or whatever else, which has a right to structure society which supersedes individual liberties. For our purposes, they key is they generally despise liberalism because it places limits on that authority. They tend to insist that liberalism makes societies weak even as liberal societies pound their favorite dictators into dust over and over again.
To put the spectrum another way, we might think in terms of publications: Jacobin (1) <-> Vox (2) <-> The Atlantic (3) <-> The Bulwark/Dispatch (4) <-> National Review (5); few major publications openly identify as being in (6) in the United States, but you can see editors at The Federalist or First Things platform political visions that [derive] from it. To the degree to which “horse-shoe theory” works it is because the thing that The Left and the Right-Authoritarians have in common is that they believe in an effectively unlimited claim on the individual by the community, whereas the core of liberal ideology is that the social claim on the individual is and must be limited.
Bret Devereaux, In a footnote to “Collections: The Philosophy of Liberty – On Liberalism”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-07-05.
January 30, 2025
Hitler Testifies, Brüning Battles On – Rise of Hitler 10, October 1930
World War Two
Published 28 Jan 2025October 1930 brings more unrest to Weimar Germany. Chancellor Brüning survives no-confidence votes, while Nazi and Communist clashes escalate into chaos. Berlin sees mass protests, Jewish businesses attacked, and rumors of a Nazi-Soviet conspiracy swirl.
(more…)
January 22, 2025
“Do not give institutional power to activists” or “moral projects to bureaucrats”, but “Progressivism systematically does both”
Lorenzo Warby on the dangers of enabling totalitarians and suffering the useful idiots in any political system:

The overthrow of Robespierre in the National Convention on 27 July 1794, Max Adamo (1870),
Wikimedia Commons.
Do not give institutional power to activists, as activism — being power without responsibility that readily lauds bad behaviour — attracts manipulative “Cluster B” personalities. Moreover, activism degrades realms of human action by imposing pre-conceived outcomes and constraints on them. We can see this is in all the entertainment franchises whose internal logics of story and canon have been debauched in the service of political messaging.1
Do not give moral projects to bureaucrats, as such projects elevate the authority of the bureaucrats who become moral masters, devaluing the authority of the citizens turned into moral subjects, and so undermines any ethic of service to said citizenry. Such projects also frustrate accountability, as the grand intentions can, and will, be used to shield the bureaucrats from scrutiny. Indeed, moral projects rapidly become moralised projects, whose grand intentions protects, even aggrandise, the self-interest of the bureaucrats.2
Progressivism systematically does both — give institutional power to activists and moral projects to bureaucrats. Hence progressivism has so often proved disastrous for human flourishing. Indeed, it has a powerful tendency to use the grandeur of its moral intentions to free itself from moral constraints: to be moralised, rather than moral.
As various folk “walk away” from what left-progressivism has become, a common sentiment is some version of “this is not the Left I remember” or “this is not what the Left used to stand for”. Yet, one of the striking things about Post-Enlightenment Progressivism (aka “wokery”) within contemporary societies is how thoroughly it is replicating mechanisms of social control familiar to any student of Communism, of Marxist Party-states.
This “not the Left I joined” is typically a notion of “the Left” that does not include Lenin, Stalin, Mao, Pol Pot, Mengistu, Ceausescu … So it is an historically illiterate, “wouldn’t-it-be-nice”, Leftism. Yet it is precisely the Left that does include Lenin, Stalin, Mao, Pol Pot, Mengistu, Ceausescu and so on whose echoes are being played out in our societies.
When we look around our contemporary societies, we have commissars/political officers (aka DEI officers, intimacy consultants, sensitivity readers, bias response teams, etc); Zhdanovism, in the remarkable ideological conformism in the arts, entertainment and gaming (usefully discussed here); Lysenkoism in science journals, especially the genderwoo sex-is-non-binary nonsense, though genetics research and male-female differences also have aspects of it; and censorship that was originally paraded as stopping “hate speech”, now being purveyed as anti-dis/mis/mal-information. Critical Pedagogy — which has become influential in Education Faculties and teacher training — is explicitly about replicating Mao’s Cultural Revolution model of permanent revolution. We have the same, disastrous, patterns of institutional power to activists and moral projects to bureaucrats.
1. There is a large difference from the “we want to be included, we want a say” activism that abolished first the slave trade and then slavery, that abolished laws against Jews and Catholics, that gave us universal male and then female suffrage — what I have called the Emancipation Sequence. Such political movements included previously excluded folk in freedoms and political processes that already existed. They did not give institutional power to activists nor moral projects to bureaucrats.
2. The institutional shrinkage of the Church has not abolished the meaning-and-morality role it used to play, it has just shifted it into academe and the welfare state apparat, making both simultaneously more arrogant and less functional.
January 21, 2025
January 10, 2025
Germany Votes – Rise of Hitler 09, September 1930
World War Two
Published 9 Jan 2025The September 1930 elections reshape Germany’s political landscape. With surging support for extremists like the Nazis and Communists, and declining votes for democratic parties, Weimar faces a deeply polarized future. This episode breaks down the results, voter shifts, and what this means for the Republic.
(more…)
January 3, 2025
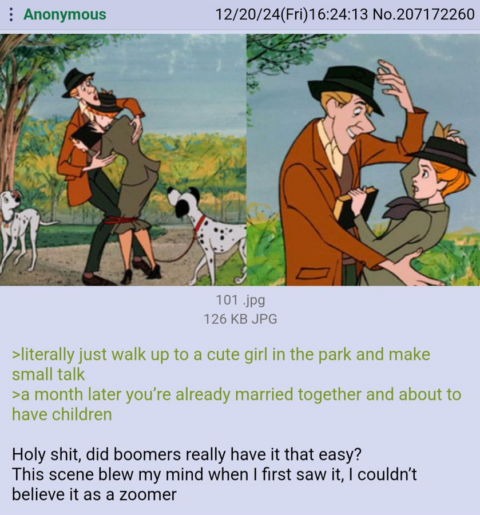
The Boomers and “reset to Year Zero”
On Twit-, er, I mean “X”, ESR responds to a post from Devon Eriksen decrying the Baby Boomers for effectively destroying the culture of the postwar “American Dream”:
… I’m a late Boomer, born in ’57. I can dimly remember the day JFK was shot. I watched the moon landing. My teens and early twenties coincided with the 1970s. I was there for it all.
And even then, even in the 1970s, feeling a sense of subtle disintegration all around me, I already dimly grasped that we weren’t just falling. We were being pushed.
But I was very young then; I wouldn’t come to fully understand why, and by whom, for almost another 30 years
We Boomers didn’t burn down our heritage in a fit of thoughtless hedonism. I mean, we did some thoughtless hedonism, yeah, but that’s not where the real damage came from.
If you want to know where the damage came from, look up Yuri Bezmenov. Listen to him explain “demoralization” and the long game of Soviet culture-jamming against the West in general and the U.S. in particular.
Reset to year zero was a Marxist idea. It was part of a suite of memetic weapons, infectious propaganda bombs deployed against the social and cultural cohesion of the “main enemy”.
Often, they were successful in damaging us by leveraging not our vices but our virtues. Valorizing tolerance and liberality until they became helplessness in the face of more and more extreme forms of deviance was one of their attacks.
We didn’t fall on our own. We were pushed. The Boomer fault wasn’t that we were hedonists or nihilists, it’s that we didn’t have sufficient cultural immune defenses against what was being done to us.
Why that is exactly is a long sad story that I’m still not sure I completely understand. But I can hit some highlights.
One is that religion failed us. This is nobody’s fault and I don’t think it could have gone differently; it’s a failure that had been on the cards ever since the mechanistic worldview reached effective completion by Darwin. One of the things the Marxists did was work to accelerate the inevitable decay of religious authority.
Secular conservatives failed us, too. They had one job — just one job — which was to explain why all those Chesterton’s fences shouldn’t be torn down. They utterly flubbed that on all three levels of awareness, analysis, and persuasion. That could have gone differently.
It didn’t help that after the Army-McCarthy hearings in 1954 conservatives developed a severe case of cowardice about calling out Communist subversion.
That may have been their single greatest dereliction of duty. The result was that over the next 50 years Communist institutional capture of academia and other institutions went almost unopposed. Which is why today we struggle with “woke”.
Most of us Boomers weren’t wreckers, even by accident. Most of us were duped. It’s easy to say in hindsight we should have done better, but the enemy was very clever and determined.
Try not to judge us too harshly, kids. It’s nice to think that a later generation might have done better, but … I haven’t seen it happen yet.
December 20, 2024
Election Fever – Rise of Hitler 08, August 1930
World War Two
Published 19 December 2024August 1930 brings Germany to a critical juncture as parties prepare for the September elections. Amid street violence, bans on political uniforms, and soaring unemployment, the stakes couldn’t be higher. This episode unpacks the campaign strategies, shifting alliances, and rising tensions shaping the Republic’s future.
(more…)
December 19, 2024
QotD: Replacing the outdated “left” and “right” with more accurate terms
Keeping the simple spectrum approach of “Left” and “Right”, I’d divide the world into the fundamentally incompatible camps of “Theory” people and “Reality” people. We all know all about the Theory People, so just one quick example: J.B.S. Haldane. Indisputably a great scientist, and not just a great scientist, a great evolutionary biologist. If there’s anyone on this earth who should’ve been convinced, right down to the very marrow of his bones, that human beings are NOT blank slates, it was J.B.S. Haldane. And yet, he was a Marxist — and not just a Marxist, a really loopy one, even by the standards of the early 20th century.
It was guys like Haldane who caused Stove to write a great essay about “The Ishmael Effect”. He said something like (from memory) it’s a striking fact about powerful minds, that even though they know better than everyone else some fact about the physical world — the conservation of energy, say — their powerful minds cause them to get caught up in all the fascinating implications of their pet theory, such that they fail to see their pet theory requires energy not to be conserved. Thus (said Stove), a guy like Kant: After telling us that no human mind can access the Thing-in-Itself, he gives us four hundred pages of extremely detailed information about the Thing-in-Itself. Or Karl Marx, who was able to soar so far above his own economic class situation as to tell us, with oracular certainty, that no one is able to transcend the cognitive limits of his economic class situation. I don’t think it’s much of an exaggeration to say that “the Ishmael Effect” pretty much IS 19th century philosophy … and thanks to entropy, 20th century politics, and now 21st century culture.
Such are the Theory People who, however many raw IQ points they have, will really see five lights if The Party tells them to, because The Party controls the Theory and the Theory is never wrong, facts be damned. Call them Rubashovs if you like (and are feeling literary), but let’s move on to the Reality People. If Rubashov is the ultimate Theory Person — marching willingly off to his destiny in the dreaded Lubyanka, because The Party requires it and The Party is never wrong — so the ultimate Reality Person is Niccolo Machiavelli.
Much hooey has been written about The Prince, that it’s ACK-shully a biting satire (you could call the Rubashovs’ junior varsity the ACK-shully kids), but Ol’ Nick meant every fucking word. Politics was a contact sport in his day — he picked the wrong side of a political dispute, and got the strappado for it. He knew exactly what he was talking about, and had the disjointed shoulders to prove it.
Machiavelli is often called a cynic, but just as everything in Clown World always turns out faker and gayer than the most jaded can imagine, so even the hardest-bitten cynic can’t touch Ol’ Nick. The Prince is beautifully written, but it’s one of the toughest reads you’ll ever have, because surely he can’t mean what he just wrote … he just can’t. But he does, and it’s true — that for example a man will more quickly get over the murder of his father than the loss of his patrimony. And you know it’s true, if only in the darkest watches of the night when you toss and turn in the coldest of cold sweats. There aren’t more than a handful of sentences in The Prince that won’t give you insomnia, if you really start thinking them through …
But just as (one hopes) even Rubashov would balk at shooting his children on The Party’s orders, so even Machiavelli marvels at the truth that no one is thoroughly, consciously evil, even when it’s in his obvious best interest to be. A man will always convince himself he’s doing good, even when he’s obviously, objectively doing the most heinous evil, and that — Nick implies — is the way to manage a tyrant. Even when doing X is the obviously advantageous thing to do, and doing Y is obviously disadvantageous, you can convince someone to do Y by changing the moral frame.
There’s obviously a spectrum here, which like all human behavior bends in on itself at the extremes. One imagines Rubashov, for instance, going through an “if only Comrade Stalin knew!” type thought process if The Party ordered him to shoot his infant children. Yes, The Party is never wrong … but even though Comrade Stalin IS The Party, The Party is, finally, the historical manifestation of a metaphysical necessity, and therefore, in the light of the Highest Truth, Comrade Stalin — though never wrong!! — is perhaps misinformed in this case … Just as Francesco Sforza or whomever balks at murdering those infants in their cribs, though it’s clearly the very best course of action, politically.
Rubashov vs. Machiavelli. That’s the best I can do.
Severian, “Mail / Grab Bag”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-09-10.
December 18, 2024
QotD: Western shaming – the grass is always greener overseas
In the late 1950s, many elites in the United States bought the Soviet Union line that the march of global communism would “bury” the West. Then, as Soviet power eroded in the 1980s, Japan Inc. and its ascendant model of state-sponsored industry became the preferred alternative to Western-style democratic capitalism.
Once Japan’s economy ossified, the new utopia of the 1990s was supposedly the emerging European Union. Americans were supposed to be awed that the euro gained ground on the dollar. Europe’s borderless democratic socialism and its “soft power” were declared preferable to the reactionary U.S.
By 2015, the EU was a mess, so China was preordained as the inevitable global superpower. American intellectuals pointed to its high-speed rail transportation, solar industries and gleaming airports, in contrast to the hollowed-out and grubby American heartland.
Now the curtain has been pulled back on the interior rot of the Chinese Communist Party, its gulag-like re-education camps, its systematic mercantile cheating, its Orwellian surveillance apparatus, its serial public health crises and its primitive hinterland infrastructure.
After the calcification of the Soviet Union, Japan Inc., the EU and the Chinese superpower, no one quite knows which alternative will next supposedly bury America.
Victor Davis Hanson, “The Cult of Western Shaming”, Townhall.com, 2020-01-29.