Forces News
Published 26 Apr 2018To British troops based in north Germany in the last two decades of the Cold War, he was a legend. But this was no commando or member of the special forces.
Check out our website: http://forces.net
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ForcesNews
May 20, 2022
The Cold War Legend That Delivered SAUSAGES To Tanks | Forces TV
April 30, 2022
Tank Chats #145 Conqueror | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 14 Jan 2022► JOIN OUR PATREON: Our Patreons have already enjoyed Early Access and AD free viewing of our weekly YouTube video! Consider becoming a Patreon Supporter today: https://www.patreon.com/tankmuseum
► TIMESTAMP:
00:00 – INTRO
00:28 – FEATURES► SHOP THE TANK MUSEUM: tankmuseumshop.org
► FOLLOW THE TANK MUSEUM:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tankmuseum/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TankMuseum
Website: https://tankmuseum.org/
________________________◈ Created by The Tank Museum
#tankkmuseum #tankchats #DavidFletcher
April 28, 2022
Britain’s Incredible Recapture of South Georgia – Falklands War Documentary
Historigraph
Published 27 Apr 2022Go to https://squarespace.com/historigraph to get a free trial and 10% off your first purchase of
a website or domain.In just three weeks after the Argentinian invasion of the Falkland islands, Britain threw together a task force out of thin air, sailed it 8000 miles around the world and started taking its territory back. This is how it happened.
Made with thanks to the Fleet Air Arm Musuem in Yeovilton, Somerset. https://www.fleetairarm.com/
To help support the creation of the rest of the Falklands series, consider supporting on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/historigraph#Falklands40 #Historigraph
Come join the historigraph discord: https://discord.gg/ygypfs3BEB
Buy Historigraph Posters here! historigraph.creator-spring.com
► Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/historigraph
► Second Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpIj…
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/historigraph
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/historigraph
Thumbnail credit Daniel Behennec: https://www.naval-history.net/FxDBMis…Sources for the Falklands War Series (so far):
Max Hastings & Simon Jenkins, Battle for the Falklands
https://archive.org/details/battlefor…
Martin Middlebrook, Operation Corporate
Martin Middlebrook, Battle for the Malvinas
Mike Norman, The Falklands War There and Back Again: The Story of Naval Party 8901
Kenneth Privratsky, Logistics in the Falklands War
Sandy Woodward, One Hundred Days
Paul Brown, Abandon Ship
Julian Thompson, No Picnic
John Shields, Air Power in the Falklands Conflict
Edward Hampshire, The Falklands Naval Campaign 1982
Hugh McManners, Forgotten Voices of the Falklands
Cedric Delves, Across an Angry Sea: The SAS in the Falklands War
Rowland White, Vulcan 607
Vernon Bogdanor, “The Falklands War, 1982” lecture https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9bWw…
Arthur Gavshon, “The sinking of the Belgrano” https://archive.org/details/sinkingof…
Gordon Smith, Battle Atlas of the Falklands War 1982 by Land, Sea and Air
http://www.naval-history.net/NAVAL198…
Hansard- https://api.parliament.uk/historic-ha…
Recording of Thatcher’s statement to the Commons is from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HvbhV…Music Credits:
“Rynos Theme” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Crypto” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Stay the Course” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Other music and SFX from Epidemic Sound
April 21, 2022
L8(T) Enfield: The British Army Fails to Make a Sniper
Forgotten Weapons
Published 14 Dec 2021http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
https://www.floatplane.com/channel/Fo…
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.forgottenweapons.com
We looked at the 7.62mm conversion of the No4 Enfield into Rifle L8 yesterday. Part of that program was an attempt to develop a new sniper rifle on the L8 platform. To this end, six good-quality No4(T) Lee Enfield sniper rifles were tested for accuracy, then made into L8 rifles and fitted with No.32 telescopic sights (the standard scope from the .303 days) and tested for accuracy again. Much to the chagrin of the Army, the new L8(T) rifles were barely able to match the performance of the .303 rifles they began as. The goal was to significantly improve on the No4(T) accuracy, and that was clearly not happening.
However, at this same time, British civilian competition shooters were having excellent success making 7.62mm versions of the No4. It was only when Enfield was willing to collaborate with the British NRA and others that they were able to successfully create the L42A1 rifle, which at last met the accuracy goals of the program.
The rifle we are looking at today is one of those original six trials L8(T) rifles. Many thanks to the generous collector who allowed me to film it for you!
Contact:
Forgotten Weapons
6281 N. Oracle 36270
Tucson, AZ 85740
April 20, 2022
The Unbreakable ROCKEX: Canada’s answer to the Enigma machine
Polyus Studios
Published 30 Dec 2021Well before digital encryption and VPNs there was Rockex, Canada’s unbreakable cipher machine that rivaled the German Enigma in its day. Although completely hidden from the public, Canada has played a noticeable role in the history of espionage. During the Cold War Canadian cipher machines worked alongside those of her allies to keep communications secure and helped to preserve the peace.
Check out cryptomuseum.com for more information about Rockex and to find the source of most of the pictures of the device I used.
April 18, 2022
7.62mm Rifle L8: The Last Gasp of the Service Lee Enfield
Forgotten Weapons
Published 13 Dec 2021http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
https://www.floatplane.com/channel/Fo…
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.forgottenweapons.com
After the British adopted the FAL as the L1A1 rifle, there was still an interest in converting stocks of existing No4 Enfield rifles to the new 7.62x51mm cartridge for reserve and training use. A conversion system was developed using a new barrel, bolt, and magazine — although the Sterling company was doing much the same thing at the same time and intellectual property lawsuits would close the project for nearly 10 years. By the time the lawsuits cleared up, it had become clear that the rifles were neither particularly successful nor particularly necessary anymore. The problem the British has was one of accuracy — the 7.62mm version just wasn’t sufficiently accurate. A thousand were sold to Sierra Leone, and a few more used in New Zealand and by cadet organizations in the UK, but the project was basically a failure.
Contact:
Forgotten Weapons
6281 N. Oracle 36270
Tucson, AZ 85740
April 15, 2022
Look at Life – Thunder in Waiting (1960)
PauliosVids
Published 20 Nov 2018The deadly cargo of the Vulcan Bomber is a crucial part of Britain’s deterrent force.
April 5, 2022
Tower Bridge Fighter Jet Incident | Tales From the Bottle
Qxir
Published 26 Nov 2021This jet pilot decided to stage a protest in the skies of London, but his actions became more well known for an incident that occurred on his journey home.
“The Hawker Hunter Tower Bridge incident occurred on 5 April 1968 when Royal Air Force (RAF) Hawker Hunter pilot Alan Pollock performed unauthorised low flying over several London landmarks and then flew through the span of Tower Bridge on the Thames. His actions were to mark the 50th anniversary of the founding of the RAF and as a demonstration against the Ministry of Defence for not recognising it.
Upon landing he was arrested and later invalided out of the RAF on medical grounds, which avoided a court martial.”
More on Wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hawker_…Merch: teespring.com/stores/qxir
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/qxir
Twitter: https://twitter.com/QxirYT
Discord: https://discord.gg/jZzvvwJ
Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/qxiryt/
Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/Qxir/
From the comments:
Qxir
3 weeks ago (edited)
Yes, I know it’s pronounced “Tems” lol
April 2, 2022
Falklands War 82: How Argentina Seized the Islands
Historigraph
Published 31 Mar 2022For up to 60% off a subscription to Babbel, head over to https://bit.ly/historigraph_babbel
To help support the creation of the rest of the Falklands series, consider supporting on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/historigraphCome join the historigraph discord: https://discord.gg/ygypfs3BEB
Buy Historigraph Posters here! historigraph.creator-spring.com
This video was sponsored by Babbel.
► Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/historigraph
► Second Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpIj…
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/historigraph
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/historigraphSources for the Falklands War Series (so far):
Max Hastings & Simon Jenkins, Battle for the Falklands
https://archive.org/details/battlefor…
Martin Middlebrook, Operation Corporate
Martin Middlebrook, Battle for the Malvinas
Mike Norman, The Falklands War There and Back Again: The Story of Naval Party 8901
Kenneth Privratsky, Logistics in the Falklands War
Sandy Woodward, One Hundred Days
Paul Brown, Abandon Ship
Julian Thompson, No Picnic
John Shields, Air Power in the Falklands Conflict
Edward Hampshire, The Falklands Naval Campaign 1982
Hugh McManners, Forgotten Voices of the Falklands
Cedric Delves, Across an Angry Sea: The SAS in the Falklands War
Rowland White, Vulcan 607
Vernon Bogdanor, “The Falklands War 1982” lecture https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9bWw…
Arthur Gavshon, The sinking of the Belgrano https://archive.org/details/sinkingof…
Gordon Smith, Battle Atlas of the Falklands War 1982 by Land, Sea and Air
http://www.naval-history.net/NAVAL198…
Hansard – https://api.parliament.uk/historic-ha…
Recording of Margaret Thatcher’s statement to the commons is from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HvbhV…Music Credits:
“Rynos Theme” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Crypto” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Stay the Course” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Other music and SFX from Epidemic Sound
From the comments:
Historigraph
1 day agoThis series has been about four months in the making, and is by far the most ambitious project I’ve set out to complete on Historigraph. It’s going to be 8 (possibly 9) videos over the next three months, charting the course of the Falklands War as it happened 40 years ago.
If you liked this video and want to help support the creation of the remaining seven videos, it would meant the world to me if you could consider supporting on Patreon https://www.patreon.com/historigraph, become a channel member, or even just share this video far and wide.
March 25, 2022
Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow; Footage from its first flight
Polyus Studios
Published 7 Jul 2020Full documentary is still in development, enjoy the teaser!
(more…)
March 22, 2022
Russia’s historical expansionism
Arthur Chrenkoff notes some plot points from his second novel, written in 2010, and the headlines from Ukraine over the last few weeks:
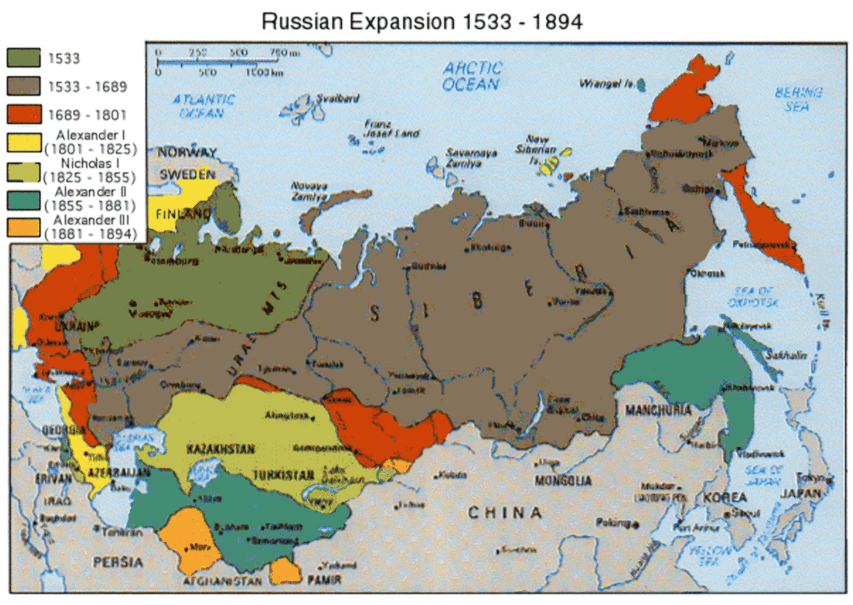
Russian expansion in Eurasia between 1533 and 1896.
Map originally from the Marxist Internet Archive via Wikimedia Commons.
Twelve years ago I wrote my second novel. The action took place in an Eastern European magic kingdom, superimposed in another dimension over what is, in this world, western Ukraine, south-east Poland, eastern Slovakia, and reaching down perhaps as far as the north-eastern corner of Hungary and the northern border of Romania. I named the kingdom after two historical regions, partly overlapping, by which this borderland of ethnicities and states had once been known. Last together as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, five independent nations now share the tectonic fault zone between Russia and the Orthodox Slavdom in the east and the Catholic Central Europe to the west.
One of the plots of the novel – titled Ruthenia & Galicia – revolved around the attempts by Russia to blackmail sections of the kingdom’s political establishment and destroy the country if unsuccessful.
If the plot sounds vaguely familiar today, I hasten to add I’m not claiming any prophetic abilities. While in 2010 Ukraine was largely at peace, two years prior Vladimir Putin briefly invaded Georgia in order to detach from it two separatist regions. In any case, the main point is that over the past five centuries, ever since overthrowing the Tartar yoke and consolidating under Ivan the Terrible, Russia has been an imperialist and expansionist power, which has repeatedly and consistently invaded, absorbed and dominated its many neighbours. Sadly, there is not much that is unusual about the current conflict in Ukraine; mid-17th century Poles, Ukrainians (to the extent there existed then any ethnic consciousness among the region’s peasantry), Cossacks and Muscovites would have been intimately familiar with the issues at stake.
Forget for a moment the Bidens, “globalists”, NATO, the “decadent West” and all other attempts to blame one’s own side first for, in effect, “provoking” Russia, and ask yourself why all of Russia’s regional neighbours, from Finland, through the Baltic states, Poland, Czechia, Slovakia, Rumania and beyond (Hungry and Serbia being two exceptions, the former contemporary political, the latter historical) are so fiercely opposed to Russia’s military actions and so supportive of Ukraine’s resistance against Putin’s aggression. Most of the historical Poland (which prior to WW2 included western Belarus and western Ukraine) had been, with small breaks, dominated, occupied and colonised by Russia (either as the centre of the empire or of the Soviet Union) for well over three centuries. Ditto for the Baltic states. Finland used to be a Russian vassal before WW1, fought Russia twice (in 1939-40 and 1941-44) and after the war had lent its very name to the concept of forced pro-Russian neutrality. Other parts of Central, Eastern and Southern Europe had only experienced Russian domination post-1945, as member states of the Warsaw Pact. Hungary and Czechoslovakia were at the receiving end of military interventions directed by Moscow; Poland almost was. Foreign policy realists like John Mearsheimer might argue for the unchanging reality of power politics in human history – from which point of view, a great power like Russia needs and will get a friendly or neutral buffer zone – but the states, which have the geographical and historical misfortune to exist within such buffer zone are by now well and truly over having to live in perpetual shadow and/or under the jackboot of an imperial power with delusions about its civilisational mission.
From that point of view, the challenge is not “de-Nazification” of Ukraine, whatever that means apart from being another example of Russia’s historical tendency, now also assumed by the Western left, of smearing everyone and everything it doesn’t like as Nazi (the Azov Battalion, whose heritage harks back to the Ukrainian collaboration with Hitler against Stalin, is a real problem – in an ideal world the Azov men and the pro-Russian Chechens would all kill each other – but as propagandictically exaggerated as attempts to portray the American right as a whole as white supremacists, bigots, extremists and terrorists). The true challenge is de-imperialising Russia.
This is perhaps a Sisyphean task. Former imperialist powers like Germany and Japan are now normal countries, liberal democracies, successful and prosperous economies and generally good international citizens. Arguably the reason for that can be traced to their unequivocal military defeat in WW2, large scale devastation and subsequent occupation, which forced a traumatic psychological reset. After “year zero”, the past was consigned to history and new society were born.
This has not happened in Russia. In fact, Russia today is much more reminiscent of Germany in the 1930s than Germany in the 1960s. Like the Imperial Wilhelmine Germany, Russia had lost the war – the cold one – without suffering a crushing military defeat or the indignity of foreign occupation. What the Versailles Peace was for the inter-war Germany, the dissolution of the Soviet Union has been for Russia – a disadvantageous and humiliating settlement, which resulted in imperial dissolution and has left millions of Russian speakers scattered beyond the borders of the Fatherland/Motherland. The newly independent states are illegitimate – both the Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union considered Poland a “bastard creation of Versailles”, just as Russian nationalists nowadays see the former Soviet republics and satellites as artificial entities that are rightfully Russia’s. If there are temperamental similarities between the Weimer Germany and Yeltsin’s Russia, Putin himself resembles Hitler circa 1938. Let us hope and pray he never graduates to 1939 and beyond (though some would argue that the invasion of Ukraine is worryingly analogous to the invasion of Poland at the start of WW2). For the international community, Russia of the past two and a bit decades represents the worst of all worlds: humiliated enough to be resentful but undefeated enough to remain unrepentant. Hence Putin can claim the fall of the Soviet Union to be the greatest tragedy of the 20th century (as opposed to both world wars or communism) and agitate for the de facto recreation of the Russian, if not the Soviet, empire.
Imperial Germany’s crushing military defeat (from the “Black Day of the German Army” through the Hundred Days to the Armistice) at the hands of the British, French, American, Canadian, and Australian forces on the western front … but stopped near the German border. The provisional government after the fall of the monarchy signed the armistice because the German army had been decisively defeated and was dissolving in the face of Allied pressure. Because the fighting didn’t penetrate into Germany proper — as it did in 1944-45 — this significantly helped solidify the myth that the Germany army had been “stabbed in the back” by the civilian government, which was so helpful to the Nazis during their rise to power.
West Germany’s Wirtschaftwunder — the staggering economic postwar recovery
Christian Monson debunks the common tale taught in western schools of reason for the amazing recovery of West Germany’s economy after World War Two:
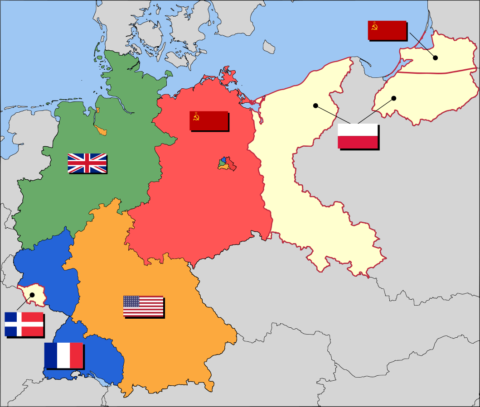
Occupation zone borders in Germany, 1947. The territories east of the Oder-Neisse line, under Polish and Soviet administration/annexation, are shown as cream as is the likewise detached Saar protectorate. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
Image based on map data of the IEG-Maps project (Andreas Kunz, B. Johnen, and Joachim Robert Moeschl of the University of Mainz) — www.ieg-maps.uni-mainz.de, via Wikimedia Commons.
This “economic miracle” is commonly referred to as die Wirtschaftswunder. But how did Germany go from rubble to riches in just a decade while neutral countries like Spain merely treaded economic water? If you ask your average American history student, they will say the Marshall Plan, of course!
Unfortunately, the ubiquity of the myth that the Marshall Plan rebuilt Germany is proof that state-controlled education favors propaganda over economic literacy. Despite the fact that most modern historians don’t give the Marshall Plan much credit at all for rebuilding Germany and attribute to it less than 5 percent of Germany’s national income during its implementation, standard history textbooks still place it at the forefront of the discussion about post-war reconstruction.
Consider this section from McDougal Littell’s World History (p. 968), the textbook I was given in high school:
This assistance program, called the Marshall Plan, would provide food, machinery, and other materials to rebuild Western Europe. As Congress debated the $12.5 billion program in 1948, the Communists seized power in Czechoslovakia. Congress immediately voted approval. The plan was a spectacular success.
Of course, the textbook makes no mention of the actual cause of the Wirtschaftwunder: sound economic policy. That’s because, for the state, the Marshall Plan makes great statist mythology.
Not only is it frequently brought up to justify the United States getting involved in foreign conflicts, but it simply gives support for central planning. Just look at the economic miracle the government was able to create with easy credit, they say.
And of course, admitting that the billions of dollars pumped into Germany after WWII accomplished next to nothing, especially when compared to something as simple as sound money, would be tantamount to admitting that the government spends most of its time making itself needed when it isn’t and thereby doing little besides getting in the way.
Credit for the turnaround should be accorded to Ludwig Erhard, according to Alasdair Macleod at the Cobden Centre:
Anyone who favours regulation needs to explain away Germany’s post-war success. Her economy had been destroyed, firstly by the Nazi war machine, and then by Allied bombing. We easily forget the state of ruin the country was in, with people in the towns and cities actually starving in the post-war aftermath. The joint British and American military solution was to extend and intensify war-time rationing and throw Marshall aid at the problem.
Then a man called Ludwig Erhard was appointed director of economics by the Bizonal Economic Council, in effect he became finance minister. He decided, against British and American misgivings, as well as opposition from the newly-recreated Social Democrats, to do away with price controls and rationing, which he did in 1948. These moves followed his currency reform that June, which contracted the money supply by about 90%. He also slashed income tax from 85% to 18% on annual incomes over Dm2,500 (US$595 equivalent).
Economists of the Austrian school would comprehend and recommend this strategy, but it goes wholly against the bureaucratic grain. General Lucius Clay, who was the military governor of the US Zone, and to whom Erhard reported, is said to have asked him, “Herr Erhard, my advisers tell me what you have done is a terrible mistake. What do you say to that?”
Erhard replied, “Herr General, pay no attention to them! My advisers tell me the same thing.”
About the same time, a US Colonel confronted Erhard: “How dare you relax our rationing system, when there is a widespread food shortage?”
Erhard replied, “I have not relaxed rationing, I have abolished it. Henceforth the only rationing ticket the people will need will be the deutschemarks. And they will work hard to get those deutschemarks, just wait and see.”
The US Colonel did not have to wait long. According to contemporary accounts, within days of Erhard’s currency reform, shops filled with goods as people realised the money they sold them for would retain its value. People no longer needed to forage for the basics in life, so absenteeism from work halved, and industrial output rose more than 50% in the second half of 1948 alone.
March 6, 2022
March 4, 2022
Germany is finally being forced to adapt to 21st century realities
In The Line, Matt Gurney outlines German history since the end of WW2 and why German governments have allowed the Bundeswehr to shrivel to almost Canadian Armed Forces status and why they have also been eager to scrap local power options in favour of imported Russian oil and gas:

A Bundeswehr Marder 1A3 Infantry Fighting Vehicle during an exercise at the Munster Training Centre, 1 September, 2010.
Photo by Bundeswehr-Fotos via Wikimedia Commons.
After 1990, the newly combined German military largely evaporated. Manpower levels plummeted; huge quantities of equipment were mothballed or sold off. German military spending fell well below that of other large European NATO allies. Indeed, despite their military history and economic clout, Germany, on a per capita basis, is more a Canada to NATO than a France or Britain.
And not by accident. Germany’s partial demilitarization was driven by a series of considerations, all of which reflected deliberate choices. Germany is still haunted by its Nazi-era history, and even its peacekeeping contribution to Afghanistan was controversial, marking the country’s first major foreign mission since 1945. A smaller, little-used military is a balm to the nation’s wounded psyche. Further, a small German military, and a Germany broadly and overtly uninterested in military affairs, did much to ease concerns of wary allies with living memories of life under the Luftwaffe and Wehrmacht.
And, well, yeah: the Germans also cut their force levels like crazy because, as noted in my recent column here, it saved them a ton of money.
It’s important to understand, though, that it’s not just about the German military, though that’s perhaps the most stark symbol. The country has emerged as a leading force for European unity and liberal-democratic values. Not for nothing was recently retired chancellor Angela Merkel touted as a leader of the free world during the rocky Trump presidency in Washington. Under Merkel, the country tried to live the ideal of the modern Europe, including by letting in a million refugees fleeing fighting in the Middle East, a decision that has opened up political fissures in Germany that remain a problem today.
Much has also been made of the country’s decision to shut down its nuclear plants and rely instead on imports of Russian natural gas for energy. Dismissed by many as foolhardy — and it was foolhardy — it’s also not hard to read a whiff of almost pathetic desperation into the move. If we are just nice enough, if we buy enough Russian gas, if we perfectly model the new amiable European ideal, maybe, just maybe, could Germany cast off some of its historical taint?
If that was the plan, it hasn’t worked, and gosh, it hasn’t worked with a vengeance. Since the Cold War ended — paused? changed? — the Germans have remained minimally armed and resolutely affable and committed to European unity. The country did increase military spending after Putin’s 2014 annexation of Crimea, but it almost had to — the German military had fallen into a state of neglect and non-functionality that any Canadian would find instantly recognizable. Hundreds of billions of Euros were budgeted, and tens of thousands of new enlistments authorized, in the first expansion of German military power since reunification. Even while embarking on this effort, though, Germany continued to shut down its nuclear plants and increase its use of Russian energy imports.
That’s over. Deader than East Germany, as much as a relic as the bits of the Berlin Wall that tourists now collect (I have a fragment myself somewhere in a file in my office, though damned if I could find it when I went searching today while procrastinating on this column). On top of the many billions of Euros already pledged to military modernization, Chancellor Olaf Scholz has committed a supplemental fund of a further €100 billion for immediate shoring up of military capabilities, and has also committed to substantially raise Germany’s baseline defence spending to the two per cent NATO target — an effectively permanent annual boost of roughly a third over the already higher level achieved since 2015.
Checkpoint Charlie – Berlin’s Cold War Frontier
Mark Felton Productions
Published 4 Dec 2018The history of Checkpoint Charlie, the most famous of Berlin’s East-West crossing points and the focus of a serious standoff between the US and Soviet Union in 1961 that could have led to World War III.
Support Mark at Patreon for $1 a Month!
https://www.patreon.com/markfeltonpro…