The first issue is what in military parlance is called the “tooth to tail” ratio. This is the ratio of the number of actual combat troops (the “tooth”) to logistics and support personnel (the “tail”) in a fighting force. Note that these are individuals in the fighting force – the question of the supporting civilian economy is separate. The thing is, the tooth to tail ratio has tended to shift towards a longer tail over time, particular as warfare has become increasingly industrialized and technical.
The Roman legion, for instance, was essentially all tooth. While there was a designation for support troops, the immunes, so named because they were immune from having to do certain duties in camp, these fellows were still in the battle line when the legion fought. The immunes included engineers, catapult-operators, musicians, craftsmen, and other specialists. Of course legions were also followed around by civilian non-combatants – camp-followers, sutlers, etc. – but in the actual ranks, the “tail” was minimal.
You can see much the same in the organization of medieval “lances” – units formed around a single knight. The Burgundian “lance” of the late 1400s was composed of nine men, eight of which were combatants (the knight, a second horsemen, the coustillier, and then six support soldiers, three mounted and three on foot) and one, the page, was fully a non-combatant. A tooth-to-tail ratio of 8:1. That sort of “tooth-heavy” setup is common in pre-industrial armies.
The industrial revolution changes a lot, as warfare begins to revolve as much around mobilizing firepower, typically in the form of mass artillery firepower as in mobilizing men. We rarely in our fiction focus on artillery, but modern warfare – that is warfare since around 1900 – is dominated by artillery and other forms of [indirect] fires. Artillery, not tanks or machine guns, after all was the leading cause of combat death in both World Wars. Suddenly, instead of having each soldier carry perhaps 30-40kg of equipment and eat perhaps 1.5kg of food per day, the logistics concern is moving a 9-ton heavy field gun that might throw something like 14,000kg of shell per day during a barrage, for multiple days on end. Suddenly, you need a lot more personnel moving shells than you need firing artillery.
As armies motorized after WWI and especially after WWII, this got even worse, as a unit of motorized or mechanized infantry needed a small army of mechanics and logistics personnel handling spare parts in order to stay motorized. Consequently, tooth-to-tail ratios plummeted, inverted and then kept going. In the US Army in WWI, the ratio was 1:2.6 (note that we’ve flipped the pre-industrial ratio, that’s 2.6 non-combat troops for every front line combat solider), by WWII it was 1:4.3 and by 2005 it was 1:8.1. Now I should note there’s also a lot of variance here too, particularly during the Cold War, but the general trend has been for this figure to continue increasing as more complex, expensive and high-tech weaponry is added to warfare, because all of that new kit demands technicians and mechanics to maintain and supply it.
[NR: Early in WW2, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill frequently harassed his various North African generals for the disparity between the “ration strength” of their commands and the much-smaller number of combat troops deployed. If General Wavell had 250,000 drawing rations, Churchill (who last commanded troops in the field in mid-WW1) assumed that this meant close to 200,000 combat troops available to fight the Italians and (later) the Germans. This almost certainly contributed to the high wastage rate of British generals in the Western Desert.]
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday, April 22, 2022”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-04-22.
December 14, 2022
QotD: The “tooth-to-tail ratio” in armies
December 10, 2022
QotD: The Western Roman Empire – “decline and fall” or “change and continuity”?
So who are our [academic] combatants? To understand this, we have to lay out a bit of the “history of the history” – what is called historiography in technical parlance. Here I am also going to note the rather artificial but importance field distinction here between ancient (Mediterranean) history and medieval European history. As we’ll see, viewing this as the end of the Roman period gives quite a different impression than viewing it as the beginning of a new European Middle Ages. The two fields “connect” in Late Antiquity (the term for this transitional period, broadly the 4th to 8th centuries), but most programs and publications are either ancient or medieval and where scholars hail from can lead to different (not bad, different) perspectives.
With that out of the way, the old view, that of Edward Gibbon (1737-1794) and indeed largely the view of the sources themselves, was that the disintegration of the western half of the Roman polity was an unmitigated catastrophe, a view that held largely unchallenged into the last century; Gibbon’s great work, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire (1789) gives this school its name, “decline and fall“. While I am going at points to gesture to Gibbon’s thinking, we’re not going to debate him; he is the “old man” of our title. Gibbon himself largely exists only in historiographical footnotes and intellectual histories; he is not at this point seriously defended nor seriously attacked but discussed as the venerable, but now out of date, origin point for all of this bickering.
The real break with that view came with the work of Peter Brown, initially in his The World of Late Antiquity (1971) and more or less canonically in The Rise of Western Christendom (1st ed. 1996; 2nd ed. 2003, 3rd ed. 2013). The normal way to refer to the Peter Brown school of thought is “change and continuity” (in contrast to the traditional “decline and fall”), though I rather like James O’Donnell’s description of it as the Reformation in late antique studies.
Among medievalists this reformed view, which focuses on continuity of culture and institutions from late antiquity to the early Middle Ages, remains essentially the orthodoxy, to the point that, for instance, the very recent (and quite excellent) The Bright Ages: A New History of Medieval Europe (2021) can present this vision as an uncomplicated fact, describing the “so-called Fall of Rome” and noting that “there was never a moment in the next thousand years in which at least one European or Mediterranean ruler didn’t claim political legitimacy through a credible connection to the empire of the Romans” and that “the idea that Rome ‘fell’ on the other hand, relies upon a conception of homogeneity – of historical stasis … things changed. But things always change” (3-4, 12-3). As we’ll see, I don’t entirely disagree with those statements, but they are absolute to a degree that suggests there is no real challenge to the position. There have been a few cracks in this orthodoxy among medievalists, particularly the work of Robin Flemming (a revision, not a clear break, to be sure), to which we’ll return, but the cracks have been relatively few.
While some ancient historians also bought into this view, purchase there has always been uneven and seems, to me at least, now to be waning further. Instead, a process of what James O’Donnell describes as a “counter-reformation” (which he stoutly resists with his own The Ruin of the Roman Empire; O’Donnell is a declared reformer) is well underway, a response to the “change and continuity” narrative which seeks to update and defend the notion that there really was a fall of Rome and that it really was quite bad actually. This is not, I should note, an effort to revive Gibbon per se; it does not typically accept his understanding of the cause of this decline (and often characterizes exactly what is declining differently). Nevertheless, this position too is sometimes termed the “decline and fall” school. My own sense of the field is that while nearly all ancient historians will feel the need to concede at least some validity to the reformed “change and continuity” vision, that the counter-reformation school is the majority view among ancient historians at this point (in a way that is particularly evident in overview treatments like textbooks or the Cambridge Ancient History (second edition)). We’ll meet many of the core works of this revised “decline and fall” school as we go.
As O’Donnell noted in a 2005 review for the BMCR, the reformed school tends to be strongest in the study of the imperial east rather than the west (something that will make a lot of sense in a moment), and in religious and cultural history; the counter-reformation school is stronger in the west than the east and in military and political history, though as we’ll see, to that list must at this point now be added archaeology along with demographic and economic history, at which point the weight of fields tends to get more than a little lopsided.
Those are our two knights – the “change and continuity” knight and the “decline and fall” knight (and our old man Gibbon, long out of his dueling days). To this we must add the nitwit: a popular vision, held by functionally no modern scholars, which represents the Middle Ages in their entirety as a retreat from a position of progress during the Roman period which was only regained during the “Renaissance” (generally represented as a distinct period from the Middle Ages) which then proceeded into the upward trajectory of the early modern period. Intellectually, this vision traces back to what Renaissance thinkers thought about themselves and their own disdain for “medieval” scholastic thinking (that is, to be clear, the thinking of their older teachers), a late Medieval version of “this ain’t your daddy’s rock and roll!”
But almost every intellectual movement represents itself as a radical break with the past (including, amusingly, many of the scholastics! Let me tell you about Peter Abelard sometime); as historians we do not generally accept such claims uncritically at face value. For a long time, well into the 19th century, the Renaissance’s cultural cachet in Europe (and the cachet of the classical period where it drew its inspiration) shielded that Renaissance claim from critique; that patina now having worn thin, most scholars now reject it, positioning the Renaissance as a continuation (with variations on the theme) of the Middle Ages, a smooth transition rather than a hard break. At the same time, knowledge of developments within the Middle Ages have made the image of one unbroken “Dark Age” untenable and made clear that the “upswing” of the early modern period was already well underway in the later Middle Ages and in turn had its roots stretching even deeper into the period. It is also worth noting here, that the term “Dark Age” has to do with the survival of evidence, not living conditions: the age was not dark because it was grim, it was dark because we cannot see it as clearly.
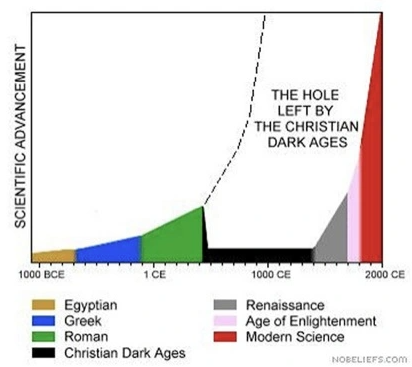
The popular version of this idea continues, however, to have a lot of sway in the popular conception of the Middle Ages, encouraged by popular culture that mistakes the excesses of the early modern period for “medieval” superstition and exaggerates the poverty of the medieval period (itself essentialized to its worst elements despite being approximately a millennia long), all summed up in this graph:
We are mostly going to just dunk relentlessly on this graph and yet we will not cover even half of the necessary dunking this graph demands. We may begin by noting that in its last century, the Roman Empire was Christian, a point apparently missed here.
While that sort of vision is not seriously debated by scholars, it needs to be addressed here too, in part because I suspect a lot of the energy behind the “change and continuity” position is in fact to counter some of the worst excesses of this thesis, which for simplicity, we’ll just refer to as “The Dung Ages” argument, but also because assessing how bad the fall of the Roman Empire in the West was demands that we consider how long-lasting any negative ramifications were.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Rome: Decline and Fall? Part I: Words”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-01-14.
December 6, 2022
QotD: Mao Zedong’s theory of “Protracted War”
The foundation for most modern thinking about this topic begins with Mao Zedong’s theorizing about what he called “protracted people’s war” in a work entitled – conveniently enough – On Protracted War (1938), though while the Chinese Communist Party would tend to subsequently represent the ideas there are a singular work of Mao’s genius, in practice he was hardly the sole thinker involved. The reason we start with Mao is that his subsequent success in China (though complicated by other factors) contributed to subsequent movements fighting “wars of national liberation” consciously modeled their efforts off of this theoretical foundation.
The situation for the Chinese Communists in 1938 was a difficult one. The Chinese Red Army has set up a base of power in the early 1930s in Jiangxi province in South-Eastern China, but in 1934 had been forced by Kuomintang Nationalist forces under Chiang Kai-shek to retreat, eventually rebasing over 5,000 miles away (they’re not able to straight-line the march) in Shaanxi in China’s mountainous north in what became known as The Long March. Consequently, no one could be under any illusions of the relative power of the Chiang’s nationalist forces and the Chinese Red Army. And then, to make things worse, in 1937, Japan had invaded China (the Second Sino-Japanese War, which was a major part of WWII), beating back the Nationalist armies which had already shown themselves to be stronger than the Communists. So now Mao has to beat two armies, both of which have shown themselves to be much stronger than he is (though in the immediate term, Mao and Chiang formed a “United Front” against Japan, though tensions remained high and both sides expected to resume hostilities the moment the Japanese threat was gone). Moreover, Mao’s side lacks not only the tools of war, but the industrial capacity to build the tools of war – and the previous century of Chinese history had shown in stark terms how difficult a situation a non-industrial force faced in squaring off against industrial firepower.
That’s the context for the theory.
What Mao observed was that a “war of quick decision” would be one that the Red Army would simply lose. Because he was weaker, there was no way to win fast, so trying to fight a “fast” war would just mean losing. Consequently, a slow war – a protracted war – was necessary. But that imposes problems – in a “war of quick decision” the route to victory was fairly clear: destroy enemy armed forces and seize territory to deny them the resources to raise new forces. Classic Clausewitzian (drink!) stuff. But of course the Red Army couldn’t do that in 1938 (they’d just lose), so they needed to plan another potential route to victory to coordinate their actions. That is, they need a strategic framework – remember that strategy is the level of military analysis where we think about what our end goals should be and what methods we can employ to actually reach those goals (so that we are not just blindly lashing out but in fact making concrete progress towards a desired end-state).
Mao understands this route as consisting of three distinct phases, which he imagines will happen in order as a progression and also consisting of three types of warfare, all of which happen in different degrees and for different purposes in each phase. We can deal with the types of warfare first:
- Positional Warfare is traditional conventional warfare, attempting to take and hold territory. This is going to be done generally by the regular forces of the Red Army.
- Mobile Warfare consists of fast-moving attacks, “hit-and-run”, performed by the regular forces of the Red Army, typically on the flanks of advancing enemy forces.
- Guerrilla Warfare consists of operations of sabotage, assassination and raids on poorly defended targets, performed by irregular forces (that is, not the Red Army), organized in the area of enemy “control”.
The first phase of this strategy is the enemy strategic offensive (or the “strategic defensive” from the perspective of Mao). Because the enemy is stronger and pursuing a conventional victory through territorial control, they will attack, advancing through territory. In this first phase, trying to match the enemy in positional warfare is foolish – again, you just lose. Instead, the Red Army trades space for time, falling back to buy time for the enemy offensive to weaken rather than meeting it at its strongest, a concept you may recall from our discussions of defense in depth. The focus in this phase is on mobile warfare, striking at the enemy’s flanks but falling back before their main advances. Positional warfare is only used in defense of the mountain bases (where terrain is favorable) and only after the difficulties of long advances (and stretched logistics) have weakened the attacker. Mobile warfare is supplemented by guerrilla operations in rear areas in this phase, but falling back is also a key opportunity to leave behind organizers for guerrillas in the occupied zones that, in theory at least, support the retreating Red Army (we’ll come back to this).
Eventually, due to friction (drink!) any attack is going to run out of steam and bog down; the mobile warfare of the first phase is meant to accelerate this, of course. That creates a second phase, “strategic stalemate” where the enemy, having taken a lot of territory, is trying to secure their control of it and build new forces for new offensives, but is also stretched thin trying to hold and control all of that newly seized territory. Guerrilla attacks in this phase take much greater importance, preventing the enemy from securing their rear areas and gradually weakening them, while at the same time sustaining support by testifying to the continued existence of the Red Army. Crucially, even as the enemy gets weaker, one of the things Mao imagines for this phase is that guerrilla operations create opportunities to steal military materiel from the enemy so that the factories of the industrialized foe serve to supply the Red Army – safely secure in its mountain bases – so that it becomes stronger. At the same time (we’ll come back to this), in this phase capable recruits are also be filtered out of the occupied areas to join the Red Army, growing its strength.
Finally in the third stage, the counter-offensive, when the process of weakening the enemy through guerrilla attacks and strengthening the Red Army through stolen supplies, new recruits and international support (Mao imagines the last element to be crucial and in the event it very much was), the Red Army can shift to positional warfare again, pushing forward to recapture lost territory in conventional campaigns.
Through all of this, Mao stresses the importance of the political struggle as well. For the guerrillas to succeed, they must “live among the people as fish in the sea”. That is, the population – and in the China of this era that meant generally the rural population – becomes the covering terrain that allows the guerrillas to operate in enemy controlled areas. In order for that to work, popular support – or at least popular acquiescence (a village that doesn’t report you because it supports you works the same way as a village that doesn’t report you because it hates Chiang or a village that doesn’t report you because it knows that it will face violence reprisals if it does; the key is that you aren’t reported) – is required. As a result both retreating Red Army forces in Phase I need to prepare lost areas politically as they retreat and then once they are gone the guerrilla forces need to engage in political action. Because Mao is working with a technological base in which regular people have relatively little access to radio or television, a lot of the agitation here is imagined to be pretty face-to-face, or based on print technology (leaflets, etc), so the guerrillas need to be in the communities in order to do the political work.
Guerrilla actions in the second phase also serve a crucial political purpose: they testify to the continued existence and effectiveness of the Red Army. After all, it is very important, during the period when the main body of Communist forces are essentially avoiding direct contact with the enemy that they not give the impression that they are defeated or have given up in order to sustain will and give everyone the hope of eventual victory. Everyone there of course also includes the main body of the army holed up in its mountain bases – they too need to know that the cause is still active and that there is a route to eventual victory.
Fundamentally, the goal here is to make the war about mobilizing people rather than about mobilizing industry, thus transforming a war focused on firepower (which you lose) into a war about will – in the Clausewitzian (drink! – folks, I hope you all brought more than one drink for this …) sense – which can be won, albeit only slowly, as the slow trickle of casualties and defeats in Phase II steadily degrades enemy will, leading to their weakness and eventual collapse in Phase III.
I should note that Mao is very open that this protracted way of war would be likely to inflict a lot of damage on the country and a lot of suffering on the people. Casualties, especially among the guerrillas, are likely to be high and the guerrillas own activities would be likely to produce repressive policies from the occupiers (not that either Chiang’s Nationalists of the Imperial Japanese Army – or Mao’s Communists – needed much inducement to engage in brutal repression). Mao acknowledges those costs but is largely unconcerned by them, as indeed he would later as the ruler of a unified China be unconcerned about his man-made famine and repression killing millions. But it is important to note that this is a strategic framework which is forced to accept, by virtue of accepting a long war, that there will be a lot of collateral damage.
Now there is a historical irony here: in the event, Mao’s Red Army ended up not doing a whole lot of this. The great majority of the fighting against Japan in China was positional warfare by Chiang’s Nationalists; Mao’s Red Army achieved very little (except preparing the ground for their eventual resumption of war against Chiang) and in the event, Japan was defeated not in China but by the United States. Japanese forces in China, even at the end of the war, were still in a relatively strong position compared to Chinese forces (Nationalist or Communist) despite the substantial degradation of the Japanese war economy under the pressure of American bombing and submarine warfare. But the war with Japan left Chiang’s Nationalists fatally weakened and demoralized, so when Mao and Chiang resumed hostilities, the former with Soviet support, Mao was able to shift almost immediately to Phase III, skipping much of the theory and still win.
Nevertheless, Mao’s apparent tremendous success gave his theory of protracted war incredible cachet, leading it to be adapted with modifications (and variations in success) to all sorts of similar wars, particularly but not exclusively by communist-aligned groups.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: How the Weak Can Win – A Primer on Protracted War”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-03-03.
December 2, 2022
QotD: Rome’s legions settle down to permanent fortresses
The end of the reign of Augustus (in 14AD) is a convenient marker for a shift in Roman strategic aims away from expansion and towards a “frontier maintenance”. The usual term for both the Roman frontier and the system of fortifications and garrisons which defended it is the limes (pronounced “lim-ees”), although this wasn’t the only word the Romans applied to it. I want to leave aside for a moment the endless, complex conversation about the degree to which the Romans can actually be said to have strategic aims, though for what it is worth I am one of those who contends that they did. We’re mostly interested here in Roman behavior on the frontiers, rather than their intent anyway.
What absolutely does begin happening during the reign of Augustus and subsequently is that the Roman legions, which had spent the previous three centuries on the move outside of Italy, begin to settle down more permanently on Rome’s new frontiers, particularly along the Rhine/Danube frontier facing Central and Eastern Europe and the Syrian frontier facing the Parthian Empire. That in turn meant that Roman legions (and their supporting auxiliary cohorts) now settled into permanent forts.
The forts themselves, at least in the first two centuries, provide a fairly remarkably example of institutional inertia. While legionary forts of this early period typically replaced the earthwork-and-stakes wall (the agger and vallum) with stone walls and towers and the tents of the camp with permanent barracks, the basic form of the fort: its playing-card shape, encircling defensive ditches (now very often two or three ditches in sequence) remain. Of particular note, these early imperial legionary forts generally still feature towers which do not project outward from the wall, a stone version of the observation towers of the old Roman marching camp. Precisely because these fortifications are in stone they are often very archaeologically visible and so we have a fairly good sense of Roman forts in this period. In short then, put in permanent positions, Roman armies first constructed permanent versions of their temporary marching camps.
And that broadly seems to fit with how the Romans expected to fight their wars on these frontiers. The general superiority of Roman arms in pitched battle (the fancy term here is “escalation dominance” – that escalating to large scale warfare favored the heavier Roman armies) meant that the Romans typically planned to meet enemy armies in battle, not sit back to withstand sieges (this was less true on Rome’s eastern frontier since the Parthians were peer competitors who could rumble with the Romans on more-or-less even terms; it is striking that the major centers in the East like Jerusalem or Antioch did not get rid of their city walls, whereas by contrast the breakdown of Roman order in the third century AD and subsequently leads to a flurry of wall-building in the west where it is clear many cities had neglected their defensive walls for quite a long time). Consequently, the legionary forts are more bases than fortresses and so their fortifications are still designed to resist sudden raids, not large-scale sieges.
They were also now designed to support much larger fortification systems, which now gives us a chance to talk about a different kind of fortification network: border walls. The most famous of these Roman walls of course is Hadrian’s Wall, a mostly (but not entirely) stone wall which cuts across northern England, built starting in 122. Hadrian’s Wall is unusual in being substantially made out of stone, but it was of-a-piece with various Roman frontier fortification systems. Crucially, the purpose of this wall (and this is a trait it shares with China’s Great Wall) was never to actually prevent movement over the border or to block large-scale assaults. Taking Hadrian’s wall, it was generally manned by something around three legions (notionally; often at least one of the legions in Britain was deployed further south); even with auxiliary troops nowhere near enough to actually manage a thick defense along the entire wall. Instead, the wall’s purpose is slowing down hostile groups and channeling non-hostile groups (merchants, migrants, traders, travelers) towards controlled points of entry (valuable especially because import/export taxes were a key source of state revenue), while also allowing the soldiers on the wall good observation positions to see these moving groups. You can tell the defense here wasn’t prohibitive in part because the main legionary fortresses aren’t generally on the wall, but rather further south, often substantially further south, which makes a lot of sense if the plan is to have enemies slowed (but not stopped) by the wall, while news of their approach outraces them to those legionary forts so that the legions can form up and meet those incursions in an open battle after they have breached the wall itself. Remember: the Romans expect (and get) a very, very high success rate in open battles, so it makes sense to try to force that kind of confrontation.
This emphasis on controlling and channeling, rather than prohibiting, entry is even more visible in the Roman frontier defenses in North Africa and on the Rhine/Danube frontier. In North Africa, the frontier defense system was structured around watch-posts and the fossatum Africae, a network of ditches (fossa) separating the province of Africa (mostly modern day Tunisia) from non-Roman territory to its south. It isn’t a single ditch, but rather a system of at least four major segments (and possibly more), with watch-towers and smaller forts in a line-of-sight network (so they can communicate); the ditch itself varies in width and depth but typically not much more than 6m wide and 3m deep. Such an obstruction is obviously not an prohibitive defense but the difficulty of crossing is going to tend to channel travelers and raids to the intentional crossings or alternately slow them down as they have to navigate the trench (a real problem here where raiders are likely to be mounted and so need to get their horses and/or camels across).
On the Rhine and the Danube, the defense of the limes, the Roman frontier, included a border wall (earthwork and wood, rather than stone like Hadrian’s wall), similarly supported by legions stationed to the rear, with road networks positioned; once again, the focus is on observing threats, slowing them down and channeling them so that the legions can engage them in the field. This is a system based around observe-channel-respond, rather than an effort to block advances completely.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part II: Romans Playing Cards”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-11-12.
November 28, 2022
QotD: The Carolingian army
In essence, the Carolingian army was an odd sort of layer-cake, in part because it represented a transitional stage from the Germanic tribal levies of the earliest Middle Ages towards to emergence and dominance of the mounted aristocracy of the early part of the High Middle Ages (note: the Middle Ages is a long period, Europe is a big place, and it moves through a lot of military systems; to talk of a single “medieval European system” is almost always a dangerous over-generalization). The top of the layer-cake consisted of the mounted aristocrats, in basically the same organization as the lords of Rohan discussed above: the great magnates (including the king) maintained retinues of mounted warriors, while smaller (but still significant) landholders might fight as individual cavalrymen, being grouped into the retinues of the great magnates tactically, even if they weren’t subordinate to those magnates politically (although they were often both). These two groups – the mounted magnate with his retinue and the individual mounted warrior – would eventually become the nobility and the knightly class, but in the Carolingian period these social positions were not so clearly formed or rigid yet. We ought to understand that to speak of a Carolingian “knight” (translated for Latin miles, which ironically in classical Latin is more typically used of infantrymen) is not the same, in social consequence, as speaking of a 13th century knight (who might also be described as a miles in the Latin sources).
But below that in the Carolingian system, you have the select levy, relatively undistinguished (read: not noble, but often reasonably well-to-do) men recruited from the smaller farmers and townsfolk. This system itself seems to have derived from an earlier social understanding that all free men (or all free property owning men) held an obligation for military service; Halsall notes in the eighth century the term arimannus (Med. Lat.: army-man) or exercitalis (same meaning) as a term used to denote the class of free landowners on whom the obligation of military service fell in Lombard and later Frankish Northern Italy (the Roman Republic of some ten centuries prior had the same concept, the term for it was assidui). This was, on the continent at least, a part of the system that was in decline by the time of Charlemagne and especially after as the mounted retinues of the great magnates became progressively more important.
We get an interesting picture of this system in Charlemagne’s efforts in the first decades of the 800s to standardize it. Under Charlemagne’s system, productive land was assessed in units of value called mansi and (to simplify a complicated system) every four mansi ought to furnish one soldier for the army (the law makes provisions for holders of even half a mansus, to give a sense of how large a unit it was – evidently some families lived on fractions of a mansus). Families with smaller holdings than four mansi – which must have been most of them – were brigaded together to create a group large enough to be able to equip and furnish one man for the army. These fellows were expected to equip themselves quite well – shield, spear, sword, a helmet and some armor – but not to bring a horse. We should probably also imagine that villages and towns choosing who to send were likely to try to send young men in good shape for the purpose (or at least they were supposed to). Thus this was a draw-up of some fairly high quality infantry with good equipment. That gives it its modern-usage name, the select levy, because it was selected out of the larger free populace.
And I should note what makes these fellows different from the infantry who might often be found in the retinues of later medieval aristocrats is just that – these fellows don’t seem to have been in the retinues of the Carolingian aristocracy. Or at least, Charlemagne doesn’t seem to have imagined them as such. While he expected his local aristocrats to organize this process, he also sent out his royal officials, the missi to oversee the process. This worked poorly, as it turned out – the system never quite ran right (in part, it seems, because no one could decide who was in charge of it, the missi or the local aristocrats) and the decades that followed would see Carolingian and post-Carolingian rulers more and more dependent on their lords and their retinues, while putting fewer and fewer resources into any kind of levy. But Charlemagne’s last-gaps effort is interesting for our purpose because it illustrates how the system was supposed to run, and thus how it might have run (in a very general sense) in the more distant past. In particular, he seems to have imagined the select levy as a force belonging to the king, to be administered by royal officials (as the nation-in-arms infantry armies of the centuries before had been), rather than as an infantry force splintered into various retinues. In practice, the fragmentation of Charlemagne’s empire under his heirs was fatal for any hopes of a centralized army, infantry or otherwise, and probably hastened the demise of the system.
Beneath the select levy there was also the expectation that, should danger reach a given region, all free men would be called upon to defend the local redoubts and fortified settlements. This group is sometimes called the general levy. As you might imagine, the general levy would be of lower average quality and cohesion. It might include the very young and very old – folks who ought not to be picked out for the select levy for that reason – and have a much lower standard of equipment. After all, unlike select levymen, who were being equipped at the expense, potentially, of many households, general levymen were individual farmers, grabbing whatever they could. In practice, the general levy might be expected to defend walls and little else – it was not a field force, but an emergency local defense militia, which might either enhance the select levy (and the retinues of the magnates) or at least hold out until that field army could arrive.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Battle oF Helm’s Deep, Part IV: Men of Rohan”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-05-22.
November 24, 2022
QotD: Roman legionary fortified camps
The degree to which we should understand the Roman habit of constructing fortified marching camps every night as exceptional is actually itself an interesting question. Our sources disagree on the origins of the Roman fortified camp; Frontinus (Front. Strat 4.1.15) says that the Romans learned it from the Macedonians by way of Pyrrhus of Epirus but Plutarch (Plut. Pyrrhus 16.4) represents it the other way around; Livy, more reliable than either agrees with Frontinus that Pyrrhus is the origin point (Liv. 35.14.8) but also has Philip V, a capable Macedonian commander, stand in awe of Roman camps (Liv. 31.34.8). It’s clear there was something exceptional about the Roman camps because so many of our sources treat it as such (Liv. 31.34.8; Plb. 18.24; Josephus BJ 3.70-98). Certainly the Macedonians regularly fortified their camps (e.g. Plb. 18.24; Liv 32.5.11-13; Arr. Alex. 3.9.1, 4.29.1-3; Curtius 4.12.2-24, 5.5.1) though Carthaginian armies seem to have done this less often (e.g. Plb. 6.42.1-2 encamping on open ground is treated as a bold new strategy).
It is probably not the camps themselves, but their structure which was exceptional. Polybius claims Greeks “shirk the labor of entrenching” (Plb. 6.42.1-2) and notes that the stakes the Romans used to construct the wooden palisade wall of the camp are more densely placed and harder to remove (Plb. 18.18.5-18). The other clear difference Polybius notes is the order of Roman camps, that the Romans lay out their camp the same way wherever it is, whereas Greek and Macedonian practice was to conform the camp to the terrain (Plb. 6.42); the archaeology of Roman camps bears out the former whereas analysis of likely battlefield sites (like the Battle of the Aous) seem to bear out the latter.
In any case, the mostly standard layout of Roman marching camps (which in the event the Romans lay siege, become siege camps) enables us to talk about the Roman marching camp because as far as we can tell they were all quite similar (not merely because Polybius says this, but because the basic features of these camps really do seem to stay more or less constant.
The basic outline of the camp is a large rectangle with the corners rounded off, which has given the camps (and later forts derived from them) their nickname: “playing card” forts. The size and proportions of a fortified camp would depend on the number of legions, allies and auxiliaries present, from nearly square to having one side substantially longer than the other. This isn’t the place to get into the internal configuration of the camp, except to note that these camps seemed to have been standardized so that the layout was familiar to any soldier wherever they went, which must have aided in both building the camp (since issues of layout would become habit quickly) and packing it up again.
Now a fortified camp does not have the same defensive purpose as a walled city: the latter is intended to resist a siege, while a fortified camp is mostly intended to prevent an army from being surprised and to allow it the opportunity to either form for battle or safely refuse battle. That means the defenses are mostly about preventing stealthy approach, slowing down attackers and providing a modest advantage to defenders with a relative economy of cost and effort.
In the Roman case, for a completed defense, the outermost defense was the fossa or ditch; sources differ on the normal width and depth of the ditch (it must have differed based on local security conditions) but as a rule they were at least 3′ and 5′ wide and often significantly more than this (actual measured Roman defensive fossae are generally rather wider, typically with a 2:1 ratio of width to depth, as noted by Kate Gilliver. The earth excavated to make the fossa was then piled inside of it to make a raised earthwork rampart the Romans called the agger. Finally, on top of the agger, the Romans would place the valli (“stakes”) they carried to make the vallum. Vallum gives us our English word “wall” but more nearly means “palisade” or “rampart” (the Latin word for a stone wall is more often murus).
Polybius (18.18) notes that Greek camps often used stakes that hadn’t had the side branches removed and spaced them out a bit (perhaps a foot or so; too closely set for anyone to slip through); this sort of spaced out palisade is a common sort of anti-ambush defense and we know of similar village fortifications in pre- and early post-contact North America on the East coast, used to discourage raids. Obviously the downside is that when such stakes are spaced out, it only takes the removal of a few to generate a breach. The Roman vallum, by contrast, set the valli fixed close together with the branches interlaced and with the tips sharpened, making them difficult to climb or remove quickly.
The gateway obviously could not have the ditch cut across the entryway, so instead a second ditch, the titulum, was dug 60ft or so in front of the gate to prevent direct approach; the gate might also be reinforced with a secondary arc of earthworks, either internally or externally, called the clavicula; the goal of all of this extra protection was again not to prevent a determined attacker from reaching the gates, but rather to slow a surprise attack down to give the defender time to form up and respond.
And that’s what I want to highlight about the nature of the fortified Roman camp: this isn’t a defense meant to outlast a siege, but – as I hinted at last time – a defense meant to withstand a raid. At most a camp might need to withstand the enemy for a day or two, providing the army inside the opportunity to retreat during the night.
We actually have some evidence of similar sort of stake-wall protections in use on the East Coast of Native North America in the 16th century, which featured a circular stake wall with a “baffle gate” that prevented a direct approach and entrance. The warfare style of the region was heavily focused on raids rather than battles or sieges (though the former did happen) in what is sometimes termed the “cutting off way of war” (on this see W. Lee, “The Military Revolution of Native North America” in Empires and Indigines, ed. W. Lee (2011)). Interestingly, this form of Native American fortification seems to have been substantially disrupted by the arrival of steel axes for presumably exactly the reasons that Polybius discusses when thinking about Greek vs. Roman stake walls: pulling up a well-made (read: Roman) stake wall was quite difficult. However, with steel axes (imported from European traders), Native American raiding forces could quickly cut through a basic palisade. Interestingly, in the period that follows, Lee (op. cit.) notes a drift towards some of the same methods of fortification the Romans used: fortifications begin to square off, often combined a ditch with the palisade and eventually incorporated corner bastions projecting out of the wall (a feature Roman camps do not have, but later Roman forts eventually will, as we’ll see).
Roman field camps could be more elaborate than what I’ve described; camps often featured, for instance, observation towers. These would have been made of wood and seem to have chiefly been elevated posts for lookouts rather than firing positions, given that they sit behind the vallum rather than projecting out of it (meaning that it would be very difficult to shoot any enemy who actually made it to the vallum from the tower).
When a Roman army laid siege to a fortified settlement, the camp formed the “base” from which siege works were constructed (particularly circumvallation – making a wall around the enemy’s city to keep them in – and contravallation – making a wall around your siege position to keep other enemies out. We’ll discuss these terms in more depth a little later). Some of the most elaborate such works we have described are Caesar’s fortifications at the Siege of Alesia (52 BC; Caes. B.G. 7.72). There the Roman line consisted of an initial trench well beyond bow-shot range from his planned works in order to prevent the enemy from disrupting his soldiers with sudden attacks, then an agger and vallum constructed with a parapet to allow firing positions from atop the vallum, with observation towers every 80 feet and two ditches directly in front of the agger, making for three defensive ditches in total (be still Roel Konijnendijk‘s heart! – but seriously, the point he makes on those Insider “Expert Rates” videos about the importance of ditches are, as you can tell already, entirely accurate), which were reinforced with sharpened stakes faced outward. As Caesar expressly notes, these weren’t meant to be prohibitive defenses that would withstand any attack – wooden walls can be chopped or burned, after all – but rather to give him time to respond to any effort by the defenders to break out or by attackers to break in (he also contravallates, reproducing all of these defenses facing outward, as well).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part II: Romans Playing Cards”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-11-12.
November 20, 2022
QotD: The Maginot Line worked
Frontier fortifications and army bases often make a degree of intuitive sense, either aimed at controlling crossings over an entire border or protecting a military force in the field. Point defenses like walled cities or castles (or defensive systems that don’t cover the entirety of a frontier) often make less sense to modern readers and students, invariably leading to the famous misquotation of George S. Patton that, “Fixed fortifications are a monument to the stupidity of man” – what he actually said was “This [the Maginot Line] is a first class case of man’s monument to stupidity“, a comment on a particular set of fortifications rather than a general statement about them and one, it must be noted, made in 1944, four years after those fortifications were taken so we also ought not credit Patton here with any great foresight.
As an aside, the purpose of the Maginot Line was to channel any attack at France through the Low Countries where it could be met head on with the flanks of the French defense anchored on the line to the right and the channel to the left. At this purpose, it succeeded; the failure was that the French army proceeded to lose the battle in the field. It was not the fixed fortifications, but the maneuvering field army which failed in its mission. One can argue that the French under-invested in that field army (though I’d argue the problem was as much doctrine than investment), but you can’t argue that the Maginot Line didn’t accomplish its goals – the problem is that those goals didn’t lead to victory.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part III: Castling”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-12-10.
November 16, 2022
QotD: Did Sparta actually aspire to supremacy in Greece?
It is hard to say to what degree Sparta ever really pursued this goal. Several Spartan leaders – kings like Cleomenes I, the regent Pausanias, Agesilaus II, along with men like Lysander – once on campaign outside Sparta seemed to have envisaged a much wider sphere of Spartan control over Greece and worked to achieve it. At the same time, the ever cautious Gerousia (along with the Ephors) almost always worked to restrain and eventually destroy such men. This should remind us that no state – not even Sparta – is really a unitary entity with one set of goals held by everyone; within the state there is a complex set of competing interests. For the Spartan kings and influential commanders, success outside of Sparta was an alluring way to potentially build power outside of the systems which restricted them within Sparta; for the Gerousia and the Ephors – who were that system – success abroad was a threat to stability at home.
Given Sparta’s inherent resources, the goal was not unrealistic: Sparta was by land area, if not by population, the largest polis in Greece. But Spartan hegemony lasted less than a decade, primarily because of the ineptness of Spartan diplomacy. While victory over Athens in 404 BC made Sparta the preeminent Greek state, the mistakes started almost immediately: the occupation/collaboration government (the “Thirty Tyrants”) in Athens was so cruel and unpopular that Sparta was forced to acquiesce to its removal after just eight months. Meanwhile, Spartan imperiousness – including a refusal to share the spoils of victory, as well as military activity against little Elis and big Persia unsanctioned by the Peloponnesian League – turned Sparta’s allies against them. Sparta’s efforts to restore their alliance militarily led to the Corinthian War in 395, which would prove that while Sparta was still strong, it was not strong enough to enforce its alliances by force of arms. If any of the Spartans ever aimed for hegemony or preeminence among the Greeks, it is safe to say they failed.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VII: Spartan Ends”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-27.
November 11, 2022
QotD: WW1 was the first war where the artillery was destructive enough to change the landscape
So why is it always muddy? The real answer is high explosive shells (particularly, but not exclusively, penetrating high explosive shells). Heavy artillery shells in the First World War were made to penetrate into the ground and then explode, sending up a rain of loose dirt – the idea was to be able to destroy or at least bury trenches and deep bunkers. The explosions were so powerful that they uprooted trees and grass, leaving behind the “blasted moonscape” so common in pictures of the Western Front. All that remained were the deep craters which collected water and turned into often fatal mud-traps (Peter Jackson’s They Shall Not Grow Old (2018), includes a horrific description of one man, unable to assist, having to watch another man sucked under the mud to his death in such a crater).
This kind of terrain – with so much of the ground-cover blasted away – would turn into mud-soaked pits the moment it rained – particularly where water collected in the shell-holes.
That also explains why these post-battle scenes often lack any kind of local terrain features. Powerful explosive shells could annihilate terrain features like forests, roads, hedgerows, fences, fields – even hills and entire villages – with extended bombardments. And without any ground-cover left, almost any rain at all will then reduce the local terrain into a mud-soaked bog, especially if the local soil drains poorly (as it did so famously in Flanders).
The problem with depicting medieval, or even early modern battlefields this way is, of course, that these armies do not possess any weapons which can deliver this kind of destruction. Even as late as the American Civil War, field artillery – even massed field artillery – was simply not that powerful (although some heavy naval and siege guns were beginning to come close). Post-battle photography of Gettysburg – even in the approaches to Cemetery Ridge and around the Wheat Field – areas of fierce fighting – shows not only trees and ground-cover, but even fences and buildings largely intact.
Field artillery firing solid shot from 6 to 20lbs to is simply not strong enough to tear apart the terrain in the way that we often see in popular depictions of historical or fantasy battlefields; as pictured above, the guns doing that in WWI were often firing 1,000+ pound shells, 100 times the weight of shot of a normal ACW cannon (lighter artillery, like the famed French 75 (Matériel de 75mm Mle 1897) still fired lighter shells – the French 75 fired a c. 12lbs shell – but still had far more explosive power due to improvements in explosives; that said, the French 75, a capable field gun, was famously too light for ideal use in the trenches). Massed musketry won’t do it either and so massed arrow or crossbow fire, catapults or whatever else certainly won’t.
(This, as a side note, may go some distance to explaining why First World War commanders were so unprepared for the challenges the new terrain they were creating in turn inflicted on them. Doctrine said that the solution to well-entrenched infantry was to mass artillery against them – blast them out of position. It had never been the case before that such massed artillery would render the ground itself impassible, because the artillery had never before been powerful enough to do so.)
Bret Devereaux, “Collection: The Battlefield After the Battle”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-10-18.
November 9, 2022
QotD: Was Temujin (aka Genghis Khan/Chinggis Khan) a “great man”?
Take, for instance, Chinggis Khan (born Temujin; I am going to use Temujin here to mean the man himself and Chinggis Khan to mean his impact as a ruler once the Mongols were fully united). The conditions for Chinggis Khan were not new in 1158; the basic technological factors with made the Steppe way of war possible had existed in the Eurasian Steppe for at least two thousand years by the time Temujin was born. Political fragmentation was also an important factor, but this was hardly the first time that nearby China had been politically fragmented (at the very least the periods 771-221BC, 220-280AD, 304-589 and 907 through to Temujin’s birth in 1158 all qualify) and the steppe had effectively always been politically fragmented. Our evidence for life on the steppe is limited (we’ll come back to this in a second) but by all appearances the key social institutions Temujin either relied on or dismantled were all centuries old at least at his birth.
What had been missing for all that time was Temujin. To buy into the strongest form of “cliodynamics” is to assume that the Steppe always would have produced a Temujin (in part because his impact is so massive that a “general law” of history which cannot predict an event of such titanic import is not actually a functional “general law”). And to be fair, it had produced nearly Temujins before: Attila, Seljuk, etc. But “nearly” here isn’t good enough because so many of the impacts of Chinggis Khan depend on the completeness of his conquests, on a single state interested in trade controlling the entire Eurasian Steppe without meaningful exception. The difference between Temujin and almost-Temujin (which is just basically “Jamukha”) is history-shatteringly tremendous, given that both gunpowder and the Black Death seem to have moved west on the roads that Chinggis opened and the subsequent closure of those routes after his empire fragmented seem to have been a major impetus towards European seaborne expansion.
Moreover, it is not at all clear that, absent Temujin in that particular moment – keeping in mind that Temujin hadn’t appeared in any other moment – that there would have inevitably risen a different Temujin sometime later. After all, for two millennia the steppe had not produced a Temujin and by 1158, the technological window for it to do so was already beginning to close as humans in the agrarian parts of the world (read: China) had already begun harnessing chemical energy in ways that would eventually come to rob the nomad of much of his strength. If Temujin dies as a boy – as he very well might have! – it is not at all clear he’d be replaced before that window closed; his most obvious near peer was Jamukha, but here personalities matter: Jamukha was committed to the old Mongol social hierarchy (this was part of why he and Temujin fell out) and was so unwilling to do the very things that made Chinggis Khan’s great success possible (obliterating clan distinctions and promoting based on merit rather than family pedigree). Jamukha could have been another Seljuk, but he could not have been another Chinggis Khan and in this case that would make all of the difference.
To get briefly into a bit of historical theory, Chinggis is an individual whose actions in life fundamentally altered many of what the “Annales School” of history would call the structures and mentalités of his (and subsequent) times. The Annales school likes to view history through a long duration lens (longue durée) and focus on big shaping structures like climate, geography, culture and so on. The difference between this and cliodynamics is that Annales thinkers propose to describe rather than predict, so it is not fatal to their method if there are occasional, sudden, unpredictable alterations to those underlying structures – indeed those are the moments which are most interesting. But it is fatal to a cliodynamics perspective, which does aim for prediction since “our prediction is absolutely right unless it is completely wrong” hardly inspires confidence and a “general law” of anything is only a “general law” in that it is generally applicable not merely to the past but also to the future.
In short, Chinggis Khan wasn’t a commodity; he couldn’t be replaced by any other Mongol warrior. And figures like that abound through history (for Roman history, it matters greatly for instance that Marius, Sulla, Pompey, Caesar and Octavian had very different personalities when they found themselves in a position to dominate the Republic with military force). Moreover, the figures like that who we think of, generally capital-g “Great Men”, are hardly the only such individuals like that. They’re only the ones we can see. What of, for instance, the old Argive mother – her name lost to history – who killed Pyrrhus of Epirus, considered the greatest general of his generation, with a lucky throw of a roofing tile, both ending his career but also setting in motion a chain of events where the power vacuum left by Epirus would be filled by Carthage and Rome in a way that would bring those former allies (allied against Pyrrhus, in fact) into a shattering conflict which would then pave the way for Roman dominance in the Mediterranean? History must be full of innumerable such figures whose actions created and closed off courses of events in ways we can never know; how do we know that there wasn’t some would-have-been Temujin on the steppe in 100AD but who was killed in some minor dispute so very minor it leaves literally no evidence behind?
(The fancy way of putting the influence of all of those factors, both the big structural ones and the little, subject-to-chance ones, is to say “history is contingent” – that is, the outcomes are not inevitable but are subject to many forces large and small, many of which the lack of evidence render historically invisible.)
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday: October 15, 2021”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-10-15.
November 5, 2022
QotD: The use of chemical weapons after WW2
During WWII, everyone seems to have expected the use of chemical weapons, but never actually found a situation where doing so was advantageous. This is often phrased in terms of fears of escalation (this usually comes packaged with the idea of MAD (Mutually Assured Destruction), but that’s an anachronism – while Bernard Brodie is sniffing around the ideas of what would become MAD as early as ’46, MAD itself only emerges after ’62). Retaliation was certainly a concern, but I think it is hard to argue that the combatants in WWII hadn’t already been pushed to the limits of their escalation capability, in a war where the first terror bombing happened on the first day. German death-squads were in the initial invasion-waves in both Poland, as were Soviet death squads in their invasion of Poland in concert with the Germans and also later in the war. WWII was an existential war, all of the states involved knew it by 1941 (if not earlier), and they all escalated to the peak of their ability from the start; I find it hard to believe that, had they thought it was really a war winner, any of the powers in the war would have refrained from using chemical weapons. The British feared escalation to a degree (but also thought that chemical weapons use would squander valuable support in occupied France), but I struggle to imagine that, with the Nazis at the very gates of Moscow, Stalin was moved either by escalation concerns or the moral compass he so clearly lacked at every other moment of his life.
Both Cold War superpowers stockpiled chemical weapons, but seem to have retained considerable ambivalence about their use. In the United States, chemical weapons seem to have been primarily viewed not as part of tactical doctrine, but as a smaller step on a nuclear deterrence ladder (the idea being that the ability to retaliate in smaller but still dramatic steps to deter more dramatic escalations; the idea of an “escalation ladder” belongs to Herman Kahn); chemical weapons weren’t a tactical option but baby-steps on the road to tactical and then strategic nuclear devices (as an aside, I find the idea that “tactical” WMDs – nuclear or chemical – could somehow be used without triggering escalation to strategic use deeply misguided). At the same time, there was quite a bit of active research for a weapon-system that had an uncertain place in the doctrine – an effort to find a use for a weapon-system the United States already had, which never quite seems to have succeeded. The ambivalence seems to have been resolved decisively in 1969 when Nixon simply took chemical weapons off of the table with an open “no first use” policy.
Looking at Soviet doctrine is harder (both because I don’t read Russian and also, quite frankly because the current epidemic makes it hard for me to get German and English language resources on the topic) The USSR was more strongly interested in chemical weapons throughout the Cold War than the United States (note that while the linked article presents US intelligence on Soviet doctrine as uncomplicated, the actual intelligence was ambivalent – with the CIA and Army intelligence generally downgrading expectations of chemical use by the USSR, especially by the 1980s). The USSR does seem to have doctrine imagine their use at the tactical and operational level (specifically as stop-gap measures for when tactical nuclear weapons weren’t available – you’d use chemical weapons on targets when you ran out of tactical nuclear weapons), but then, that had been true in WWII but when push came to shove, the chemical munitions weren’t used. The Soviets appear to have used chemical weapons as a terror weapon in Afghanistan, but that was hardly a use against a peer modern system force. But it seems that, as the Cold War wound down, planners in the USSR came around to the same basic idea as American thinkers, with the role of chemical weapons – even as more and more effective chemicals were developed – being progressively downgraded before the program was abandoned altogether.
This certainly wasn’t because the USSR of the 1980s thought that a confrontation with NATO was less likely – the Able Archer exercise in 1983 could be argued to represent the absolute peak of Cold War tensions, rivaled only by the Cuban Missile Crisis. So this steady move away from chemical warfare wasn’t out of pacifism or utopianism; it stands to reason that it was instead motivated by a calculation as to the (limited) effectiveness of such weapons.
And I think it is worth noting that this sort of cycle – an effort to find a use for an existing weapon – is fairly common in modern military development. You can see similar efforts in the development of tactical nuclear weapons: developmental dead-ends like Davy Crockett or nuclear artillery. But the conclusion that was reached was not “chemical weapons are morally terrible” but rather “chemical weapons offer no real advantage”. In essence, the two big powers of the Cold War (and, as a side note, also the lesser components of the Warsaw Pact and NATO) spent the whole Cold War looking for an effective way to use chemical weapons against each other, and seem to have – by the end – concluded on the balance that there wasn’t one. Either conventional weapons get the job done, or you escalate to nuclear systems.
(Israel, as an aside, seems to have gone through this process in microcosm. Threatened by neighbors with active chemical weapons programs, the Israelis seem to have developed their own, but have never found a battlefield use for them, despite having been in no less than three conventional, existential wars (meaning the very existence of the state was threatened – the sort of war where moral qualms mean relatively little) since 1948.)
And I want to stress this point: it isn’t that chemical munitions do nothing, but rather they are less effective than an equivalent amount of conventional, high explosive munitions (or, at levels of extreme escalation, tactical and strategic nuclear weapons). This isn’t a value question, but a value-against-replacement question – why maintain, issue, store, and shoot expensive chemical munitions if cheap, easier to store, easier to manufacture high explosive munitions are both more obtainable and also better? When you add the geopolitical and morale impact on top of that – you sacrifice diplomatic capital using such weapons and potentially demoralize your own soldiers, who don’t want to see themselves as delivering inhumane weapons – it’s pretty clear why they wouldn’t bother. Nevertheless, the moral calculus isn’t the dominant factor: battlefield efficacy – or the relative lack thereof – is.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Why Don’t We Use Chemical Weapons Anymore?”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-03-20.
November 1, 2022
QotD: Spartan strategy during the Persian wars
At the core of strategy is deciding on strategic ends and then coordinating the right means which will actually achieve those goals. For instance, if the strategic goal is to gain control of a key economic population center (read: a city), you don’t want to try to achieve that by, say, carpet bombing – you’ll destroy the very asset you wish to gain even if you win. In this respect, Sparta’s strategic thinking is straight-jacketed to a very narrow model of warfare. Sparta is the fellow in the aphorism that “when all you have is a hammer” but placed in a world of screws.
The hammer Sparta has, of course, is hoplite battle. Sparta seeks to solve almost all of its issues by applying a hoplite phalanx to the problem, regardless of if the problem can be solved by a hoplite phalanx. Spartan strategic thinking is thus marred by both a failure to consider military solutions that did not consist of traditional hoplite battles, as well as an inability to consider or execute non-military solutions at all.
We can see the former weakness in Spartan planning in the Persian Wars. Spartan planning is both direct and unrealistic: find a choke-point, fortify it and hold it indefinately with a hoplite army. Attempted at Thermopylae this plan fails; the Battle of Thermopylae is often represented in popular culture as an intentional delaying action, but it was nothing of the sort – Herodotus is clear that this was supposed to be the decisive land engagement (Hdt. 7.175; Cf. Diodorus 11.4.1-5). The Spartans then attempt to recreate this plan at the Isthmus of Corinth and have to be rescued from their strategic stupidity by the Athenians, who threaten to leave the alliance if the plan isn’t abandoned (Hdt. 8.49-62). A blockade at the Isthmus would be easy for the Persian army to bypass – assuming it didn’t simply defeat it with generally superior Persian siegecraft – and worse yet was a diplomatic disaster given that it meant essentially writing Athens off as a loss, when the Athenian navy provided the bulk of the ships protecting the Isthmus.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VII: Spartan Ends”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-27.
October 28, 2022
QotD: “Cliodynamics”, aka “megahistory”
For this week’s musing, I want to discuss in a fairly brief way, my views of “megahistory” or “cliodynamics” – questions about which tend to come up a fair bit in the comments – and also Isaac Asimov, after a fashion. Fundamentally, the promise of these sorts of approaches is to apply the same kind of mathematical modeling in use in many of the STEM fields to history with the promise of uncovering clear rules or “laws” in the noise of history. It is no accident that the fellow who coined the term “cliodynamics”, Peter Turchin, has his training not in history or political science but in zoology; he is trying to apply the sort of population modeling methods he pioneered on Mexican Bean Beetles to human populations. One could also put Steven Pinker, trained as a psychologist, and his Better Angels in this category as well and long time readers will know how frequently I recommend that folks read Azar Gat, War in Human Civilization instead of The Better Angels of our Nature.1
Attentive readers will have already sensed that I have issues with these kinds of arguments; indeed, for all of my occasional frustrations with political science literature (much of which is perfectly fine, but it seems a frequent and honestly overall positive dynamic that historians tend to be highly critical of political scientists) I consider “cliodynamics” to generally take the worst parts of data-driven political science methodologies to apotheosis while discarding most of the virtues of data-driven poli-sci work.
As would any good historian, I have a host of nitpicks, but my objection to the idea of “cliodynamics” has to do with the way that it proposes to tear away the context of the historical data. I think it is worth noting at the outset the claim actually being made here because there is often a bit of motte-and-bailey that goes on, where these sorts of megahistories make extremely confident and very expansive claims and then when challenged is to retreat back to much more restricted claims but Turchin in particular is explicit in Secular Cycles (2009) that “a basic premise of our study is that historical societies can be studied with the same methods physicists and biologists used to study natural systems” in the pursuit of discovering “general laws” of history.
Fundamentally, the approach is set on the premise that the solution to the fact that the details of society are both so complex (imagine charting out the daily schedules of every person one earth for even a single day) and typically so poorly attested is to aggregate all of that data to generate general rules which could cover any population over a long enough period. To my mind, there are two major problems here: predictability and evidence. Let’s start with predictability.
And that’s where we get to Isaac Asimov, because this is essentially also how the “psychohistory” of the Foundation series functions (or, for the Star Trek fans, how the predictions in the DS9 episode “Statistical Probabilities“, itself an homage to the Foundation series, function). The explicit analogy offered is that of the laws that govern gasses: while no particular molecule of a gas can modeled with precision, the entire body of gas can be modeled accurately. Statistical probability over a sufficiently large sample means that the individual behaviors of the individual gas molecules combine in the aggregate to form a predictable whole; the randomness of each molecule “comes out in the wash” when combined with the randomness of the rest.2
I should note that Turchin rejects comparisons to Asimov’s psychohistory (but also embraced the comparison back in 2013), but they are broadly embraced by his boosters. Moreover, Turchin’s claim at the end of that blog post that “prediction is overrated” is honestly a bit bizarre given how quick he is when talking with journalists to use his models to make predictions; Turchin has expressed some frustration with the tone of Graeme Wood’s piece on him, but “We are almost guaranteed” is a direct quote that hasn’t yet been removed and I can speak from experience: The Atlantic‘s fact-checking on such things is very vigorous. So I am going to assume those words escaped the barrier of his teeth and also I am going to suggest here that “We are almost guaranteed” is, in fact, a prediction and a fairly confident one at that.
The problem with applying something like the ideal gas law – or something like the population dynamics of beetles – to human societies is fundamentally interchangeability. Statistical models like these have to treat individual components (beetles, molecules) the way economists treat commodities: part of a larger group where the group has qualities, but the individuals merely function to increase the group size by 1. Raw metals are a classic example of a commodity used this way: add one ton of copper to five hundred tons of copper and you have 501 tons of copper; all of the copper is functionally interchangeable. But of course any economist worth their pencil-lead will be quick to remind you that not all goods are commodities. One unit of “car” is not the same as the next. We can go further, one unit of “Honda Civic” is not the same as the next. Heck, one unit of 2012 Silver Honda Civic LX with 83,513 miles driven on it is not the same as the next even if they are located in the same town and owned by the same person; they may well have wildly different maintenance and accident histories, for instance, which will impact performance and reliability.
Humans have this Honda Civic problem (that is, they are not commodities) but massively more so. Now of course these theories do not formally posit that all, say, human elites are the same, merely that the differences between humans of a given grouping (social status, ethnic group, what have you) “come out in the wash” at large scales with long time horizons. Except of course they don’t and it isn’t even terribly hard to think of good examples.
1 Yes, I am aware that Gat was consulted for Better Angels and blurbed the book. This doesn’t change my opinion of the two books. my issue is fundamentally evidentiary: War is built on concrete, while Better Angels is built on sand when it comes to the data they propose to use. As we’ll see, that’s a frequent issue.
2 Of course the predictions in the Foundation series are not quite flawlessly perfect. They fail in two cases I can think of: the emergence of a singular exceptional individual with psychic powers (the Mule) and situations in which the subjects of the predictions become aware of them. That said Seldon is able to predict things with preposterous accuracy, such that he is able to set up a series of obstacles for a society he knows they will overcome. The main problem is that these challenges frequently involve conflict or competition with other humans; Seldon is at leisure to assume such conflicts are predictable, which is to say they lack Clausewitzian (drink!) friction. But all conflicts have friction; competition between peers is always unpredictable.
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday: October 15, 2021”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-10-15.
October 24, 2022
An overview of strategic airpower
Bret Devereaux wants to provide a basic idea of what we mean when we use the military term “strategic airpower”:

USAF B-52 Stratofortress near the North Pole on 31 July, 2016 during the Polar Roar exercise.
Detail of original USAF photo by Senior Airman Joshua King via Wikimedia Commons.
This week, I’m going to offer a fairly basic overview of the concept of strategic airpower, akin to our discussions of protracted war and nuclear deterrence. While the immediate impetus for this post has been Russian efforts to use airpower coercively in Ukraine, we’re going to focus more broadly on the topic: what is strategic airpower, where did the idea come from, how has it been used and does it actually work? As with nuclear deterrence, this is a much debated topic, so what I am going to present here is an overview of the sort I’d provide for an introductory class on the topic and then at the end we’ll cover some of the implications for the current conflict in Ukraine. That said, this is also an issue where I think most historians of the topic tend to part ways with both some things the public think they know about the topic and some of the things that occasionally the relevant branches of the military want to know about the topic; in any case I am going to try to present a fairly “down the middle” historian’s view of the question.
Before we dive in, we need to define what makes certain uses of airpower strategic because strategic airpower isn’t the only kind. The reason for the definition will emerge pretty quickly when we talk about origins, but let’s get it out of the way here: strategic airpower is the use of attack by air (read: bombing) to achieve “strategic effects”. Now that formal definition is a bit tautological, but it becomes clarifying when we talk about what we mean by strategic effects; these are effects that aim to alter enemy policy or win the war on their own.
Put another way, if you use aircraft to attack enemy units in support of a ground operation (like an invasion), that would be tactical airpower; the airpower is a tactic that aims to win a battle which is still primarily a ground (or naval) battle. We often call this kind of airpower “close air support” but not all tactical airpower is CAS. If you instead use airpower to shape ground operations – for instance by attacking infrastructure (like bridges or railroads) or by bombing enemy units to force them to stay put (often by forcing them to move only at night) – that’s operational airpower. The most common form of this kind of airpower is “interdiction” bombing, which aims to slow down enemy ground movements so that friendly units can out-maneuver them in larger-scale sweeping movements.
By contrast strategic airpower aims to produce effects at the strategic (that is, top-most) level on its own. Sometimes that is quite blunt: strategic airpower aims to win the war on its own without reference to ground forces, or at least advance the ball on winning a conflict or achieving a desired end-state (that is, the airpower may not be the only thing producing strategic effects). Of course strategic effects can go beyond “winning the war” – coercing or deterring another power are both strategic effects as well, forcing the enemy to redefine their strategy. That said, as we’ll see, this initially very expansive definition of strategic airpower really narrows quite quickly. Aircraft cannot generally hold ground, administer territory, build trust, establish institutions, or consolidate gains, so using airpower rapidly becomes a question of “what to bomb” because delivering firepower is what those aircraft can do.
As an aside, this sort of cabined definition of airpower and thus strategic airpower has always been frustrating to me. It is how airpower is often discussed, so it’s how I am going to discuss it, but of course aircraft can move more than bombs. Aircraft might move troops – that’s an operational use of airpower – but they can also move goods and supplies. Arguably the most successful example of strategic airpower use anywhere, ever is the Berlin Airlift, which was a pure airpower operation that comprehensively defeated a major Soviet strategic aim, and yet the U.S. Air Force is far more built around strategic bombing than it is around strategic humanitarian airlift (it does the latter, but the Army and the Navy, rather than the Air Force, tend to take the lead in long-distance humanitarian operations). Nevertheless that definition – excessively narrow, I would argue – is a clear product of the history of strategic airpower, so let’s start there.
And once again before we get started, a reminder that the conflict in Ukraine is not notional or theoretical but very real and is causing very real suffering, including displacing large numbers of Ukrainians as refugees, both within Ukraine and beyond its borders. If you want to help, consider donating to Ukrainian aid organizations like Razom for Ukraine or to the Ukrainian Red Cross. As we’re going to see here, airpower offers no quick solution for the War in Ukraine for either party, but the recent Russian shift to air attacks on civilian centers sadly promises more suffering and more pressing need for humanitarian assistance for Putin’s many victims.
Finally, a content warning: what we’re discussing today is largely (though not entirely) the application of airpower against civilian targets because it turns usually what “strategic” airpower ends up being. This is a discussion of the theory, which means it’s going to be pretty bloodless, but nevertheless this topic ought to be uncomfortable.
On with our topic, starting with the question of where the idea of strategic airpower comes from.
October 23, 2022
QotD: Sparta’s military reputation in the Peloponnesian War
Herodotus’ work was well known, even in antiquity, and he set the tone for all subsequent retellings of the Persian wars (despite the frequent complaints by later ancient authors that Herodotus’ reliability was – let’s say, complicated. I don’t want to give the wrong impression: Herodotus is a valuable source, just one that – like all sources – has his own agenda at play). The Spartan reputation thus seems to be the product of half a century spent fighting far, far weaker opponents, combined with one very skilled propagandist with an agenda.
That reputation was already deeply held even by the early stages of the Peloponnesian War, such that Thucydides notes that “Nothing that happened in the war so shocked the Greeks so much as” the surrender of 120 Spartiates at Pylos/Sphacteria, instead of dying with their weapons in their hands (Thuc. 4.40.1). The Athenians had, in the event, managed to trap a force of Spartans – Spartiates and other Laconians – on an island and harassed them with arrow fire from a distance, never closing with them, until the Spartans surrendered. This is, I must stress, in the context of a war that obliterated entire poleis, shredded the diplomatic fabric of Greece and was by far the largest war between Greeks that any of them knew of. But this, the shattering – if just for a moment – of the Spartan reputation, that was what shocked people. The image of Sparta – whatever the reality – was that deeply set.
Thucydides, amusingly, relates that some Greeks were so shocked that they couldn’t believe it, and one ally of Athens inquired to the Spartiates – then held as captives in Athens – if perhaps what had happened was that all of the brave men (you know, the real Spartiates) had been felled by the arrows, to which the Spartans responded, “an arrow would be worth a great deal if it could pick out noble and good men from the rest, in allusion to the fact that the killed were those whom the stones and the arrows happened to hit” (Thuc. 4.40.2).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VI: Spartan Battle”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-20.