Forgotten Weapons
Published 29 Nov 2016The Japanese Army made significant use of snipers (or in today’s terminology, designated marksmen) as part of its infantry combined arms doctrine, and produced about 22,000 Type 97 sniper rifles for use in WWII and the Sino-Japanese War. In 1941, shortly after the adoption of the new 7.7mm rifle cartridge, it was decided that a sniper rifle variant of the Type 99 should be made in addition to the Type 97 (which was basically a scoped Type 38).
Testing through 1941 determined that there was almost no practical difference in accuracy between scoped examples of the Type 99 long and short rifles, and so the short rifle was chosen to be the basis for the Type 99 sniper (the Type 99 long rifles would drop from production altogether pretty quickly anyway). About 1,000 of the scoped 99s were manufactured by the Kokura Arsenal using the same 2.5x scope as on the Type 97 sniper, while the Nagoya Arsenal instead used a 4x scope, offering more magnification at the expense of a narrower field of view. Nagoya would produce approximately 10,000 of these rifles, with 4x scopes except for a period between serial numbers 5,000 and 7,000 with 2.5x scopes (most likely the remainder stored at Kokura when that plant ceased production). The rifles made into snipers were given no special selection criteria; simply taken at random from normal production. The utility of the weapon in Japanese practice came not from it being mechanically more accurate than any other issue rifle, but rather from the optical sight allowing better exploitation of that standard rifle’s inherent accuracy.
(more…)
February 23, 2023
Type 99 Arisaka Sniper Rifles
QotD: Academic types
Let’s […] circle back to that list of school shooters. Actually they’re university shooters — a crucial distinction. [He] points out that most of them were grad students, and all of them were too damn old to still be hanging around in college. There’s a bit of chicken-and-egg going on here, but the point’s still valid. Even if you claim that every single grad school outside STEM is utterly worthless — and you’ll get no argument from me, buddy — the fact remains that grad students are functionally much closer to the aeronautical engineers and their 50-nerd slap fight than they are to the homies in the inner city. If a solution can’t be found in a very tight-knit environment, by a bunch of very concerned people who are constantly on the lookout for Oppressed People to champion, what chance do we normals have to even diagnose, let alone solve, the problems of half the fucking country?
You do acknowledge, of course, that it’s in the nature of math that 50% of the population are below average?
Our default “solution” for university shooters […] is psychiatry. More access to better “mental health care”, we say, would’ve prevented this. Maybe, maybe not, but at least it’s something. The problem, though, is that the only diagnostic criterion you can realistically use is “So-and-So is a twitchy, weird loner”, which — trust me — exactly describes 99% of grad students and 100% of professors. Do we force feed all of them powerful prescription psychotropics on the off-chance?
Before you jump to agree — and yes, I fully acknowledge how awesome that would be, if you put it on Pay-per-View I’d be the first to sign up […] I’d ask you to consider two things:
First, it’s the government doing this. The same stupid motherfuckers who can’t manage to rig a poll where only a handful of addled old farmers vote. Do you really want to bet America’s future social stability on them loading the right drug into the sprayers? Given the federal bureaucracy’s sterling reputation for basic competence, they’d probably crop-dust the ‘hood with meth.
Severian, “The Scientific Management of Populations”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-02-15.
February 22, 2023
Mosquito Bombers Bust Out French Resistance – War Against Humanity 098
World War Two
Published 21 Feb 2023Across Europe the anti-Nazi Resistance continues to rise as does the infighting. In France the RAF carry out Operation Jericho to break out captured resistance members held at the prison in Amiens.
(more…)
Toward a taxonomy of military bullshit
Bruce Gudmundsson linked to this essay from “Shady Maples“, a serving officer in the Canadian Army, on the general topic of bullshit in the military:
Armies, as a rule, are quagmires of bullshit. The Canadian Army is no exception. We accept that bullshit is an occupational hazard in the Army, but it’s a hazard that we struggle to manage and it’s one that threatens our effectiveness as a force.
In order to understand bullshit we need a taxonomy, that is, a map of bullshit and the common varieties found in the wild. Using our taxonomy, we can develop diagnostic tools to detect bullshit and expose its corrosive effects on our integrity and professional culture. I assume that bullshit is also a hazard in other environments and government departments, but since my experience is in the land force I will be focusing my attention on that.
The subject of bullshit entered the mainstream in 2005 when Princeton University Press issued a hardcover edition of Harry G. Frankfurt’s 1988 essay “On Bullshit“. Frankfurt doesn’t mince words: “[one] of the most salient features of our culture is that there is so much bullshit. Everyone knows this. Each of us contributes his share.” He argues that even though we treat bullshit as a lesser moral offence than lying, it’s actually more harmful to a culture of truth. I believe this wholeheartedly, for reasons which will become clear.
In Frankfurt’s view, even though a liar and a bullshitter both aim to deceive their targets, bullshitting and lying require different mental states. In order to lie, someone must believe that they know the truth and intentionally make a false account of it. For example, if you believe that today is Monday but today is in fact Tuesday, and somebody asks you what day it is, you’re not a liar if you say “today is Monday”. You’re not lying because you really do believe that today is Monday, even though this belief is incorrect. In order to lie, you have to intentionally make a statement that is contrary to the truth as you understand it. In this example, you would be lying if you said “today is Tuesday” while believing that today is actually Monday. You would be accidentally correct, but you would still be lying because you are providing a false account of what you believe is true.
This means that lying actually requires a tacit respect for the truth on the part of the liar. The liar has to at least acknowledge the existence of truth in order to avoid it. To provide a false account of the truth, the liar must first believe in the truth.
The bullshitter, by contrast, does not operate under this constraint. Bullshit according to Frankfurt is speech without any regard for the truth whatsoever. To Frankfurt, “[the bullshitter] does not care whether the things he says describe reality correctly. He just picks them out, or makes them up, to suit his purpose.” Bullshit, Frankfurt argues, is speech that is disconnected from a concern for truth. The bullshitter will say anything if it helps them achieve their desired ends.
[…]
Let’s move on to the topic of “bull”, which is discussed at length by British psychologist Norman F. Dixon, author of On the Psychology of Military Incompetence. Dixon beat Frankfurt to the punch by publishing his own theory of bullshit in 1976, twelve years before “On Bullshit”. Dixon is a Freudian psychologist writing in the 1970s, so I am skeptical of the scientific merit of his book. Nonetheless, he provides an interesting outsider’s perspective of British military culture from the Crimean War up to the Second World War and how that culture enabled terrible officers while punishing competent ones (spoiler: aristocrats and nepotism are bad for meritocracy).
There is an entire chapter of the book about bullshit as a contributing factor to military incompetence. Dixon attributes the origin of the word “bullshit” to Australian soldiers, who in 1916 “were evidently so struck by the excessive spit and polish of the British Army that they felt moved to give it a label”. His theory of the Australian origin of bullshit is supported by Australian philosopher David Stove, who believed that it’s a signature national expression.
[…]
Canadian political philosopher G. A. Cohen added some depth to the discourse when he responded to Frankfurt in “Deeper into Bullshit“. Cohen wasn’t satisfied that Frankfurt had explored full range of bullshit as a social phenomenon. Frankfurt anchors his definition of bullshit in the intention or mental state of the speaker (the bullshitter) whose lack of concern for truth is what makes their statements bullshit. Cohen responds to this by pointing out that there are many people who honestly profess their bullshit beliefs. Reading this brought me back to my undergrad days. I had a TA in a 300-level philosophy course who claimed that he doubted his own existence. Personally, I wondered whether he would still doubt his own existence if I punched him in the balls for spewing such performative bullshit in class. So I think that Cohen makes a good point: there are bullshitters who honestly believe their own bullshit.
Cohen’s argument is squarely aimed at a certain style of academic writing, which he calls “unclarifiable unclarity.” These are intentionally vague statements which cannot be clarified without distorting their apparent meaning or dropping the veil of profundity altogether. If you want an example, you can try reading Hegel or a postmodernist philosopher, or just save yourself the effort and click on this postmodern bullshit generator (trust me, it’s indistinguishable from the real thing). Pennycook et al. label statements of this type as “pseudo-profound bullshit“. Hilariously, they ran a series of experiments to see if test subjects would find the appearance of profound truth in both real and algorithmically-generated Deepak Chopra tweets. The result, disappointingly, was yes.
Cohen adds a fourth type of bullshit to our taxonomy: “irretrievably speculative comment”. Basically, when someone is arguing for a proposition which they have no way of knowing is true or false, or they put forward an argument that’s completely unsupported by readily available evidence, then that argument is bullshit.
[…]
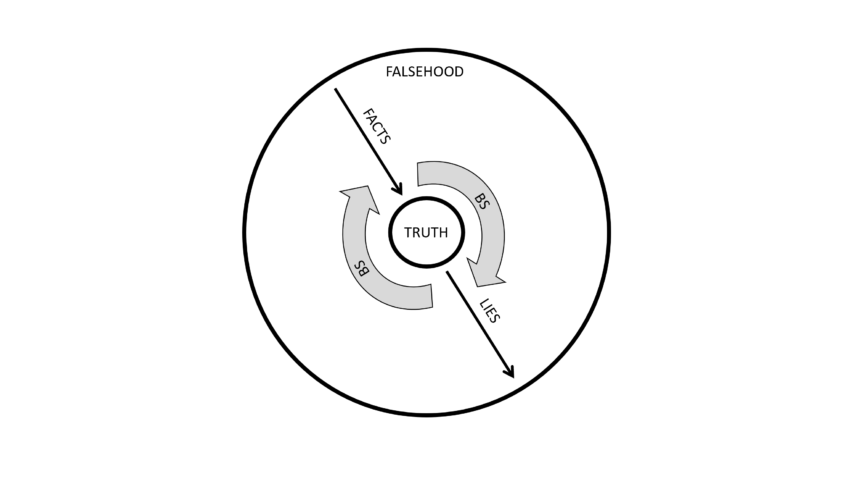
Still with me? So far we’ve identified and defined four types of bullshit (BS):
BS1 (Frankfurt): propositions made without concern for truth.
BS2 (Dixon): ritualistic activity which doesn’t serve its stated aim or justification.
BS3 (Cohen/Pennycook): unclarifiable unclarity aka pseudo-profound bullshit.
BS4 (Cohen): speculation beyond what’s reasonably permitted by the evidence.
The common denominator of all four types of bullshit is their disconnection from reality. Bullshit statements don’t enhance our understanding and bullshit activity doesn’t get us any closer to achieving our goals in the real world. Bullshit doesn’t necessarily move us further away from truth, like lies do, but it certainly doesn’t get us any closer to it either. Essentially, bullshit lowers the signal-to-noise ratio of discourse.
True Size of a Roman Legion
Invicta
Published 29 Oct 2022The True Size of a Roman Legion.
A history documentary on the True Size of a Roman Legion. This is our first episode in the new True Size series which seeks to bring history to life in 3D using Unreal Engine 5. In this episode we cover the organization of a Roman Legion from the soldier to the Contubernium, the Century, the Cohort, and the Legion. Along the way we not only include the troops and their officers but all the slaves, mules, support, staff, and gear which accompanied them. This makes for a much better understanding of the Roman army structure.
We then put these into context by looking at a Roman army camp, a Roman army on the march, and a Roman army in battle order. This gives the viewer a full 3D history of a legion like never before.
(more…)
QotD: The soul of the bureaucrat
It is amazing how a small circumstance can in a trice overturn a mood from one of equanimity to one of anxiety and irritation. What most upset me was the thought of having to deal with the British bureaucracy in order to obtain some kind of travel document or other. I could just see in my mind’s cinema the drab room in the consulate where a minor official, who hated his work and was thoroughly bored with and disgusted by the procession of incompetents, liars, and con men who day after day appeared before him claiming that their case was particularly urgent or in some way deserving of his special attention, eked out his miserable existence, praying every day for the time of closure of the consulate to approach quickly rather than at its usual snail’s pace. Nominally, of course, he was the servant of the citizenry whose taxes paid his salary, but drawing this to his attention would only have slowed him down and made him more determined than ever to draw out the agony of the scum with whom he had always to deal. The fact is that no Middle Eastern or Central Asian peasant at the diwan of the potentate’s vizier was ever more a powerless petitioner than is the average Western citizen in a situation such as this. The citizen is nothing and the bureaucrat is everything.
I had all kinds of documents with me to prove that I was the person I said I was, namely me; besides which, it was surely obvious, even to the most casual observer, that I was a respectable citizen not given to obtaining travel or other documents by false pretensions. But these days we live under a regime, if not exactly of laws rather than of men, at least of regulations rather than of men, and an official such as the one with whom I would have to deal would be allowed to exercise no discretion in case he thereby revealed his social prejudices. “Let justice be done though the heavens fall,” said Cicero, which we have changed to “Though the heavens fall, let the forms be filled and the boxes ticked.”
To do my imaginary official justice, I would have behaved just like him if our positions had been reversed. There are many jobs whose sole pleasure or delight must be in disobliging the public. Bureaucrats are themselves so oppressed by bureaucracy that their only way of finding relief is to make others suffer like them. The wonder, then, is not that they are bad, but that they are not worse.
Theodore Dalrymple, “The Bureaucrat’s Point of View”, Taki’s Magazine, 2018-05-12.
February 21, 2023
“… sub-replacement fertility is probably an inevitable product of female emancipation”
In Ed West’s weekly round-up, he ends the post on this rather grim (from a demographic viewpoint) note:
In The Guardian, Martha Gill on the great vexation of modern life: people can’t have as many children as they’d like.
OK: so it’s about social structures, then? Lack of childcare, unequal parental leave and career penalties for mothers. Not so – or not primarily. In our fecund recent past, remember, career penalties for mothers were even higher. Mothers still suffer a career penalty almost everywhere, but attempting to remove it doesn’t seem to alter their decisions that much. Since 2008, amid unequalled progress in gender equality and some of the most generous parental support schemes on the planet, birthrates in Sweden, Norway and Iceland have fallen precipitously. Nordic countries are, comparatively, parental utopias, yet birthrates tick along slightly above the EU average and still well below the replacement rate.
I agree with her basic premise. Aside from Georgia, no country has successful brought fertility rates above replacement rates, whatever the childcare incentives, because sub-replacement fertility is probably an inevitable product of female emancipation. In particular the issue is that women don’t tend to marry men with lower education and income levels, so the modern system ensures that a large minority of men are simply unmarriagable.
I’m not convinced by Gill’s solution, since outcomes for the children of single parents are way worse on average, and even with huge state support it’s going to be incredibly hard to raise children alone. Even without grandparental support it’s hard with two parents. I also think this problem is inevitably helping the drive towards poly-acceptance. As Rob Henderson wrote earlier this month:
In a deregulated market, power laws dominate. This is true not only in the economic realm, but in the romantic realm as well. At no point in history have all men in a given society been equally desirable. Today, though, the disparity between men is particularly pronounced. And the gap shows no sign of slowing or closing. The polyamorous movement may be a reaction to shifts in sex ratios among attractive individuals. Many individuals who do not identify as poly are likely practicing some version of it, knowingly or otherwise, as the case of West Elm Caleb demonstrated. The majority desirable young males using dating apps almost certainly have at least three women in their rotation, if not more.
As with so many things, post-Christian society is reverting to pre-Christian norms, in this case the norm where a large proportion of men were thrown onto the romantic scrapheap.
Larry Correia’s In Defense of the Second Amendment
In the latest Libertarian Enterprise, Charles Curley reviews Larry Correia’s latest non-fiction book:
The name Larry Correia may ring a bell for Libertarian Enterprise readers. He has written fiction since 2008. He started with Monster Hunter, a self-published novel that later got a contract from Baen Books. He has since become a New York Times best selling author, and a finalist for the John Campbell award.
He also originated the Sad Puppies campaign, an effort to turn the Hugos away from their politically correct drift.
Yeah, guns and science fiction. TLE readers should appreciate that combination.
First off, this is not a scholarly exercise, nor does it break much new ground in the gun control arena. If you want scholarly language, look elsewhere, to, say, Don Kates, Stephen Halbrook, or David Kopel: in places this book is more of a rant than a treatise. So if you enjoy the snark of L. Neil Smith or H. L. Mencken, you’ll like this book. None the less, it has 12 pages of end notes and five pages of index. (But, oddly enough, no table of contents.)
Correia says so: “This book isn’t intended for policy wonks and pundits. I’m not an academic. I’m not a statistician. I’m a writer who knows a lot about guns.” (p. 23) And he’s tired of hearing the same tired old stuff trotted out again and again in any discussion about gun control. This book is his reply. “I won’t lie, I’d like this book to give ammo to the people on my side of the debate. To those of you who are on the fence, undecided, I want to help you understand more about how crime and gun control laws actually work.” (p. 23)
Chapter One is entitled Guns and Vultures. The vultures are the people who feed on every tragedy, trying to fit it into their agenda of more gun control and more dependence on the state. The people who heed Rahm Emmanuel’s famous dictum: “You never want a serious crisis to go to waste.” The people who wring their hands and say, we have to do something! even when the something has been tried before and found wanting, or even found impossible.
Much of the book is devoted to refuting the anti-gun arguments. I trust I needn’t outline those to TLE readers.
Note that while he’s confident that the book is well worth reading, he hasn’t actually read any of Larry’s fiction writing, so he can’t be dismissed as a fan who’d automatically recommend the book.
Smart people are at least as likely to fall for false beliefs as anyone else
Gurwinder explains why people well above average intelligence are actually more likely to adopt irrational ideas:
What causes delusion?
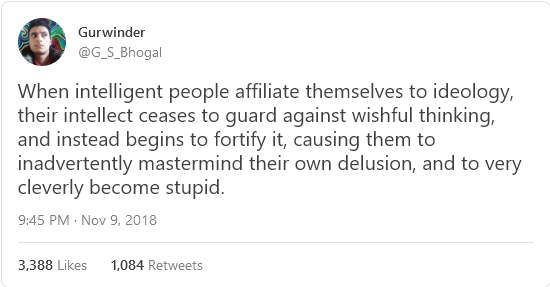
The prevailing view is that people adopt false beliefs because they’re too stupid or ignorant to grasp the truth. This may be true in some cases, but just as often the opposite is true: many delusions prey not on dim minds but on bright ones. And this has serious implications for education, society, and you personally.
In 2013 the Yale law professor Dan Kahan conducted experiments testing the effect of intelligence on ideological bias. In one study he scored people on intelligence using the “cognitive reflection test”, a task to measure a person’s reasoning ability. He found that liberals and conservatives scored roughly equally on average, but the highest scoring individuals in both groups were the most likely to display political bias when assessing the truth of various political statements.
In a further study (replicated here), Kahan and a team of researchers found that test subjects who scored highest in numeracy were better able to objectively evaluate statistical data when told it related to a skin rash treatment, but when the same data was presented as data regarding a polarizing subject — gun control — those who scored highest on numeracy actually exhibited the greatest bias.
[…]
Since we’re a social species, it is intelligent for us to convince ourselves of irrational beliefs if holding those beliefs increases our status and well-being. Dan Kahan calls this behavior “identity-protective cognition” (IPC).
By engaging in IPC, people bind their intelligence to the service of evolutionary impulses, leveraging their logic and learning not to correct delusions but to justify them. Or as the novelist Saul Bellow put it, “a great deal of intelligence can be invested in ignorance when the need for illusion is deep”.
What this means is that, while unintelligent people are more easily misled by other people, intelligent people are more easily misled by themselves. They’re better at convincing themselves of things they want to believe rather than things that are actually true. This is why intelligent people tend to have stronger ideological biases; being better at reasoning makes them better at rationalizing.
This tendency is troublesome in individuals, but in groups it can prove disastrous, affecting the very structure and trajectory of society.
For centuries, elite academic institutions like Oxford and Harvard have been training their students to win arguments but not to discern truth, and in so doing, they’ve created a class of people highly skilled at motivated reasoning. The master-debaters that emerge from these institutions go on to become tomorrow’s elites — politicians, entertainers, and intellectuals.
Master-debaters are naturally drawn to areas where arguing well is more important than being correct — law, politics, media, and academia — and in these industries of pure theory, secluded from the real world, they use their powerful rhetorical skills to convince each other of FIBs. During their master-debatery circlejerks, the most fashionable delusions gradually spread from individuals to departments to institutions to societies.
Some of these FIBs can now be found everywhere. A particularly prominent example is wokeism, a popularized academic worldview that combines elements of conspiracy theory and moral panic. Wokeism seeks to portray racism, sexism, and transphobia as endemic to Western society, and to scapegoat these forms of discrimination on white people generally and straight white men specifically, who are believed to be secretly trying to enforce such bigotries to maintain their place at the top of a social hierarchy.
Medieval Mardi Gras
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 22 Feb 2022
(more…)
QotD: The Gods as (literal) machines
So we have the basic rules in place: in order to achieve a concrete, earthly result, we need to offer something to the appropriate god and in exchange, they’ll use their divine power to see that things turn out our way.
But what do we offer? What do we ask for? How do we ask? This isn’t write-your-own-religion, after all: you can’t just offer whatever you feel like (or more correctly, you can, and the god’s silent disapproval will be the response). After all, if your plan is to get me to do something, and you show up at my door with awful, nasty Cherry Pepsi, you are bound to be disappointed; if you show up with some delicious Dr. Pepper, you may have better luck. That’s how people work – why would the gods be any different?
So different gods prefer different things, delivered in different ways, with different words, at different times. There are so many possible details and permutations – but this is important, it matters and you must get it right! So how can you be sure that you are offering the right thing, at the right time, in the right way, to the right god, for the right result?
And that’s where our knowledge from last week comes in. You aren’t left trying to figure this out on your own from scratch, because you can draw on the long history and memory of your community and thus perform a ritual which worked in the past, for the same sort of thing.
The thing to understand about that kind of knowledge is that it’s a form of black box tech; the practitioner doesn’t know why it works, only that it works because – as we discussed – the ritual wasn’t derived from some abstract first-principles understanding of the gods, but by trial and error. Thinking about the ritual as a form of functional, but not understood, technology can help us understand the ancient attitude towards ritual.
Let’s say we discovered a functioning alien spaceship with faster-than-light propulsion, but no aliens and no manual. We don’t understand anything about how it works. What would we do? We might try to copy the ship, but remember: we don’t know what parts are functional and what parts are just cosmetic or what does what. So we’d have to copy the ship exactly, bolt for bolt, to be sure that it would work when we turned it on.
Ritual in ancient polytheistic religions is typically treated the same way: given an unknowable, but functional system, exactitude is prized over understanding. After all, understanding why the ritual works does not help it work any better – only performing it correctly. An error in performance might offend the god, or create confusion about what effect is desired, or for whom. But an error in understanding causes no problems, so long as the ritual was performed exactly anyway. Just as it doesn’t matter what you think is happening when you, say, turn on your TV – it turns on anyway – it doesn’t matter what you think is happening in the ritual. It happens anyway.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Practical Polytheism, Part II: Practice”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-11-01.
February 20, 2023
Monocultures are risky in agriculture … and even more so in politics
Unlike his usual bite-sized quips-with-links at Instapundit, Glenn Reynolds occasionally writes at length for his Substack page:

The western front of the United States Capitol. The Neoclassical style building is located in Washington, D.C., on top of Capitol Hill at the east end of the National Mall. The Capitol was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1960.
Photo via Wikimedia Commons.
Our modern ruling class is peculiar. One of its many peculiarities is its penchant for fads, and what can only be called mass hysteria. Repeatedly, we see waves in which something that nobody much cared about suddenly comes to dominate ruling class discourse. Almost in synchrony, a wide range of institutions begin to talk about it, and to be preoccupied by it, even as every leading figure virtue-signals regarding this subject which, only a month or two previously, hardly any of them even knew about, much less cared about.
There are several factors behind this, but one of the most important, I think, is that our ruling class is a monoculture.
In agriculture, a monoculture exists when just a single variety dominates a crop. “Monoculture has its benefits. The entire system is standard, so there are rarely new production and maintenance processes, and everything is compatible and familiar to users. On the other hand, as banana farmers learned, in a monoculture, all instances are prone to the same set of attacks. If someone or something figures out how to affect just one, the entire system is put at risk.”
In a monoculture, if one plant is vulnerable to a disease or an insect, they all are. Thus diseases or pests can rip through it like nobody’s business. (As John Scalzi observes in one of his books, it’s also why clone armies, popular in science fiction, are a bad idea in reality, as they would be highly vulnerable to engineered diseases.) A uniform population is a high-value target.
[…]
Codevilla wrote the essay [here] over a decade ago, and it has only grown more true in the interim. Despite its constant invocation of “diversity”, in many important ways our ruling class is much less diverse than it has ever been. And, as a monoculture, it is vulnerable to viruses of a sort. Including what amount to viruses of the mind.
When Elon Musk referred to the dangers of the “woke mind virus“, he knew exactly what he was talking about. Ideas can be contagious, and can be viewed as analogous to viruses, entities that reproduce by infecting individuals and coopting those individuals into spreading them to others. Richard Dawkins, in his The Selfish Gene, coined the term “meme” to describe these infectious ideas, though the term has since acquired a more popular meaning involving photos of cats, etc. with captions. And yet those pictures are themselves memes, to the extent they “go viral” and persuade others to copy and spread them.
Our ruling class is particularly vulnerable to mind viruses for several reasons. First, it is a monoculture, so that what is persuasive to one member is likely to be persuasive to many.
Second, it suffers from deep and widespread status anxiety – not least because most of its members have status, but few real accomplishments to rely on – and thus requires constant reassurance in the form of peer acceptance, reassurance that is generally achieved by repeating whatever the popular people are saying already. And third, it has few real deeply held values, which might otherwise provide guard rails of a sort against believing crazy things.
In a more diverse ruling class, ideas would not spread so swiftly or be received so uncritically. People with different worldviews would respond differently to ideas as they entered the world of discourse. There would be criticism and there would be debate. (Indeed, this is how things generally worked during the earlier, more diverse, era described by Codevilla, though intellectual fads – lobotomy, say, or eugenics – spread then, too, though mostly through the Gentry/Academic stratum of society that now dominates the ruling class.)
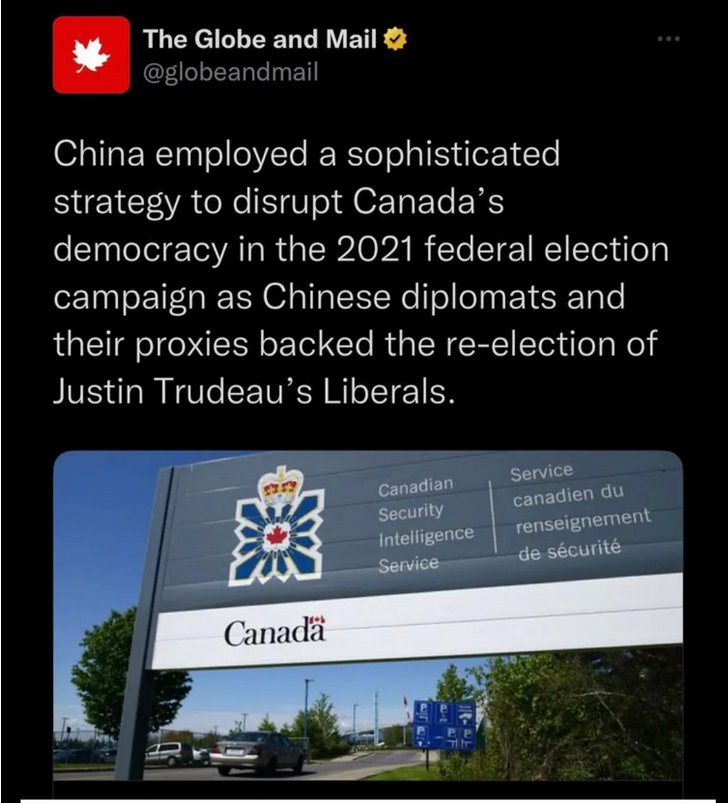
“There is no way Justin Trudeau won any of the last three elections”
Elizabeth Nickson on recent rather alarming confirmation of many things told by various “conspiracy theorists” and purveyors of “misinformation”:
Cracks are beginning to appear in the massive election fraud strategy prosecuted against western democracies. Berlin last week reversed its city election because it had been stolen by the left, and Berliner-Zeitung revealed that a team of reporters from The Marker, Haaretz and Radio France had gone undercover for six months as clients of a company that did nothing but election theft. That company, Jorge, had “intervened in 33 national election campaigns and votes. In 27 cases, it is said to have influenced the elections in favor of its clients. In order to control the opinion on the Internet, the secret company controls over 30,000 credible fake accounts on social media platforms”.
And in Canuckistan this morning, in the organ of the bien-pensant liberal establishment, there was this nugget.
There is no way Justin Trudeau won any of the last three elections. And, honey, this little story from Canada’s most prestigious newspaper is just the beginning.
But first, a story of my own …
When I turned right I had been hired to write an op-ed column for the above Globe and Mail, and what unfurled from my fingers was pure conservatism. I’d hold up my fingers and think, What the hell? Where did that come from? But I continued, and as I did, family and friends sheered away until, except for my mother, I was left virtually friendless.
I had moved back to Canada, you see, and we are 100% captured by the left. There are a handful of conservative writers in the country, but they are soft and weak and they prevaricate because otherwise they would not eat. Luckily I had spent most of my adult life out of the country, had a broader pool to draw from, and given my new thinking, mirable dictu for every friend I lost, I made five new ones. And they were smarter, more responsible, more interesting people. I missed the clothes, restaurants and parties for a while, then I gave up on those too. Essentially, sickening. Finally corrupting.
But it continues, since we live in a hard-left community. We are isolated. Even Jamie, because he lives with me, has lost friends and family. We have his sons, his ex-wife, one of my brothers. The rest are just cold, pitiless. Cruel.
This has happened to hundreds of thousands of people. It’s called “bad-jacketing” and is part of the Fifth Generation Warfare launched against malcontents large and small (like me) up and down the social ladder. Millions. Tens of millions. The competent are targeted, isolated and bad jacketed. It is meant to drive the competent out of the culture. Why is everything breaking? Why is the economy failing? Everyone left in the system is incompetent and vicious with it. It’s why Soviet Russia failed, why the Eastern Bloc collapsed, it is why China went for a capitalist hybrid. Everywhere socialism is tried it destroys the competent and then destroys everything else.
The left is implacable and they punish. They hurt you until you give up. They will break anything you have. Thinking about helping a young neighbor last month, which would require a week or more of brutal work, I finally thought: I have not helped or befriended one single socialist — and she was an avowed socialist — who hasn’t eventually stabbed me in the back. Not one.
When I was driven out of the profession, I spent ten years studying. Was I right? Was I wrong? I should have signed up for a remote doctoral program, because I worked. I study, therefore I am. I studied therefore I was, should be written on my cremation plaque in the family plot. Not that they’ll let me in.
We are all intimidated by that level of hate and exclusion. All of us, politicians, editors, bureaucrats, charities, all of us are terrified of being taken down in our personal lives. Bad-jacketed, rejected by those you love deeply. I know how that feels and I bet you do too.
Thirteen reasons the Dutch did better financially than the English in the Seventeenth Century
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes investigates the huge differences between the rival English and Dutch financial markets in the 17th century:

The courtyard of the exchange in Amsterdam (De binnenplaats van de beurs te Amsterdam), 1653.
Oil painting by Emanuel de Witte (1617-1692) from the Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen collection via Wikimedia Commons.
One of the weird things about Britain, despite its being the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution, is that its financial infrastructure was for a long time remarkably backward. Its “Financial Revolution”, by which both people and the state began to borrow at ever lower interest rates, only really took off in the early eighteenth century — long after London’s extraordinary growth in 1550-1650, when it had suddenly expanded eightfold to become one of Europe’s most important commercial hubs. Indeed, even for much of the late seventeenth century, England lacked many of the most basic financial institutions that had been used for decades and decades by their most important rival and trading partner, the Dutch Republic.
I was especially intrigued when I stumbled across a discussion of Dutch policies and customs, written up in around 1665 by the young merchant Josiah Child, and published a few years later: a kind of wishlist of many of the things that made the Dutch so wealthy, and which the English continually failed to emulate:
- The Dutch councils of state and war always included merchants who had experience of trading and living abroad — Child was perhaps just angling for some influence here, but for all that merchants were getting more influential, in England they were not actually in charge.
- Gavel-kind succession laws, whereby all children got an equal share of their parents’ estates, rather than it all going to the eldest. English primogeniture, by contrast, apparently left a lot of gentlemen’s younger sons having to become apprenticed to merchants.
- High regulatory standards for goods. A barrel of Dutch-packed herring or cod would apparently be accepted by buyers just by viewing the marks, without having to open them up to check. English-packed goods, by contrast, were rarely trusted because the fish would turn out to be rotten or even missing — the English regulators’ stamps of approval were reputedly given to anyone who would pay.
- Encouragement for inventors of new products, techniques, and import trades, who received rewards from the state, and not just temporary monopoly patents.
- Ships, called fluyt, which were cheaper to build, required fewer sailors, and were easier to handle. Despite being only very lightly armed, they sailed in fleets for protection, when necessary being convoyed by ships of war. English trading ships, by contrast, were each heavily armed, but with those cannon taking up room and weight that could have been used for carrying merchandise.
- Education of all children, even girls, in arithmetic and keeping accounts. As Child put it, this infused in the Dutch “a strong aptitude, love, and delight” for commerce. It also meant that husbands and wives were real partners in many businesses — something that impressed almost all foreign visitors to the Netherlands.
- Low customs duties, but high consumption taxes. Very low customs duties, on both imports and exports, meant that it was often very profitable to trade with the Netherlands. The Dutch were famed for their many ships, and for their granaries bursting with grain, despite growing hardly any trees or crops themselves. To fund their state, they instead overwhelmingly relied on the gemene middelen — taxes on the sale of wine, beer, meat, fuel, candles, salt, soap, flour, cloth, and a host of other goods, with many of the higher rates reserved for expensive luxuries. Much like modern value-added taxes, these taxes on consumption raised revenue while preserving the all-important incentive to save and invest.
- Thrifty living — which, come to think of it, was probably related to the high consumption taxes, although Childs doesn’t seem to have noticed the connection. Dutch thrift was thought by the English to be especially useful because it allowed wage costs to be kept low — essential for maintaining competitiveness in international markets — while preventing the country having a trade deficit. The English always worried they were sending too much of their silver abroad to pay for French wines and other luxuries, but the Dutch appeared to have prevented this without resorting to import tariffs that might annoy trading partners and prompt retaliation.
- Religious toleration, which attracted all sorts of industrious immigrants to bring their families and wealth. (Incidentally, as I’ve mentioned before, this was also one of the key attractions of Livorno, set up by the Medici Dukes of Tuscany to be a major trading hub.)
- The use of the Law-Merchant, which meant that all controversies between merchants and tradesmen were decided in just 3 or 4 days’ time. England, rather strangely for such an increasingly commercial nation, did not develop merchant courts with a specific jurisdiction or a distinct body of merchant law — disputes instead had to be resolved in the royal common-law or equity courts, in the Admiralty court, or else abroad. The English courts, however, were often slow. Child complained that cases often took half a year, and often much longer. (Incidentally, slow and rotten justice in the Court of Chancery, the key equity court used by merchants in England, was one of the reasons Francis Bacon was impeached by Parliament and sacked as Lord Chancellor.)
- Transferrable bills of exchange — in other words, the circulation of credit notes as a currency. These were not properly supported by English laws, but allowed Dutch merchants to trade a lot more frequently. English merchants often had to wait some six months to a year before receiving all the coin from selling their foreign goods in London, so as to purchase goods again to make fresh trades. They spent much of their time chasing shopkeepers for payment. But the Dutch, by being able to easily buy and sell their credit notes, could “turn their stocks twice or thrice in trade”, immediately settling their accounts and making fresh purchases. (I intend to look into this in a lot more detail soon, as finding a way to bills of exchange transferrable in England appears to have been a major project for many of the mid-seventeenth-century inventors and improvers — after just a cursory glance, transferability was only secured in law as late as 1704.)
- Banks. Or rather, as Child actually put it, “BANKS”. In England many of the functions of banks gradually evolved from the practices of individual goldsmiths and the scriveners — legal clerks who specialised in property transfers and mortgages. There was certainly nothing so secure as the municipal Wisselbank of Amsterdam, established in 1609, which had various monopoly powers as a clearing-house for bills of exchange and was backed by a vault full of bullion. Nor the municipal Bank van Lening, established in 1614, which was a pawnbroker modelled on the Italian Monte di Pietà, or mounts of piety, designed to make small and low-cost loans to the poor.
- “PUBLIC REGISTERS” — again capitalised by Child — of all lands and houses sold or mortgaged. This item on the policy wishlist would not be ticked off for England until two centuries later, but the key advantage was to prevent lawsuits over land titles — still cited as a major problem even in the 1690s — and so make land more genuinely secure for mortgages.
Finally, the result of many of these policies was the Dutch had significantly lower interest rates — often just 3-4% when the English were still lending and borrowing at 6-8%. Indeed, this list was made because of a long-standing English policy debate I’ve been researching, on whether to lower the legal maximum rate of interest.