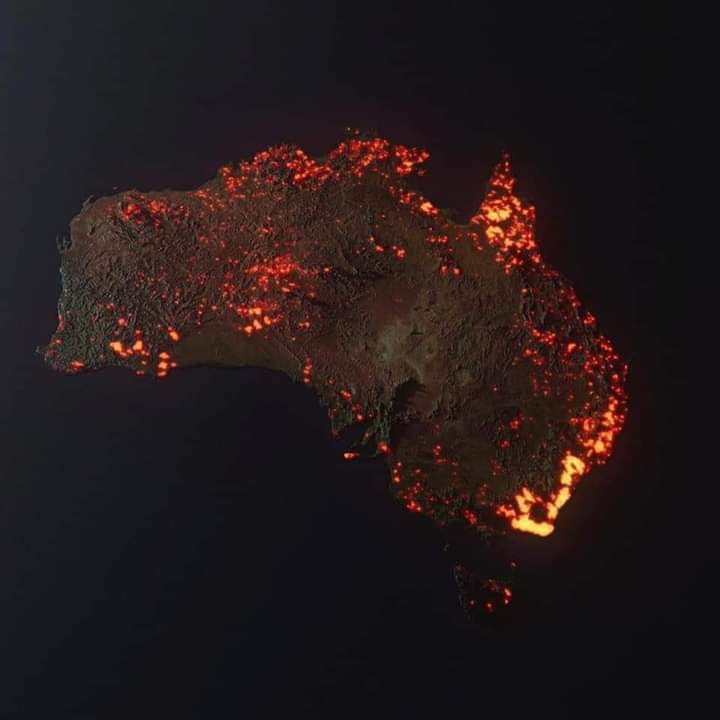
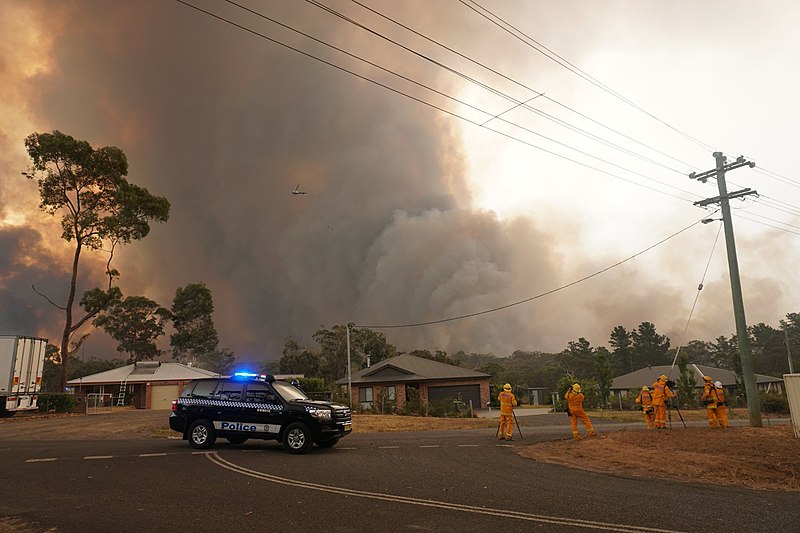
It’s funny that no matter what the claimed crisis, the answers always go in the same direction, as Kristian Niemietz points out with the demands to turn our still unending lockdown toward “protecting the environment”:
The change, superficially, is to encourage “a safe return to work” allowing more social distancing between pedestrians, but more substantially in order to preserve the cleaner air that has resulted from the lockdown.
The health and safety excuse for the policy change can be largely dismissed. The simple truth of the pandemic and national policy is that if social distancing matters, the centre of London is not safe to return to work. It is too densely populated and almost entirely reliant on mass transit which cannot operate above 10-15% capacity with 2m exclusion rules. With average commutes over 9 miles each way, substitution effects to walking and cycling will be extremely limited and temporary.
It is then hard to see then how the policy’s architects imagine the streets will fill up to the extent urgent measures are needed. Conversely, if social distancing does not matter (and it will cease to matter eventually), then a policy to enable more social distancing outside by widening the pedestrian streetscape is redundant. If it is safe to sit on a crowded train, it is safe to walk on a crowded pavement. It is not hard then to cut through the pandemic packaging to note that the motive for this policy is opportunistic, to accelerate a pedestrianisation plan that is the dream of many an urban planner.
Many will see this as self-evidently a good thing. Removing vehicle traffic from densely populated narrow streets will reduce air pollution, congestion and road traffic accidents. As a policy it will have more supporters than opponents; very few people drive into the centre of London to commute and there is very little capacity for parking. London’s leaders are not wrong to think that this is the future, the question is really one of timing and how they go about it, which is far more difficult and does not have anything to do with managing a coronavirus.
What the pandemic allows is the ability to use emergency powers for something that is not an emergency. This matters, in normal times it took several years to close one dangerous junction at Bank to most traffic, and this under a hail of protests from local businesses and taxi drivers. The same result can now be achieved in a few weeks across many streets. The democratic checks and balances that differentiate the UK from authoritarian states can be ditched and London officialdom granted extraordinary powers to do as they please. If the protestors don’t like it this time, they should note the right to protest has also been suspended, at least for now.