In The Critic, Peter Caddick-Adams outlines the state of Europe four hundred years ago:
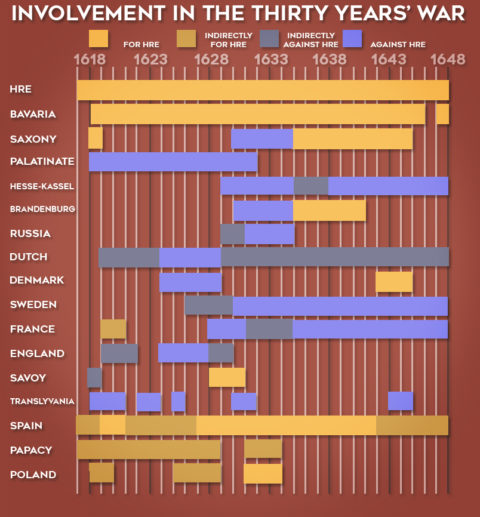
A war as long and as complex requires something like this to help keep the narrative somewhat understandable.
Exactly four hundred years ago, a dark shadow was slithering across mainland Europe. It stretched its bleak, cold presence into each hearth and home. Everything it touched turned to ruin. Musket and rapier, smoke and fire, ruled supreme. Nothing was immune. Animals and children starved to death, mothers and adolescent girls were abused and tortured. The lucky ones died, alongside their brothers and fathers, slain in battle. Possessions were looted, crops destroyed, barns and houses burned. There seemed no end to the evil and pestilence. Sixteen generations ago, many believed the end of the world had arrived.
This was not a tale of Middle Earth. The place was central Europe in the early 17th century. In 1618 the future Holy Roman emperor Ferdinand II, a zealous follower of the Jesuits, had attempted to restore the Catholic Church as the only religion in the Empire and exterminate any form of religious dissent. Protestant nobles in Bohemia and Austria rose up in rebellion. The conflict soon widened, fuelled by the political ambitions of adjacent powers. In Europe’s heartland, three denominations fought it out: Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism and Calvinism.
The result was an interwoven tangle of diplomatic plot twists, temporary alliances and coalitions, as princes, bishops and potentates beseeched outside powers to help. The struggle, which lasted for thirty years, boiled down to the Roman Catholic and Habsburg-led Holy Roman Empire, fighting an incongruous array of Protestant towns and statelets, aided by the anti-Catholic powers of Sweden under Gustavus Adolphus, and the United Netherlands. France and Spain also took advantage of the distractions of war to indulge in their own sub-campaigns. Britain took no formal part but was about to become embroiled in her own civil war.
The principal battleground for this collective contest of arms centred on the towns and principalities of what would become Germany, northern Italy, the Netherlands and the Czech Republic. The war devastated many regions on a scale unseen again until 1944–45. For example, at Magdeburg on the River Elbe, 20,000 of 25,000 inhabitants died, with 1,700 of its 1,900 buildings ruined. In Czech Bohemia, 40 per cent of the population perished, with 100 towns and more than a thousand villages laid waste. At Nordlingen in 1634, around 16,000 soldiers were killed in a single day’s battle. The town took three centuries for its population to return to pre-war levels. Refugees from smaller settlements swelled the many walled cities, increasing hunger and spreading disease.
Too diminutive to defend themselves, all states hired mercenaries, of whom a huge number flourished in the era, enticed by the prospect of quick wealth in exchange for proficiency with sword and musket. Employed by every antagonist, but beholden to no one, these armed brigands — regiments would be too grand a term for the uniformed thugs they were — roamed at will. With their pikes and their muskets, they plundered the countryside in search of booty, food and transport. In their wake, they left burning towns, ruined villages, pillaged farms. Lead was stripped from houses and church roofs for ammunition.
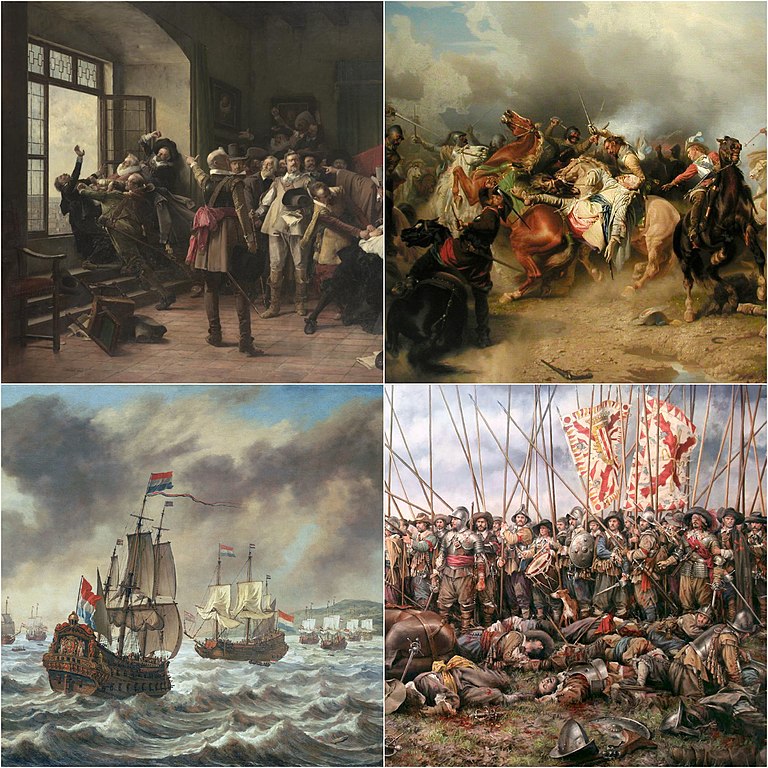
Left to right:
The Defenestration of Prague (23 May, 1618), The death of Gustavus Adolphus at Lützen (16 November, 1632), Dutch warships prior to the Battle of the Downs (21 October, 1639), and The Battle of Rocroi (19 May, 1643).
Collage by David Dijkgraaf via Wikimedia Commons.When in the winter of 1634 Swedish mercenaries were refused food and wine by the inhabitants of Linden, a tiny Bavarian settlement, they raped and looted their way through the village, leaving it uninhabitable. Across Europe, travellers noted the human and animal carcasses that decorated the meadows, streams polluted by the dead and rotting crops, presided over only by ravens and wolves. No respect was shown for the lifeless. Survivors stripped corpses of clothing and valuables; if lucky, the deceased were tossed into unmarked mass graves, since lost to history.
Having triggered the war, Ferdinand predeceased its end. We can never know how many died in Europe’s last major conflagration triggered by religion. Archives perished in the flames, and survivors were not interested in computations. Historians now put the death toll at between 8 and 12 million. Probably 500,000 perished in battle, with the rest, mostly civilians, expiring through starvation and disease. We think these casualties may equate to as much as 20 per cent of mainland Europe’s population and perhaps one-third of those in modern Germany, bringing the Thirty Years’ War a potency similar to the Black Death or either world war. The region did not recover for at least three generations.
Economic activity, land use and ownership altered terminally. When the exhausted powers finally met in October 1648 at Osnabrück and Münster in the German province of Westphalia to end the directionless slaughter, of whom self-serving militias were the only beneficiaries, Europe’s balance of power had shifted tectonically. Fresh rules of conflict and the legitimacy of a new network of 300 sovereign states, independent from a Holy Roman Emperor or a Pope, marked the struggle as a watershed moment, leading to the Enlightenment and an era that disappeared only with Napoleon.








