Niall Ferguson from The Spectator:
“War:, in Prussian military theorist Carl von Clausewitz’s most famous dictum, “is nothing but a continuation of politics with the admixture of other means.” A generation of Democrats — the American variety, but also European Christian and Social Democrats — have sought to ignore that truth. Appalled by the violence of war, they have vainly searched for alternatives to waging it. When Vladimir Putin ordered the annexation of Crimea in 2014, Barack Obama responded with economic sanctions. When Putin intervened in the Syrian civil war, they tried indignant speeches.
When it became clear that Putin intended a further and larger military incursion into Ukraine, Joe Biden and his national security team opted for sanctions once again. If Putin invaded Ukraine, they said, Russia would face “crippling” or “devastating” economic and financial penalties. When these threats did not deter Putin, they tried a new tactic, publishing intelligence on the likely timing and nature of the Russian assault. Cheerleaders for the administration thought this brilliant and original. It was, in reality, a species of magical thinking, as if stating publicly when Putin was going to invade would make him less likely to do so.
Those who dread war approach diplomacy the wrong way, as if it is an alternative to war. This gives rise to the delusion that, so long as talks are continuing, war is being averted. But unless you are prepared ultimately to resort to force yourself, negotiations are merely a postponement of the other side’s aggression. They will avert war only if you concede peacefully what the aggressor is prepared to take by force.
Putin decided on war against Ukraine some time ago, probably in July when he published a lengthy essay, “On the Historical Unity of the Russians and Ukrainians”, in which he argued tendentiously that Ukrainian independence was an unsustainable historical anomaly. This made it perfectly clear that he was contemplating a takeover of the country. Even before Putin’s essay appeared, Russia had deployed around 100,000 troops close to Ukraine’s northern, eastern and southern borders. The response of the United States and the European Union was to make clear that Ukraine was a very long way indeed from either Nato or EU membership, confirming to Putin that no one would fight on Ukraine’s side if he went ahead with his planned war of subjugation.
Over the past few months, Putin has used diplomacy in the classical fashion, seeking to gain his objectives at the lowest possible cost while at the same time carefully preparing for an invasion. Western leaders have achieved nothing more than to remain united in saying they will impose sanctions if he invades. But a Russian invasion of Ukraine beyond the Donbas will create an entirely new situation. Politicians on both sides of the Atlantic may express a common outrage, but it will not take long for their unity to be eroded by the altered reality and their fundamentally divergent interests. The US does not need Russia’s natural gas. At least in the short run, Europe does.
Arthur Chrenkoff offers what he calls “disjointed thoughts at a tragic time”:
Putin is invading Ukraine – not just sending “peacekeepers” into the breakaway pro-Russia regions in the east of the country – in order to “denazify” and “demilitarise” the country. The former is an outrageous slur in a long communist tradition from Stalin to today’s Western left of smearing anyone they don’t like and agree with as a Nazi. Ukraine is as Nazi as Australia or Greece, or Russia for that matter. “Demilitarisation” is the more pertinent excuse. What Putin wants is a cordon sanitaire separating Russia from the West (which now includes Poland and the Baltic states). His vision for Ukraine is a pro-Russia puppet state or at least a neutral and impotent non-entity. According to Putin, Russia’s got a legitimate security interest in not being bordered by hostile (read pro-Western) states. Why this should trump Ukraine’s (or any other country’s) legitimate security interest in its own security, territorial sovereignty and the choice of international friends is unknown, except that might makes right and Russia fancies itself as a special case on the basis of its past great power status.
No country has an obligation to send it troops to fight a conventional war with Russia in Ukraine. But countries have moral obligation to offer any and all assistance to the people of Ukraine, including military equipment, as they defend themselves against unprovoked aggression. Countries also have moral obligation to punish Putin and Russia with utmost severity, including – if only they had the guts – complete economic and trade sanctions. Not a drop of Russian oil or a cubic foot of its gas. Let Putin swim in his unsold carbohydrates. Sadly that won’t happen because the Western European governments have, despite numerous warnings, made themselves energy dependent on imports from Russia. Shutting down coal, closing nuclear power plants and praying to the sun and the wind are now coming home to roost.
At First Things before the invasion began, George Weigel explained what was being obscured by Russian propaganda and western media complaisance:
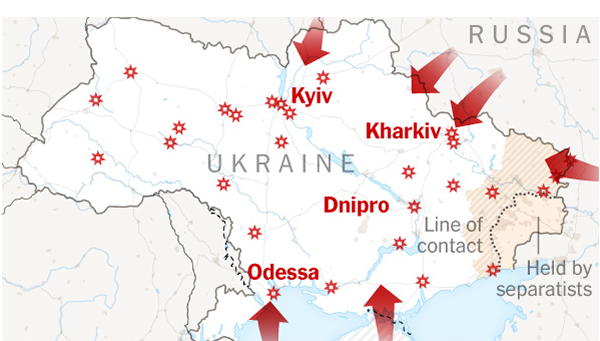
For months now, the world press has described Russian troop deployments along Ukraine’s borders as spearheads of a possible invasion. The truth, however, is that Russia invaded Ukraine seven years ago, when it annexed Crimea and Russian “little green men” ignited a war in eastern Ukraine that has taken over 14,000 lives and displaced over a million people. Whatever the current military developments, a Russian invasion of Ukraine has not been “imminent”; the invasion is ongoing.
That fact has been obscured by a massive Russian propaganda and disinformation campaign. So some truth-telling is imperative.
The first fact: This is a Russian crisis, not a “Ukraine crisis”. What is typically called the “Ukraine crisis” is entirely of Russian autocrat Vladimir Putin’s making. Ukraine did not create this crisis. The United States did not create it, and neither did NATO. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, which is, was, and always will be a defensive alliance, is no more a threat to Russian national security than NATO is to Botswana’s national security. The claim that NATO threatens Russia is a Big Lie that obfuscates the security realities in central and eastern Europe: Former Soviet satellites (Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria) and the Baltic states (Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia) joined NATO because they fear Russia, not because they intend to invade Russia. The same rationale explains Ukraine’s NATO application.
The second fact: This artificially created crisis, aimed at Ukraine’s destabilization and subjugation, is one expression of Putin’s determination to reverse history’s verdict in the Cold War. Putin has been quite clear about this for twenty years, and only fools or those peering through the ideologically befogged lenses of the new “national conservatism” fail to grasp what is afoot here. Putin, the old KGB apparatchik, is bent on overturning the victory of imperfect democracies over pluperfect tyrannies in the Revolution of 1989 and the Soviet crack-up of 1991. That grand strategic goal is at the cold heart of the recently announced alliance of purpose between Putin’s kleptocratic regime in Russia and Xi Jinping’s genocidal regime in China — an announcement these two wicked men made just before the Winter Olympics. Putin and Xi want nothing less than a fundamental re-ordering of world affairs in which their oppressive regimes call the tune. In the tyrants’ bid for global hegemony, Ukraine and Taiwan are in the role played by Austria and Czechoslovakia in the late 1930s: If they fall to the tyrant-regimes, others will follow.
At Samizdata, Perry de Havilland notes that not every single thing that happens in the wider world is linked to or directed by American action:
Yes, the United States is the richest and most powerful nation on earth and it has been since World War II. And yes, it has interfered under presidents of all stripes for good or ill in a great many places, in pursuit of its perceived geopolitical interests, sometimes benignly, other times with a breathtaking lack of judgement.
But just as the leaders of that great nation have often overestimated the USA’s ability to impose its will in far away lands, many people in many places similarly overestimate America’s involvement everywhere. They largely deny that local people have agency, oblivious to the fact people everywhere are capable of organising politically in ways not directed and driven from an agency in Langley, Virginia. As a friend of mine who was deeply involved in the 2014 Maidan revolt in Kyiv said to me once:
“Woah! I’ve just heard we’re all CIA puppets on Washington’s payroll. There must have been an oversight as me and my friends never got a penny. You know people in America, so can you get me an address to apply for that lovely CIA money I’m apparently due?”
He was of course joking, but Maidan was a golden example of how something overwhelmingly driven and executed by Ukrainians, in Ukraine, in response to Ukrainian political and social pressures becoming intolerable, was nevertheless written off as CIA mischief-making.And whilst that was pushed hard by Russia when their pet oligarch was deposed, its entirely possible Putin himself believes it too. It is actually more supportive of his worldview than the notion it really happened because millions of Ukrainians loathed Putin, his Ukrainian’s puppet in Kyiv, and the malign influence of Russia generally.
But so many people seek a simpler world, a bipolar one in which everything is down to the Big Actors (with America still the biggest at the moment). Understanding that and feeding into it grants profound insight into Russian (and to some extent Chinese) propaganda. Add to that the rightly shattered confidence in Western institutions the last two years has wrought, and it is not surprising otherwise discerning folk fall for it.
And with bombs dropping and people being killed in Ukraine, John Kerry keeps his laser focus on the important issue — climate change: