Not only does it have a high cost, UBI drains the labour force by discouraging work and boosting leisure time, says one big-picture study
Earlier this month, a cross-border team of North American economists published the results of a landmark study, probably the best and most careful yet done, of how low-income workers respond to an unconditional guaranteed income. Not so long ago this would have been a plus-sized news item in narcissistic Canada, for the lead author of the study is a rising economics star at the University of Toronto, Eva Vivalt. The economists, working through non-profit groups, recruited 3,000 people below a certain income cutoff in the suburbs of Dallas and Chicago. A thousand of these, chosen at random, were given a thousand dollars a month for three years. The rest were assigned to a control group that got just $50 a month, plus small extra amounts to encourage them to stay with the study and fill in questionnaires.
That randomization is an important source of credibility, and the study has several other impressive methodological bona fides. If you have an envelope to scribble on the back of, you can see that the payments alone were beyond the wildest dreams of most social science: most of the money was provided by the AI billionaire Sam Altman. But the study also had help from state governments, who agreed to forgo welfare clawbacks from the participants to make sure the observed effects weren’t obscured by local circumstances. Participant households were also screened carefully to make sure nobody in them was already receiving disability insurance. (Free money doesn’t discourage work among people who can’t work — or who absolutely won’t.) And the study combined questionnaire data with both smartphone tracking and state administrative records, yielding an unusually strong ability to answer difficult behavioural questions.
The big picture shows that the free cash — a “universal basic income” (UBI) for a small group of individuals — discouraged paying work, even though everybody in the study was starting out poor. Labour market participation among the recipients fell by two percentage points, even though the study period was limited to three years, and the earned incomes of those getting the cheques declined by $1,500 a year on average. There is no indication that the cash recipients used their augmented bargaining power to find better jobs, and no indication of “significant effects on investments in human capital”, i.e., training and education. The largest change in time use in the experiment group was — wait for it! — “time spent on leisure”.
Colby Cosh, “Universal basic income is a recipe for fiscal suicide (for so many reasons)”, National Post, 2024-07-30.
November 2, 2024
QotD: UBI discourages low-income workers
October 30, 2024
Zuckerberg’s bad bet on Virtual Reality
Ted Gioia notes the anniversary of Mark Zuckerberg’s worst financial decision — the plunge into virtual reality:
A big birthday happens tomorrow. But don’t expect a celebration.
There will be no party, no disco. There will be no cake, no clown, no bouncy house for the kids. No Marilyn Monroe cooing the birthday song.
Just dead silence. But make no mistake — this is a very expensive birthday.
Exactly three years ago, Mark Zuckerberg placed a huge bet on virtual reality. On October 28, 2021, he even changed the name of his company — from Facebook to Meta.
A new company was born. But that’s now a huge embarrassment.
The name Meta is a lasting reminder of the most foolish decision Zuck ever made — even worse than Facemash or those ugly T-shirts.
Of course, that’s not how he saw things three years ago.
“Meta’s focus will be to bring the metaverse to life,” the company announced. “In the metaverse,” Zuckerberg bragged, “you’ll be able to do almost anything you can imagine.”
There was a catch — the tech billionaire needed to convince millions of people to wear virtual reality headsets.
But they looked ridiculous — you literally had to wear blinders if you wanted to enter Mr. Zucker’s neighborhood.
The very next day, I declared that “Meta is for losers”.
“This will never be cool.”
Zuckerberg was “making the wrong bet”, I warned — and gave my reasons:
The interface looks goofy and cartoonish. Instead of entering the gritty, exciting world of Blade Runner, you’re trapped inside a bad episode of Family Guy …
And users will look creepy too. You need to lock yourself into a headset to get the full benefit of the metaverse — and there’s no way that Zuckerberg can make that look cool. The people who spend hour after hour in his metaverse will be the subject of jokes and mockery …
They will be nerds and incels and the most disgruntled members of society, each desperate for escape.
Mark Zuckerberg eventually figured this out. But the company lost more than $20 billion over the next two years in a desperate attempt to convince normal people to abandon reality and enter his fake world.
Even as consumers resisted, Meta refused to admit it had made such a colossal mistake. Just last year, Zuckerberg still denied that he was abandoning virtual reality.
“A narrative has developed that we’re somehow moving away from focusing on the metaverse,” he told shareholders. “So I just want to say upfront that that’s not accurate.”
Then he did exactly that — retreating from the metaverse he had spent so much money building.
Fortune warned three months ago that Mr. Z’s metaverse “may finally be running out of cash”. Then in August, Meta cancelled the development of a next generation VR headset.
October 24, 2024
It’s called “piercing the corporate veil” and it’s a terrible idea
Tim Worstall explains why the EU’s latest brain fart is not just a bad idea in its own right, but a truly horrific precedent for the future:
… But now, this, now this is even more important than that. We can deal with free speech by the judicious use of lampposts. This is worse:
The European Union has warned X that it may calculate fines against the social-media platform by including revenue from Elon Musk’s other businesses, including Space Exploration Technologies Corp. and Neuralink Corp., an approach that would significantly increase the potential penalties for violating content moderation rules.
Under the EU’s Digital Services Act, the bloc can slap online platforms with fines of as much as 6% of their yearly global revenue for failing to tackle illegal content and disinformation or follow transparency rules.
In English law that’s known as “piercing the corporate veil”. It’s also something we don’t do. Because that corporate veil is the very thing, the only thing, that makes large scale economic activity possible.
It has actually been said — and not just by me — that the invention of the limited company is the third grand invention of all time. Agriculture, the scientific method, the limited company.
Before the limited co everything was done through partnerships. Every individual involved in the ownership of something was liable for all of the debts of that thing. Which, when you’ve got 5 or 10 blokes trading isn’t that bad an incentive upon them to be honest.
Now think of large scale activity. We want a blast furnace — plenty of folk say Britain should have one after all. £3 to £5 billion these days. OK. No one’s got that much. So, we need to mobilise the savings of many thousands of people to go build it. But without limited liability that means all of those thousands are liable for all the debts — off into the future — of that blast furnace.
“Invest £500 in the new, new British Steel. And if we fuck up then in 10 years’ time they’ll come and take your house.”
Err, yes.
Large scale economic activity depends upon being able to separate the debts of one specific activity from the general economic life of all its backers. If this is not true then no one will invest in large scale economic activity. Therefore we won’t have large scale economic activity. Which would, you know, be bad.
October 19, 2024
The worst month for legacy media … so far
Ted Gioia has a (paywalled) post on the awful, terrible, bad, no-good month for the mainstream media. I think the headline needs an appropriate meme:
These events all happened in the last few days.
They are NOT unconnected:
- SEPTEMBER 24: The Financial Times reports that a Substack launched two years ago by Bari Weiss is now worth $100 million, and has just raised $15 million from investors.
- OCTOBER 1: One week later, journalist Taylor Lorenz announces that she is leaving the Washington Post to launch an online periodical on Substack. She plans to hire other writers and offer in-depth coverage of tech and internet culture.
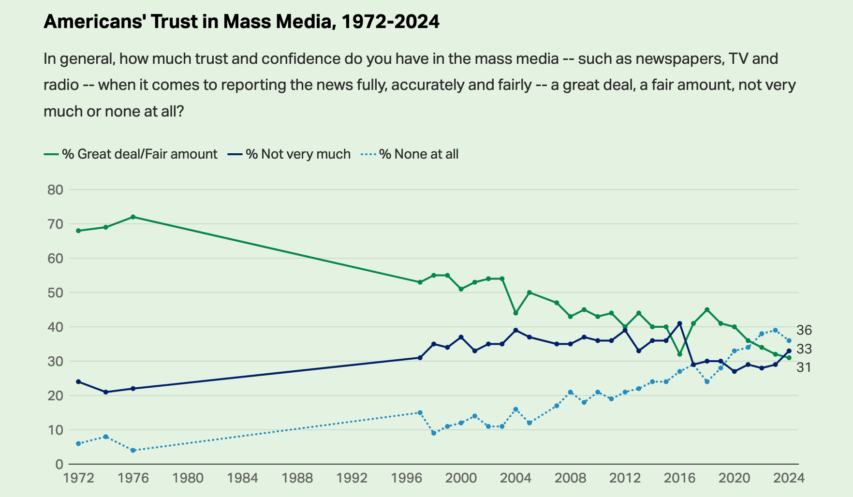
- OCTOBER 14: Gallup announces the results of a new poll showing that trust in mass media has reached an all-time low.
Source – Gallup
- OCTOBER 15: The Wall Street Journal reports that bestselling novelist James Patterson is launching on Substack. He has sold 480 million books since publishing his first novel in 1976, but now will sell subscriptions to readers at a price of six dollars per month.
- OCTOBER 15: That same day the New York Times reports that the “queen of legacy media” Tina Brown — formerly editor of The New Yorker and Vanity Fair — is now launching on Substack. She is also charging six dollars per month.
Changing gender balance in occupations and in higher education
At Postcards from Barsoom, John Carter ruminates on the likely downward path of many institutes of higher learning as current gender balance changes continue:
An occupation that flips from male to female dominance invariably suffers not only diminished prestige, but also a decline in wages … which, once again, makes sense in the context of sexual psychology. A man’s income is one element (and a big element) of a woman’s attraction to him, but the reverse is not true; if women are paid less, this does not really hurt their value in the sexual marketplace at all, and so they will push back against it much less than men would. This is probably what lies behind the tendency of women to be less forceful when negotiating salaries.
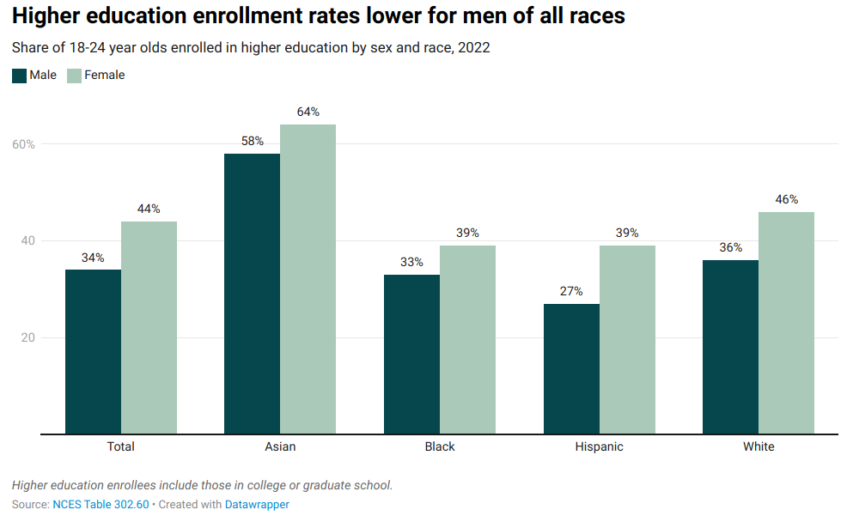
To the point: ever since the 1970s, women have overtaken and gradually eclipsed men within higher education. There is a gap in enrolment, consistent across racial groups:
[…]
Across all programs, at all academic levels, American universities recently reached the threshold of 60% of the student body being female.
This will be a disaster for academia.
Indeed, it’s already a disaster. About a year ago, I analyzed a Gallup poll which revealed that the confidence of the American public in the trustworthiness and overall value of the academic sector had declined precipitously over the course of the 2010s.
In that article I examined several factors contributing to this DIEing confidence in the academy: the explosive growth in tuition fees, even as continuous relaxation of academic standards dilutes the actual value of a degree; the deplorable state of scholarship, with endless revelations of fraud, a seemingly irresolvable replication crisis, and the torrent of psychotic nonsense that passes for ‘research’; the increasingly frigid social environment enforced by the armies of overpaid, sour-faced administrators. Almost all of these, however, are related in some way or another to the feminization of academia.
And it is probably going to get much worse before it gets better.
As discussed in this recent article by Celeste Davis of Matriarchal Blessing, research on male flight indicates that a 60% female composition represents the tipping point beyond which men perceive an environment as feminine, which then leads to a precipitous decline in male participation. Davis appears to be some sort of feminist3, but I want you to look past that and give her article a read; it is very thorough, well-researched, and thought-provoking (and also the direct inspiration for this article).
[…]
Universities are belatedly starting to notice that male enrolment is dropping fast, particularly among white men (I wonder why…), and are starting to make noises about maybe thinking about perhaps looking into ways of trying to recruit and retain more men (albeit, not specifically white men).
This seems unlikely to succeed.
Even if universities are successful in setting up programs to increase male recruitment, they will be fighting an uphill battle against the sexual perception that has already set in. Once something is coded as being a feminine hobby, it is extremely difficult to change that code. While it’s very easy to list examples of professions that have switched from male to female dominance, off the top of my head I have a hard time coming up with examples of the reverse. This suggests that female dominance tends to be sticky. There’s no reason to expect this will be any different with academia, either within individual programs, or across the sector as a whole.
This is an entirely different problem from the one faced by female entryism. In the initial phases of female entry, the primary difficulty faced by women is that it is simply more difficult to compete with men – in the case of athletics, effectively impossible. Women must therefore either work extremely hard, or the work must be made easier for them. In practice, since the 1970s we’ve seen both of these, with “working twice as hard as the boys” predominating in the early years, and assistance from special programs predominating later on.
By contrast, the central obstacle faced by anyone trying to attract men to a female-dominated environment is that men are deeply reluctant to enter. As a third of young men told Pew when asked why they didn’t attend or complete university: they just didn’t want to. It isn’t because they can’t compete with women. They can, usually with ease, but competition is pointless because it will gain them nothing. Special programs to assist men are beside the point; if anything, they work against you, because the implicit message with any special program for men is that they need help to compete with women … thereby making competition even more pointless. “You beat a girl but you needed help to do it”, is going to impress the girls even less than beating a girl unaided.
October 18, 2024
QotD: Californian wine
Of course, there is another reason why Californians so eagerly turned to science and machinery when they finally decided to make serious wine: American wineries were in horrific condition. Andrew Barr, in his social history Drink, tells us that even in the late 1930s there were rats swimming happily in the vats of Sauvignon Blanc at Beaulieu and vinegar flies in the other wines. “The wine is so excellent,” the resident wine maker cooed, “that all the flies go to it. It doesn’t do any damage.” Open fermentation tanks let off clouds of carbon dioxide which got birds flying overhead drunk; stunned, they would fall into the vats and stay there.
Lawrence Osborne, The Accidental Connoisseur: An Irreverent Journey Through the Wine World, 2004.
October 12, 2024
Canadians don’t hate their banks enough
In the latest SHuSH newsletter, Ken Whyte follows up on an earlier item thanks to the many Canadians who responded with their own tales of woe in their dealings with Canadian banks:
Since I mentioned a couple of weeks ago that we have published Andrew Spence’s Fleeced: Canadians Versus Their Banks, the latest edition of Sutherland Quarterly, I’ve been inundated with people’s horror stories of their dealings with Canada’s chartered banks. Jack David’s tale in the above interview is a classic of the genre.
In Fleeced, Andrew lays out in aggravating detail how Canadian banks, although chartered by the federal government to facilitate economic activity in the broader economy, do all they can to avoid lending to small and medium businesses, never mind that small and medium businesses employ two-thirds of our private-sector labour force and account for half of Canada’s gross domestic product.
By OECD standards, small businesses in Canada are starved of bank credit, and when they are able to secure a loan, they pay through the nose. The spread between interest rates on loans to small businesses and large businesses in Canada is a whopping 2.48 percent, compared to .42 percent in the US — more than five times higher.
Why? Because Canada’s banks are a tight little oligopoly, impervious to meaningful competition. Their cozy situation allows them to be exceedingly greedy. Their profits and returns to shareholders are wildly beyond those of banks in the US and UK (and, as Andrew demonstrates, their returns from their Canadian operations are far in excess of those from the US market, meaning they screw the home market hardest.)
Our banks never miss an opportunity to impose a new fee, or off-load risk. From their perspective, small business involves too much risk — some of them will inevitably fail. The banks prefer that publishers and dry-cleaners and restaurateurs either finance themselves by pledging their homes, or use their credit cards to cover fluctuations in cash flow or make investments that will help them hire, expand, and grow. And that’s what entrepreneurs do. According to a survey by the Canadian Federation of Independent Business, only one in five respondents accessed a bank loan or line of credit. Half of respondents financed themselves, tapped existing equity and personal lines of credit, and about 30 percent used their high-interest credit cards.
By severely rationing credit and making it exceedingly expensive, Canada’s banks siphon off an ungodly share of entrepreneurial profit to themselves while leaving the entrepreneur with all the risk. Their insistence on putting their own profits above service to the Canadian economy is one of the main reasons Canada has such a slow-growing, unproductive economy and a stagnant standard of living.
There is much else in this slim volume to make your blood boil: exorbitant fees on chequing and savings accounts; mutual fund expenses that torpedo investments; ridiculous mortgage restrictions, infuriating customer service …
Fleeced: Canadians Versus Their Banks is a stunning exposé of the inner workings of our six major banks — something only a reformed banker and financial services veteran such as Andrew could write. He also explodes the myth that a bloated, uncompetitive banking sector is the price we have to pay for stability in times of financial crisis.
We are in desperate need of banking reform in Canada. Read this book and you’ll be shouting at your member of Parliament for prompt action.
QotD: From conspicuous consumption to junk science
I used to be amused that Whole Foods could gouge its customers and get them to pay a “designer label premium” for regular groceries. Like patrons of Saks or Nieman Marcus, Whole Foods’ affluent customers could feel a sense of affluent superiority to those who shop at mass market grocery stores. But it’s now clear that Whole Foods isn’t just putting a fancy hood ornament on its groceries — its business model also promotes fear — a fear that if you don’t stretch your wallet for “safe” organic groceries, then you are imperiling the health and safety of yourself and your loved ones. That is wicked. And very effective. The organic food obsessives I know include cash strapped individuals who do not have the means to afford the Whole Foods lifestyle. But they shop there anyhow. They have to. Out of fear.
Buck Throckmorton, “Organic Food & Anti-Vaxxers – Does The Fear of Safe Food Lead to Fear of Safe Vaccines”, Ace of Spades H.Q., 2019-12-08.
September 29, 2024
Fleeced: Canadians Versus Their Banks by Andrew Spence
In the latest SHuSH newsletter, Ken Whyte talks about one of Sutherland House’s most recent publications:
I could write about eight versions of this post based on the many revelations in Andrew Spence’s Fleeced: Canadians Versus Their Banks, the latest edition of Sutherland Quarterly, released this week. I’m going to run with the version most relevant to my fellow publishers and small business people in Canada.
Andrew lays out in aggravating detail how Canadian banks, although chartered by the federal government to facilitate economic activity in the broader economy, do all they can to avoid lending to small and medium businesses, never mind that small and medium businesses employ two-thirds of our private-sector labour force and account for half of Canada’s gross domestic product.
By OECD standards, small businesses in Canada are starved of bank credit, and when they are able to secure a loan, they pay through the nose. The spread between interest rates on loans to small businesses and large businesses in Canada is a whopping 2.48 percent, compared to .42 percent in the US—more than five times higher.
Why? Because Canada’s banks are a tight little oligopoly, impervious to meaningful competition. Their cozy situation allows them to be exceedingly greedy. Their profits and returns to shareholders are wildly beyond those of banks in the US and UK (and, as Andrew demonstrates, their returns from their Canadian operations are far in excess of those from the US market, meaning they screw the home market hardest.)
Our banks never miss an opportunity to impose a new fee, or off-load risk. From their perspective, small business involves too much risk — some of them will inevitably fail. The banks prefer that publishers and dry-cleaners and restaurateurs either finance themselves by pledging their homes, or use their credit cards to cover fluctuations in cash flow or make investments that will help them hire, expand, and grow. And that’s what entrepreneurs do. According to a survey by the Canadian Federation of Independent Business, only one in five respondents accessed a bank loan or line of credit. Half of respondents financed themselves, tapped existing equity and personal lines of credit, and about 30 percent used their high-interest credit cards.
(The banks, incidentally, claim they need to keep credit card rates around 20 percent because their clients are high credit risks when their own data shows the risk is minimal. They simply prefer to gouge customers. To a banker, forcing hundreds of thousands of small businesses to use their credit cards to finance their businesses rather than giving them proper small business loans at reasonable rates is great business.)
By severely rationing credit and making it exceedingly expensive, Canada’s banks siphon off an ungodly share of entrepreneurial profit to themselves while leaving the entrepreneur with all the risk. Their insistence on putting their own profits above service to the Canadian economy is one of the main reasons Canada has such a slow-growing, unproductive economy and a stagnant standard of living.
There is much else in this slim volume to make your blood boil: exorbitant fees on chequing and savings accounts; mutual fund expenses that torpedo investments; ridiculous mortgage restrictions, infuriating customer service …
September 26, 2024
Glimmers of hope for lower taxes on US taxpayers
J.D. Tuccille welcomes the discussion among the Presidential candidates about lowering the taxes Americans have to pay, and points out that the economic distortions of the current tax code (including “temporary” measures introduced during WW2) make everyone less well-off:
Three months after proposing to end federal taxing of tips — an idea promptly confiscated without compensation by Kamala Harris’s campaign — Donald Trump doubled down by saying “we will end all taxes on overtime” if he’s elected president. Without a doubt, millions of Americans who resent government’s ravenous bite out of their paychecks immediately began contemplating just how much of their income they could shield from the tax man that way.
Tips and Overtime for Everybody!
“Can someone get paid in primarily tips and overtime?” quipped the Cato Institute’s Scott Lincicome. “Asking for a few million friends.”
On a more serious note, the Competitive Enterprise Institute’s Sean Higgins thought exempting overtime pay “wouldn’t necessarily be a bad idea … but, overall, it is not likely to make that much of a difference to most workers because overtime isn’t that common”. He’d been more strongly supportive of exempting tips because that “would put more money directly in the pockets of working Americans without either costing employers more or raising prices for customers”. He also liked that freeing tips from taxation would “keep tipping out of the reach of the regulatory state”.
But what if overtime pay becomes more common precisely because it’s not taxed?
The people at the Tax Foundation expect that’s exactly what will happen, just as Lincicome joked. Thinking through the implications of exempting overtime pay from taxation, Garrett Watson and Erica York warned that “exempting overtime pay from income tax would significantly distort labor market decisions. Employees would be encouraged to take more overtime work, and hourly or salaried non-exempt jobs may become more attractive if the benefit is not extended to salaried employees who are exempt from Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) overtime rules.”
The Tax Foundation’s Alex Muresianu had a similar reaction to the proposals to exempt tips from taxes from both Trump and Harris. He thinks “the proposal would make more employees and businesses interested in moving from full wages to a tip-based payment approach”. He foresaw “substantial behavioral responses, such as previously untipped occupations introducing tipping”.
Of course, a world in which more Americans receive their pay beyond the reach of the tax man is a welcome prospect to many of us. If politicians want to phase out income taxes, even unintentionally, who are we to complain? Hang on a minute while I set up my virtual tip jar. In fact, there’s precedent for government policy around wages to cause major unintended consequences. Take, for example, employer-provided healthcare coverage.
Government Policy Has Distorted Compensation Before
“One of the most important spurs to growth of employment-based health benefits was — like many other innovations — an unintended outgrowth of actions taken for other reasons during World War II,” according to the 1993 book, Employment and Health Benefits: A Connection at Risk. “In 1943 the War Labor Board, which had one year earlier introduced wage and price controls, ruled that contributions to insurance and pension funds did not count as wages. In a war economy with labor shortages, employer contributions for employee health benefits became a means of maneuvering around wage controls. By the end of the war, health coverage had tripled.”
Given that health benefits became a substitute form of compensation to escape a wage freeze, it’s not difficult to imagine the United States moving toward a situation in which a lot more people receive the bulk of their pay from untaxed tips and overtime pay.
September 18, 2024
September 17, 2024
Noormohamed: “Nice newspaper, National Post. It’d be a shame if …”
One of the more blatant examples of Liberals saying the quiet part out loud:
We need to talk about Liberal MP Taleeb Noormohamed and his not so subtle reminder to the National Post that it wouldn’t exist without the benefaction of Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s government.
Noormohamed, Parliamentary Secretary for Heritage – the ministry responsible for media welfare – did so via a post on X in which he told NP Comment senior editor Terry Newman: “Your paper wouldn’t be in business were it not for the subsidies that the government that you hate put in place — the same subsidies your Trump-adjacent foreign hedge fund owners gladly take to pay your salary.”
I wrote at length about this for The Line and, being aware that there is some crossover among subscribers, I won’t repeat that, but here’s a summary, followed by an update and then we’ll dig a little deeper into government funding for media, trans activist extremism in the Senate and other juicy stuff.
As I wrote in The Line concerning the government’s willingness to put the squeeze on media, “Nothing Noormohamed said was untrue. He and I are in perfect alignment in the view that were it not for the patronage of the Justin Trudeau government, Postmedia (and likely the Toronto Star) would by now have ceased to exist. Some of its titles may have sold for parts, but most of its zombie products would have been dispatched long ago with a bankruptcy bullet to the brain, allowing new media to spring forth from decay.”
You can read it all here.
But the most alarming part of this story isn’t that Noormohamed said what he said. That was appalling but predictable. What’s truly chilling is that he could flex his muscles, whip out his influence and intimidate what was once a free and independent press in this country and get away with it.
There were just a handful of media responses to his highly inappropriate but not unexpected behaviour. A week later, I could find no fiery or even gentle editorials condemning his statements. My Google search revealed just three news stories (Western Standard, True North & Rebel News) while none of the nation’s leading commentators cleared their throats to object.
Perhaps this is because media decided it was no big deal that an influential government MP was reminding them to keep in mind just who is paying their bills when they sit down to write. It could also be that they are bothered by it but don’t wish to draw the public’s attention to their new role as government dependents because they know it undermines public trust in them. Or, they have just given up on the idea of freedom of the press but want to keep it as their dirty little secret. Maybe all three. All I could hear was the silence of the lambs being led to the slaughter.
September 16, 2024
QotD: The origins of Marmite
The story of Marmite begins in the late 19th century when a German scientist, Justus Freiherr von Liebig, discovered that the waste product from yeast used in brewing beer could be made into a meaty-flavoured paste which was completely vegetarian. He also produced bouillon, a meat extract which kept well in jars without needing refrigeration. This eventually became the product known as Oxo.
In 1902 the Marmite Food Extract Company was formed in Burton upon Trent, two miles from the Bass brewery which had been there since 1777. Yeast is a single-cell fungus originally isolated from the skin of grapes, used in brewing, winemaking and baking since ancient times. I have read somewhere that the yeast Bass used was descended from the original batch employed since its inception, endlessly reproducing itself right up to the present time.
The waste product from brewing was transported to the Marmite factory, where salt, enzymes and water were added to the slurry before it was simmered for several hours then poured into vats ready for bottling.
The product was an instant hit and within five years a second factory had to be built in Camberwell Green, south London. Marmite was given a huge boost with the discovery of vitamins. It was found to be a rich source of vitamin B, deficiency of which was responsible for the condition beriberi which afflicted British troops during the Great War. They were subsequently issued with Marmite as part of their rations. In the 1930s the folic-acid-rich product was used to treat anaemia in Bombay mill workers, and malnutrition during a malaria epidemic in Ceylon, now Sri Lanka.
Alan Ashworth, “That Reminds Me: My mate Marmite”, The Conservative Woman, 2024-06-05.
September 8, 2024
The last dispatch from Toronto before the catastrophe began
Toronto, in fact all of Ontario, may no longer be there when you get up tomorrow morning. As Chris Selley explained in his brave, final communiqué from the doomed province:
Dear non-Toronto friends,
This city is in crisis. This may be my last communiqué before the telex goes down for good, and I feel honour-bound to tell the world of my city’s plight. If the worst should occur, which it almost certainly will, please tell our story.
The unthinkable has occurred: Doug Ford’s madmen and women at Queen’s Park have licensed hundreds upon hundreds of new locations — called “convenience stores”, in local parlance — to sell beer, wine, cider and pre-mixed cocktails.
They did this instead of fixing health care, if you can believe that. And, outrage upon outrage, the government even made a map of such locations — as if delivering fallen Ontarians one by one to Mr. Booze himself.
Why, within just a few hundred metres of where I write, through my tears, I can discern on the map more than five such new locations. There’s Mei Convenience, Mimi Variety, Lucy Grocery and Meat, Queen & Jarvis Convenience … the list goes on, and on, my God. Church attendance is reportedly soaring as Torontonians steel themselves for the forthcoming.
Ford’s government did this entirely to solicit corporate donations to his party (some say that’s actually illegal, but whatever) from his buddies at convenience-store empires 7-Eleven and Couche-Tard … and presumably from Mimi and Lucy, whoever they are. Very rich women, clearly.
Instead of fixing health care!
Until recently, some semblance of sanity prevailed: The nearest government-run liquor store to where I sit now is a 15-minute walk away; the nearest Beer Store, the privately owned former quasi-monopoly where you’re still supposed to return your bottles and cans, is nearer to 20 minutes.
And now, suddenly, a bottle or can is shockingly near to hand. And this will lead to more alcohol-related harms. Of this there is no doubt, as one expert recently told the Toronto Methodist Star: “Harm will increase in Ontario. That is straightforward.”
It is true that many jurisdictions around the world report similar or lower levels of alcohol consumption and related harms than Ontario despite having much greater access to retail alcohol — Italy, Greece, the United States — but that is not germane to this discussion. Ontarians are not like other people. Ontario is not like other places. We are worse. Or maybe better. Or some combination of the two.
It’s true! Even saintly Bowmanville has been sullied with the demon liquor thanks to Premier Ford’s diabolical plan:
September 6, 2024
QotD: “Discount” airlines
Some thoughts on discount airlines. The ticket price sounds good, yes, but the discount is eaten away by overweight baggage charges and the price of rail/coach tickets each way to and from your destination city and hinterland airport. Big savings for the inconvenience and expense are retained by the airline are while each souvenir of your visit jacks up your fare to exactly where it would be had you flown with a proper carrier. At least, such is the guesstimate of the travelling book collector. If stamps and other light-weight antiquities are your game you may not face the same problem.
Ghost of a Flea, “Sic transit gloria mundi“, Ghost of a Flea, 2005-05-23.