World War Two
Published 24 Apr 2024It’s time for another thrilling installment of Out of the Foxholes, but what sort of questions does Indy answer today? Well, it’s good stuff — about Allied security and logistics at the major conferences, about what the British navy was doing once the Atlantic and Mediterranean were secure, and about the skills (or lack thereof) of the soldiers of the Waffen SS. How can you live without knowing about such things? I suppose it’s possible, but it would be a sad life indeed, so check it out!
(more…)
April 25, 2024
Were the Waffen-SS Really Germany’s Elite Fighters? – WW2 – OOTF 35
March 31, 2024
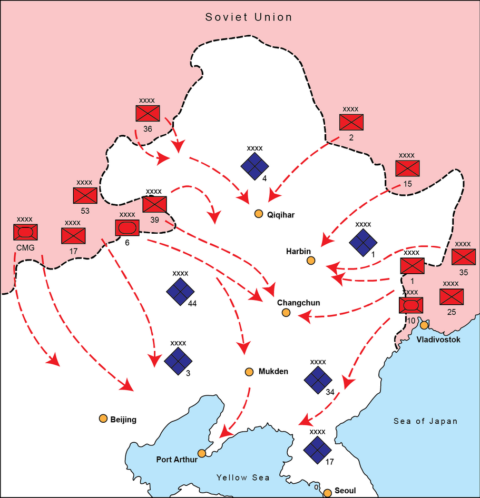
August, 1945 – The Soviets enter the war in China
Big Serge outlines the Soviet invasion of Manchuria in August 1945 and its devastating impact on the Japanese Kwantung Army, finally shattering any remaining illusions that the Soviets would broker a peace between Japan and the western allies:
The Second World War had a strange sort of symmetry to it, in that it ended much the way it began: namely, with a well-drilled, technically advanced and operationally ambitious army slicing apart an overmatched foe. The beginning of the war, of course, was Germany’s rapid annihilation of Poland, which rewrote the book on mechanized operations. The end of the war — or at least, the last major land campaign of the war — was the Soviet Union’s equally totalizing and rapid conquest of Manchuria in August 1945.
Manchuria was one of the many forgotten fronts of the war, despite being among the oldest. The Japanese had been kicking around in Manchuria since 1931, consolidating a pseudo-colony and puppet state ostensibly called Manchukuo, which served as a launching pad for more than a decade of Japanese incursions and operations in China. For a brief period, the Asian land front had been a major pivot of world affairs, with the Japanese and the Red Army fighting a series of skirmishes along the Siberian-Manchurian border, and Japan’s enormously violent 1937 invasion of China serving as the harbinger of global war. But events had pulled attention and resources in other directions, and in particular the events of 1941, with the outbreak of the cataclysmic Nazi-Soviet War and the Great Pacific War. After a few years as a major geopolitical pivot, Manchuria was relegated to the background and became a lonely, forgotten front of the Japanese Empire.
Until 1945, that is. Among the many topics discussed at the Yalta Conference in the February of that year was the Soviet Union’s long-delayed entry into the war against Japan, opening an overland front against Japan’s mainland colonies. Although it seems relatively obvious that Japanese defeat was inevitable, given the relentless American advance through the Pacific and the onset of regular strategic bombing of the Japanese home islands, there were concrete reasons why Soviet entry into the war was necessary to hasten Japanese surrender.
More specifically, the Japanese continued to harbor hopes late into the war that the Soviet Union would choose to act as a mediator between Japan and the United States, negotiating a conditional end to war that fell short of total Japanese surrender. Soviet entry into the war against Japan would dash these hopes, and overrunning Japanese colonies in Asia would emphasize to Tokyo that they had nothing left to fight for. Against this backdrop, the Soviet Union spent the summer of 1945 preparing for one final operation, to smash the Japanese in Manchuria.
The Soviet maneuver scheme was tightly choreographed and well conceived — representing in many ways a sort of encore, perfected demonstration of the operational art that had been developed and practiced at such a high cost in Europe. Taking advantage of the fact that Manchuria already represented a sort of salient — bulging as it did into the Soviet Union’s borders — the plan of attack called for a series of rapid, motorized thrusts towards a series of rail and transportation hubs in the Japanese rear (from north to south, these were Qiqihar, Harbin, Changchun, and Mukden).
By rapidly bypassing the main Japanese field armies and converging on transit hubs in the rear, the Red Army would effectively isolate all the Japanese armies both from each other and from their lines of communication to the rear, effectively slicing Manchuria into a host of separated pockets.
There were, of course, a host of reasons why the Japanese had no hope of resisting this onslaught. In material terms, the overmatch was laughable. The Soviet force was lavishly equipped and bursting with manpower and equipment — three fronts totaling more than 1.5 million men, 5,000 armored vehicles, and tens of thousands of artillery pieces and rocket launchers.
The Japanese (including Manchurian proxy forces) had a paper strength of perhaps 900,000 men, but the vast majority of this force was unfit for combat. Virtually all of the Japanese army’s veteran units and equipment had been steadily transferred to the Pacific in a cannibalizing trickle — a vain attempt to slow the American onslaught. Accordingly, by 1945 the Japanese Kwantung Army had been reduced to a lightly armed and poorly trained conscript force that was suitable only for police actions and counterinsurgency against Chinese partisans.
Really, there was nothing for the Japanese to do. The Kwantung Army had far less of a fighting chance in 1945 than the Wehrmacht had in the spring of that year, and everyone knows how that turned out. Unsurprisingly, then, the Soviets broke through everywhere at will when they began the assault on August 9. Soviet armored forces found it trivially easy to overrun Japanese positions (armed primarily with archaic, low caliber antitank weaponry that could not penetrate Soviet armor even at point blank range), and by the end of the first day the Soviet pincers were driving far into the rear.
It is easy, in hindsight, to write off the Manchuria campaign as something of a farce: a highly experienced, richly equipped Red Army overrunning and abusing an overmatched and threadbare Japanese force. In many ways, this is an accurate assessment. However, what the offensive demonstrated was the Red Army’s extreme proficiency at organizing enormous operations and moving at high speeds. By August 20 (after only 11 days), the Red Army had reached the Korean border and captured all their objectives in the Japanese rear, in effect completely overrunning a theater that was even larger than France. Many of the Soviet spearheads had driven more than three hundred miles in a little over a week.
To be sure, the combat aspects of the operation were farcical, given the totalizing level of Soviet overmatch. Red Army losses were something like 10,000 men — a trivial number for an operation of this scale. What was genuinely impressive — and terrifying to alert observers — was the Red Army’s clear demonstration of its capacity to organize operations that were colossal in scale, both in the size of the forces and the distances covered.
More to the point, the Japanese had no prospect of stopping this colossal steel tidal wave, but who did? All the great armies of the world had been bankrupted and shattered by the great filter of the World Wars — the French, the Germans, the British, the Japanese, all gone, all dying. Only the US Army had any prospect of resisting this great red tidal wave, and that force was on the verge of a rapid demobilization following the surrender of Japan. The enormous scale and operational proclivities of the Red Army thus presented the world with an entirely new sort of geostrategic threat.
HMS Unicorn (I72) – Guide 367
Drachinifel
Published Dec 23, 2023The Unicorn, a fleet maintenance carrier of the British Royal Navy, is today’s subject.
(more…)
March 27, 2024
The Volkssturm – a Million men to save the Reich?
World War Two
Published 26 Mar 2024The Volkssturm is the last-ditch people’s army of the Third Reich. Sure, on paper, there are millions of old men and boys ready to defend Germany. But how will they be armed? Are they truly willing to die for Hitler? Will they make any difference at all?
(more…)
March 26, 2024
QotD: Cavalry logistics for Steppe raiders
War parties, as noted, often moved without bringing the entire camp, the non-combatants or the sheep with them. This was actually a crucial operational concern on the steppe, since the absence of a war party might render an encampment – stocked full of the most valuable resources (livestock, to be clear) – effectively unguarded and ripe for raiding, but at the same time, attempting to chase down a moving encampment with an equally slow moving encampment was obviously a non-starter. Better to race over the steppe, concealed (as we’ll see) and quick moving to spring a trap on another group of nomads. But how did a war party make those high speed long-distance movements over the steppe? Horse-string logistics (a term, I should note, that I did not coin, but which is too apt not to use).
Each steppe warrior rode to battle with not one horse, but several: typically five to eight. For reasons that will rapidly become obvious, they preferred mares for this purpose. The Steppe warrior could ride the lead horse and keep the rest of them following along by connecting them via a string (thus “horse-string logistics”), such that each steppe warrior was his own little equine procession. These horses are, you will recall, fairly small and while they are hardy, they are not necessarily prodigiously strong, so the warrior is going to shift between them as he rides, sparing his best mount for the actual fight. Of course we are not looking at just one warrior on the move – that would be very dangerous – but a group on the move, so we have to imagine a large group (perhaps dozens or hundreds or even thousands) of warriors moving, with something like 5-8 times that many horses.
[Edit: It is worth noting that a horse-string war party might well also bring some number of sheep with them as an additional food supply, herding them along as the army rode. So even here, sheep maintain their importance as a core part of the subsistence system.]
Now of course the warriors are going to bring rations with them from the camp, including milk (both liquid in leather containers and dried to qurut-paste) as well as dried meat. But the great advantage of moving on mares is that they when they are lactating, mares are already a system for turning the grass of the steppe into emergency rations. As Timothy May (op. cit.) notes, a mare produces around 2.25-2.5 quarts of milk in excess of the needs of her foal per day during her normal five-month lactation period, equal to about 1,500kcal/day, half of the daily requirement for a human. So long as at least two of the horses in the horse-string were lactating, a steppe warrior need not fear shortfall. This was more difficult in the winter when less grass was available and thus mare’s milk became scarce, which could impose some seasonality on a campaign, but a disciplined band of steppe warriors could move massive distances (the Mongols could make 60 miles a day on the move unencumbered, which is a lot) like this in just a few months.
In adverse conditions (or where time permitted because meat is tasty), steppe warriors on the move could also supplement their diet by hunting, preserving the meat as saddle-jerky. In regions where water became scarce, we are frequently told that the Mongols could keep going by opening a vein on their horse and drinking the blood for both nourishment and hydration; May (op. cit.) notes that a horse can donate around 14 pints of blood without serious health risk, which is both hydrating, but also around 2,184kcal, about two-thirds of the daily requirement. This will have negative impacts on the horses long term if one keeps doing it, so it was an emergency measure.
The major advantage of this kind of horse-string logistics was that a steppe warrior party could move long distances unencumbered by being essentially self-sufficient. It has a second major advantage that I want to note because we’ll come back to it, they light no fires. For most armies, camp fires are essential because food preparation – particularly grains – essentially requires it. But a steppe warrior can move vast distances – hundreds of miles – without lighting a fire. That’s crucial for raiding (and becomes a key advantage even when steppe warriors transition to taking and holding territory in moments of strength, e.g. the Mongols) because sight-lines on the steppe are long and campfires are visible a long way off. Fireless logistics allow steppe warriors to seemingly appear from the steppe with no warning and then vanish just as quickly.
That said, these racing columns of steppe warriors, while they could move very fast and be effectively independent in the short term, don’t seem generally to have been logistically independent of the camp and its herds of sheep in the long term. Not only, of course, would there be need for things like hides and textiles produced in the camp, but also the winter snows would drastically reduce the mares milk the horses produced, making it more difficult to survive purely on horse-string logistics. Instead, the camp formed the logistical base (and store of resources, since a lot of this military activity is about raiding to get captives, sheep and horses which would be kept in the camp) for the long range cavalry raids to strike out from. To the settled peoples on the receiving end of a Mongol raid, it might seem like the Mongols subsisted solely on their horses, but the Mongols themselves knew better (as would anyone who stayed with them for any real length of time).
Bret Devereaux, “That Dothraki Horde, Part II: Subsistence on the Hoof”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-12-11.
March 13, 2024
“They won’t be in Gaza, but they’ll be just offshore — a few hundred yards from Gaza”
Apparently a bunch of former military types are getting their collective panties in a bunch just because Biden is sending part of a highly specialized US Army support brigade to install a temporary offshore unloading facility to get “humanitarian aid” in to Hamas fighters the civilian population of Gaza. All the political advisors to the President want to assure everyone that there will be no “boots on the ground”, so there’s no real risk …
The Pentagon has said something that should make us all sit up and pay attention.
Quick background first:
Elements of the US Army’s 7th Transportation Brigade are on the way to Gaza. […] They won’t be in Gaza, but they’ll be just offshore — a few hundred yards from Gaza. Now read this, and take the time to read it closely. I’ll split it into two screencaps to get it all in, which will be awkward to look at, but you can just click on the link to see it all whole (and subscribe to keep up with “Cynical Publius” as all of this develops):
The extremely important part of all of that is that transportation troops aren’t combat arms troops; they’re armed for some degree of self-protection, but “they lack the organic ability to defend themselves against high-intensity attacks by enemies.” In a hostile environment, they need to be screened: they need to be protected by combat-focused forces, both on-shore and off. They need infantry in front of them, warships behind them, and aircraft overhead.
Now, via this account, look at this transcript of an … interesting Pentagon press briefing on March 8, in which a major general talks at length about the security plan for the 7th Transportation Brigade when it gets to Gaza. Sample exchange:
Q: (Inaudible) partner nations on the ground, but you’re talking about operational security, you can’t discuss what will be (inaudible).
GEN. RYDER: Right. I mean, we will — these forces will have the capability to provide some organic security. I’m just not going to get into the specifics of that.
But they don’t — or they do, but the capability of transportation troops, from a combat service support branch, is extremely limited. Again, these are not combat arms troops, and aren’t armed or trained as combat arms troops. Talking about their organic security capability is an interesting choice.
March 12, 2024
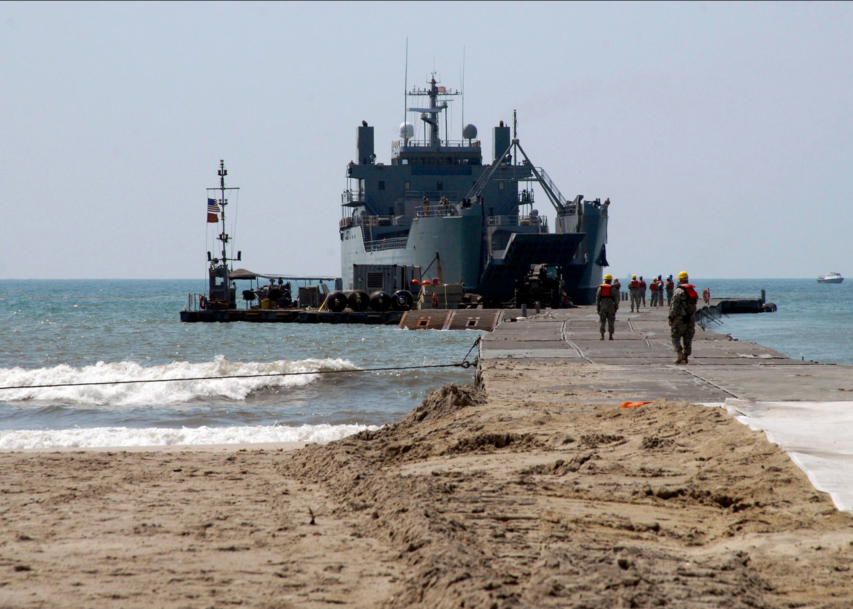
A JLOTS for Gaza?
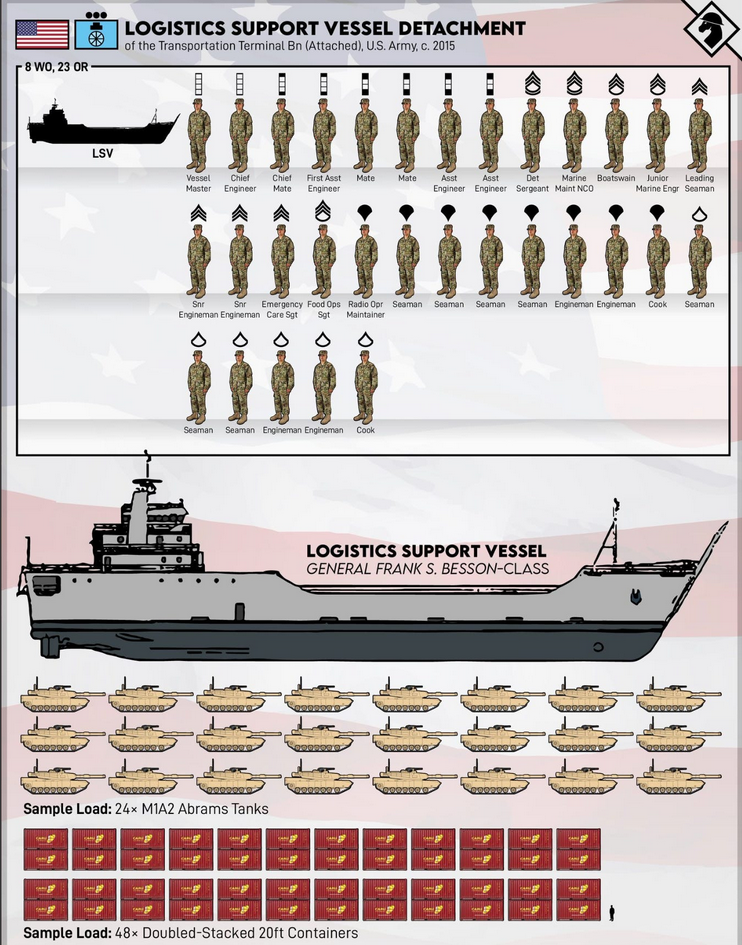
The Biden administration has made a decision to create a temporary shore unloading facility to provide Gaza with “humanitarian aid”. The particular installation is called an Army Joint Logistics Over-the-Shore (JLOTS) and will be delivered by a US Army logistics ship, USAV General Frank S. Besson (LSV-1) which was reported as departing a base in Virginia and will arrive as soon as its 12-knot top speed will allow. CDR Salamander has the details:
… and yes my friends — the Army has its own navy. Let’s take a quick look at the Besson.
Yep’r, that 243 foot, 4,200 ton ship is commanded by … a Warrant Officer. Discuss amongst yourselves.
If you’re wondering what she looks like putting a JLOTS in place;
This will take about 1,000 personnel to accomplish. I don’t know a single maritime professional who thinks this is a good idea given the location and conditions ashore, but orders are orders. Make the best attempt you can.
An interesting note; this is not a Navy operation, but an Army operation. Remember what I told you about the fate of the East Coast Amphibious Construction Battalion TWO (ACB2) last summer? This story aligns well with the Anglosphere’s problem with seablindness we discussed on yesterday’s Midrats with James Smith.
As for my general thought on doing this? I’ll avoid the politics as much as I can, but I have concerns.
Generally speaking, no operation starts out on the right foot with a lie.
“We’re not planning for this to be an operation that would require U.S. boots on the ground,” said a senior administration official.
I’m not mad at the official. They are just making sure their statement is in line with higher direction and guidance. President Biden was clear in his SOTU speech;
The United States has been leading international efforts to get more humanitarian assistance into Gaza. Tonight, I’m directing the U.S. military to lead an emergency mission to establish a temporary pier in the Mediterranean on the coast of Gaza that can receive large shipments carrying food, water, medicine, and temporary shelters.
No U.S. boots will be on the ground.
You cannot build a pier, even JLOTS, without putting boots on the ground. Just look at the above picture again.
February 28, 2024
Why Germany Lost the First World War
The Great War
Published Nov 10, 2023Germany’s defeat in the First World War has been blamed on all kinds of factors or has even been denied outright as part of the “stab in the back” myth. But why did Germany actually lose?
(more…)
February 13, 2024
QotD: War elephant logistics
From trunk to tail, elephants are a logistics nightmare.
And that begins almost literally at birth. For areas where elephants are native, nature (combined, typically, with the local human terrain) create a local “supply”. In India this meant the elephant forests of North/North-Eastern India; the range of the North African elephant (Loxodonta africana pharaohensis, the most likely source of Ptolemaic and Carthaginian war elephants) is not known. Thus for many elephant-wielding powers, trade was going to always be a key source for the animals – either trade with far away kingdoms (the Seleucids traded with the Mauyran Indian kingdom for their superior Asian elephants) or with thinly ruled peripheral peoples who lived in the forests the elephants were native to.
(We’re about to get into some of the specifics of elephant biology. If you are curious on this topic, I am relying heavily on R. Sukumar, The Asian Elephant: Ecology and Management (1989). I’ve found that information on Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) much easier to come by than information on African elephants (Loxodonta africana and Loxodonta cyclotis).)
In that light, creating a breeding program – as was done with horses – seems like a great idea. Except there is one major problem: a horse requires about four years to reach maturity, a mare gestates a foal in eleven months and can go into heat almost immediately thereafter. By contrast, elephants reach adulthood after seventeen years, take 18-22 months to gestate and female elephants do not typically mate until their calf is weaned, four to five years after its birth. A ruler looking to build a stable of cavalry horses thus may start small and grow rapidly; a ruler looking to build a corps of war elephants is looking at a very slow process. This is compounded by the fact that elephants are notoriously difficult to breed in captivity. There is some speculation that the Seleucids nonetheless attempted this at Apamea, where they based their elephants – in any event, they seem to have remained dependent on imported Indian elephants to maintain the elephant corps. If a self-sustaining elephant breeding program for war elephants was ever created, we do not know about it.
To make matters worse, elephants require massive amounts of food and water. In video-games, this is often represented through a high elephant “upkeep” cost – but this often falls well short of the reality of keeping these animals for war. Let’s take Total War: Rome II as an example: a unit of Roman (auxiliary) African elephants (12 animals), costs 180 upkeep, compared to 90 to 110 upkeep for 80 horses of auxiliary cavalry (there are quite a few types) – so one elephant (with a mahout) costs 15 upkeep against around 1.25 for a horse and rider (a 12:1 ratio). Paradox’s Imperator does something similar, with a single unit of war elephants requiring 1.08 upkeep, compared to just 0.32 for light cavalry; along with this, elephants have a heavy “supply weight” – twice that of an equivalent number of cavalry (so something like a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio of cost).
Believe it or not, this understates just how hungry – and expensive – elephants are. The standard barley ration for a Roman horse was 7kg of barley per day (7 Attic medimnoi per month; Plb. 6.39.12); this would be supplemented by grazing. Estimates for the food requirements of elephants vary widely (in part, it is hard to measure the dietary needs of grazing animals), but elephants require in excess of 1.5% of their body-weight in food per day. Estimates for the dietary requirements of the Asian elephant can range from 135 to 300kg per day in a mix of grazing and fodder – and remember, the preference in war elephants is for large, mature adult males, meaning that most war elephants will be towards the top of this range. Accounting for some grazing (probably significantly less than half of dietary needs) a large adult male elephant is thus likely to need something like 15 to 30 times the food to sustain itself as a stable-fed horse.
In peacetime, these elephants have to be fed and maintained, but on campaign the difficulty of supplying these elephants on the march is layered on top of that. We’ve discussed elsewhere the difficulty in supplying an army with food, but large groups of elephants magnify this problem immensely. The 54 elephants the Seleucids brought to Magnesia might have consumed as much food as 1,000 cavalrymen (that’s a rider, a horse and a servant to tend that horse and its rider).
But that still understates the cost intensity of elephants. Bringing a horse to battle in the ancient world required the horse, a rider and typically a servant (this is neatly implied by the more generous rations to cavalrymen, who would be expected to have a servant to be the horse’s groom, unlike the poorer infantry, see Plb. above). But getting a war elephant to battle was a team effort. Trautmann (2015) notes that elephant stables required riders, drivers, guards, trainers, cooks, feeders, guards, attendants, doctors and specialist foot-chainers (along with specialist hunters to capture the elephants in the first place!). Many of these men were highly trained specialists and thus had to be quite well paid.
Now – and this is important – pre-modern states are not building their militaries from the ground up. What they have is a package of legacy systems. In Rome’s case, the defeat of Carthage in the Second Punic War resulted in Rome having North African allies who already had elephants. Rome could accept those elephant allied troops, or say “no” and probably get nothing to replace them. In that case – if the choice is between “elephants or nothing” – then you take the elephants. What is telling is that – as Rome was able to exert more control over how these regions were exploited – the elephants vanished, presumably as the Romans dismantled or neglected the systems for capturing and training them (which they now controlled directly).
That resolves part of our puzzle: why did the Romans use elephants in the second and early first centuries B.C.? Because they had allies whose own military systems involved elephants. But that leaves the second part of the puzzle – Rome doesn’t simply fail to build an elephant program. Rome absorbs an elephant program and then lets it die. Why?
For states with scarce resources – and all states have scarce resources – using elephants meant not directing those resources (food, money, personnel, time and administrative capacity) for something else. If the elephant had no other value (we’ll look at one other use next week), then developing elephants becomes a simple, if difficult, calculation: are the elephants more likely to win the battle for me than the equivalent resources spent on something else, like cavalry. As we’ve seen above, that boils down to comparisons between having just dozens of elephants or potentially hundreds or thousands of cavalry.
The Romans obviously made the bet that investing in cavalry or infantry was a better use of time, money and resources than investing in elephants, because they thought elephants were unlikely to win battles. Given Rome’s subsequent spectacular battlefield success, it is hard to avoid the conclusion they were right, at least in the Mediterranean context.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: War Elephants, Part II: Elephants against Wolves”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-08-02.
February 12, 2024
Look at Life – Amphibian DUKW (1962)
Classic Vehicle Channel
Published Apr 23, 2020The military have finished with their amphibious truck know as the DUKW. They’re sold off to the general public for use in civilian life, including divers and even a group of monks.
February 6, 2024
QotD: Sparta’s actually mediocre military performance
Sparta was one of the largest Greek city-states in the classical period, yet it struggled to achieve meaningful political objectives; the result of Spartan arms abroad was mostly failure. Sparta was particularly poor at logistics; while Athens could maintain armies across the Eastern Mediterranean, Sparta repeatedly struggled to keep an army in the field even within Greece. Indeed, Sparta spent the entirety of the initial phase of the Peloponnesian War, the Archidamian War (431-421 B.C.), failing to solve the basic logistical problem of operating long term in Attica, less than 150 miles overland from Sparta and just a few days on foot from the nearest friendly major port and market, Corinth.
The Spartans were at best tactically and strategically uncreative. Tactically, Sparta employed the phalanx, a close-order shield and spear formation. But while elements of the hoplite phalanx are often presented in popular culture as uniquely Spartan, the formation and its equipment were common among the Greeks from at least the early fifth century, if not earlier. And beyond the phalanx, the Spartans were not innovators, slow to experiment with new tactics, combined arms, and naval operations. Instead, Spartan leaders consistently tried to solve their military problems with pitched hoplite battles. Spartan efforts to compel friendship by hoplite battle were particularly unsuccessful, as with the failed Spartan efforts to compel Corinth to rejoin the Spartan-led Peloponnesian League by force during the Corinthian War.
Sparta’s military mediocrity seems inexplicable given the city-state’s popular reputation as a highly militarized society, but modern scholarship has shown that this, too, is mostly a mirage. The agoge, Sparta’s rearing system for citizen boys, frequently represented in popular culture as akin to an intense military bootcamp, in fact included no arms training or military drills and was primarily designed to instill obedience and conformity rather than skill at arms or tactics. In order to instill that obedience, the older boys were encouraged to police the younger boys with violence, with the result that even in adulthood Spartan citizens were liable to settle disputes with their fists, a tendency that predictably made them poor diplomats.
Bret Devereaux, “Spartans Were Losers”, Foreign Policy, 2023-07/22.
February 2, 2024
The Sad Story of Churchill’s Iceman, Geoffrey Pyke
World War Two
Published Jan 31, 2024Geoffrey Pyke is remembered as an eccentric scientist who spewed out ideas like giant aircraft carriers made of icy Pykerete. But there was much more to him than that. He was a spy, a special operations mastermind, and his novel ideas contributed to the success of D-Day.
(more…)
January 12, 2024
Eastern Front Deployments, January 11, 1945 – a WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 11 Jan 2024The Soviets are just about to kick off a series of enormous offensives all along the Eastern Front. Here’s a look at the forces who are to attack, and those who will be defending.
(more…)
January 7, 2024
Every Type of Railcar Explained in 15 Minutes
Practical Engineering
Published 19 Sept 2023How many of these cars have you spotted before?
Trains are one of the most fascinating engineered systems in the world, and they’re out there, right in the open for anyone to have a look! Once you start paying attention, it’s pretty satisfying to look for all the different types of railcars that show up on the tracks.
(more…)
December 10, 2023
Engines of War: How Wars Were Won and Lost on the Railways
WW2TV
Published 15 Jun 2023Engines of War: How Wars Were Won and Lost on the Railways With Christian Wolmar
Before the nineteenth century, armies had to rely on slow and unreliable methods of transportation to move soldiers and equipment during times of conflict. But with the birth of the railroad in the early 1830s, the way wars were fought would change forever. In this show renowned expert Christian Wolmar tells the story of that transformation with a focus on railways in WWII and especially the Normandy campaign.
Christian Wolmar is a British journalist, author, railway historian and Labour Party politician. He is known for his commentary on transport, especially as a pundit on Britain’s railway industry, and was named Transport Journalist of the Year in the National Transport Awards in 2007.
(more…)