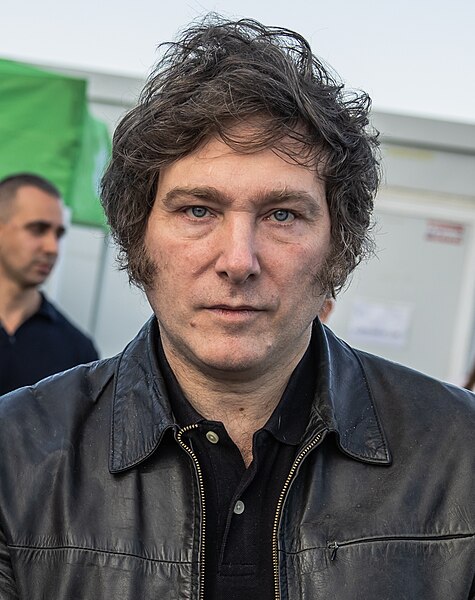
Jon Miltimore compares the Venezuelan experience after electing Hugo Chavez in 2007 to Argentina’s radically opposed choice to elect Javier Milei as President late in 2023:
In November, the country elected libertarian Javier Milei as its new president. And whereas Hugo Chavez said, “All that was privatized, let it be nationalized”, Milei is essentially saying the opposite: All that was nationalized, let it be privatized.
Milei started by cutting in half the number of federal ministries in Argentina, reducing them from 18 to nine. This was followed by a massive currency devaluation.
Milei did not stop there. In a recent televised announcement, he said he would “repeal rules that impede the privatization of state companies”.
Those words were backed up by a 300-measure order designed to deregulate internet services, eliminate various government price controls, repeal laws that discourage foreign capital investment, abolish the Economy Ministry’s price observatory, and “prepare all state-owned companies to be privatized”.
Milei capped it off on Wednesday with a 351-page omnibus bill that takes aim at Argentina’s regulatory state and would grant Milei emergency powers “until December 31, 2025”.
Giving any president emergency powers is no small thing, even during a genuine crisis. Though Milei’s bill is designed to curb state power, not to expand it — a notable contrast to the typical crisis response paradigm — history and recent events in El Salvador show how emergency powers can be abused and used to violate human rights and liberty.
Whether Milei can get his full agenda through is unclear, but there’s reason for optimism.
His stunning election is itself evidence that Argentines are hungry for change. He’s already shown an impressive pragmatism to wed to his undeniable political flair, surrounding himself with a slew of talented policy experts. This includes Federico Sturzenegger, a former chief economist of Argentina’s central bank who two decades ago managed to turn around the failing Bank of the City of Buenos Aires. Sturzenegger’s reforms were so effective they became a Harvard case study.
Success is by no means certain, of course.
Recovering from decades of Peronism — a blend of socialism, nationalism, and fascism, which dominated Argentina’s political system for years — will not happen overnight. And Argentina’s political class has spent the last few years making a bad situation worse.
Still, the great economist Adam Smith once observed that the key to economic prosperity is surprisingly simple.
“Little else is requisite to carry a state to the highest degree of opulence from the lowest barbarism, but peace, easy taxes, and a tolerable administration of justice,” the Wealth of Nations author said.
Milei knows this. He has not just read Smith (in addition to Austrian school economists such as Friedrich Hayek and Ludwig von Mises). In a 2017 profile, he dubbed himself “Adam Smith’s heir.”
A heavy dose of Adam Smith is precisely what Argentina needs, and Milei has correctly diagnosed the affliction of Argentina’s once-prosperous economy.
“The state doesn’t create wealth; it only destroys it,” Milei said in a widely viewed 2023 interview.