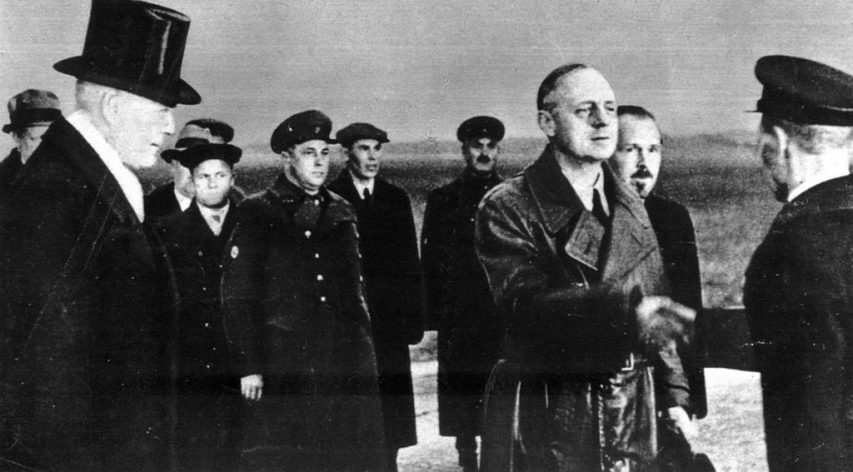
The Tank Museum
Published 28 Jul 2018The JS III or IS III was debuted by the Soviet Union at the Second World War Victory Parade, in September 1945.
This particular JS III was at The Tank Museum temporarily, for its appearance at TANKFEST 2018, and has now returned home to The Belgian Royal Military Museum.
Support the work of The Tank Museum on Patreon: ► https://www.patreon.com/tankmuseum
Or donate http://tankmuseum.org/support-us/donateVisit The Tank Museum SHOP: ► https://tankmuseumshop.org/
Twitter: ► https://twitter.com/TankMuseum
Tiger Tank Blog: ► http://blog.tiger-tank.com/
Tank 100 First World War Centenary Blog: ► http://tank100.com/ #tankmuseum #tanks #tankchats
November 19, 2019
Tank Chats #54 JS III | The Tank Museum
November 17, 2019
Britain shows Japan how to Attack Pearl Harbor – WW2 – 064 – November 16, 1940
World War Two
Published 16 Nov 2019Japan has two wins this week, and one might turn out to be very consequential for the rest of the war. In the meantime, the British RAF fights the Luftwaffe and Italy struggles in their offensive against Greece.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: EastoryColorisations by: Julius Jääskeläinen, https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Eastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.Sources:
– Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
– IWM: CM 164, C 1244
– Destroyed house icon by Gan Khoon Lay, people icon by Gregor Cresnar from the Noun ProjectA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
2 days ago
Do you want more World War Two in realtime? We have a great Instagram page, where we make a daily post about what happened in the war on that day. This might be something completely different from what’s covered in these videos, or might add some more details. You can follow it by searching @world_war_two_realtime or by clicking here: https://www.instagram.com/world_war_two_realtime/. See you there!
Cheers, Joram
November 12, 2019
The Brief Independence of Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan I THE GREAT WAR 1919
The Great War
Published 11 Nov 2019Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan used the power vacuum after the 1917 revolution in Russia and after the collapse of the Central Powers in 1918 to gain their independence. But the Caucasus region was of vital strategic importance to the new Russian regime, to the British and to the Turks.
» SUPPORT THE CHANNEL
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thegreatwar
Merchandise: https://shop.spreadshirt.de/thegreatwar/» SOCIAL MEDIA
Instagram: https://instagram.com/the_great_war
Twitter: https://twitter.com/WW1_Series
Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/TheGreatWarChannel»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Toni Steller
Editing: Toni Steller
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Daniel Kogosov (https://www.patreon.com/Zalezsky)
Research by: Jesse Alexander
Fact checking: Florian WittigChannel Design: Alexander Clark
Original Logo: David van StepholdA Mediakraft Networks Original Channel
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2019
November 11, 2019
The Berlin Wall – A Street Party With Sledgehammers – Extra History
Extra Credits
Published 9 Nov 2019Thanks to World of Tanks for sponsoring this episode. Download the game on PC and use the invite code
CHECKPOINTCto claim your $15 starter pack https://tanks.ly/2NoVfjx.The Berlin Wall has become a symbol of the Cold War. It encircled West Berlin, separating it from the Soviet-controlled East Berlin, placed to try and stop the flood of skilled professionals leaving to the West. Multiple US presidents had penned speeches about tearing down the wall, to no effect. But the Wall did fall. As the USSR underwent massive reforms and the Velvet Revolution was underway, East Germany was undergoing its own reform. And one clerical oversight in a press conference will destroy the Wall for good.
Update: Austin Bay linked to a column he wrote in 2009 on the 20th anniversary of these events.
Many in the West, including the U.S., believed that the communists had history on their side. The wry debate reply from the defeatist lefties favoring unilateral U.S. nuclear disarmament was “better Red than dead.” For decades — I repeat, decades — this crowd had a media pulpit from which its self-proclaimed intelligentsia preached the moral equivalency of the U.S. and the Soviet Union, and at times dropped the all pretense and fingered the U.S. as the “fascist state” and global oppressor.
In the language of the defeatist left, the U.S. was the jailer, the warmonger, the threat to world peace.
The Berlin Wall’s collapse exposed that Big Lie, as did the documented moral, political, economic and ecological wretchedness of the Soviet Union. Unfortunately, we still hear echoes of this “blame America” cant lacing al-Qaida propaganda and the lectures of hard-left reactionaries like Bill Ayers. The great anti-American lies of the Cold War are recast as the great anti-American lies of the War on Terror.
Breaching the wall in 1989 was bloodless, but the Cold War certainly wasn’t. World War III did not break out along the intra-German border and produce a nuclear conflagration, but the Cold War’s battles on the periphery (e.g., Greece, Korea, Vietnam, El Salvador, Angola, Afghanistan) were expensive, fatiguing and deadly.
October 30, 2019
QotD: Trotskyism
[The word “Trotskyist”] is used so loosely as to include Anarchists, democratic Socialists and even Liberals. I use it here to mean a doctrinaire Marxist whose main motive is hostility to the Stalin regime. Trotskyism can be better studied in obscure pamphlets or in papers like the Socialist Appeal than in the works of Trotsky himself, who was by no means a man of one idea. Although in some places, for instance in the United States, Trotskyism is able to attract a fairly large number of adherents and develop into an organised movement with a petty fuehrer of its own, its inspiration is essentially negative. The Trotskyist is against Stalin just as the Communist is for him, and, like the majority of Communists, he wants not so much to alter the external world as to feel that the battle for prestige is going in his own favour. In each case there is the same obsessive fixation on a single subject, the same inability to form a genuinely rational opinion based on probabilities. The fact that Trotskyists are everywhere a persecuted minority, and that the accusation usually made against them, i.e. of collaborating with the Fascists, is obviously false, creates an impression that Trotskyism is intellectually and morally superior to Communism; but it is doubtful whether there is much difference. The most typical Trotskyists, in any case, are ex-Communists, and no one arrives at Trotskyism except via one of the left-wing movements. No Communist, unless tethered to his party by years of habit, is secure against a sudden lapse into Trotskyism. The opposite process does not seem to happen equally often, though there is no clear reason why it should not.George Orwell, “Notes on Nationalism”, Polemic, 1945-05.
October 22, 2019
QotD: The Soviet contribution to defeating Hitler
Stalin emerged from the second world war as its most successful warlord, head of a nation whose contribution to the destruction of Nazism had won worldwide admiration. Although the leaders of the western states quickly understood the threat posed by the new Soviet Empire to freedom and democracy, many of their citizens did not.
Between 1941 and 1945 so much praise had been heaped upon Uncle Joe, the defenders of Stalingrad, heroic factory workers of the Volga and suchlike, that thereafter it proved a hard task to disabuse many people of their illusions about Mother Russia. They were not wrong in believing that hundreds of thousands of young British and American men were alive in 1945 because Red soldiers had done more than their rightful share of dying.
Any examination of the Bolshevik revolution and its legacy must linger on the Great Patriotic War, because that victory remains the only indisputable and durable achievement the rulers of Russia can boast since 1917, save the invention of some remarkable weapons systems and spacecraft.
Max Hastings, “The centenary of the Russian revolution should be mourned, not celebrated”, The Spectator, 2016-12-10.
October 15, 2019
The Tide Is Turning – Russian Civil War Fall 1919 I THE GREAT WAR 1919
The Great War
Published 14 Oct 2019Support 16 Days in Berlin: https://realtimehistory.net/indiegogo
The White Russian advance on Moscow comes to a crashing end as the Red Army manages to turn the tide of the Russian Civil War in Fall 1919.
» SUPPORT THE CHANNEL
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thegreatwar
Merchandise: https://shop.spreadshirt.de/thegreatwar/» SOURCES
Figes, Orlando. A People’s Tragedy. The Russian Revolution (London: The Bodley Head, 2017 [1996]).
Mawdsley, Evan. The Russian Civil War (New York: Pegasus Books, 2005).
Smele, Jonathan. The “Russian” Civil Wars 1916-1926 (London: Hurst, 2015).
Sumpf, Alexandre. “Russian Civil War,” in 1914-1918 online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War. https://encyclopedia.1914-1918-online.
Engelstein, Laura. Russia in Flames (Oxford University Press, 2017).»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Toni Steller
Editing: Toni Steller
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Daniel Kogosov (https://www.patreon.com/Zalezsky)
Research by: Jesse Alexander
Fact checking: Florian WittigChannel Design: Alexander Clark
Original Logo: David van StepholdA Mediakraft Networks Original Channel
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2019
October 8, 2019
QotD: Russian life under Soviet rule
No believable economist would claim that the Russian people benefited from Leninist or Stalinist social and economic policies. It is easier to project an upward trend for Russian living standards after 1918 had the Tsarist regime survived than to make a case that the Soviet system profited anyone, save the commissars. It has proved a common characteristic of communist regimes around the world that — to paraphrase Orwell — all pigs are equal, but some secure access to bigger troughs than others. British visitors to Moscow in the darkest days of the second world war cringed at the extravagance of the banquets they were served at a time when most of the country was starving and even — in extreme circumstances, such as those of besieged Leningrad — eating each other.
Yet until the last years of the 20th century the supply of useful idiots — western apologists for the Soviet Union — seemed limitless, and included such figures as Tony Benn. Anthony Powell’s novel Books Do Furnish a Room captures the enthusiasm for Soviet communism that pervaded post-1945 London socialist sitting rooms and literary gatherings.
No modern reader can set down the works of Solzhenitsyn, Robert Conquest, Robert Service or Anne Applebaum without a sense of awe at the cruelties committed in the name of “the people”, the cause of Russian communism; cruelties indulged almost to this day by their western defenders.
Max Hastings, “The centenary of the Russian revolution should be mourned, not celebrated”, The Spectator, 2016-12-10.
October 1, 2019
QotD: The Great Patriotic War
Even by the usual standards of historical irony, it remains astonishing that Hitler’s June 1941 invasion of the Soviet Union not only failed to destroy Bolshevism, but instead conferred a new legitimacy on Stalin’s dictatorship, and probably protracted by a generation the existence of his empire. Successful resistance to Hitler was only possible because of the Soviet leader’s industrialisation programme, which had been carried out at appalling human cost.
The Russian people’s 21st-century notion of what they call “the Great Patriotic War” bears little relationship to our own. It ignores Stalin’s 1939-41 pact with Hitler, and the fact that the Luftwaffe planes that bombed London in the Blitz were powered by Russian fuel. President Putin has made unlawful all published mention of the unspeakable cruelties the Soviet regime inflicted on its own citizens — shooting an estimated 300,000 soldiers for alleged desertion or cowardice — in order to prevail. Antony Beevor’s books, and for that matter my own, are nowadays banned because they describe the Red Army’s 1945 campaign of rape and pillage in Germany.
I have argued elsewhere that the ruthlessness of Stalin’s tyranny was essential to contrive the defeat of Hitler’s tyranny; that if the liberation of Europe had proceeded at a pace determined by the US and British armies, we might still stand short of the Elbe.
Max Hastings, “The centenary of the Russian revolution should be mourned, not celebrated”, The Spectator, 2016-12-10.
September 28, 2019
The Freikorps Fights On – Estonia and Latvia War For Independence I THE GREAT WAR 1919
The Great War
Published 27 Sep 2019Support 16 Days in Berlin: https://realtimehistory.net/indiegogo
After the Battle of Cesis it seemed the situation in Latvia and Estonia was about to quieten down. But the German soldiers in the region and the ongoing conflict with Bolshevik Russia meant the 2nd half of 1919 saw even more fighting in the Baltics.
» SUPPORT THE CHANNEL
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thegreatwar
Merchandise: https://shop.spreadshirt.de/thegreatwar/»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Toni Steller
Editing: Toni Steller
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Daniel Kogosov (https://www.patreon.com/Zalezsky)
Research by: Jesse Alexander
Fact checking: Florian WittigChannel Design: Alexander Clark
Original Logo: David van StepholdA Mediakraft Networks Original Channel
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2019
September 27, 2019
The Holodomor – the Communists’ Holocaust | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1932 Part 3 of 4
TimeGhost History
Published 26 Sep 2019What do you get when you combine vigorous grain-tax policies, bad harvests with Stalins fear and animosity for the rural population of Ukraine? A man-created murder famine, designed to kill millions of Ukrainian men, women and children.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Subscribe to our World War Two series: https://www.youtube.com/c/worldwartwo…
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Indy Neidell and Spartacus Olsson
Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Naman Habtom and Spartacus Olsson
Edited by: Danliel Weiss
Sound design: Marek KaminskiSources:
– Applebaum, Anne, Red Famine: Stalin’s War on Ukraine (2017).
– Davies, R. W. and Stephen G, “Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932-33: A Reply to Ellman”, in: Europe-Asia Studies 58-4 (2006), 625-633, https://www.uio.no/studier/emner/hf/i…
– Lewin, M, “The Immediate Background of Soviet Collectivization,” in: Soviet Studies 17-2 (1965) 162–197.
– Kuromiya, Hiraoki, “Ukraine and Russia in the 1930’s”, in Harvard Ukrainian Studies 18-3/4 (1994) 327–341.
– Marples, David R, “Ethnic Issues in the Famine of 1932-1933 in Ukraine,” in: Europe-Asia Studies 61-3 (2009) 505–518.
– Watstein, Joseph, “The Role of Foreign Trade in Financing Soviet Modernization,” in: The American Journal of Economics and Sociology 29-3 (1970) 305–319.
– Wolowyna et al., “Regional Variations of 1932–1934 Famine Losses in Ukraine”.A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
TimeGhost History
4 hours ago (edited)
This might have been one of the hardest episodes we have written, both historically and emotionally. Nothing could ever do justice to the millions of men, women and children who suffered, starved and died during this episode of history. Let us never forget them. We acknowledge that this topic is surrounded by many opposing agendas, myths so that talking about it can get emotional. This is why, as should be known by now, will UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES tolerate any kind of Stalinist apologism, falsification of known facts, or outright denial of the Holodomor. The sources, which are clearly presented in our video, the description and in this comment, are unequivocal about the events covered in this episode. Anywhere were there is an assumption based on deduction from these facts, we mention it. Keep that in mind when discussing this under the episode. We will moderate any comments that can’t abide to these clear and simple rules.
September 14, 2019
Stalin’s 5 Year Plan for Economic Mass Murder | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1932 Part 1 of 4
TimeGhost History
Stalin has to deal with the consequences of forcibly changing the Soviet Union from an agrarian economy into a modern industrialized society as his first five-years plan reaches its final year.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Spartacus Olsson and Naman Habtom
Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Naman Habtom
Edited by: Daniel Weiss en Wieke Kapteijns
Sound design: Marek KaminskiA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
TimeGhost History
1 hour ago (edited)
Debating the concepts, definition and framework of Marxism, Communism and Socialism is something that historians don’t seem to get enough of, much like applying these theories to historical and contemporary phenomena. The study of how these theories turned into ideology and what effect that had on nations, cultures, peoples and wars is a very interesting field of history, which can be debated to great lengths, which we ourselves also like to engage and participate in. However, we want to once again emphasise that we will only allow debate within the generally accepted rules of academic debate. Keep it civil, substantiated, name your sources whenever possible and stay away from pseudo-science and contemporary politics. We are fierce believers in the benefits of academic debate and don’t want to resort to turning off the comments, as other channels might do when talking about subjects like the 5-year plan or the Holodomor.Cheers, Joram
September 3, 2019
An alternative end to the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact?
On the anniversary of the German invasion of Poland, Arthur Chrenkoff wonders if Stalin’s greatest miscalculation wasn’t refraining from attacking the Nazi forces after they’d been fighting the Polish army for three weeks in 1939:
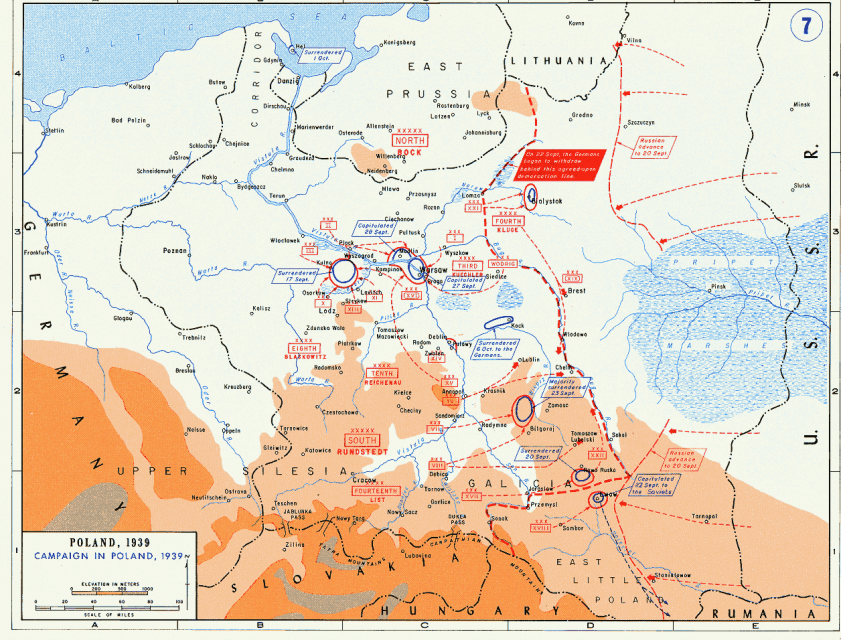
Military situation in Poland, 14 September 1939 (map does not show Slovak Army activity in southern Poland).
United States Military Academy, Department of History via Wikimedia Commons.
In late August, the Soviet Union signed the infamous Ribbentrop-Molotov non-aggression pact with Germany, effectively green-lighting Hitler’s invasion of Poland a few days later. The secret protocols attached to the pact stipulated for the division of Central Europe between the two powers, with the Soviet Union being rewarded for its cooperation with the Nazis with the gift of eastern Poland, the Baltic states and Bessarabia, or the north-eastern Romania (as well as, it transpired later, the German non-interference during the Soviet invasion of Finland).
The Soviets were not naive (even if Stalin discounted all the indications of the coming German attack in 1941) to believe in a long-term friendship with Nazi Germany. There are strong indications that the Soviet Union intended to attack Germany, perhaps sometime in 1942, but Hitler beat it to the punch. The official Russian justification for the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact has certainly always been that the Soviet Union needed to buy itself extra time to prepare for this eventual showdown, since in 1939 it was still nowhere near ready (not least because of Stalin’s decapitation of the Red Army’s top leadership during the Great Terror a few years before).
But what if that was Stalin’s greatest miscalculation ever? By 17 September, when the Red Army crossed the eastern borders of Poland in accordance with the secret partition agreement, it was pretty clear to all that Poland was close to a military defeat (it would have hold on for longer, of course, without the Soviet stab in the back, but this would not have changed much without the Western allies’ military involvement, which never eventuated). While the German armed forces were winning, they were also overcommitted and overstretched. The German high command expected a quicker and easier victory and were taken aback by the ferocity of Polish resistance, despite clear German superiority in armour, air power and logistics. By the second half of September, some ammunition stocks were beginning to run low (particularly bombs) and motorised equipment, from tanks to trucks, has been significantly degraded through a combination of attrition and significant wear and tear in Polish autumn.
So what if the Red Army, instead of eventually coming to a halt along the previously agreed demarcation line, kept going west? There was no significant Polish military force to take into account and German army was tired and weakened after three weeks of hard fighting (losing a third of its tanks and 25 per cent of its air force in the process). While Wehrmacht had numerical advantage on the ground, this was only because the Red Army chose to invade Poland with half a million men, which was certainly enough to subdue the thinly-held eastern marches, but should they have needed it, the Soviets had reserves to draw upon to even out the field against the Germans. Even with their 33 committed divisions, the Red Army had a significant advantage over the German armed forces in the Polish theatre in terms of armour and air power (two to one for the former).
Who would have triumphed in this 1939 clash of the rival totalitarian war machines? We don’t know, of course, except that at the time of the invasion of Poland, Germany was militarily at its weakest point it would be until the final months of World War Two. Should the Red Army have proven victorious in September and October 1939, it would have likely ended up in Berlin in a matter of weeks, instead of years it eventually took. It’s a reasonable guess that Great Britain and France, faced with the Soviet invasion of the Reich and the looming defeat of Hitler, would have overcome their initial inertia and moved into Germany from the west so as to prevent having the communists proverbially water their horses in the Rhine. In this scenario, we would have ended up with a divided Germany and a divided Europe (though without much of the rest of Central and south-Eastern Europe in the Soviet camp) some six years earlier and without the tens of millions of dead, a ruined continent, and the Holocaust that accompanied World War Two as it actually unfolded.
Alas.
August 30, 2019
“Stalingrad” – World War Two – Sabaton History 030 [Official]
Sabaton History
Published on 29 Aug 2019The Sabaton song “Stalingrad” is about the devastating battle of the Russian city of Stalingrad, which lasted for 5 months from August 1942 till February 1943. The battle is infamous for its brutal street fighting and high casualties on both sides.
Support Sabaton History on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/sabatonhistory
Listen to Primo Victoria (where “Stalingrad” is featured):
CD: http://bit.ly/PrimoVictoriaStore
Spotify: http://bit.ly/PrimoVictoriaSpotify
Apple Music: http://bit.ly/PrimoVictoriaAppleMusic
iTunes: http://bit.ly/PrimoVictoriaiTunes
Amazon: http://bit.ly/PrimoVictoriaAmzn
Google Play: http://bit.ly/PrimoVictoriaGooglePlayHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Markus Linke and Indy Neidell
Directed by: Astrid Deinhard and Wieke Kapteijns
Produced by: Pär Sundström, Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Executive Producers: Pär Sundström, Joakim Broden, Tomas Sunmo, Indy Neidell, Astrid Deinhard, and Spartacus Olsson
Maps by: Eastory
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Sound Editing by: Marek KaminskiEastory YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCElybFZ60Hk1NSjgCf7I2sg
Archive by: Reuters/Screenocean https://www.screenocean.com
Music by Sabaton.Sources:
– Photo of Stalingrad field hospital – Natalia Bode
– Photo of the Soviet loudspeaker by Arkady Shaikhet
– Colorization by Klimbim: German soldier in Stalingrad, Soviet machine gunners
– IWM: TR 153An OnLion Entertainment GmbH and Raging Beaver Publishing AB co-Production.
© Raging Beaver Publishing AB, 2019 – all rights reserved.
August 26, 2019
Russia attempts to retroactively “normalize” the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
Just before the outbreak of World War II on the Polish-German frontier, the Soviet Union concluded a non-aggression pact with Hitler’s Germany that included a large slice of Polish territory and a free hand in the Baltic for Soviet expansion (only the early Finnish success prevented total Soviet domination of the eastern Baltic region). The current Russian government is conducting a public relations (propaganda) campaign to recast this pact as being unexceptional diplomatic activity by attempting to cast Britain, France, and all the other countries that had active diplomatic arrangements with Germany as being “just the same” as the infamous Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. Wikipedia sums up the fate of the two chief diplomats:
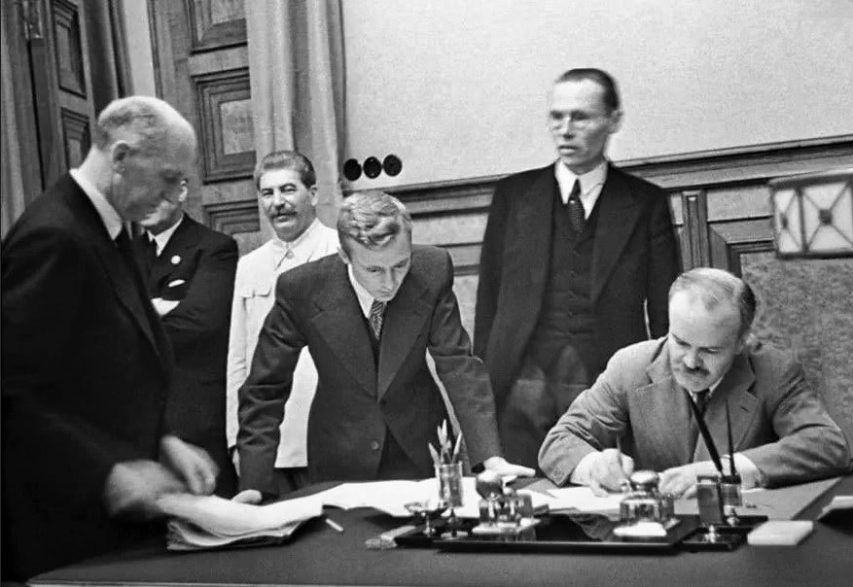

Translation of the Russian caption for this image:
People’s Commissar of Foreign Affairs of the USSR V.M. Molotov signs a friendship and border treaty between the USSR and Germany. Among those present: I.V. Stalin, translator of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs V.N. Pavlov, German diplomat G. Hilger (“truncated” version of the photograph of M. Kalashnikov distributed on the net)
Photograph attributed to Mikhail Mikhaylovich Kalashnikov (1906-1944) via Wikimedia Commons.
The Pact was terminated on 22 June 1941, when Nazi Germany launched Operation Barbarossa and invaded the Soviet Union (thus as well executing the ideological goal of Lebensraum). After the war, von Ribbentrop was convicted of war crimes and executed. Molotov died aged 96 in 1986, five years before the USSR’s dissolution. Soon after World War II, the German copy of the secret protocol was found in Nazi archives and published in the West, but the Soviet government denied its existence until 1989, when it was finally acknowledged and denounced. Vladimir Putin, while condemning the pact as “immoral”, has also defended the pact as a “necessary evil”, a U-turn following his earlier condemnation
Arthur Chrenkoff explains why we should vigorously resist this attempt to “normalize” Molotov-Ribbentrop:
1. While the shameful Western appeasement of Hitler, culminating in the infamy of Munich, allowed the Reich to bloodlessly dismember the sovereign and democratic Czechoslovakia, neither Great Britain nor France participated in or benefited from Germany’s cannibalism of this “faraway country of which we know little”. The difference is that while the West remains ashamed of Munich (a name which quickly become synonymous with a craven sell-out), a few years back, Russia’s culture minister Vladimir Medinsky called the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact “a great achievement of Soviet diplomacy”.
2. Unlike all the other agreements signed with Germany during the 1930s, it was the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact that green-lit the armed German aggression and led to the outbreak of the deadliest war in human history. It’s difficult to blame Germany’s neighbours or countries threatened by the Soviet Union (like Poland, Romania and the Baltic states) for trying to stay on Germany’s good side. It was naive and in any case it didn’t work in the end, as they all later found out to their detriment and downfall. Soviet Union, on the other hand, not only climbed into bed with Nazi Germany but it fully and enthusiastically consummated this marriage of convenience.
3. Unlike other agreements cited above, thanks to the “secret protocols” attached to the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact, the Soviet Union was both a co-aggressor in and a co-beneficiary of the start of World War Two. Stalin has relatively bloodlessly acquired the by-then (mid-September) almost defenseless eastern Poland (subsequently incorporated into Belarussian and Ukrainian Soviet Republics; these historically Polish areas remain today parts of Belarus and Ukraine), Bessarabia from Romania (incorporated into the Moldovan Soviet Republic), the Baltic States of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, as well as being given a free hand in the invasion of Finland, a country which otherwise might have counted on German friendship and support. All these aggressive territorial gains were the consequence of the Ribbentrop-Molotov division of Eastern Europe between the Reich and the Soviet Union into the respective spheres of interest, soon confirmed as the “facts on the ground” by Wehrmacht and Red Army.
4. While Britain and France, their empires and their allies, fought Germany for almost two years after September 1939, first through the period of the “phony war”, then through the Blitzkrieg in the West and the Battle of Britain, the Soviet Union remained a de facto Nazi ally, continuing to cooperate in security matters and supplying Germany with food and raw materials. Grain trains were still rolling west across the border with the Reich as Wehrmacht was launching Operation Barbarossa in the morning of 22 June 1941. During the period of Nazi-Soviet cooperation, Germany conquered Poland, Norway, Denmark, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, France, Yugoslavia and Greece. Soviet exports helped to feed and build up the German war machine before it was unleashed against the West in 1940; German troops surging into the Low Countries walked on their stomachs (to borrow from Napoleon) full of bread baked from Russian wheat or were carried on the tanks and trucks made with Russian coal and ores. Never forget that for Russia, World War Two – or the Great Patriotic War as it is called there – begins only in June 1941, not September 1939, as it does in all Western history books.
5. It’s true that the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact was partly defensive in nature as far as the Soviet Union was concerned, aiming to postpone the inevitable armed clash between the two rival totalitarianisms and in the meantime give Russia some essential breathing space to build up its army and strategic reserves (the top leadership of the Soviet armed forces was decapitated by Stalin during the purges in 1937-8, leaving them even more unprepared to face Germany than would have otherwise been the case). But as I pointed out above, it was also offensive and directly benefited Stalin’s territorial ambitions while it lasted. In some ways, the legacy of the pact lives on in the shape of Poland’s post-war borders, which have nothing to do with its thousand-year history. This is the real #TruthAboutWWII and this is why the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact remains singled out in the infamy of the interwar European democracy.














