TIK
Published 17 May 2016Erwin Rommel faces the might of the British Empire. In 3D animation, we’ll see the units, the battlefield and the tactics The Desert Fox uses to overcome the British and Australian forces at Mersa Brega and throw them out of Italian Libya. Except for Tobruk of course! The video covers Erwin Rommel’s arrival in Italian Libya up to the beginning part of the Battle of Tobruk 1941.
This video is Part 2 of the Western Desert Campaign – Part 1 (Operation Compass) is in the link below
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b71kd…Bibliography
Battistelli, Pier Paolo. Erwin Rommel (Command). Osprey Publishing, 2010.
Beckett, Ian F. Rommel: A Reappraisal. Great Britain, 2013.
Beevor, Antony. The Second World War. Phoenix, 2014.
Bickers, Richard Townshend. The Desert Air War: 1939-1945. Endeavour Press Ltd, 2015.
Butler, Daniel Allen. Field Mashal: the Life and Death of Erwin Rommel. Casemate Publishers, 2015.
Dimbleby, Jonathan. Destiny in the Desert: The Road to El Alamein – the Battle that Turned the Tide. Great Britain, 2012.
Liddell Hart, B.H. A History of the Second World War. Pan Books, 2015.
Hastings, Max. All Hell Let Loose: The World at War 1939-1945. HarperPress, 2011.
Jorgensen, Christer. Afrika Korps: Rommel’s 1941 Offensive (Rapid Reads). Brown Bear Books, 2014.
LaFace, Major Jeffrey L. Tactical Victory Leading to Operational Failure: Rommel in North Africa. Pickle Partners Publishing, 2014.
Lyman R. The Longest Siege: Tobruk – The Battle That Saved North Africa. Pan Books, 2011.
Moorehead, Alan. The Desert War: the Classic Trilogy on the North Africa Campaign 1940-43. CPI Group, 2012.
Nash, N. Strafer Desert General: The Life and Killing of Lieutenant General WHE Gott. Pen and Sword Books Ltd, 2013.
Neillands, Robert. The Desert Rats: 7th Armoured Division 1940-45. UK, 2005.
Neillands, Robert. Eighth Army: From the Western Desert to the Alps, 1939-1945. John Murray Publishers, 2004.
Pitt, Barrie. The Crucible of War: Volume 1: Wavell’s Command. Cassell & Co, 2001.
Playfair, Major-General I.S.O. The Mediterranean and Middle East, Volume II, “The Germans come to the help of their Ally” (1941). The Naval & Military Press Ltd, 2004.
Raugh, H. Wavell in the Middle East 1939-1941: A Study in Generalship. USA, 2013.
Reuth, Ralf Georg. Rommel: The End of a Legend. Haus Publishing, 2005.
Thompson, Dennis H. Discarded Victory – North Africa, 1940-1941. Pickle Partners, 2014.
Williamson, Gordon. Afrikakorps 1941-43 (Elite). Osprey Publishing, 2009.
January 14, 2020
The Desert Fox | Rommel’s FIRST Battle in the North African Campaign | BATTLESTORM
January 12, 2020
Fighting Far Away From Home – Allied Advance in Africa – WW2 – 072 – January 11 1941
World War Two
Published 11 Jan 2020Action in Albania. Action in North-Africa. Action in East-Africa. Action in China and action on the Mediterranean. It looks like every belligerent party is amping up its efforts to get a foothold wherever they are. And if your enemy is gaining ground? You just throw more material and men at them.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Daniel Weiss
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
– Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
– Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/Sources:
IWM (A 4161), (E 872), (A 4162), (A 9793), (A 13509).
Division Coat of Arms by Noclador
oil barrel by BomSymbols from the Noun Project
can by Anniken & Andreas from the Noun ProjectSoundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
– “Arriving in Ancient Rome” – Kikoru
– “Easy Target” – Rannar Sillard
– “Split Decision” – Rannar Sillard
– “Road To Tibet 5” – Rannar Sillard
– “Death And Glory 1” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “The Inspector 4” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “Not Safe Yet” – Gunnar JohnsenArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
3 days ago (edited)
It looks like all fronts are heating up this week. And that the German reaction to the British offensive in North-Africa and the Greek progress in Albania is to move more German troops southward. This week already shows how that potentially threatens Britains position in the Mediterranean. Well, just like the British and Germans, we hope to increase our manpower in 1941. Do your part and expand our community of loyal supporters and history buffs by joining the TimeGhost Army on https://www.patreon.com/timeghosthistory and https://timeghost.tv. The war effort needs you!
Cheers, Joram
January 9, 2020
Operation Compass 1940-41 | BATTLESTORM North African Campaign Documentary
TIK
Published 21 Dec 2015The most in-depth look at Operation Compass out there! Using animations and detailed maps, let’s find out what happened in one of the greatest British (and Commonwealth) victories of the war and who was responsible for the destruction of the Italian 10th Army. This video covers the start of the North African Campaign up to the Battle of Beda Fomm.
Sources:
Barnett, C. The Desert Generals. Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 2011.
Bierwirth, J. Beda Fomm: An Operational Analysis. Pickle Partners, 1994.
Christie H. Fallen Eagles: The Italian 10th Army in the Opening Campaign in the Western Desert, June 1940. Pickle Partners 1999.
Dimbleby, J. Destiny in the Desert. Britain 2013.
Moorehead, A. The Desert War: The Classic Trilogy on the North Africa Campaign 1940-43. Aurum Press, 2014.
Playfair, I.S.O. The Mediterranean and Middle East Volume 1: Early Successes against Italy [to May 1941]. 1954.
Wahlert, G. The Western Desert Campaign. Australia, 2011.Music is my own!
January 5, 2020
It’s 1941 – A World at War – WW2 – 071 – January 4 1941
World War Two
Published 4 Jan 20201941 begins with action in North-Africa and China, but Indy also takes a moment to assess the current stakes and stakeholders in the East-Asian theatre. What is sure, is that 1941 will be an eventful year!
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
– Adrien Fillon – https://www.instagram.com/adrien.colo…
– Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/Sources:
– IWM: MH 2718, C 1850, E2294, E 18542, E 378, E 443, E 3721E, E 1573
– Bundesarchiv, Bild 101I-783-0104-09 / Moosmüller / CC-BY-SA 3.0
– Prison by FORMGUT. from the Noun Project
– Artillery by Creative Mania from the Noun ProjectSoundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
– “Easy Target” – Rannar Sillard
– “The Inspector 4” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “Magnificent March 3” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “March Of The Brave 10” – Rannar Sillard
– “March Of The Brave 9” – Rannar Sillard
– “Deviation In Time” – Johannes Bornlof
– “Disciples of Sun Tzu” – Christian Andersen
– “Last Point of Safe Return” – Fabien TellArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
2 days ago (edited)
Happy New Year to you all!! We hope you all had a great turn of the decade. We certainly have! Here’s a casual, spoiler-free statement: 1941 will be an interesting year. We are all very grateful for those who found us at the very start with the Invasion of Poland, during the Phoney War, the early fighting Northern and Western Europe and the more recent conflicts in Greece and North-Africa. Those of you who joined the TimeGhost Army and support us financially on patreon.com/timeghosthistory or Timeghost.tv deserve extra praise – as we would not have made 1941 without you! And we have BIG plans for the coming year, so please consider supporting us as well! Make history with us and join the TimeGhost Army!!Here’s to a great 2020 and ‘interesting’ 1941.
Cheers, Joram
December 22, 2019
December 21, 2019
Christmas In Tobruk (1943)
British Pathé
Published 13 Apr 2014Full title reads: “CHRISTMAS IN TOBRUK”.
Tobruk, Libya.
Several shots of Pathe cameraman Terry Ashwood in his pyjamas as he gets up from his bed in the desert. He looks into his Christmas stocking and reads his cards. Bell on Tobruk Church ringing. Various shots of sacks of mail being sorted at desert sorting post. Several shots of ruined buildings in Tobruk where the Tommies are having their own. They write Merry Xmas on the wall and seem to be enjoying themselves. Soldiers ironing their clothes, “dress up” set the table and serve dinner. Men sitting at table with “Merry Christmas” written on the wall behind them. Christmas feast. Christmas pudding with a twig instead of piece of holly. Men drinking. Terry Ashwood leaving building and it is “snowing”. Pan up to show the men ripping paper into small pieces and throwing it from the balcony.
(Mute & Track Negs.)
FILM ID:1071.21A VIDEO FROM BRITISH PATHÉ. EXPLORE OUR ONLINE CHANNEL, BRITISH PATHÉ TV. IT’S FULL OF GREAT DOCUMENTARIES, FASCINATING INTERVIEWS, AND CLASSIC MOVIES. http://www.britishpathe.tv/
FOR LICENSING ENQUIRIES VISIT http://www.britishpathe.com/
British Pathé also represents the Reuters historical collection, which includes more than 136,000 items from the news agencies Gaumont Graphic (1910-1932), Empire News Bulletin (1926-1930), British Paramount (1931-1957), and Gaumont British (1934-1959), as well as Visnews content from 1957 to the end of 1984. All footage can be viewed on the British Pathé website. https://www.britishpathe.com/
December 15, 2019
The Empire Strikes Back – Britain’s Operation Compass – WW2 – 068 – December 14, 1940
World War Two
Published 14 Dec 2019The First British offensive of the War begins in North Africa. Meanwhile, the German Knickebein system is designed for bombers to accurately bomb British targets at night. This is what the Brits do to stop them.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Thumbnail Colorization (Archie Wavell) by:
– Julius Jääskeläinen – https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/Colorizations by:
– Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
– Adrien Fillon – https://www.instagram.com/adrien.colo…Sources:
– IWM: F 4539, B 10600, CM 355, E 6600, E 3720E, E 1416, E 1378, E 4792
– Tropenmuseum, part of the National Museum of World Cultures– Prison icon by FORMGUT. from the Noun Project; Compass by RULI from the Noun Project.
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
August 24, 2019
Italy’s African Destiny | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1931 Part 1 of 3
TimeGhost History
Published on 23 Aug 2019When Mussolini wants to solidify Italy’s North African colonies, he faces massive opposition by one man: Omar Mukhtar, the Lion of the Desert.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Subscribe to our World War Two series: https://www.youtube.com/c/worldwartwo…
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Spartacus Olsson
Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Naman Habtom
Edited by: Daniel Weiss
Sound design: Iryna DulkaArchive by Reuters/Screenocean http://screenocean.com
Sources:
Online:
https://www.politico.com/blogs/ben-sm…
Muslim Fascist Party and Youth Wing
http://countrystudies.us/libya/21.htm (Library of Congress)
https://www.nam.ac.uk/explore/senussi…
https://awayfromthewesternfront.org/c…
https://www.brookings.edu/blog/order-…
https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/ar…Journal Articles:
Arielli, Nir. “Italian Involvement in the Arab Revolt in Palestine, 1936-1939.” British Journal of Middle Eastern Studies, vol. 35, no. 2, 2008, pp. 187–204. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/20455584.Bussotti, L. (2016) “A History of Italian Citizenship Laws during the Era of the Monarchy (1861-1946)”. Advances in Historical Studies, 5, 143-167. doi: 10.4236/ahs.2016.54014.
Cooke, James J. “Destino Affricano De Popolo Italiano: Franco-Italian Controversy Over Tunisia, 1936-1940.” Proceedings of the Meeting of the French Colonial Historical Society, 13/14, 1990, pp. 203–216. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/42952205.
Collins, Carole. “Imperialism and Revolution in Libya.” MERIP Reports, no. 27, 1974, pp. 3–22. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/3011335.
KOPANSKI, ATAULLAH BOGDAN. “ISLAM IN ITALY AND IN ITS LIBYAN COLONY (720-1992).” Islamic Studies, vol. 32, no. 2, 1993, pp. 191–204. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/20840121.
Pankhurst, Richard. “Education in Ethiopia during the Italian Fascist Occupation (1936-1941).” The International Journal of African Historical Studies, vol. 5, no. 3, 1972, pp. 361–396. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/217091.
Pretelli, Matteo. “Education in the Italian colonies during the interwar period.” Modern Italy, Vol. 16, No. 3, August 2011, 275–293
Books:
Mark I. Choate: Emigrant nation: the making of Italy abroad, Harvard University Press, 2008, ISBN 0-674-02784-1, page 175.Peter Bandella The Eternal City: Roman Images in the Modern World, Chapter 7 – The University of North Carolina Press, 1987, ISBN 0-8078-6511-7
Ahmad Hassanein Bey The Lost Oases (read a Swedish translation by Ulla Ericson), American University of Cairo, reprinted 2006 (original 1925), ISBN 978-91-87771-41-5
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
TimeGhost History
1 hour ago
As we approach one year of WW2 In Real Time we cannot express our gratitude for your support enough. It is the financial and spiritual involvement of the TimeGhost Army at https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory and https://timeghost.tv that has made it possible for us to do all of this – so thank you, once again!This episode comes out as our WW2 series is covering the first battles in the North African theatre. The Second World War there will have major impact on world events between 1940 and 1944. And this is the second episode covering the background to the conflict in North Africa and the Middle East. We will return to Africa again, but before that we will look at what is going on in Germany, Japan and the USSR in the early 1930s – as some of you might already guess or know, those are dramatic times in those places and it is in these years that the world takes its first concrete steps towards the conflict that erupts into world war in 1939.
June 22, 2019
QotD: Militant Islam and the arts
What I’ve learned since 9/11 is that the small pleasures — music, theatre, film — have to be earned. In the Muslim world, there is no music. In Libya they destroyed all the musical instruments — music was considered an abomination. When the demography changes, there will be no concert halls. Artists who take a multicultural view should be aware of this. Count the number of covered women in London’s West End. In Birmingham, where I went to high school, you have a provincial symphony orchestra in a Muslim city — I’m not sure it will survive. All art, all popular culture, is endangered by Islam, because there’s no room for it. It’s considered libertinism. And I’m not even talking about Miley Cyrus twerking at the music awards. What turned Sayyid Qutb against the morality of the West is that he attended a church dance in Greeley, Colorado, which was a dry town in 1948, and he heard the song “Baby, It’s Cold Outside”. He thought it was evil. And now things are getting a lot worse. Ugly things are happening.
Mark Steyn, interviewed by John Bloom, “Mark Steyn, Cole Porter and Free Speech”, Quadrant, 2017-05-11.
March 10, 2019
There’s something bigger at stake in the SNC-Lavalin affair than Trudeau’s career
Chris Selley explains why SNC-Lavalin is an example of Canada’s less-than-stellar record of holding corporations to account:
… University of Michigan law professor David Uhlmann argues in a 2016 paper, “criminal prosecution of corporations upholds the rule of law, validates the choices of law-abiding companies, and promotes accountability. … When corporations face no consequences for their criminal behavior, we minimize their lawlessness, and increase cynicism about the outsized influence of corporations.”
No kidding. And in a country like Canada, not to say a province like Quebec, it’s safe to say these lines of accountability and trust get severely tangled. Once a government deems any company “too big to fail,” whether it’s because of political donations or connections, or because its pension plan is heavily invested, or because it has acquired a creepy semi-sacred status among otherwise normal people — or indeed, because of an alleged 9,000 jobs — all these nice theories about the rule of law break down. That’s what we’ve been witnessing.
But there’s an even bigger breakdown going on that’s received far less attention. Employees allegedly behind Lavalin’s Libyan capers were criminally charged as well. Between them, former vice-president Sami Bebawi and former controller Stéphane Roy faced charges including defrauding the Libyan state, money laundering, violating UN sanctions, bribing Saadi Gadhafi — Moammar’s soccer-playing, Montreal-enjoying third son — and trying to extract him from Libya once it all kicked off in 2011.
Those charges were laid in February 2014. Last month, some against Bebawi and all against Roy were dismissed because the Crown didn’t manage to bring them to trial in five blessed years. In a scathing decision, judge Patricia Compagnone characterized the Crown’s behaviour as a perfect illustration of the “culture of complacency” and the “culture of delays” the Supreme Court had assailed in its landmark 2016 Jordan decision, which established empirical standards for the Charter right “to be tried within a reasonable time.”
It is an ever-more-curious mystery that Canada’s comprehensively screwed-up justice system never rises to the level of political crisis. In the first year after the Jordan decision alone, some 200 cases were thrown out on grounds of excessive delays. Some of the accused make the Friends of Moammar look like saints. They include alleged murderers, child molesters and drunk drivers.
The charges against SNC-Lavalin were laid in February 2015. More than four years later, we’re still fighting over whether to pursue them — and not, it must be said, in a way that makes us look like a terribly serious country. How nauseatingly fitting it would be if a court threw the case out before the feds even got a chance to decide what to do with it.
September 10, 2017
In search of silphium, the lost herb of the Roman empire
Zaria Gorvett recounts the story of a Roman-era herb that was at one point literally worth its weight in gold:
Long ago, in the ancient city of Cyrene, there was a herb called silphium. It didn’t look like much – with stout roots, stumpy leaves and bunches of small yellow flowers – but it oozed with an odiferous sap that was so delicious and useful, the plant was eventually worth its weight in gold.
To list its uses would be an endless task. Its crunchable stalks were roasted, sauteed or boiled and eaten as a vegetable. Its roots were eaten fresh, dipped in vinegar. It was an excellent preservative for lentils and when it was fed to sheep, their flesh became delectably tender.
Perfume was coaxed from its delicate blooms, while its sap was dried and grated liberally over dishes from brains to braised flamingo. Known as “laser”, the condiment was as fundamental to Roman haute cuisine as eating your food horizontally in a toga.
[…]
Indeed, the Romans loved it so much, they referenced their darling herb in poems and songs, and wrote it into great works of literature. For centuries, local kings held a monopoly on the plant, which made the city of Cyrene, at modern Shahhat, Libya, the richest in Africa. Before they gave it away to the Romans, the Greek inhabitants even put it on their money. Julius Caesar went so far as to store a cache (1,500lbs or 680kg) in the official treasury.A coin of Cyrene depicting the stalk of a Silphium plant. (Source: 1889 edition of Principal Coins of the Ancients, plate 35, via Wikimedia)
But today, silphium has vanished – possibly just from the region, possibly from our planet altogether. Pliny wrote that within his lifetime, only a single stalk was discovered. It was plucked and sent to the emperor Nero as a curiosity sometime around 54-68AD.
With just a handful of stylised images and the accounts of ancient naturalists to go on, the true identity of the Romans’ favourite herb is a mystery. Some think it was driven to extinction, others that it’s still hiding in plain sight as a Mediterranean weed. How did this happen? And could we bring it back?
March 4, 2016
The US Arms Industry – The Fight for Douaumont I THE GREAT WAR – Week 84
Published on 3 Mar 2016
The fierce Battle of Verdun continues but as the Germans under Crown prince Wilhelm push harder and harder, the German casualties begin to rise to the same levels as the French. The French Army is only kept alive through the sacred road which brings men to the front without a pause. One French soldier that gets captured around Verdun, is Charles De Gaulle. At the same time, on the almost forgotten Libyan Front South African cavalry saves the day like in the glorious past of the British Army.
November 20, 2015
The Forgotten Front – World War 1 in Libya I THE GREAT WAR – Week 69
Published on 19 Nov 2015
12 war zones were not enough for this global war and this week an often forgotten theatre of war opens in Libya. Local Arab tribesmen fight against the British in guerrilla war. As if the Italians did not have enough problems at the Isonzo Front where Luigi Cardona is still sending his men into certain death against the Austrian defences. The situation for the Serbs is grim too and on the Western Front the carnage continues unchanged.
September 30, 2014
“…the outcomes of U.S. military intervention in Iraq and Libya disprove libertarianism”
Nick Gillespie responds to a really dumb argument against libertarianism:
As one of the folks (along with Matt Welch, natch), who started the whole “Libertarian Moment” meme way back in 2008, it’s been interesting to see all the ways in which folks on the right and left get into such a lather at the very notion of expanding freedom and choice in many (though sadly not all) aspects of human activity.
Indeed, the brain freeze can get so intense that it turns occasionally smart people into mental defectives.
To wit, Damon Linker’s recent essay in The Week (a great magazine, by the way), which argues that the outcomes of U.S. military intervention in Iraq and Libya disprove libertarianism, in particular, the Hayekian principle of “spontaneous order.”
No shit. Linker is being super-cereal here, kids:
Now it just so happens that within the past decade or so the United States has, in effect, run two experiments — one in Iraq, the other in Libya — to test whether the theory of spontaneous order works out as the libertarian tradition would predict.
In both cases, spontaneity brought the opposite of order. It produced anarchy and civil war, mass death and human suffering.
You got that? An archetypal effort in what Hayek would call “constructivism,” neocon hawks would call “nation building,” and what virtually all libertarians (well, me anyways) called a “non sequitur” in the war on terror that was doomed to failure from the moment of conception is proof positive that libertarianism is, in Linker’s eyes, “a particularly bad idea” whose “pernicious consequences” are plain to see.
In the sort of junior-high-school rhetorical move to which desperate debaters cling, Linker even plays a variation on the reductio ad Hitlerum in building case:
Some bad ideas inspire world-historical acts of evil. “The Jews are subhuman parasites that deserve to be exterminated” may be the worst idea ever conceived. Compared with such a grotesquely awful idea, other bad ideas may appear trivial. But that doesn’t mean we should ignore them and their pernicious consequences.
Into this category I would place the extraordinarily influential libertarian idea of “spontaneous order.”
What nuance: Exterminating Jews may be the worst idea…! When a person travels down such a rhetorical path, it’s best to back away quickly, with a wave of the hand and best wishes for the rest of his journey. Who can seriously engage somebody who starts a discussion by saying, “You’re not as bad as the Nazis, I’ll grant you that”…? I’d love to read his review of the recent Teenage Mutant Ninjas movie: “Not as bad as Triumph of the Will, but still a bad film…”
August 6, 2014
Who is to blame for the outbreak of World War One? (Part eight of a series)
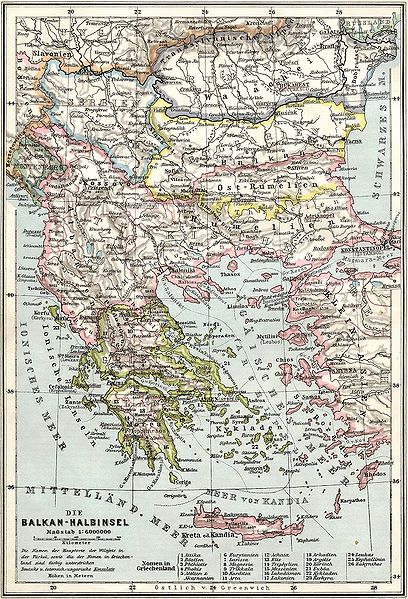
We’re getting closer to the end of the series now … you can catch up to the earlier posts here: part one, part two, part three, part four, part five, part six, and part seven. The previous post touched on Russia’s disaster in the far east and the dangerous domestic situation it faced after the war. In this post we discover that Italy could be at least as perfidious as “Perfidious Albion”, and that the Balkans are a hell of a place to wage a war.
Italy tips the first domino … in Africa
In The Sleepwalkers, Christopher Clark talks about a war I don’t think I’d ever heard of … an Italian campaign against the Ottoman Empire:
At the end of September 1911, only six months after the foundation of Ujedinjenje ili smrt! [“Union or death!” aka The Black Hand], Italy launched an invasion of Libya. This unprovoked attack one one of the integral provinces of the Ottoman Empire triggered a cascade of opportunistic attacks on Ottoman-controlled territory in the Balkans.
Italy’s attack on the Ottoman Empire was literally planned to steal what is now Libya and incorporate it into a new Italian Empire. Although the formal war was over in thirteen months, indigenous Arabs were still fighting back twenty years later. This attack broke the public-but-informal international understandings about leaving the remaining parts of the Ottoman Empire alone to prevent the risk of great power struggles breaking out. Britain and France had gone to war in 1854 to ensure that Russia did not gain access to the straits and thus a warm-water route to the Mediterranean and the coastlines of southern Europe, but the outcome of both the 1870-71 Franco-Prussian War and the 1877-78 Russo-Turkish War (and the secret Reinsurance Treaty with Germany) meant that Russia’s hands were largely free as long as Constantinople and the straits were not directly attacked. Italy’s attack broke with that understanding, and could be said to have started the most recent (and also most fatal) scramble for territory in the Balkans.
However, Italy did not act completely outside the norm for a would-be great power: they had an understanding with the French government that was formalized in a secret treaty in 1902 — Italy would not oppose French designs on Tunisia in exchange for French acceptance of Italy’s similar hopes for Tripolitania and Cyrenaica (modern day Libya). Italy’s attack was only possible because of the anomaly of the British position in Egypt: although still formally part of the Ottoman Empire, day-to-day Egyptian affairs were run by or overseen by British officials. Egypt was militarily occupied, but not a colony of the British Empire, and the country was — in theory — still run by the government of the Khedive. The Ottomans could not move formed bodies of troops through Egypt, and the Ottoman navy did not have the ships to transport them from Anatolia directly to Libya. This gave Italy the opportunity to concentrate against the weaker Ottoman forces.
The otherwise obscure Italo-Turkish War was interesting for several reasons, as the Wikipedia article notes:
Although minor, the war was a significant precursor of the First World War as it sparked nationalism in the Balkan states. Seeing how easily the Italians had defeated the weakened Ottomans, the members of the Balkan League attacked the Ottoman Empire before the war with Italy had ended.The Italo-Turkish War saw numerous technological changes, notably the airplane. On October 23, 1911, an Italian pilot, Captain Carlo Piazza, flew over Turkish lines on the world’s first aerial reconnaissance mission, and on November 1, the first ever aerial bomb was dropped by Sottotenente Giulio Gavotti, on Turkish troops in Libya, from an early model of Etrich Taube aircraft. The Turks, lacking anti-aircraft weapons, were the first to shoot down an aeroplane by rifle fire.
It was also in this conflict that the future first president of Turkey and leader of the Turkish War of Independence, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, distinguished himself militarily as a young officer during the Battle of Tobruk.
Although Italy ended up with possession of the disputed land, it did not come easily or cheaply:
The invasion of Libya was a costly enterprise for Italy. Instead of the 30 million lire a month judged sufficient at its beginning, it reached a cost of 80 million a month for a much longer period than was originally estimated. The war cost Italy 1.3 billion lire, nearly a billion more than Giovanni Giolitti estimated before the war. This ruined ten years of fiscal prudence.
After the withdrawal of the Ottoman army the Italians could easily extend their occupation of the country, seizing East Tripolitania, Ghadames, the Djebel and Fezzan with Murzuk during 1913. The outbreak of the First World War with the necessity to bring back the troops to Italy, the proclamation of the Jihad by the Ottomans and the uprising of the Libyans in Tripolitania forced the Italians to abandon all occupied territory and to entrench themselves in Tripoli, Derna, and on the coast of Cyrenaica. The Italian control over much of the interior of Libya remained ineffective until the late 1920s, when forces under the Generals Pietro Badoglio and Rodolfo Graziani waged bloody pacification campaigns. Resistance petered out only after the execution of the rebel leader Omar Mukhtar on September 15, 1931. The result of the Italian colonisation for the Libyan population was that by the mid-1930s it had been cut in half due to emigration, famine, and war casualties. The Libyan population in 1950 was at the same level as in 1911, approximately 1.5 million in 1911.
The war ended well — at least geographically speaking — for Italy, having gained title not only to Libya but also to the Dodecanese: a group of twelve large and about 150 small islands in the Aegean Sea. The largest and most economically valuable island was Rhodes, which became a useful base for Italian forces for more than 40 years. The treaty ending the Italo-Turkish War required Italy to vacate the islands, but due to both fuzzy wording and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire at the end of the First World War, Italy managed to retain possession.
The Ottoman tide ebbs
The remaining Ottoman territories in Europe were under constant pressure both from external forces (Austria and Russia) and internal linguistic, religious, and cultural separatist movements. Austria preferred to view the separatists as potential new provinces for the Dual Monarchy, while Russia saw the possibility of new independent Russophile political groupings that might allow indirect Russian access to the Mediterranean, bypassing Constantinople (or, perhaps more realistically, additional bases from which to launch an attack against the straits).Italy’s attack was the first domino falling. Christopher Clark writes:
The First World War was the Third Balkan War before it became the First World War. How as this possible? Conflicts and crises on the south-eastern periphery, where the Ottoman Empire abutted Christian Europe, were nothing new. The European system had always accommodated them without endangering the peace of the continent as a whole. But the last years before 1914 saw fundamental change. In the autumn of 1911, Italy launched a war of conquest on an African province of the Ottoman Empire, triggering a chain of opportunistic assaults on Ottoman territories across the Balkans. The system of geopolitical balances that had enabled local conflicts to be contained was swept away. In the aftermath of the two Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913, Austria-Hungary faced a new and threatening situation on its south-eastern periphery, while the retreat of Ottoman power raised strategic questions that Russian diplomats and policy-makers found it impossible to ignore.
Margaret MacMillan, in The War That Ended Peace:
It was in the Balkans […] that the greatest dangers were to arise: two wars among its nations, one in 1912 and a second in 1913, nearly pulled the great powers in. Diplomacy, bluff and brinksmanship in the end saved the peace but although Europeans could not know it, they had had a dress rehearsal for the summer of 1914. As they say in the theatre, if that last run-through goes well, the opening night will be a disaster.
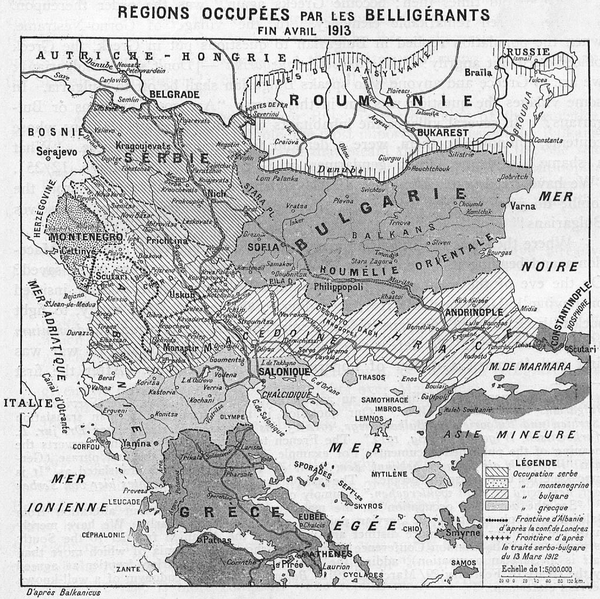
The First Balkan War of 1912 — A Pan-Slavic triumph
To some, the Balkans were a comic opera assemblage of exotic uniforms, passionate actors, indecipherable languages, a bit of bloodshed, but no real source of international danger or worry. Margaret MacMillan explains that much happened beneath the surface of the above-ground culture: much that portended danger to the entire region and beyond.
To the rest of Europe the Balkan states were something of a joke, the setting for tales of romance such as the Prisoner of Zenda or operettas (Montenegro was the inspiration for the The Merry Widow), but their politics were deadly serious — and frequently deadly with terrorist plots, violence and assassinations. In 1903 King Peter’s unpopular predecessor as King of Serbia and his equally unpopular wife had been thrown from the windows of the palace and their corpses hacked to pieces. […] The growth of national movements had welded peoples together but it had also divided Orthodox from Catholic or Muslim, Albanians from Slaves, and Croats, Serbs, Slovenes, Bulgarians or Macedonians from each other. While the peoples of the Balkans had coexisted and intermingled, often for long periods of peace through the centuries, the establishment of national states in the nineteenth century had too often been accompanied by burning of villages, massacres, expulsions of minorities and lasting vendettas.
Politicians who had ridden to power by playing on nationalism and with promises of national glory found they were in the grip of forces they could not always control. Secret societies, modelling themselves on an eclectic mix which included Freemasonry, the underground Carbonari, who had worked for Italian unity, the terrorists who more recently had frightened much of Europe, and old-style banditry, proliferated throughout the Balkans, weaving their way into civilian and military institutions of the states.
In addition to the ethnic, proto-national, cultural, and religious aspects of Balkan conflict, it was also an inter-generational conflict:
Comic opera states or not, they proved to be more than a match for their Ottoman overlords. Taking advantage of the Italian attack on Libya, Serbia allied with Bulgaria, Greece, and Montenegro to invade and capture much of the Balkan peninsula, stopping just a few miles outside Constantinople. The First Balkan War triggered vast population shifts, as nearly half a million Muslims fled from the conquered territory to escape religious persecution (and many thousands died through privation, disease, and starvation. Between the actual combat between military forces, forced evacuations, and the early use of genocidal policies, several million people were forced out of their homes and moved at gunpoint to wherever the armed groups wanted them to go. Cultural patterns nearly a millennia old were uprooted and dispersed to suit the tastes of local warlords and jumped-up military leaders.The younger generation who were attracted to the secret societies were often more extreme than their elders and frequently at odds with them. “Our fathers, our tyrants,” said a Bosnian radical nationalist, “have created this world on their model and are now forcing us to live in it.” The young members were in love with violence and prepared to destroy even their own traditional values and institutions in order to build the new Greater Serbia, Bulgaria, or Greece. (Even if they had not read Nietzsche, which many of them had, they too had heard that God was dead and that European civilization must be destroyed in order to free humankind.) In the last years before 1914, the authorities in the Balkan states either tolerated or were powerless to control the activities of their own young radicals who carried out assassinations and terrorist attacks on Ottoman or Austrian-Hungarian official as oppressors of the Slavs, on their own leaders whom they judged to be insufficiently devoted to the nationalist cause, or simply on ordinary citizens who happened to be in the wrong religion or the wrong ethnicity in the wrong place.
And there it might have ended, but the unexpectedly successful campaign by the Balkan League left just a few too many loose ends, which almost immediately led to conflict among the victorious allies. Since I’ve already tipped you to the fact that there was more than one Balkan War, you probably won’t be surprised to find that the Second Balkan War happened quite soon after the first one. But that’s a tale for another day.