Andrew Sullivan wonders if there’s any room for debate any more:
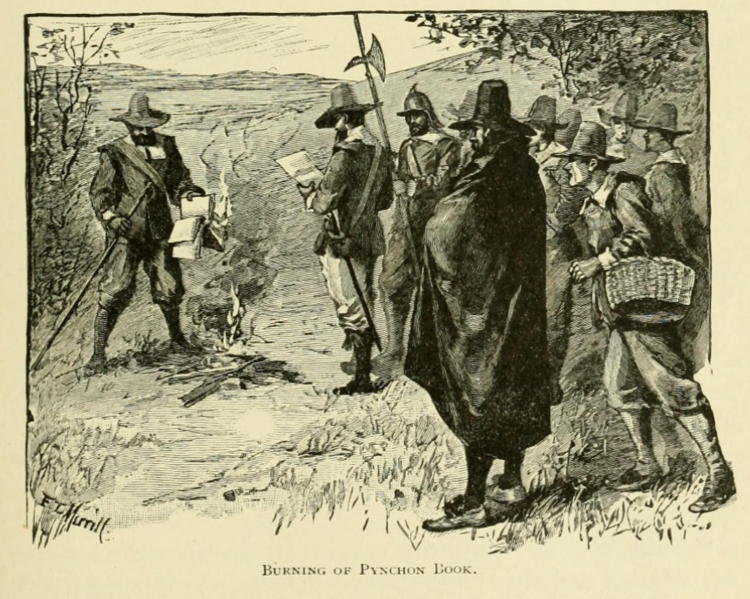

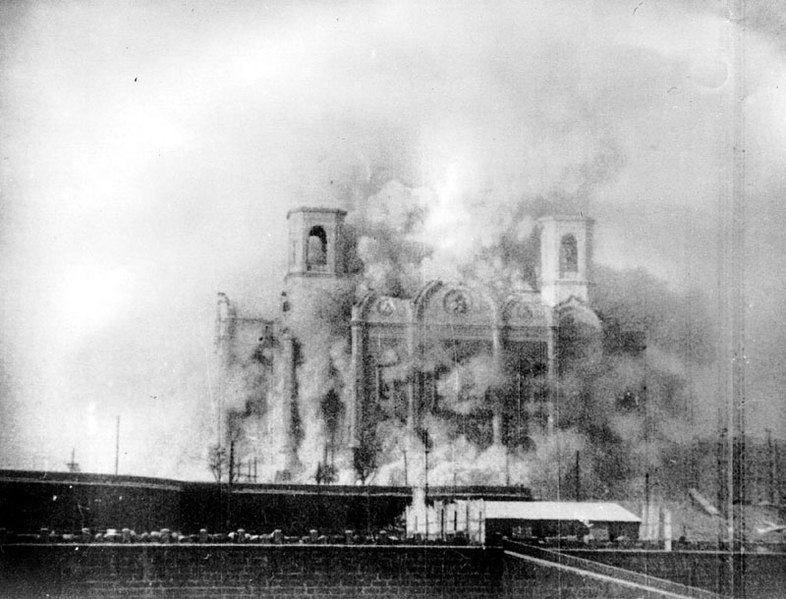
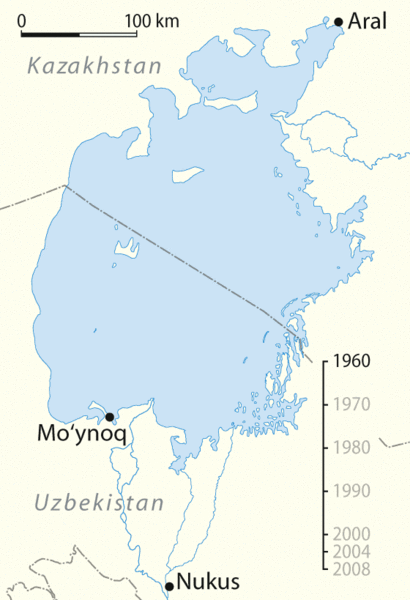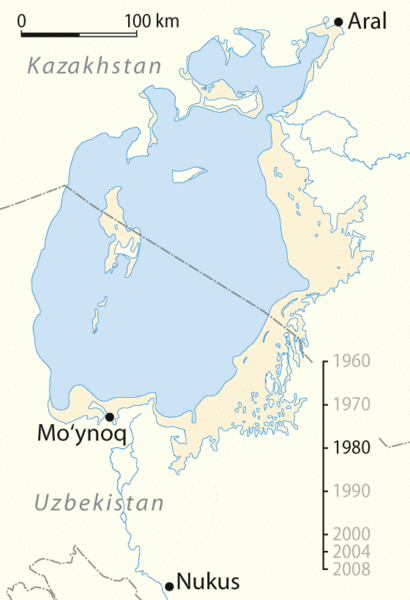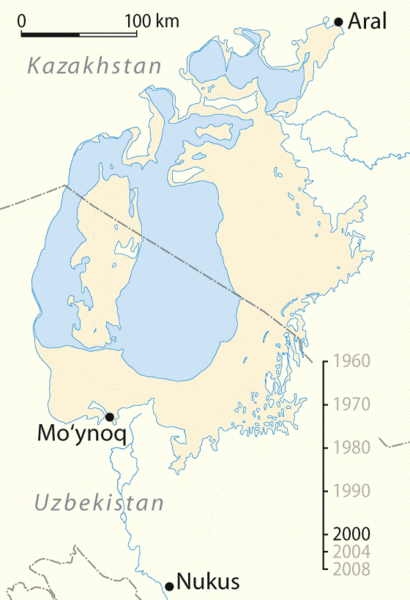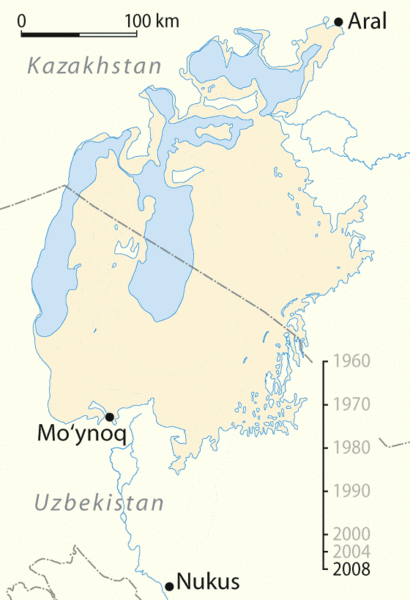
Portrayal of the burning of copies of William Pynchon’s book The Meritous Price of Our Redemption by early colonists of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, who saw his book as heresy; it was the first-ever banned book in the New World and only 4 original copies are known to survive today.
Engraving by F.T. Merrill in The History of Springfield for the Young by Charles Barrows, 1921.
In the last couple of weeks, as the purges of alleged racists have intensified in every sphere, and as so many corporations, associations, and all manner of civic institutions have openly pledged allegiance to anti-racism, with all the workshops, books, and lectures that come with it, I’m reminded of a Václav Havel essay, “The Power of the Powerless.”
It’s about the dilemma of living in a world where adherence to a particular ideology becomes mandatory. In Communist Czechoslovakia, this orthodoxy, with its tired slogans, and abuse of language, had to be enforced brutally by the state, its spies, and its informers. In America, of course, with the First Amendment, this is impossible. But perhaps for that very reason, Americans have always been good at policing uniformity by and among themselves. The puritanical streak of shaming and stigmatizing and threatening runs deep. This is the country of extraordinary political and cultural freedom, but it is also the country of religious fanaticism, moral panics, and crusades against vice. It’s the country of The Scarlet Letter and Prohibition and the Hollywood blacklist and the Lavender Scare. The kind of stifling, suffocating, and nerve-racking atmosphere that Havel evokes is chillingly recognizable in American history and increasingly in the American present.
The new orthodoxy — what the writer Wesley Yang has described as the “successor ideology” to liberalism — seems to be rooted in what journalist Wesley Lowery calls “moral clarity.” He told Times media columnist Ben Smith this week that journalism needs to be rebuilt around that moral clarity, which means ending its attempt to see all sides of a story, when there is only one, and dropping even an attempt at objectivity (however unattainable that ideal might be). And what is the foundational belief of such moral clarity? That America is systemically racist, and a white-supremacist project from the start, that, as Lowery put it in The Atlantic, “the justice system — in fact, the entire American experiment — was from its inception designed to perpetuate racial inequality.” (Wesley Lowery objected to this characterization of his beliefs — read his Twitter thread about it here.)
This is an argument that deserves to be aired openly in a liberal society, especially one with such racial terror and darkness in its past and inequality in the present. But it is an argument that equally deserves to be engaged, challenged, questioned, interrogated. There is truth in it, truth that it’s incumbent on us to understand more deeply and empathize with more thoroughly. But there is also an awful amount of truth it ignores or elides or simply denies.
It sees America as in its essence not about freedom but oppression. It argues, in fact, that all the ideals about individual liberty, religious freedom, limited government, and the equality of all human beings were always a falsehood to cover for and justify and entrench the enslavement of human beings under the fiction of race. It wasn’t that these values competed with the poison of slavery, and eventually overcame it, in an epic, bloody civil war whose casualties were overwhelmingly white. It’s that the liberal system is itself a form of white supremacy — which is why racial inequality endures and why liberalism’s core values and institutions cannot be reformed and can only be dismantled.
This view of the world certainly has “moral clarity.” What it lacks is moral complexity. No country can be so reduced to one single prism and damned because of it. American society has far more complexity and history has far more contingency than can be jammed into this rubric. No racial group is homogeneous, and every individual has agency. No one is entirely a victim or entirely privileged. And we are not defined by black and white any longer; we are home to every race and ethnicity, from Asia through Africa to Europe and South America.