Johnny66
Published 21 Jun 2015A well-considered documentary by the noted scholar, Dr Francis Pryor. The names Cerdic, Ceawlin, Cedda and Caedwalla are not exactly Germanic in origin? Cerdic’s father, Elesa, has been identified by some scholars with the Romano-Briton Elasius, the “chief of the region,” met by Germanus of Auxerre.
April 7, 2020
Britain AD: The Invasion That Never Was – The Anglo-Saxon Invasion (BBC Documentary)
June 29, 2019
Determining who the “original” inhabitants were
It’s become quite common in some countries to pay formal lip service to the “original” peoples who inhabited the land before being dispossessed of that territory by various Europeans. Actually determining who were the first human inhabitants, however, is much more fraught … you can’t exactly expiate some residual guilt of your culture by acknowledging the previous culture if the previous culture in their turn dispossessed an even earlier group, can you? How far down the rabbit hole do you need to go? Tim Worstall explains:
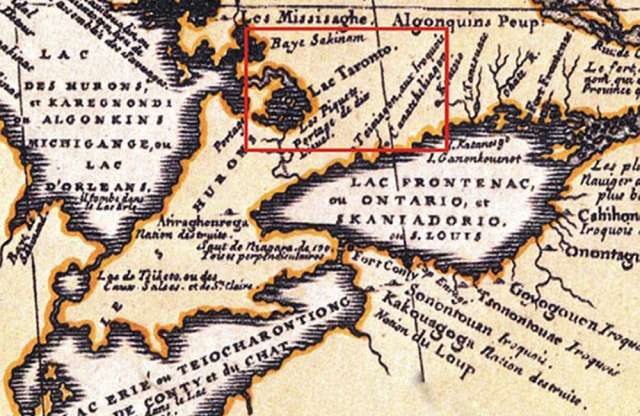
Detail from a 1688 map of western New France by Vincenzo Coronelli that locates “Lac Taronto” at Lake Simcoe.
City of Toronto Culture Division/Library and Archives Canada via the National Post
… within all that the accurate answer to “Whose land are we on?” is the land of the latest bunch of murderous bastards who killed all the previous inhabitants. Perhaps moderated to say the peeps who killed all the previous men then dated the remaining womenfolk. Because once we’ve got past that nullius stage that’s the way it has been. The Moriori are in short supply these days on the Chatham Islands given that the Maori decided to eat them.
The original inhabitants of the British Isles, the Beaker Folk, were entirely replaced by the next lot, the Iron Age Celts and similar. The Angles displaced to the west the Romano Celts in their turn, detailed DNA studies showing rather more of the female side of the R-C’s bred into the new population than the male. The Franks weren’t indigenous to France, the Allemani to Germany, the Turks to Turkey.
In fact, we’ve between little and no proof that the varied Amerinds were the original inhabitants of the lands where the White Europeans found then from 1492 onwards. In the case of both the Incas and Aztecs as political powers, proof they weren’t. And horses and Plains Indians simply weren’t a thing until the Eurasian horse was introduced post 1492.
Basically, this is indeed true. Anywhere is the possession of simply the last group of people to have slaughtered, or outbred, the previous group.
An interesting observation – if we apply the oft stated Americas example elsewhere, that Whitey stole it all and should give it back, then the Bantu should be back in Nigeria and Central Africa returned to the Pygmies, Southern to the Khoi San. We don’t say that and for the life of me I can’t work out why.
May 17, 2019
The EU’s trade distortions harm African farmers in many ways
One of the unifying themes of the European Union is its dedication to farm subsidies, which are very popular among some European farmers. EU farming subsidies and trade policies also do significant measurable harm to African farmers:
spiked: How does the EU harm African economies?
Sam Akaki: Thanks to the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy, which heavily subsidises EU farmers, Africa’s markets are flooded with their cheap excess produce. If you go to any African market, you can buy all kinds of European produce sold at very, very cheap prices. This is driving African farmers out of the market. At the same time, the EU imposes strict limitations on what African countries can export to the European market. In particular, African farmers cannot export value-added goods. So if a farmer in Ghana is producing cocoa, or a farmer in Kenya is producing coffee, they can perhaps get less than a dollar for their product as they have to export it raw. Only a fraction of the money you pay for a jar of coffee goes to an African farmer. The value-added goods, such as processed coffee, are then produced in Europe. Germany, especially, has been doing a lot of harm.
EU lobby groups and NGOs are not working in the interests of Africa and are opposed to African attempts to get themselves out of poverty. For instance, many African farmers work with genetically modified (GM) crops. One of the big issues about GM food is that Western companies sell GM seeds that don’t produce new seeds for the next season. Farmers have to go back to companies like Monsanto every year. In Uganda, at the Kawanda Agricultural Research Institute, scientists have been working on their own way of producing local GM seeds that will be reusable each year. Europe is against this and tries to stop it.
[…]
spiked: How have EU sanctions affected Africa?
Akaki: The clearest examples are Zimbabwe and Eritrea. Of course, these countries have human-rights issues. But human rights are a question of development. Countries go through developmental stages. There would have been enormous human-rights abuses in Europe 100 years ago. The UK and the EU use their influence selectively to impose economic and diplomatic sanctions on African countries. We should follow a consistent policy. We impose sanctions on African countries but we are happy to trade with other human-rights abusers like Saudi Arabia. One danger is that these sanctions are driving African countries closer and closer into the arms of the Chinese. This is a real own goal.
Sanctions are a blunt instrument. The leaders responsible for human-rights abuses are protected. They still have access to the best lifestyles money can buy. Their money is stashed away in British and other foreign banks. Sanctions don’t touch them at all. Instead, they hit the poorest hardest. Sanctions are directly contributing to poverty and mass migration. We should promote human rights, certainly, but we shouldn’t use human rights to punish the very poorest.
March 11, 2019
Misery was
exurb1a
Published on 10 Mar 2019Goodbye to closed-source human history. Maybe.
The Fifth Science Paperback ► https://tinyurl.com/y5zj33s5 (you may need to change your region accordingly: .co.uk, etc)Sample story from the book (The Lantern) ► https://youtu.be/um6cGuJ4mNE
The Fifth Science Treasure Hunt:
Minimal clues will be provided in the videos below. If you happen to live in one of these countries, then all the very best of luck finding the books. They’re not hidden elaborately, just out of sight of passers-by. If you need to do any heavy lifting, trespassing, or scale walls, you’re definitely in the wrong place. Hint: strange fonts and geography.
England ► https://youtu.be/HQDeKPNUF4U
Germany ► https://youtu.be/qfKd134AETo
Bulgaria ► https://youtu.be/XLLaa7G97B8
I also make horrendous music ► https://soundcloud.com/exurbia-1
Help me to do this full-time, if you’re deranged enough ► https://www.patreon.com/exurb1r?ty=h
The rest of my books ► https://tinyurl.com/ycnl5bo3Incidentally:
So, one of the many issues I didn’t get around to yelling at you about was the line between ‘genetic disorder’ and an individual’s unique features. I’ve mentioned before I’m more or less blind in one eye and this is almost definitely a result of a mutation in my family line. And you know, given the option, I’m not sure if I’d have it removed. Or, I’d need to give it a very, very long think.
There are plenty of lovely and bizarre anomalies specific to individuals, and it’s not for me to say – or even speculate really – where the line should be drawn when it comes to one day potentially making alterations to our descendants. I’m not a public educator, philosopher, scientist, or policy maker. Just an idiot with a USB microphone. I’m not the person to talk about this stuff. So I hope you’ll forgive my glossing over of it.
October 25, 2018
The History of Australia
History With Hilbert
Published on 23 Aug 2017The entire history of Australia from the earliest humans until somewhere after World War II where I lost interest.
September 12, 2018
QotD: Origins of India’s caste system
In India, the notion of Hindu culture as a giant conspiracy by Aryan invaders to enshrine their descendants at the top of the social order for the rest of eternity perhaps struck a little too close to home.
But Reich’s laboratory has found that the old Robert E. Howard version is actually pretty much what happened. Conan the Barbarian-like warriors with their horse-drawn wagons came charging off the Eurasian steppe and overran much of Europe and India. Reich laments:
The genetic data have provided what might seem like uncomfortable support for some of these ideas — suggesting that a single, genetically coherent group was responsible for spreading many Indo-European languages.
Much more acceptable to Indian intellectuals than the idea that ancient conquerors from the Russian or Kazakhstani steppe took over the upper reaches of Indian culture has been the theory of Nicholas B. Dirks, the Franz Boas Professor of History and Anthropology at Columbia, that the British malignantly transformed diverse local Indian customs into the suffocating system of caste that we know today.
Now, though, Reich’s genetic evidence shows that caste has controlled who married whom in India for thousands of years:
Rather than inventions of colonialism as Dirks suggested, long-term endogamy as embodied in India today in the institution of caste has been overwhelmingly important for millennia.
This is in harmony with economic historian Gregory Clark’s recent discovery in his book of surname analysis, The Son Also Rises (Clark loves Hemingway puns), that economic mobility across the generations is not only lower than expected in most of the world, but it is virtually nonexistent in India.
Steve Sailer, “Reich’s Laboratory”, Taki’s Magazine, 2018-03-28.
May 29, 2018
ESR’s thumbnail sketch on the origins of the Indo-European language families
When you mash historical linguistics hard enough into paleogenetics, interesting things fall out:
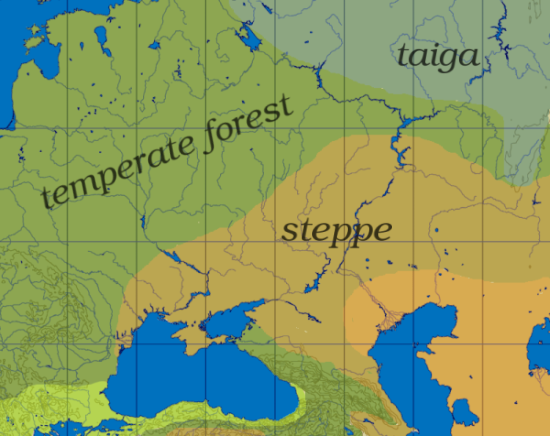
The steppe extends roughly from the Dniepr to the Ural or 30° to 55° east longitude, and from the Black Sea and the Caucasus in the south to the temperate forest and taiga in the north, or 45° to 55° north latitude.
Via Wikipedia
What we can now say pretty much for sure: Proto-Indo-European was first spoken on the Pontic Steppes around 4000 BCE. That’s the grasslands north of the Black Sea and west of the Urals; today, it’s the Ukraine and parts of European Russia. The original PIE speakers (which we can now confidently identify with what archaeologists call the Yamnaya culture) were the first humans to domesticate horses.
And – well, basically, they were the first and most successful horse barbarians. They invaded Europe via the Danube Valley and contributed about half the genetic ancestry of modern Europeans – a bit more in the north, where they almost wiped out the indigenes; a bit less in the south where they mixed more with a population of farmers who had previously migrated in on foot from somewhere in Anatolia.
The broad outline isn’t a new idea. 400 years ago the very first speculations about a possible IE root language fingered the Scythians, Pontic-Steppe descendants in historical times of the original PIE speakers – with a similar horse-barbarian lifestyle. It was actually a remarkably good guess, considering. The first version of the “modern” steppe-origin hypothesis – warlike bronze-age PIE speakers domesticate the horse and overrun Europe at sword- and spear-point – goes back to 1926.
But since then various flavors of nationalist and nutty racial theorist have tried to relocate the PIE urheimat all over the map – usually in the nut’s home country. The Nazis wanted to believe it was somewhere in their Greater Germany, of course. There’s still a crew of fringe scientists trying to pin it to northern India, but the paleogenetic evidence craps all over that theory (as Cochran explains rather gleefully – he does enjoy calling bullshit on bullshit).
Then there have been the non-nutty proposals. There was a scientist named Colin Renfrew who for many years (quite respectably) pushed the theory that IE speakers walked into Europe from Anatolia along with farming technology, instead of riding in off the steppes brandishing weapons like some tribe in a Robert E. Howard novel.
Alas, Renfrew was wrong. It now looks like there was such a migration, but those people spoke a non-IE language (most likely something archaically Semitic) and got overrun by the PIE speakers riding in a few thousand years later. Cochran calls these people “EEF” (Eastern European Farmers) and they’re most of the non-IE half of modern European ancestry. Basque is the only living language that survives from EEF times; Otzi the Iceman was EEF, and you can still find people with genes a lot like his in the remotest hills of Sardinia.
Even David Anthony, good as he is about much else, seems rather embarrassed and denialist about the fire-and-sword stuff. Late in his book he spins a lot of hopeful guff about IE speakers expanding up the Danube peacefully by recruiting the locals into their culture.
Um, nope. The genetic evidence is merciless (though, to be fair, Anthony can’t have known this). There’s a particular pattern of Y-chromosome and mitochondrial DNA variation that you only get in descendant population C when it’s a mix produced because aggressor population A killed most or all of population B’s men and took their women. Modern Europeans (C) have that pattern, the maternal line stuff (B) is EEF, and the paternal-line stuff (A) is straight outta steppe-land; the Yamnaya invaders were not gentle.
How un-gentle were they? Well…this paragraph is me filling in from some sources that aren’t Anthony or Cochran, now. While Europeans still have EEF genes, almost nothing of EEF culture survived in later Europe beyond the plants they domesticated, the names of some rivers, and (possibly) a murky substratum in some European mythologies.
The PIE speakers themselves seem to have formed, genetically, when an earlier population called the Ancient Northern Eurasians did a fire-and-sword number (on foot, that time) on a group of early farmers from the Fertile Crescent. Cochrane sometimes calls the ANEs “Hyperboreans” or “Cimmerians”, which is pretty funny if you’ve read your Howard.
April 1, 2018
When science itself becomes politically incorrect
Andrew Sullivan discusses the unwelcome discoveries of geneticists:
Last weekend, a rather seismic op-ed appeared in the New York Times, and it was for a while one of the most popular pieces in the newspaper. It’s by David Reich, a professor of genetics at Harvard, who carefully advanced the case that there are genetic variations between subpopulations of humans, that these are caused, as in every other species, by natural selection, and that some of these variations are not entirely superficial and do indeed overlap with our idea of race. This argument should not be so controversial — every species is subject to these variations — and yet it is. For many on the academic and journalistic left, genetics are deemed largely irrelevant when it comes to humans. Our large brains and the societies we have constructed with them, many argue, swamp almost all genetic influences.
Humans, in this view, are the only species on Earth largely unaffected by recent (or ancient) evolution, the only species where, for example, the natural division of labor between male and female has no salience at all, the only species, in fact, where natural variations are almost entirely social constructions, subject to reinvention. We are, in this worldview, alone on the planet, born as blank slates, to be written on solely by culture. All differences between men and women are a function of this social effect; as are all differences between the races. If, in the aggregate, any differences in outcome between groups emerge, it is entirely because of oppression, patriarchy, white supremacy, etc. And it is a matter of great urgency that we use whatever power we have to combat these inequalities.
Reich simply points out that this utopian fiction is in danger of collapse because it is not true and because genetic research is increasingly proving it untrue. On the male-female divide, for example, Reich cites profound differences, “reflecting more than 100 million years of evolution and adaptation.” On race, he is both agnostic about what we will eventually find out with respect to the scale of genetic differences, and also insistent that genetic differences do exist: “You will sometimes hear that any biological differences among populations are likely to be small, because humans have diverged too recently from common ancestors for substantial differences to have arisen under the pressure of natural selection. This is not true. The ancestors of East Asians, Europeans, West Africans and Australians were, until recently, almost completely isolated from one another for 40,000 years or longer, which is more than sufficient time for the forces of evolution to work.” Which means to say that the differences could be (and actually are) substantial.
This will lead to subtle variations in human brains, and thereby differences in intelligence tests, which will affect social and economic outcomes in the aggregate in a multiracial, capitalist, post-industrial society. The danger in actively suppressing and stigmatizing this inconvenient truth, he maintains, is that a responsible treatment of these genetic influences will be siloed in the academic field of genetics, will be rendered too toxic for public debate, and will thereby only leak out to people in the outside world via the worst kind of racists and bigots who will distort these truths to their own ends. If you don’t establish a reasonable forum for debate on this, Reich argues, if you don’t establish the principle is that we do not have to be afraid of any of this, it will be monopolized by truly unreasonable and indeed dangerous racists. And those racists will have the added prestige for their followers of revealing forbidden knowledge. And so there are two arguments against the suppression of this truth and the stigmatization of its defenders: that it’s intellectually dishonest and politically counterproductive.
March 19, 2018
Prehistoric migrations
In a Science article from last year, Ann Gibbons discusses the ancient migrations that can now be traced using DNA analysis:
After World War II, many scholars recoiled from studying migrations, in reaction to the Nazi misuse of history and archaeology. The Nazis had invoked migrations of “foreign” groups to German territory to justify genocide. “The whole field of migration studies was ideologically tainted,” says archaeologist Kristian Kristiansen of the University of Gothenburg in Sweden. Some researchers also resisted the idea that migration helped spread key innovations such as farming, partly because that might imply that certain groups were superior.
Nor did researchers have a reliable method to trace prehistoric migrations. “Most of the archaeological evidence for movement is based on artifacts, but artifacts can be stolen or copied, so they are not a real good proxy for actual human movement,” says archaeologist Doug Price of the University of Wisconsin in Madison, who tracks ancient migration by analyzing isotopes. “When I started doing this in 1990, I thought people were very sedentary and didn’t move around much.”
Today, however, new methods yield more definitive evidence of migration, sparking an explosion of studies. The isotopes Price and others study are specific to local water and food and thus can reveal where people grew up and whether they later migrated. DNA from ancient skeletons and living people offers the “gold standard” in proving who was related to whom.
The new data confirm that humans have always had wanderlust, plus a yen to mix with all manner of strangers. After the first Homo sapiens arose in Africa, several bands walked out of the continent about 60,000 years ago and into the arms of Neandertals and other archaic humans. Today, almost all humans outside Africa carry traces of archaic DNA.
That was just one of many episodes of migration and mixing. The first Europeans came from Africa via the Middle East and settled there about 43,000 years ago. But some of those pioneers, such as a 40,000-year-old individual from Romania, have little connection to today’s Europeans, Reich says.
His team studied DNA from 51 Europeans and Asians who lived 7000 to 45,000 years ago. They found that most of the DNA in living Europeans originated in three major migrations, starting with hunter-gatherers who came from the Middle East as the glaciers retreated 19,000 to 14,000 years ago. In a second migration about 9000 years ago, farmers from northwestern Anatolia, in what is now Greece and Turkey, moved in.
That massive wave of farmers washed across the continent. Ancient DNA records their arrival in Germany, where they are linked with the Linear Pottery culture, 6900 to 7500 years ago. A 7000-year-old woman from Stuttgart, Germany, for example, has the farmers’ genetic signatures, setting her apart from eight hunter-gatherers who lived just 1000 years earlier in Luxembourg and Sweden. Among people living today, Sardinians retain the most DNA from those early farmers, whose genes suggest that they had brown eyes and dark hair.
H/T to PaleoAnthropology+ for the link.
February 27, 2018
The notion of “uploading” your consciousness
Skeptic author Michael Shermer pours cold water on the dreams and hopes of Transhumanists, Cryonicists, Extropians, and Technological Singularity proponents everywhere:
It’s a myth that people live twice as long today as in centuries past. People lived into their 80s and 90s historically, just not very many of them. What modern science, technology, medicine, and public health have done is enable more of us to reach the upper ceiling of our maximum lifespan, but no one will live beyond ~120 years unless there are major breakthroughs.
We are nowhere near the genetic and cellular breakthroughs needed to break through the upper ceiling, although it is noteworthy that companies like Google’s Calico and individuals like Abrey deGrey are working on the problem of ageing, which they treat as an engineering problem. Good. But instead of aiming for 200, 500, or 1000 years, try to solve very specific problems like cancer, Alzheimer’s and other debilitating diseases.
Transhumanists, Cryonicists, Extropianists, and Singularity proponents are pro-science and technology and I support their efforts but extending life through technologies like mind-uploading not only cannot be accomplished anytime soon (centuries at the earliest), it can’t even do what it’s proponents claim: a copy of your connectome (the analogue to your genome that represents all of your memories) is just that—a copy. It is not you. This leads me to a discussion of…
The nature of the self or soul. The connectome (the scientific version of the soul) consists of all of your statically-stored memories. First, there is no fixed set of memories that represents “me” or the self, as those memories are always changing. If I were copied today, at age 63, my memories of when I was, say, 30, are not the same as they were when I was 50 or 40 or even 30 as those memories were fresh in my mind. And, you are not just your memories (your MEMself). You are also your point-of-view self (POVself), the you looking out through your eyes at the world. There is a continuity from one day to the next despite consciousness being interrupted by sleep (or general anaesthesia), but if we were to copy your connectome now through a sophisticated fMRI machine and upload it into a computer and turn it on, your POVself would not suddenly jump from your brain into the computer. It would just be a copy of you. Religions have the same problem. Your MEMself and POVself would still be dead and so a “soul” in heaven would only be a copy, not you.
Whether or not there is an afterlife, we live in this life. Therefore what we do here and now matters whether or not there is a hereafter. How can we live a meaningful and purposeful life? That’s my final chapter, ending with a perspective that our influence continues on indefinitely into the future no matter how long we live, and our species is immortal in the sense that our genes continue indefinitely into the future, making it all the more likely our species will not go extinct once we colonize the moon and Mars so that we become a multi-planetary species.
November 12, 2017
The great “bitter versus sweet” war
Megan McArdle is trapped behind enemy lines in the latest outbreak of the great taste war:
At this point I should put my cards on the table: Geographically and demographically, I belong in bitter country. But I am an exile-in-residence, because bitter foods make me wince.
I mean that literally. Really bitter things — a Negroni, say — produce in me a physical aversion that is close to pain. Black coffee I find merely extraordinarily unpleasant, and hoppy beer is just barely endurable. If I really had to endure it. Say, if consuming a bottle of IPA were the only way to save a busload of orphans who had been kidnapped by a beer snob.
Given where I live here in Washington, DC, and my known interest in food, the presumption of the bitter evangelists is that I must simply need re-education. I have been subjected to many hours of lectures on how I just need to clear my palate from all the sweet garbage I’m used to, so that I can appreciate the subtle joys of bitterness. I have refrained from suggesting that they hold still while I teach them to enjoy the subtle joys of being repeatedly kicked in the shins.
For over years of learning about food — and living with a bitter-loving craft cocktail enthusiast — I’ve come to realize that my aversion to bitter foods is almost certainly genetic. The Romans who coined the adage “de gustibus non est disputandum” were righter than they knew; science now tells us that there is indeed no sense arguing over taste, because you’re not going to change someone’s genome. Many seemingly mystifying divides over foods like cilantro come from the fact that some people have taste receptors that others don’t. If you have no receptors for the “soapy” compound in cilantro, this herb adds a marvelously tangy note to a dish. If you have those receptors, anything cooked with it tastes like Irish Spring en cocotte.
In my case, I probably have more bitter receptors than most people, so that a drink my husband finds intriguingly astringent would hit me like a punch to the tongue. I can no more get over my instinct to spit out bitter foods than he could get over his instinct to take his hand off a hot stove.
October 16, 2017
What Happens When You Inbreed? – Brit Lab
BBC Earth Lab
Published on 17 Dec 2015Does inbreeding really lead to deformities and nasty diseases could inbreeding actually be a good thing? Greg Foot finds out the answers.
August 22, 2017
QotD: Writing about the past
If you’re writing in the past — or even if you are just living in the present — you should have an idea of how the past was different, and the factors that shaped that.
If you assume the past was just like the present only less “enlightened” you’re presupposing history comes with an arrow, and that today is of course more “advanced” than the past. While this is true of science — of course — it’s not always true of what was inside people’s heads. In many ways because even the poorest of us struggle less than in the Middle Ages, it’s become easier to develop mental habits of laziness and other “rich person” vices. What you think is enlightenment might be considered sheer nonsense by your descendants. For instance the enlightened thing at one time (even Heinlein has a whiff of it) was genetic culling. Now we’re finding that what we know about genes isn’t that straightforward. Throw in epigenetics and someone with a gene to be a “moron” can turn out to be a genius. More, even overtly bad disease genes are linked to genes we need and can’t survive without. BUT the enlightened opinion in the early twentieth century was to improve humanity and save human suffering by culling out the sick and the lame and the “inferior races.” (No, Hitler didn’t invent that.)
Some of our concepts (and I’m not going to name any because it’s a fight I don’t need, but I’m sure you can think of some) will prove just as monstrous to our descendants.
If you don’t have a sense of that, you don’t have a sense of the past, which unfortunately means you don’t have a sense of the present.
If you think that there is an objective way to end poverty or stop drug use, or whatever, and it’s ONLY your way, and even your opponents think your way is right and are being villainous and “evil” by opposing it you not only shouldn’t be writing historical fiction, you definitely shouldn’t be voting. You should find the nearest kindergarten and use it as a safe space.
Because out here in the real adult world, the past and the present and complicated places, with different modes of arranging life that worked with the circumstances at that time, even if they now set our teeth (or our hair) on edge.
If you can’t accept your ancestors were different from you, thought differently and responded to different necessities, you have no business preaching multiculturalism.
Because what makes a culture different is not the hairstyles, the dresses or what they ate, but how one must live to survive. And yes, some cultures are factually worse than others at providing their people with the necessities (or the luxuries) of life. Arguably most past cultures were (barring our finding some atlantian high-developed scientific culture we’ve heard nothing about.)
That doesn’t give you the right to to stomp your feet and rewrite the past to justify your boorish self-regard in the present.
Your ancestors were both more and less enlightened than you in ways you can’t even understand, and your superimposing your beliefs on them is the act of a mental midget standing on the shoulders of giants and peeing down.
Sarah A. Hoyt, “What Has Gone Before Us”, According to Hoyt, 2015-08-03.
June 13, 2017
Vegetable impostors on your table
The vegetable pushers are clever: they can disguise vegetables in such a way that you don’t realize where they came from. A prime set of examples are all variations of a common Mediterranean weed called Brassica oleracea:
Brassica is also known as the wild mustard plant.
“The wild plant is a weedy little herb that prefers to grow on limestone outcroppings all around the coastal Mediterranean region,” Jeanne Osnas, a researcher at Purdue University who blogs as “The Botanist in the Kitchen,” writes of Brassica oleracea.
“It is a biennial plant that uses food reserves stored over the winter in its rosette of leaves to produce a spike of a few yellow flowers at the end of its second summer before dying. Those nutritious leaves make its domesticated derivatives important food crops in much of the world now.”
This one plant was selectively bred over hundreds of years to create dozens of wildly different vegetables.
By selecting and breeding plants with bigger leaves, or larger buds, the various cultivars were created.
[…]
The amazing evolution of Brassica oleracea goes to show that humans have been tinkering with the genetics of our food – creating what are now known as genetically modified foods, or GMOs – for a very long time.
New lab techniques just let us do that in a more precise and directed way.
March 30, 2017
You can now have beer brewed to your taste (as encoded in your genome)
For those with a taste for custom-brewed beer (and a very big budget), you can now have a batch of beer created to match your taste preferences, scientifically:
London-based Meantime Brewing Company, acquired a year ago by Belgian beverage multinational Anheuser-Busch InBev, wants to sell you beer tuned to your taste.
To do so, the company plans to direct willing customers to genetic testing service 23andMe – the Silicon Valley personal genomics biz that’s slowly emerging from its near death experience at the hands of US health regulators – to evaluate their genetic taste proclivities.
For a mere £25,000 (~$31,200), beer lovers who prefer entrusting purchasing decisions to science rather than self-knowledge can buy 12 hectolitres (about 2,100 Imperial pints or 2,500 US pints) of ale tailored to taste preferences encoded in their genome.
Customers supply their saliva, 23andMe sorts the genes, and Meantime crafts a beer to fit inborn affinities.
“Pioneering personal genetics company 23andMe will assess hereditary variations in your oral taste receptors (the TAS2R38 gene) to reveal the genetic variants that could explain personal preferences towards specific flavour profiles within beer, such as sweetness and bitterness,” the company explains on its website.
And if the genetically dictated balance of flavors doesn’t align with actual taste preferences, Meantime has left itself an out – customers get a consultation with Brewmaster Ciaran Giblin to adjust the flavors if necessary.
That’s almost certainly for the best since, as 23andMe points out, the role of genetics in taste preferences is uncertain. “Scientists aren’t yet sure how much of our taste preferences are genetic, but estimates are generally around 50 per cent,” the company says in the Taste report it offers subscribers.