Southern Plains Railfan
Published Jan 6, 2024In today’s video, we recount the time Penn Central let nearly all of Maine’s potato harvest rot in Selkirk yard; ruining thousands of lives and nearly taking down other railroads in the process.
Merch Shop: http://okieprint.com/SPR/shop/home
April 15, 2024
The MOST INCOMPETENT Railroad You’ve Ever Seen!
QotD: Cereal cultivation also helped grow the centralized state
Sumer just before the dawn of civilization was in many ways an idyllic place. Forget your vision of stark Middle Eastern deserts; in the Paleolithic the area where the first cities would one day arise was a great swamp. Foragers roamed the landscape, eating everything from fishes to gazelles to shellfish to wild plants. There was more than enough for everyone; “as Jack Harlan famously showed, one could gather enough [wild] grain with a flint sickle in three weeks to feed a family for a year”. Foragers alternated short periods of frenetic activity (eg catching as many gazelles as possible during their weeklong migration through the area) with longer periods of rest and recreation.
Intensive cereal cultivation is miserable work requiring constant toil with little guarantee of a good harvest. Why would anyone leave this wilderness Eden for a 100% wheat diet?
Not because they were tired of wandering around; Scott presents evidence that permanent settlements began as early as 6000 BC, long before Uruk, the first true city-state, began in 3300. Sometimes these towns subsisted off of particularly rich local wildlife; other times they practiced some transitional form of agriculture, which also antedated states by millennia. Settled peoples would eat whatever plants they liked, then scatter the seeds in particularly promising-looking soil close to camp – reaping the benefits of agriculture without the back-breaking work.
And not because they needed to store food. Hunter-gatherers could store food just fine, from salting animal meat to burying fish and letting it ferment to just having grain in siloes like everyone else. There is ample archaeological evidence of all of these techniques. Also, when you are surrounded by so much bounty, storing things takes on secondary importance.
And not because the new lifestyle made this happy life even happier. While hunter-gatherers enjoyed a stable and varied diet, agriculturalists subsisted almost entirely on grain; their bones display signs of significant nutritional deficiency. While hunter-gatherers were well-fed, agriculturalists were famished; their skeletons were several inches shorter than contemporaneous foragers. While hunter-gatherers worked ten to twenty hour weeks, agriculturalists lived lives of backbreaking labor. While hunter-gatherers who survived childhood usually lived to old age, agriculturalists suffered from disease, warfare, and conscription into dangerous forced labor.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Against The Grain“, Slate Star Codex, 2019-10-15.
March 28, 2024
Why European farmers are revolting
spiked
Published Mar 27, 2024Europe’s farmers are rising up – and the elites are terrified. From the Netherlands to Germany to Ireland, farmers are taking to the streets, parking their tractors on the establishment’s lawn, spraying buildings with manure and bringing life to a standstill. The reason? Because unhinged green regulations, dreamt up by European Union bureaucrats, are immiserating them. In this spiked video polemic, Fraser Myers explores the roots of the farmers’ revolt across the continent – and explains why it must succeed. Watch, share and let us know what you think in the comments.
Support spiked:
https://www.spiked-online.com/support/
Sign up to spiked‘s newsletters: https://www.spiked-online.com/newslet…
Check out spiked‘s shop: https://www.spiked-online.com/shop/
March 9, 2024
Salt – mundane, boring … and utterly essential
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes looks at the importance of salt in history:
There was a product in the seventeenth century that was universally considered a necessity as important as grain and fuel. Controlling the source of this product was one of the first priorities for many a military campaign, and sometimes even a motivation for starting a war. Improvements to the preparation and uses of this product would have increased population size and would have had a general and noticeable impact on people’s living standards. And this product underwent dramatic changes in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, becoming an obsession for many inventors and industrialists, while seemingly not featuring in many estimates of historical economic output or growth at all.
The product is salt.
Making salt does not seem, at first glance, all that interesting as an industry. Even ninety years ago, when salt was proportionately a much larger industry in terms of employment, consumption, and economic output, the author of a book on the history salt-making noted how a friend had advised keeping the word salt out of the title, “for people won’t believe it can ever have been important”.1 The bestselling Salt: A World History by Mark Kurlansky, published over twenty years ago, actively leaned into the idea that salt was boring, becoming so popular because it created such a surprisingly compelling narrative around an article that most people consider commonplace. (Kurlansky, it turns out, is behind essentially all of those one-word titles on the seemingly prosaic: cod, milk, paper, and even oysters).
But salt used to be important in a way that’s almost impossible to fully appreciate today.
Try to consider what life was like just a few hundred years ago, when food and drink alone accounted for 75-85% of the typical household’s spending — compared to just 10-15%, in much of the developed world today, and under 50% in all but a handful of even the very poorest countries. Anything that improved food and drink, even a little bit, was thus a very big deal. This might be said for all sorts of things — sugar, spices, herbs, new cooking methods — but salt was more like a general-purpose technology: something that enhances the natural flavours of all and any foods. Using salt, and using it well, is what makes all the difference to cooking, whether that’s judging the perfect amount for pasta water, or remembering to massage it into the turkey the night before Christmas. As chef Samin Nosrat puts it, “salt has a greater impact on flavour than any other ingredient. Learn to use it well, and food will taste good”. Or to quote the anonymous 1612 author of A Theological and Philosophical Treatise of the Nature and Goodness of Salt, salt is that which “gives all things their own true taste and perfect relish”. Salt is not just salty, like sugar is sweet or lemon is sour. Salt is the universal flavour enhancer, or as our 1612 author put it, “the seasoner of all things”.
Making food taste better was thus an especially big deal for people’s living standards, but I’ve never seen any attempt to chart salt’s historical effects on them. To put it in unsentimental economic terms, better access to salt effectively increased the productivity of agriculture — adding salt improved the eventual value of farmers’ and fishers’ produce — at a time when agriculture made up the vast majority of economic activity and employment. Before 1600, agriculture alone employed about two thirds of the English workforce, not to mention the millers, butchers, bakers, brewers and assorted others who transformed seeds into sustenance. Any improvements to the treatment or processing of food and drink would have been hugely significant — something difficult to fathom when agriculture accounts for barely 1% of economic activity in most developed economies today. (Where are all the innovative bakers in our history books?! They existed, but have been largely forgotten.)
And so far we’ve only mentioned salt’s direct effects on the tongue. It also increased the efficiency of agriculture by making food last longer. Properly salted flesh and fish could last for many months, sometimes even years. Salting reduced food waste — again consider just how much bigger a deal this used to be — and extended the range at which food could be transported, providing a whole host of other advantages. Salted provisions allowed sailors to cross oceans, cities to outlast sieges, and armies to go on longer campaigns. Salt’s preservative properties bordered on the necromantic: “it delivers dead bodies from corruption, and as a second soul enters into them and preserves them … from putrefaction, as the soul did when they were alive”.2
Because of salt’s preservative properties, many believed that salt had a crucial connection with life itself. The fluids associated with life — blood, sweat and tears — are all salty. And nowhere seemed to be more teeming with life as the open ocean. At a time when many believed in the spontaneous generation of many animals from inanimate matter, like mice from wheat or maggots from meat, this seemed a more convincing point. No house was said to generate as many rats as a ship passing over the salty sea, while no ship was said to have more rats than one whose cargo was salt.3 Salt seemed to have a kind of multiplying effect on life: something that could be applied not only to seasoning and preserving food, but to growing it.
Livestock, for example, were often fed salt: in Poland, thanks to the Wieliczka salt mines, great stones of salt lay all through the streets of Krakow and the surrounding villages so that “the cattle, passing to and fro, lick of those salt-stones”.4 Cheshire in north-west England, with salt springs at Nantwich, Middlewich and Northwich, has been known for at least half a millennium for its cheese: salt was an essential dietary supplement for the milch cows, also making it (less famously) one of the major production centres for England’s butter, too. In 1790s Bengal, where the East India Company monopolised salt and thereby suppressed its supply, one of the company’s own officials commented on the major effect this had on the region’s agricultural output: “I know nothing in which the rural economy of this country appears more defective than in the care and breed of cattle destined for tillage. Were the people able to give them a proper quantity of salt, they would … probably acquire greater strength and a larger size.”5 And to anyone keeping pigeons, great lumps of baked salt were placed in dovecotes to attract them and keep them coming back, while the dung of salt-eating pigeons, chickens, and other kept birds were considered excellent fertilisers.6
1. Edward Hughes, Studies in Administration and Finance 1558 – 1825, with Special Reference to the History of Salt Taxation in England (Manchester University Press, 1934), p.2
2. Anon., Theological and philosophical treatise of the nature and goodness of salt (1612), p.12
3. Blaise de Vigenère (trans. Edward Stephens), A Discovrse of Fire and Salt, discovering many secret mysteries, as well philosophical, as theological (1649), p.161
4. “A relation, concerning the Sal-Gemme-Mines in Poland”, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 5, 61 (July 1670), p.2001
5. Quoted in H. R. C. Wright, “Reforms in the Bengal Salt Monopoly, 1786-95”, Studies in Romanticism 1, no. 3 (1962), p.151
6. Gervase Markam, Markhams farwell to husbandry or, The inriching of all sorts of barren and sterill grounds in our kingdome (1620), p.22
February 26, 2024
The Freedom Convoy’s European echoes
Niccolo Soldo on the widespread protests against the EU and various national governments’ intrusive and anti-human attempts to restrict or destroy European farmers in pursuit of their climate change agenda:
I wish there was a way to measure the gulf between ruling elites and the people that they lord over. Don’t Political Scientists have such a methodology already on hand? I don’t know.
What I do know is that this gulf is very palpable on both sides of The Pond, and that this gulf shows no signs of narrowing any time soon. Whether the issue is migration, crime, COVID-19, etc., it seems that the views of the people are simply ignored by those who can and do ignore them, and proceed to make policy that suits their own interests and the interests of their allies and class.
Judging by American media reporting, you would most likely not be aware that massive farmers’ protests are rocking the European continent as we speak. From Portugal to Poland, farmers are protesting the EU’s drive to push policies like “Net Zero” in order to “combat Climate Change” … policies that would severely impact the livelihoods of our food producers. These proposed changes are entirely top-down, indicative of just how divorced the Brussels elites are from the daily lives of the people whose lives they wish to upend with a stroke the pen. “Oppose us? You must be far right … probably a Nazi too.”
The “far-right” political libel against hard-pressed farmers is really a sign of how far the EU elites have lost touch with the reality of life for the peoples of Europe. We should ignore the slurs, and get behind the fighting farmers.
The protests by angry farmers have spread across the European Union, with mighty convoys of tractors blockading roads and cities from Romania to Rome, from Portugal to Poland, from Bulgaria to Brussels and beyond.
There might be some national variations in the farmers’ specific demands. But what unites them all is opposition to the way that the EU elites are subordinating agricultural policy to their Green agenda and Net Zero obsession, leading to more hardship for farmers and higher food prices for other Europeans.
As tractor convoys blockaded German cities in January, farmers’ association president Joachim Rukwied spelt out that they were protesting not just against the government’s proposed cuts in fuel subsidies, but against an EU-wide system where “agricultural policy is being made from an unworldly, urban bubble and against farming families and rural areas”.
This week in Poland, 62-year-old protesting farmer Janusz Bialoskorski told the media that, “They’re talking about climate protection. But why should it be done at farmers’ expense?” Farmers, he pointed out, are not responsible for industrial pollution, and “nor do we fly to Davos on our jets”.
Pitchfork Populism. The fact that the elites in Brussels have invited this in a year when elections for the EU’s Parliament are scheduled to occur indicates just how out of touch they really are.
These farmers are now in the front line of a wider populist revolt, against those elitists who DO fly in their private jets to the World Economic Forum in luxurious Davos, Switzerland, where they lecture the rest of us about how to save the planet by sacrificing our living standards.
Their protests expose the yawning gap between the high-minded talk of the Brussels Green oligarchy, and the grim reality of what those Net Zero policies mean for normal people in the muddy fields of Flanders or on the supermarket shelves of Florence.
If you can’t shut them up, call them “far right”:
Last weekend, UK Observer newspaper (Sunday sister of the liberal Guardian), the most pro-EU voice in the British media, worried aloud about how the European farmers’ cause “has been enthusiastically adopted by a resurgent populist far-right”.
Similar fears have repeatedly been expressed in the Brussels-backing news media this year: “Brussels struggles to placate farmers as far-right stokes protests,” and “EU farmers egged on by the far-right” (Financial Times); “How the far-right aims to ride farmers’ outrage to power in Europe” (Politico); “Far-right harvests farmers’ anger across Europe” (France 24) etc., etc.
The EU establishment and its media pals are so out of touch with the reality of people’s lives that they apparently imagine Europe’s naïve farmers are protesting only because they have been “egged on” or “stoked up” by “far-right” agitators. The idea that these farmers might be entirely reasonable, hard-working people who are simply at the end of their collective tether with EU bureaucracy seems beyond the comprehension of those bureaucrats and their media mouthpieces.
“A Silent War on Farming”:
As the title of a recent report by the think-tank MCC Brussels puts it, Europe’s agricultural communities are facing nothing less than a “Silent War on Farming,” waged from Brussels.
For decades, EU agricultural policy was about the efficient, cheap, and safe production of food to feed the peoples of Europe and ensure that the continent never suffered famine again. Now, that policy has instead been captured by Green ideology, which demands that farmers use less land and less intensive methods to produce lower emissions. In sum, that must mean less farming—and less food being produced.
Farmers are bearing the brunt of the ideologically-driven regulations imposed by the EU, with falling incomes and the closure of family farms. The rest of Europe faces a scarcity-driven surge in prices—with shortages being met by food imports from countries with far higher emissions than the EU’s hi-tech farming sector.
For many Europeans now supporting the farmers, however, this is about even more than the price of food on their table. Farming and rural communities are at the heart of traditional European ideas of community and self-image. People who live far from the countryside can now identify with farmers who are resisting the same sort of threat to their way of life that they see posed by, for example, EU policies on mass migration.
All Brussels seems to be able to do these days is pass laws to micromanage the lives of Europeans, while increasing the contempt that these same people have for them.
February 17, 2024
Apparently Confucius “had a based libertarian streak”
N.S. Lyons points out some very helpful advice from Confucius that pretty much every western government would benefit from heeding:
I was watching a bit of recent footage of some peasants in revolt, as they are at the moment basically everywhere across the West, and was suddenly struck by the recollection that I’d definitely read a wise saying about the general situation somewhere on a fortune cookie. No, wait, I realized, this time it must actually have been from Master Confucius himself! So I went digging through my copy of the Analects …
Lo and behold, right there in Book 12, Chapter 7, is this straightforward lesson:
A disciple asks Confucius what, fundamentally, it takes to govern a state without it collapsing.
Confucius says: “Simply make sure there is enough armaments, enough food, and that you have the trust of the common people.” (足食,足兵,民信之矣.)
“If sacrificing one of these three things becomes unavoidable, which would you give up first?” the disciple asks. (必不得已而去,於斯三者何先?)
“The weapons,” Confucius replies. (去兵.)
“If two things?” the disciple asks. (必不得已而去,於斯二者何先?)
“The food,” Confucius says, because while even death is a part of life “without the trust of the people, a state cannot stand.” (去食. 自古皆有死,民無信不立.)
What is most notable to me from this little dialogue from almost 2,500 years ago is how much, in comparison, our political leaders, in their hubris and absorption in grand projects (and graft), seem to have forgotten the very basics.
Indeed it strikes me that they already failed on maintaining enough armaments (at least in Europe, though even America now seems to be struggling to produce the most basic munitions). More broadly speaking, they can no long provide security for citizens or defend their own borders.
And now they’ve suddenly got the wise idea of going after the food too, which is a plan that will surely work out great.
January 31, 2024
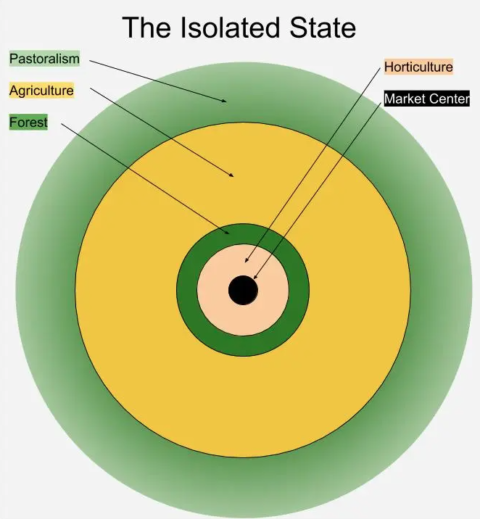
QotD: The inner-most “zones” outside a typical pre-modern city
Diagram of von Thünen’s model from The Isolated State, after Morley (1996), 62. The agriculture ring is subdivided by intensity (intensive, long-lay and three-field), but here I have merged them for simplicity. The agriculture zone is wider because it did, in fact, tend to cover a larger area. The fade in the pastoralism zone is meant to indicate shifts from ranching to transhumance.
We’ll start at the inside, right next to the city and move outward. Imagine each “zone” as a wider concentric circle, moving outward from the city (see the image to the right). Because transportation costs (especially overland) are so high, distance from the city plays a dominant role in how the land is used and thus consequently what the countryside around the city looks like. As you move further and further away, transportation costs interact with the structure of agriculture to make different activities make more sense, creating somewhat predictable patterns.
Land very close to the city is valuable because its produce can reach the market with much lower transportation costs (and pretty much always in a single day’s walk). As a result, if the land can support any kind of productive use, it will not be left empty. Instead, the land is going to be put to the most productive use possible. Improvements that – because of cost or labor – might not be attempted on less valuable land further out will likely be done in close proximity to the city. Stepping out of our ideal model for a moment: this is especially true of irrigation, since cities tend to be on waterways (especially rivers) anyway, making irrigation both more valuable due to low transport costs and easier to accomplish.
Thus land in this innermost zone is likely to be heavily improved (irrigation, terracing to get maximum space out of hills, etc). Labor use will also be intensive, both because it is readily available (you are right next to the major population center) and because labor costs are small compared to the high value of the land. If you have managed to get some farmland right outside the city gates, it is very much worth your time to hire whatever labor you need to get the most out of it, so as to recoup the cost of buying or holding such valuable land.
The other improvement one is likely to do in this zone, at least for growing crops, is make extensive use of fertilizer, which in this case generally means manure. The good news is that this zone is directly next to the city, with its intense concentration of animals and people producing manure, making manure cheaper (yes, people did pay for it). Extensive use of manure lets the fields stay under cultivation more often – being fallowed less frequently. At greater distance, the cost of the manure for this begins to outweigh the value of the extra crops, but so close to the city, land this valuable ought to be kept producing as much as possible.
So what kinds of land use does this lead to? The two key activities that von Thünen identifies are horticulture and dairying, to which I’ll add trough-fed animals like pigs (not quite dairy, but as we’ll see, similar from an economic perspective). Why? Horticulture – the intensive growing of fruits and vegetables, often in small “market gardens” – is labor intensive and offers a high economic yield for the space. Land used for horticulture can be kept under almost continual cultivation (if manured, but see above), but gardens can be fussy and demand quite a lot of labor, compared to hardier plants (like maize corn or wheat). Likewise, dairy animals (which, up close to a large city, will be stall-fed rather than grazed or else transported in “on the hoof” and grazed much further out) and pigs (fed by trough) don’t require much space and offer a high economic yield. Both also produce manure which is in demand near the city for the reasons described above.
The other reason to keep these activities so close to the city is access to the market, for two related reasons. First, fresh dairy products, meats and vegetables spoil rapidly, so they must be gotten to market quickly. Remember that this is a world without refrigeration, so as soon as the plant is picked, the cow is milked or the pig is killed, the clock is ticking on spoilage (yes, there are ways to preserve meat, of course – but we’re talking fresh animal products). Precisely because these foods don’t travel or keep well, they tend to be luxury products as well – something produced for the market and bought by rich non-farmers who live in the city.
So what kind of terrain should we see here? Not open grassland or nice wide open fields. Instead, expect small plots, with clustered buildings, typically clinging to the roads leading into the city. Now – especially in the post-gunpowder age – there might be laws forbidding certain kinds of structures close to the city walls (if the city is walled), which might create some open space (but typically not vast). Likewise, when looking at historical city maps, also be wary: this innermost land-use zone was often contained within the city walls of smaller cities.
The next zone – also quite close to the city in von Thünen’s model is – perhaps somewhat surprisingly – a forest zone. That’s not to say that this is generally wild, uncontrolled forest. The reason for a forest zone at such close distance to the city is to provide wood, particularly firewood for heating. Trees might be arranged intentionally along field separations or on spots of agriculturally marginal land close to the city. Forests like these in the Middle Ages would often have been coppiced or pollarded – that is, the trees would have been intentionally cut to produce lots of long, thin straight branches which can be easily harvested to produce nice, evenly sized bits of wood.
Wood is obviously at no risk of spoiling, but it is heavy and bulky, making a close supply valuable. Moreover, the city will need quite a lot of it, for cooking and heating. That said, trees can often be grown either on very marginal (for agriculture) land or else between fields and farms outside of the city, so these patches of forest might often go on land that is a touch too rough or poor for intensive agriculture, or otherwise be squeezed in between land used for other purposes. Still, it is quite common to find spots of forest next to cities and villages alike.
(To answer a quibble in advance: of course this assumes wood is a key heating element. Societies in more arid climates often lack sufficient wood and might use dung, while wet enough areas may use peat. Historically, London shifted over to using mineral coal earlier than most places. All of these choices will impact the role and importance of forest near the city.)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Lonely City, Part I: The Ideal City”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-07-12.
January 24, 2024
The father of the “Green Revolution”
In the latest review at Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, Jane Psmith reviews The Wizard and the Prophet by Charles C. Mann:
Norman Borlaug is generally estimated to have saved the lives of about a billion people who would otherwise have starved to death.
Yet despite all this — and Borlaug’s is a great story, which Charles Mann tells better and in far more detail than I do above — his book isn’t really a biography of Borlaug or of its other framing figure, early environmentalist William Vogt.1 Rather, it’s a compellingly-written and frankly fascinating overview of various environmental issues facing humanity, and of two different sorts of approaches one can take to addressing them. Mann opens by introducing the two men, but as soon as he’s done that they function mostly as symbols, examples and stand-ins, for these two schools of thought about the world and its problems.
Borlaug is the Wizard of the title, the avatar of techno-optimism: with hard work and clever application of scientific knowledge, we can innovate our way out of our problems. Vogt is the Prophet, the advocate of caution: he points to our limitations, all the things we don’t know and the complex systems we shouldn’t disturb, warning that our constraints are inescapable — but also, quietly, that they are in some sense good.
It’s not hard to identify the Wizards all around us. Inventors and innovators, transhumanists and e/acc, self-driving cars and self-healing concrete … every new device or technique for solving some human problem — insulin pumps! heck, synthetic insulin at all! — is a Wizardly project.
It’s a little more difficult to pin down what exactly the Prophets believe, in part because they spend so much time criticizing Wizardly schemes as dangerous or impractical that it’s easy to take them for small-souled enemies of human achievement.2 That isn’t fair, though — there’s a there there, a holistic vision of the world as an integral organic unity that we disturb at our peril, because the constraints are inextricably linked to the good stuff.
If that seems too abstract, here’s an example. Imagine for a moment (or maybe you don’t have to imagine) that you have a friend who subsists entirely on Soylent. It’s faster and easier than cooking, he says, and cheaper than eating out. He’s getting all his caloric needs met. And he’s freed up so much time for everything else! Now, anyone might express concern for his physical health: does Soylent actually have the right balance of macronutrients to nourish him? Is he missing some important vitamins or other micronutrients that a normal diet might provide? Is the lack of chewing going to make his jaw muscles atrophy? And those are all reasonable concerns about your friend’s plan, but they all have possible Wizardly solutions. (A multivitamin and some gum would be a start.)
If you’re a Prophet sort, on the other hand, you’re probably going to start talking about everything else your friend is missing out on. There’s the taste of food, for one, but also the pleasures of color and texture and scent, the connection to the natural world, the role of community and tradition in shared meals, the way cooking focuses thought and attention on incarnate reality. You might throw around words like “lame” and “artificial” and “sterile” and “inhuman”. Your friend’s Soylent-only plan assumes that the whole point of food is to consume an appropriate number of calories as quickly and easily as possible, hopefully in a way that doesn’t meaningfully degrade his health, but a Prophet rejects his premise entirely. Instead, a Prophet argues that your friend’s food “problem” is actually part of the richly textured beauty of Creation. Yes, feeding yourself and your loved ones delicious, healthful, and economical meals takes time and effort, but that’s simply part of being human.5 You should consider that a challenge to be met rather than a threat to be avoided.
Unfortunately, Mann does the Prophets a disservice by choosing William Vogt as their exemplar. Yes, he was an important figure in the history of the modern environmental movement. Yes, he wrote a very influential book.4 And yes, his careful attention to the integrity of the ecosystems he studied was quintessentially Prophet. But he saw human beings mostly as disruptions to the integrity of those ecosystems, and pretty much every one of his specific predictions — not to mention the predictions of his many followers, most famously Paul Erlich in The Population Bomb5 — have simply failed to come true. Compared to Borlaug’s obvious successes, Vogt’s dire warnings that humanity will soon exhaust the Earth’s capacity and doom ourselves to extinction (unless we abort and contracept our way there first; his second act was as director of Planned Parenthood) seem laughable. Reading about his life can leave you with the impression that Prophets are just people who are more worried about a spotted owl than a starving child, and frankly who cares what those people think?
1. They were roughly contemporaries, but this is emphatically not the story of a pair of rivals; they encountered each other in person only once, in passing, after which Vogt wrote an angry letter to the Rockefeller Foundation demanding they cease Borlaug’s Mexican project at once.
2. And, to be fair, a lot of the language and arguments pioneered by Prophets does get employed by a sclerotic managerial class opposed to anything they can’t fit neatly into their systems and processes and domain-agnostic expertise. But more on that later.
3. Incidentally, this is more or less the argument between the Wizards and the Prophets when it comes to soil. Wizards are delighted with the Haber-Bosch process and artificial fertilizers; Prophets decry the “NPK mentality” that sees the soil as a passive reservoir of chemicals and instead laud composting, manure, and other techniques that encourage the complex interactions between soil organisms, plant roots, and the physical characteristics of humus. This is the origin of the fad for “organic”, a label that doesn’t mean much when applied to industrial-scale food production and is often more trouble than it’s worth for small-time farmers and ranchers. Still, Mann’s story of the movement’s birth is interesting.
4. You’ve probably never heard of it, but it was influential!
5. Apparently out of print! Good.
January 16, 2024
Why Real Dijon Mustard Is So Expensive | So Expensive Food | Business Insider
Insider Business
Published 12 Jul 2022Dijon mustard has a tangier, sharper, and spicier flavor compared to other types of mustard. It takes its name from the town of Dijon in Burgundy, France, where it originated. But despite its name, the majority of Dijon mustard that is sold all over the world doesn’t come from France. The few jars that do will cost you up to six times more than regular Dijon mustard (or double if we want to compare it to Grey Poupon). So how is real Dijon mustard different? And why is it so expensive?
Editor’s Note: In this video, the translations at 2:10 and 3:16 are incorrect. The rind of the mustard seed is wrongly referred to as “sound of mustard”. The correct translation is mustard bran. Insider regrets the error.
(more…)
November 26, 2023
QotD: From Industrial Revolution labour surplus to modern era academic surplus
Back in Early Modern England, enclosure led to a massive over-supply of labor. The urge to explore and colonize was driven, to an unknowable but certainly large extent, by the effort to find something for all those excess people to DO. The fact that they’d take on the brutal terms of indenture in the New World tells you all you need to know about how bad that labor over-supply made life back home. The same with “industrial innovation”. The first Industrial Revolution never lacked for workers, and indeed, Marxism appealed back in its day because the so-called “Iron Law of Wages” seemed to apply — given that there were always more workers than jobs …
The great thing about industrial work, though, is that you don’t have to be particularly bright to do it. There’s always going to be a fraction of the population that fails the IQ test, no matter how low you set the bar, but in the early Industrial Revolution that bar was pretty low indeed. So much so, in fact, that pretty soon places like America were experiencing drastic labor shortages, and there’s your history of 19th century immigration. The problem, though, isn’t the low IQ guys. It’s the high-IQ guys whose high IQs don’t line up with remunerative skills.
My academic colleagues were a great example, which is why they were all Marxists. I make fun of their stupidity all the time, but the truth is, they’re most of them bright enough, IQ-wise. Not geniuses by any means, but let’s say 120 IQ on average. Alas, as we all know, 120-with-verbal-dexterity is a very different thing from 120-and-good-with-a-slide-rule. Academics are the former, and any society that wants to remain stable HAS to find something for those people to do. Trust me on this: You do not want to be the obviously smartest guy in the room when everyone else in the room is, say, a plumber. This is no knock on plumbers, who by and large are cool guys, but it IS a knock on the high-IQ guy’s ego. Yeah, maybe I can write you a mean sonnet, or a nifty essay on the problems of labor over-supply in 16th century England, but those guys build stuff. And they get paid.
Those guys — the non-STEM smart guys — used to go into academia, and that used to be enough. Alas, soon enough we had an oversupply of them, too, which is why academia soon became the academic-industrial complex. 90% of what goes on at a modern university is just make-work. It’s either bullshit nobody needs, like “education” majors, or it’s basically just degrees in “activism”. It’s like Say’s Law for retards — supply creates its own demand, in this case subsidized by a trillion-dollar student loan industry. Better, much better, that it should all be plowed under, and the fields salted.
Any society digging itself out of the rubble of the future should always remember: No overproduction of elites!
Severian, “The Academic-Industrial Complex”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-30.
November 20, 2023
QotD: Flax and linen in the ancient and medieval world
Linen fabrics are produced from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. This common flax plant is the domesticated version of the wild Linum bienne, domesticated in the northern part of the fertile crescent no later than 7,000 BC, although wild flax fibers were being used to produce textiles even earlier than that. Consequently the use of linen fibers goes way back. In fact, the oldest known textiles are made from flax, including finds of fibers at Nahal Hemar (7th millennium BC), Çayönü (c. 7000 BC), and Çatalhöyük (c. 6000 BC). Evidence for the cultivation of flax goes back even further, with linseed from Tell Asward in Syria dating to the 8th millennium BC. Flax was being cultivated in Central Europe no later than the second half of the 7th millennium BC.
Flax is a productive little plant that produces two main products: flax seeds, which are used to produce linseed oil, and the bast of the flax plant which is used to make linen. The latter is our focus here so I am not going to go into linseed oil’s uses, but it should be noted that there is an alternative product. That said, my impression is that flax grown for its seeds is generally grown differently (spaced out, rather than packed together) and generally different varieties are used. That said, flax cultivated for one purpose might produce some of the other product (Pliny notes this, NH 19.16-17)
Flax was a cultivated plant (which is to say, it was farmed); fortunately we have discussed quite a bit about farming in general already and so we can really focus in on the peculiarities of the flax plant itself; if you are interested in the activities and social status of farmers, well, we have a post for that. Flax farming by and large seems to have involved mostly the same sorts of farmers as cereal farming; I get no sense in the Greco-Roman agronomists, for instance, that this was done by different folks. Flax farming changed relatively little prior to mechanization; my impression reading on it is that flax was farmed and gathered much the same in 1900 BC as it was in 1900 AD. In terms of soil, flax requires quite a lot of moisture and so grows best in either deep loam or (more commonly used in the ancient world, it seems) alluvial soils; in both cases, it should be loose, unconsolidated “sandy” (that is, small particle-sized) soil. Alluvium is loose, often sandy soil that is the product of erosion (that is to say, it is soil composed of the bits that have been eroded off of larger rocks by the action of water); the most common place to see lots of alluvial soil are in the flood-plains of rivers where it is deposited as the river floods forming what is called an alluvial plain.
Thus Pliny (NH 19.7ff) when listing the best flax-growing regions names places like Tarragona, Spain (with the seasonally flooding Francoli river) or the Po River Basin in Italy (with its large alluvial plain) and of course Egypt (with the regular flooding of the Nile). Pliny notes that linen from Sætabis in Spain was the best in Europe, followed by linens produced in the Po River Valley, though it seems clear that the rider here “made in Europe” in his text is meant to exclude Egypt, which would have otherwise dominated the list – Pliny openly admits that Egyptian flax, while making the least durable kind of linen (see below on harvesting times) was the most valuable (though he also treats Egyptian cotton which, by his time, was being cultivated in limited amounts in the Nile delta, as a form of flax, which obviously it isn’t). Flax is fairly resistant to short bursts of mild freezing temperatures, but prolonged freezes will kill the plants; it seems little accident that most flax production seems to have happened in fairly warm or at least temperate climes.
Flax is (as Pliny notes) a very fast growing plant – indeed, the fastest growing crop he knew of. Modern flax grown for fibers is generally ready for harvesting in roughly 100 days and this accords broadly with what the ancient agronomists suggest; Pliny says that flax is sown in spring and harvested in summer, while the other agronomists, likely reflecting practice further south suggest sowing in late fall and early winter and likewise harvesting relatively quickly. Flax that is going to be harvested for fibers tended to be planted in dense bunches or rows (Columella notes this method but does not endorse it, De Rust. 2.10.17). The reason for this is that when placed close together, the plants compete for sunlight by growing taller and thinner and with fewer flowers, which maximizes the amount of stalk per plant. By contrast, flax planted for linseed oil is more spaced out to maximize the number of flowers (and thus the amount of seed) per plant.
Once the flax was considered ready for harvest, it was pulled up out of the ground (including the root system) in bunches in handfuls rather than as individual plants […] and then hung to dry. Both Pliny and Columella (De Rust. 2.10.17) note that this pulling method tended to tear up the soil and regarded this as very damaging; they are on to something, since none of the flax plant is left to be plowed under, flax cultivation does seem to be fairly tough on the soil (for this reason Columella advises only growing flax in regions with ideal soil for it and where it brings a good profit). The exact time of harvest varies based on the use intended for the flax fibers; harvesting the flax later results in stronger, but rougher, fibers. Late-pulled flax is called “yellow” flax (for the same reason that blond hair is called “flaxen” – it’s yellow!) and was used for more work-a-day fabrics and ropes.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Clothing, How Did They Make It? Part I: High Fiber”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-03-05.
November 10, 2023
QotD: Economic distortions of slavery in the Antebellum South
This notion that slavery somehow benefited the entire economy is a surprisingly common one and I want to briefly refute it. This is related to the ridiculously bad academic study (discussed here) that slave-harvested cotton accounted for nearly half of the US’s economic activity, when in fact the number was well under 10%. I assume that activists in support of reparations are using this argument to make the case that all Americans, not just slaveholders, benefited from slavery. But this simply is not the case.
At the end of the day, economies grow and become wealthier as labor and capital are employed more productively. Slavery does exactly the opposite.
Slaves are far less productive than free laborers. They have no incentive to do any more work than the absolute minimum to avoid punishment, and have zero incentive (and a number of disincentives) to use their brain to perform tasks more intelligently. So every slave is a potentially productive worker converted into an unproductive one. Thus, every dollar of capital invested in a slave was a dollar invested in reducing worker productivity.
As a bit of background, the US in the early 19th century had a resource profile opposite from the old country. In Europe, labor was over-abundant and land and resources like timber were scarce. In the US, land and resources were plentiful but labor was scarce. For landowners, it was really hard to get farm labor because everyone who came over here would quickly quit their job and headed out to the edge of settlement and grabbed some land to cultivate for themselves.
In this environment the market was sending pretty clear pricing signals — that it was simply not a good use of scarce labor resources to grow low margin crops on huge plantations requiring scores or hundreds of laborers. Slave-owners circumvented this pricing signal by finding workers they could force to work for free. Force was used to apply high-value labor to lower-value tasks. This does not create prosperity, it destroys it.
As a result, whereas $1000 invested in the North likely improved worker productivity, $1000 invested in the South destroyed it. The North poured capital into future prosperity. The South poured it into supporting a dead-end feudal plantation economy. As a result the south was impoverished for a century, really until northern companies began investing in the South after WWII. If slavery really made for so much of an abundance of opportunities, then why did very few immigrants in the 19th century go to the South? They went to the industrial northeast or (as did my grandparents) to the midwest. The US in the 19th century was prosperous despite slavery in the south, not because of it.
Warren Meyer, “Slavery Made the US Less Prosperous, Not More So”, Coyote Blog, 2019-07-12.
October 28, 2023
The transition from burning wood to burning coal
The latest Age of Invention newsletter touches on some of the details Anton Howes uncovered while researching some work on commission for Britain’s NESTA (formerly the National Endowment for Science, Technology and the Arts):

An image of coal pits in the Black Country from Griffiths’ Guide to the iron trade of Great Britain, 1873.
Image digitized by the Robarts Library of the University of Toronto via Wikimedia Commons.
Here are a few key things that I hadn’t really fully appreciated until undertaking this particular commission, though each has provided even more threads I still need to pull on:
ONE. The transition to coal was started by finding ways to exploit the lower-grade, cheaper and more sulphurous coals: initially by finding ways to burn it in people’s homes that would not leave everyone crying and coughing from the stinking fumes; and then with the expanded supply of even the lowest-grade coals making it cost-effective to do things like boil seawater in pans to make salt. The very lowest-grade coal was termed simply “pan coal”. While I’m pretty certain that these innovations were responsible for much of the rise of coal — coal-fuelled salt pans were even the foundation of the Scottish Lowlands economy going into the eighteenth century — the actual inventors involved are still a bit of a mystery. It’s something I need to return to, as “lots of anonymous people just invented through trial and error and adaptation” just doesn’t cut it for me — I’ve never found such stories to be true upon closer investigation.
TWO. Nobody ever talks about lime! Lime was one of the few things burnt with coal since ancient times, but largely to produce mortar for building. The increased availability of cheaper coal in the sixteenth century, however, meant that lime also soon found much wider use as a soil acidity regulator, as well as to control some pests and improve the absorption of fertilisers. It was especially favoured for sandy soils, allowing the conversion of barren heaths to agricultural land by increasing the soil’s water retention.
Yet lime is a huge blind spot for economic historians, despite it increasing the productivity of what was still by far the largest portion of the economy: agriculture. I have a rough and ready test of whether economic historians are paying enough attention to an industry, which is to look up the word in Stephen Broadberry et al.’s British Economic Growth 1270-1870, most scholars’ go-to resource on how historical British output is estimated. Lime is mentioned only once, and only as an input to the construction industry, for mortar. We should know more about lime’s impact.
THREE. Coal, through its various effects on agriculture, also led to an increase in the availability of grain, in turn leading to an abundance of muscle power. Horses were the literal workhorses of industrial cities, grinding the pigments for dyes and paints, tobacco for snuff, charred bones for shoe polish, tannin-rich oak bark for leather, flint for glass and ceramics, and grain for flour, beer, and spirits. Horses fulled cloth, pounded rags into paper, flatted metal into sheets, and bored pipes, guns and even cannon. And of course they powered the transportation infrastructure, hauling the waggons and barges laden with goods.
A theme I keep coming across when I do my research is that there was a lot of effort put into what we might call the “improvement of animals”. I’ve touched on this briefly before, but I get a sense that there’s a whole lot of iceberg lying in wait under the surface for me to uncover. It likely extended to dogs, for example, who like horses were also often used for mechanical tasks. Just yesterday, for example, I read an account by a visitor to 1630s Bristol mentioning how the roasting spits at its inns were driven by dogs in treadwheels. At some point I need to go through all this evidence I’ve inadvertently collected.
FOUR. The Dutch Republic’s Golden Age did not fail because it lacked energy sources. I had already suspected this, as it never rang true, but had not quite appreciated the extent of the evidence: the fairly rapid collapse of so many Dutch industries in the 1650s-80s was, if anything, accompanied by a super-abundance of energy. Both peat and grain were in fact cheaper than ever, largely as a result of plummeting demand. Even the products made using wind —such as the timber sawn for ships along the windy banks of the Zaan river — failed to survive the general collapse in demand.
If energy had been lacking, we would have expected the prices of peat and grain to have been at all-time highs, not in a slump. Indeed, the lack of demand for peat and grain, by sapping demand for infrastructure projects like bog drainage and canal-building, is what led to the re-flooding of much of the Dutch countryside. The causes of the collapse are still something of a mystery to me, but I now feel very confident in ruling the energy theory out.
October 27, 2023
Whisky Folklore – What Is Bourbon? Where Did It Come From?
Townsends
Published 2 Jul 2023Bourbon Whiskey is as American as Hamburgers or the 4th of July. Where did it come from? Where did the tradition start? This episode digs into the history of Bourbon and tries to answer the questions behind this traditional American spirit.
(more…)
September 25, 2023
QotD: The economics of American slavery
Growing cotton … unlike sugar or rice, never required slavery. By 1870, freedmen and whites produced as much cotton as the South produced in the slave time of 1860. Cotton was not a slave crop in India or in southwest China, where it was grown in bulk anciently. And many whites in the South grew it, too, before the war and after. That slaves produced cotton does not imply that they were essential or causal in the production.
Economists have been thinking about such issues for half a century. You wouldn’t know it from the King Cottoners. They assert, for example, that a slave was “cheap labor”. Mistaken again. After all, slaves ate, and they didn’t produce until they grew up. Stanley Engerman and the late Nobel Prize winner Robert Fogel confirmed in 1974 what economic common sense would suggest: that productivity was incorporated into the market price of a slave. It’s how any capital market works. If you bought a slave, you faced the cost of alternative uses of the capital. No supernormal profits accrued from the purchase. Slave labor was not a free lunch. The wealth was not piled up.
The King Cotton school has been devastated recently in detail by two economic historians, Alan Olmstead of the University of California at Davis and Paul Rhode of the University of Michigan. They point out, for example, that the influential and leftish economist Thomas Piketty grossly exaggerated the share of slaves in U.S. wealth, yet Edward Baptist uses Piketty’s estimates to put slavery at the center of the country’s economic history. Olmstead and Rhode note, too, from their research on the cotton economy that the price of slaves increased from 1820 to 1860 not because of institutional change (more whippings) or the demand for cotton, but because of an astonishing rise in the productivity of the cotton plant, achieved by selective breeding. Ingenuity, not capital accumulation or exploitation, made cotton a little king.
Slavery was of course appalling, a plain theft of labor. The war to end it was righteous altogether — though had the South been coldly rational, the ending could have been achieved as in the British Empire in 1833 or Brazil in 1888 without 600,000 deaths. But prosperity did not depend on slavery. The United States and the United Kingdom and the rest would have become just as rich without the 250 years of unrequited toil. They have remained rich, observe, even after the peculiar institution was abolished, because their riches did not depend on its sinfulness.
Dierdre McCloskey, “Slavery Did Not Make America Rich: Ingenuity, not capital accumulation or exploitation, made cotton a little king”, Reason, 2017-07-19.