… humans are hierarchical apes who crave rules. The astonishing number of western converts to Islam (astonishing considering what Islam is as a way of life) particularly the women shows the craving for rules, spoken and unspoken is far stronger than rationality. And the fact that young men aren’t converting en masse to Islam (which gives them a much greater power than any western culture) means some traces of Noblesse Oblige remain. The idea of keeping your women imprisoned and veiled for their protection; the idea that those other men will of course rape them and hurt them; the idea that strange women are fair game, are still revolting and repulsive to men who were told “never hit a girl. Never, ever, ever” as little boys.
Sarah Hoyt, “Noblesse Oblige and Mare’s Nests”, According to Hoyt, 2015-05-05.
February 16, 2019
QotD: The attraction of Islam to would-be converts
February 7, 2019
Cultural nationalism versus cultural imperialism at the CBC
Andrew Coyne reflects on the odd musings of CBC president Catherine Tait:
“There was a time,” Catherine Tait was saying, “when cultural imperialism was absolutely accepted.”
The CBC president was musing, at an industry conference in Ottawa last week, about the heyday of the British and French Empires, when if “you were the viceroy of India you would feel that you were doing only good for the people of India.” Or, “if you were in French Africa, you would think ‘I’m educating them, I’m bringing their resources to the world, and I’m helping them.’ ”
The comments have since come back to bite her, not because many people have a kind word for imperialism these days but because she was comparing those colonial empires, which invaded and conquered territory by force of arms, to the “new empire” of Netflix. As more than one commentator has objected, none of the six million Canadians who subscribe to Netflix was made to do so at the point of a gun.
Neither is it evident what comparable “damage” is done by a service that gives willing viewers in this country access to well-made television programs from around the world. It was, in short, an altogether silly line of argument.
And yet it seems wrong to heap such particular scorn on Tait. For in truth she was only giving voice to the sort of thinking typical of her generation and class: middle-aged cultural bureaucrat/subsidized private producer, of a kind found in particular abundance in the Montreal-Toronto corridor. The same defensive attitudes, what is more, have for decades formed the foundation of much government policy on culture, even if they are largely incomprehensible to a generation raised on Netflix and YouTube.
There was a time, that is, when cultural nationalism was absolutely accepted — when it was taken as a given among the educated classes that it was the responsibility of government to protect and defend Canadian culture, if necessary from Canadians themselves. Hence the whole apparatus of CanCon, most of which is still with us today.
QotD: Generation Z begins to hit adulthood
Those born after 1998 are currently (and quite unimaginatively) being called Generation Z. And, by Pew’s math, the eldest members of this nascent generation are turning 18 this year [2017].
Welcome to adulthood, Gen Z!
As one of the oldest members of your immediate ancestors in American youth, I’d like to officially transfer the think-piece mantle your way. As millennials’ misadventures in youthful entitlement and narcissism dwindle, may your place as a scapegoat for societal fears about sex, technology, and general change shine bright. May Gen X prove as much a collective nemesis for you as boomers have so generously done for my generation. And, perhaps most importantly, may you please be patient in a few years when you’re trying to explain to us how to upload a hologram snap to Mind Twitter.
Also, for what it’s worth, millennials may have spawned Facebook, but don’t blame us if Americans are more politically polarized these days. According to another recent generational study, it’s the oldest Americans who have grown the most polarized within their own generation in recent decades. While many people attribute political polarization to social media or the internet more broadly, the study’s authors found that, between 1996 and 2012, the increase in polarization was “largest among the groups least likely to use the internet and social media.” On a nine-point measure of different sorts of polarization, the gap grew by 0.38 index points for respondents ages 75 and older, but just 0.05 index points for adults ages 39 and below.
Lastly, don’t get too comfortable, kids — your generational predecessors are already arriving. Going by Pew’s parameters, the typical generation spans about 17 years … which means that the last of Gen Z babies were likely born in 2016. A new generation starts being born this year.
Welcome to the world, post-Gen Z generation! What a weird, absurdist time to be starting your lives. May we course correct a bit here before you hit adulthood. (Alternately, tell your kids to give President Ivanka’s reanimated corpse and V.P. Chelsea Clinton’s cryogenically frozen head my love, and sorry about the Kardashians. That one really is our fault.)
Elizabeth Nolan Brown, “Welcome to Adulthood, Gen Z: The post-millennial generation starts turning 18 this year, while the eldest members of the post-Gen Z cohort are starting to be born.”, Reason, 2017-03-22.
February 6, 2019
“The haggis croquette is the most London-thing ever done in London”
At the IEA, Andy Mayer reports on the first attempted Burns Night Supper in the City of London:
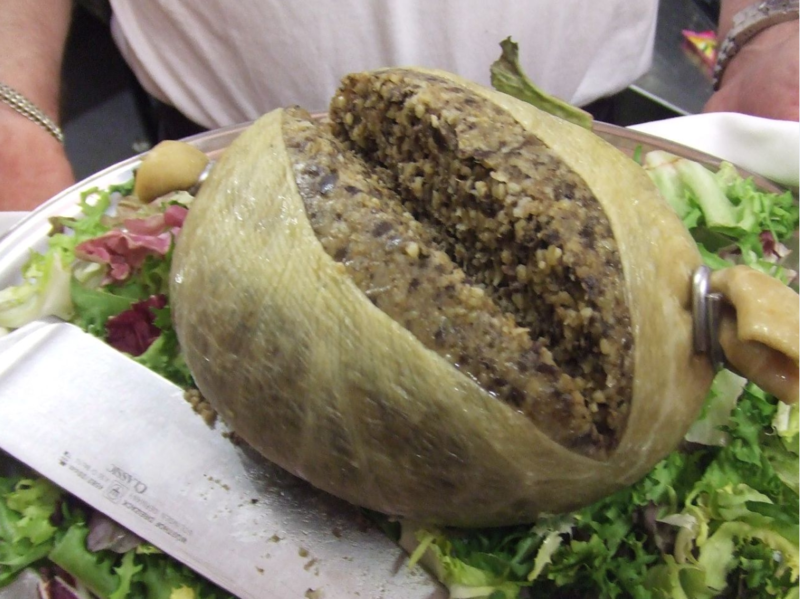

Haggis is a traditional Scottish dish made with sheep’s heart, liver and lungs, and stomach (or sausage casing); onion, oatmeal, suet, and spices. It’s either a local delicacy or an elaborate joke played on the English (take your pick).
Photo by “Lordvolom1” via Wikimedia Commons.
Last week the City of London held their first attempt at a Burns night supper, with the First Minister and representatives of the Scottish Government as guests of honour.
It is a difficult tradition to get wrong. Largely it requires steaming piles of Scotland’s revenge on the sausage, poetry that the English politely pretend to understand while feeling vaguely threatened, and bonhomie to overcome it, enabled through litres of distillate infused with the flavour of an entire peat bog.
The City served haggis croquettes, with wine.
There’s possibly a Glaswegian satirist somewhere who’s just given up. “Ach I canne compete. The sassenach dough-monkeys just served wee Nicola a haggis croquette, on Rabbie Burns night! I’m breaking-me pen.”
Meanwhile in Shoreditch two Millenials have just set up the Haggis Croquette Cafe, serving Organic Iron-Bru made from recycled plastic girders. The haggis croquette is the most London-thing ever done in London.
I spent much of the evening talking to trade officials. Their job is to sell Scottish opportunity around the world and open up its markets.
This was interesting – how would descendants of Adam Smith visiting the birthplace of trade economist David Ricardo define their comparative advantage? What can Scotland do better than anyone else? What might they do well enough that they can carve out positions, despite larger rivals, better off leaving such things to Scotland? Fundamentally, how are they going to compete?
There was an uneasy pause after these questions. And then to paraphrase, “Oh no, we don’t want to compete, we want to cooperate! With everyone! Not being threatening, that’s our advantage!”
I feel very sure that Smith, on hearing this, would have reached out, to extend the invisible hand of history across time, to give this official a mild slap. “Encouraging competition, with and from other places, and then getting out of the way, is the whole point”, he might say.
February 4, 2019
Jane Austen – Sarcasm and Subversion – Extra History
Extra Credits
Published on 2 Feb 2019Jane Austen wrote in the name of making critical social commentary of the privileges she and others held while the rest of Europe was in political turmoil. Her novels like Pride and Prejudice, Mansfield Park, and Emma made waves in their time for how they criticized
VictorianRegency-era society.
Join us on Patreon! http://bit.ly/EHPatreon
From the comments:
Extra Credits
2 days ago
Jane Austen saw the hypocrisy of an entire class of the most powerful empire on Earth taking tea and planning balls while the world burned. And from a young age she took up arms against that hypocrisy with the only weapon she had: her pen.(Comment from Belinda) I don’t know if anyone else has had this experience with Jane Austen’s works, but in the educational culture I grew up in, the historical context of Austen’s writing was almost never emphasized. Pride & Prejudice in particular is frequently reduced to being the original formula for romantic comedies (to say nothing of its own spin-off movies of the same name). I remember in high school class it seemed really weird to me that we would be talking about this 19th century novel as a progressive feminist work because it’s already a given in the 21st century world that marrying for love is extremely commonplace. I’m really proud of our writers Jac and Rob, and our artist Ali, for bringing to life the “extra History” of Jane Austen that gets glossed over by popular culture. <3
February 3, 2019
January 22, 2019
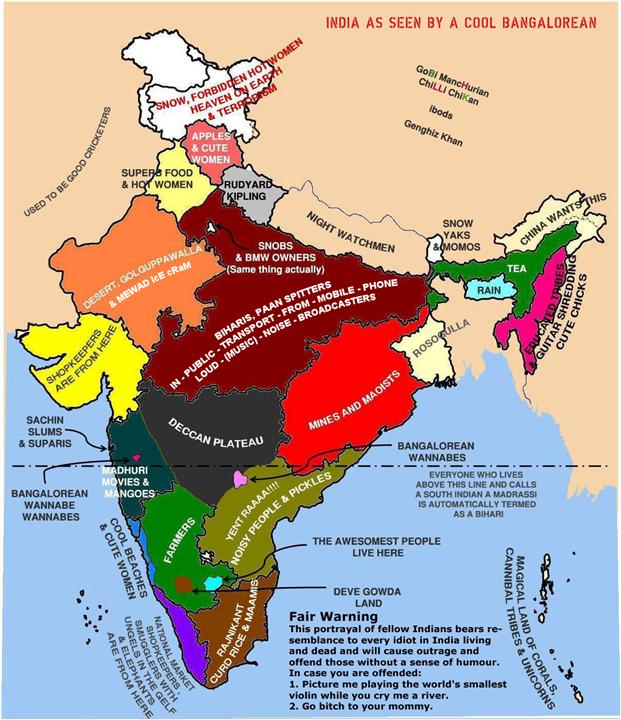
Ending India’s longstanding caste system privileges
In the Continental Telegraph, Tim Worstall outlines the political change that might end up undermining the caste system to a large degree:
India has long had a series of reservations and quotas for varied classes. Dalits – formerly the untouchables – have long had privileges in access to university and government jobs for example. Over time, as such political systems do, the list of those classes privileged has grown.
Obviously enough, as such political systems do work, a major cause of unrest has been further classes, castes and groupings demanding that they be added to the list of groups that receive such privileges. And given electoral cycles that list has grown. The cynic will not be surprised to find that the surest method of a group being added to the list is to be the swing vote in a hotly contested election. We’re not talking about purity of motive here.
Of course, such a system eats away at the nation – we get into that communal division of the spoils rather than the lovely capitalist and free market game of increasing the spoils to be argued over. Which leaves us with a certain problem, leaves India with a certain problem.
[…]
If everyone’s covered by a reservation, if all are so privileged, then sure, we’ve an inefficient system still but we have also effectively abolished the value of having a reservation, a privilege. Thus the solution, the end game. So devalue the privilege as to make it effectively not exist by extending it to everyone.
January 10, 2019
QotD: Pacifism
The majority of pacifists either belong to obscure religious sects or are simply humanitarians who object to the taking of life and prefer not to follow their thoughts beyond that point. But there is a minority of intellectual pacifists whose real though unadmitted motive appears to be hatred of western democracy and admiration of totalitarianism. Pacifist propaganda usually boils down to saying that one side is as bad as the other, but if one looks closely at the writings of younger intellectual pacifists, one finds that they do not by any means express impartial disapproval but are directed almost entirely against Britain and the United States. Moreover they do not as a rule condemn violence as such, but only violence used in defence of western countries. The Russians, unlike the British, are not blamed for defending themselves by warlike means, and indeed all pacifist propaganda of this type avoids mention of Russia or China. It is not claimed, again, that the Indians should abjure violence in their struggle against the British. Pacifist literature abounds with equivocal remarks which, if they mean anything, appear to mean that statesmen of the type of Hitler are preferable to those of the type of Churchill, and that violence is perhaps excusable if it is violent enough. After the fall of France, the French pacifists, faced by a real choice which their English colleagues have not had to make, mostly went over to the Nazis, and in England there appears to have been some small overlap of membership between the Peace Pledge Union and the Blackshirts. Pacifist writers have written in praise of Carlyle, one of the intellectual fathers of Fascism. All in all it is difficult not to feel that pacifism, as it appears among a section of the intelligentsia, is secretly inspired by an admiration for power and successful cruelty. The mistake was made of pinning this emotion to Hitler, but it could easily be retransfered.
George Orwell, “Notes on Nationalism”, Polemic, 1945-05.
January 8, 2019
QotD: RINOs and other soft conservatives
The RINOs you complain about are RINOs now but they weren’t always. I don’t know how many of you remember the seventies. The right here was kind of like the right in Europe. It assumed that in the end communism would not only win, but DESERVED to win, and what the right disagreed with was the way to get there. It is useful to remember this was a time when William Buckley’s dictum that conservatism was “Standing astride History yelling stop” found deep resonance. Unpack that phrase. It assumes history comes with an arrow, that it’s not going our way, and that at best we can get it to pause.
Those RINOs who, by the way, took immense flack back then were as conservative as anyone dared to be. Because everyone knew in the end the reds won.
Then the wall fell down and we knew what true horrors lurked on the other side.
Individuals process these things fast enough. Well, my generation, at any rate, awakened by Reagan and shown that the win of the dark side was not inevitable, was more pro-freedom than people ten years older than us.
But when we saw the wall fall down, it pushed many of us further into the liberty side of the isle. Not only wasn’t a communist win inevitable, but their vaunted “strengths” like superior planning and better minority integration didn’t exist unless you really wanted to plan for three million size thirty boots for the left foot only, and integration meant grinding the minorities very fine and spreading them in the soil.
However cultures aren’t individuals. Cultures re-orient and process startling events very slowly.
Yeah, those older Republicans are still with us, and they were over 45 when the wall fell, which means they couldn’t reorient anymore. (Studies have been done.)
Sarah Hoyt, “The Long March”, According to Hoyt, 2015-12-20.
January 1, 2019
Whither European fine art?
It’s apparently not just problematic because the vast majority of it was produced by dead white males, but it’s also now considered to be a totem of white supremacist beliefs:
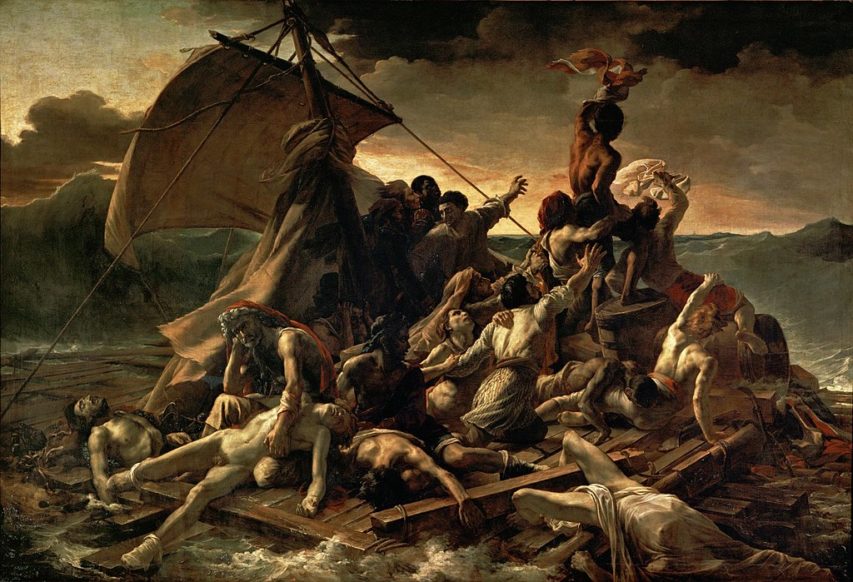

“The Raft of the Medusa” (French: Le Radeau de la Méduse) by Théodore Géricault 1818-19, an oil-on-canvas painting measuring 491 cm × 716 cm (16 ft 1 in × 23 ft 6 in)
Louvre, image via Wikimedia Commons.
A Philadelphia-based art historian and curator believes exhibitions of European art in American museums should be “reconsidered” in light of “a surge in white supremacist violence” across the country.
Alexander Kaufmann says that “[b]ecause the centering of Europe is baked into the architecture” of museums, and “usually inhabit the largest and most central galleries,” people might not notice a connection to white supremacy.
“But white supremacists do,” he adds ominously.
“Europe’s cultural prestige is their evidence for the racial superiority of white America,” Kaufmann writes in Hyperallergic. White supremacists and white nationalists gather at museums because that’s “where Europe’s cultural patrimony is most visibly singled out as exceptional.”
White supremacy notwithstanding, American museums’ original missions — “provid[ing] instruction for the industrial classes” and helping the country achieve the goal of becoming the “noblest development of humanity” — have long required a response, Kaufmann argues, and the activism of groups like the Black Emergency Cultural Coalition and the Guerrilla Girls can provide just that.
“After the violence in Charlottesville, Charleston, and Pittsburgh,” Kaufmann says, “our encyclopedic museums must take steps within their galleries of European Art to combat white supremacist ideology.” (But are women who run around in gorilla masks “to expose gender and ethnic bias [and] corruption in politics, art, film, and pop culture” really part of a serious solution?)
December 21, 2018
Why do we celebrate Christmas in December?
The obvious answer is quite wrong: December 25th isn’t actually the birth date of Jesus … we don’t know when he was born (rather like the Queen’s Official Birthday, it’s been set to a particular date rather than tracking the actual natal day of the current monarch). So why did we end up with a fixed date in December? Tim Worstall explains:
… if you’re sitting in the middle of a culture that has a religious holiday that sends all children into a frenzy, you’re not part of that dominant religion, then you’d better come up with something quick. Don’t and you’ll find your hold on the minds – thus future religion of – the children loosening. Thus Hanukkah’s elevation in the holiday, if not liturgical, calendar. Thus, also, obviously the invention of Kwanzaa by those who would very much prefer not to be part of that dominant culture but were rather geographically stuck with it.
But then that’s why Jesus wasn’t born at Christmas too. We have absolutely no evidence at all that he turned up even one winter night let alone on Dec 25. What the Catholic Church in Europe did have – and at the relevant time there really only was the Catholic Church – was this inconvenient fact of a massive winter feast, what we might call Yuletide. This was very definitely pre-Christian and was sorta determined by climate.
You’re in Europe, you’re doing subsistence or at least peasant farming, this means you’ve not got enough fodder to keep all the animals going until the spring. Thus you slaughter near all – pigs not so much as they eat scraps, can forage for themselves etc – except your breeding stock. This gives you lots and lots of fresh meat and few good methods of meat preservation. This is also the last fresh meat you’re going to get until those spring lambs are ready in, say, April. So, you gorge on all that fresh meat.
Also, it’s cold outside, the days are short, why the heck not stay in by the fire while you burp through it all? Hey, bring the family ’round! And Pops, didn’t you get that beer going earlier in the year? OK, no hops, so ale. But mead maybe. Wine in many areas would be just about drinkable by now from that autumn crop.
This had been going on perhaps 6,000 years by the time those Christians turned up. The Church really needed to impose its views and authority on all of this, seriously, we can’t have the peasants continuing to celebrate the Old Gods, can we? Thus the invention of Christmas, a time for celebration, that called for lots of feasting of a happy event just about the time when everyone would be feasting anyway.
This is also the explanation for Halloween, All Hallows Eve. Or, All Souls Day followed By All Saints Day to replace the Celtic Samhaim. Hell, the oiks are going to be celebrating anyway, better make it a Church celebration.
Thus Hanukkah, thus Kwanzaa and thus whatever the next religion will come up with assuming that it’s one that initially grows in a European influenced culture. Even, perhaps any Northern Hemisphere, or northerly part of it, influenced one. Islam’s going to have a problem as it uses the lunar calendar and so no fixed feast will work, it’ll precess though the calendar and miss the yearly meeting with midwinter.
Hanukkah’s a big thing for the same reason Jesus wasn’t born at Christmas. At which point you’re expecting me to say Happy Holidays, aren’t you? Bah, Humbug!
QotD: “Baby, it’s cold outside”
Speaking of immorality, MGM’s censors cut the wrong song. A few decades back, a young middle-class Egyptian spending some time in the US had the misfortune to be invited to a dance one weekend and was horrified at what he witnessed:
The room convulsed with the feverish music from the gramophone. Dancing naked legs filled the hall, arms draped around the waists, chests met chests, lips met lips …
Where was this den of debauchery? Studio 54 in the 1970s? Haight-Ashbury in the summer of love? No, the throbbing pulsating sewer of sin was Greeley, Colorado, in 1949. As it happens, Greeley, Colorado, in 1949 was a dry town. The dance was a church social. And the feverish music was “Baby, It’s Cold Outside,” as introduced by Esther Williams in Neptune’s Daughter. Revolted by the experience, Sayyid Qutb decided that America (and modernity in general) was an abomination, returned to Egypt, became the leading intellectual muscle in the Muslim Brotherhood, and set off a chain that led from Qutb to Zawahiri to bin Laden to the Hindu Kush to the Balkans to 9/11 to the brief Muslim Brotherhood takeover of Egypt to the Islamic State marching across Syria and Iraq. Indeed, Qutb’s view of the West is the merest extension of “Baby, It’s Cold Outside” — America as the ultimate seducer, the Great Satan.
I’m a reasonable chap, and I’d be willing to meet the Muslim Brotherhood chaps halfway on a lot of the peripheral stuff like beheadings, stonings, clitoridectomies and whatnot. But you’ll have to pry “Baby, It’s Cold Outside” from my cold dead hands and my dancing naked legs. A world without “Baby, It’s Cold Outside” would be very cold indeed.
Mark Steyn, “Baby, It’s Cold Outside”, Steyn Online, 2014-12-01.
December 20, 2018
China’s Cultural Revolution
In Quillette, James David Banker describes the beginnings of Mao Zedong’s Cultural Revolution:

“The Chinese People’s Liberation Army is the great school of Mao Zedong Thought”, 1969.
A poster from the Cultural Revolution, featuring an image of Chairman Mao, published by the government of the People’s Republic of China.
Image via Wikimedia Commons.
“Nobody is more dangerous than he who imagines himself pure in heart,” wrote James Baldwin, “for his purity, by definition, is unassailable.” This observation has been confirmed many times throughout history. However, China’s Cultural Revolution offers perhaps the starkest illustration of just how dangerous the “pure in heart” can be. The ideological justification for the revolution was to purge the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), and the nation more broadly, of impure elements hidden in its midst: capitalists, counter-revolutionaries, and “representatives of the bourgeoisie.” To that end, Mao Zedong activated China’s youth — unblemished and uncorrupted in heart and mind — to lead the struggle for purity. Christened the “Red Guards,” they were placed at the vanguard of a revolution that was, in truth, a cynical effort by Mao to reassert his waning power in the Party. Nevertheless, it set in motion a self-destructive force of almost unimaginable depravity.
The Cultural Revolution commenced in spirit when Mao published a letter indicting a number of Party leaders on May 16, 1966. But it was a seemingly minor event nine days later that ignited the revolution in effect: a young philosophy professor at Peking University named Nie Yuanzi placed a “big-character poster” (a handwritten propaganda sheet featuring large Chinese characters) on a public bulletin board denouncing the university president and others in the administration as bourgeois revisionists. Mao immediately endorsed her protest, which set off a chain reaction of student revolt that swept through China.
That chain reaction was accelerated by “working groups” of ideologues sent to administer schools. Under their tenure, schools became centers of activism rather than learning. Students were encouraged to create big-character posters exposing their own teachers, officials, and even parents. The accused were humiliated in daily “struggle sessions” in which their students and colleagues interrogated them and demanded confessions. The viciousness of these sessions rapidly intensified. Students beat, spat upon, and tortured — in horrifically creative ways — their often elderly teachers and professors. In one case, students demanded their biology professor stare at the sun with wide open eyes. If he blinked or looked away, they beat him. Even middle and elementary school students participated in the struggle sessions, sometimes beating their teachers to death with sticks and belt buckles.
Students were also encouraged to turn on their classmates. As the sins of one generation passed to the next, a new hierarchy was born: the children of revolutionaries on top and the children of “landlords,” “capitalists,” and “rightists” at the bottom. These students were labeled “rotten eggs” and were fair game for the same treatment meted out to their parents. The current president of the People’s Republic of China, Xi Jinping, endured this fate. He was only 15 years old when his father, a loyal Maoist and one-time propaganda chief, was purged, his sister executed, and his own mother forced to denounced Xi as a reactionary. Amid the hysteria, teachers, professors, and intellectuals did not dare to stand up to the students or defend their colleagues lest they suffer similar fates. But they could not escape by being bystanders. With every word and action becoming potential evidence of capitalist sympathy, teachers and intellectuals enthusiastically joined their students in the struggle sessions and screaming rallies.
QotD: An “authentic” peasant diet
The fact is that you wouldn’t want to eat like a European peasant of yesteryear, or a Chinese peasant, either. Sure, peasants ate well when the garden was producing and the harvest was ripe. A lot of the year, they ate pretty meager, dull fare. Many of the spices we now take as ordinary — salt and pepper, for example — were pretty pricey. So were meat and cheese, which, like everything else, tended to get pretty scarce in winter. When you read about what people were actually eating most of the year, you realize that diets were dull, repetitive, and heavy on grains and legumes, lightly complimented by salted and dried things (home canning, like many of the other things we think of as traditional, was another Industrial Revolution contribution, and before modern farming practices, cows tended to be “dried off” in the winter to save the expense of the extra feed a milking cow needed). And this stayed true throughout the 19th century for large swaths of the population in both America and abroad.
The farther north you went, the more this was true — it’s probably no accident that Ireland and Scandinavia are not, let us say, renowned for their fantastic contributions to world cuisine. When your growing season is a short cloudy period between miserable winters, you don’t have the raw materials to construct amazing dining experiences. (Sure, every country has at least one or two really good fairly traditional foods. But the shorter the time fresh ingredients are available, the fewer culinary marvels you’ll be able to produce.)
Too, we must remember that not everyone was a good cook. Cooking was a job, not an absorbing hobby, and as with any other job, many people did it badly. Every farm wife could produce enough calories to feed her family (at least, if the raw materials were available). Not all of them could produce anything you’d want to eat. Modern food-processing technology has relieved us of that most “authentic” culinary experience: boring ingredients processed by an indifferent cook into something that you’d only voluntarily consume if you were pretty hungry. Even the memory of these cooks has fallen away, though you’ll encounter a lot of them if you read old novels.
Megan McArdle, “‘Authentic’ Food Is Not What You Think It Is”, Bloomberg View, 2017-02-24.
December 10, 2018
QotD: No one “owns” a culture
To own something is to have the rights (1) to determine exclusively how it is used, (2) to appropriate exclusively any income or other benefits it yields, and (3) to transfer the foregoing rights to others by sale, gift, or bequest. In this light, it is clear that no one owns a culture, and hence no one may legitimately seek state violence for the defense of such asserted property rights.
One may have preferences about culture. One may have affections for or aversions to a culture or particular elements of a culture. But such preferences do not entail any rights of ownership. Moreover, all cultures are constantly changing to a greater or lesser degree by spontaneous, decentralized processes, including interaction with other cultures. Such interaction has always been the case except for the cultures of people completely isolated from the rest of the world.
To treat the arrival of new members of society who live to some degree in accordance with different cultures as if these persons were “invaders” who threaten to destroy one’s culture is simultaneously to evince little faith in the attractiveness and strength of one’s culture and to seek its defense as the enforcement of property rights where no such rights exist.
Robert Higgs, “No One Owns a Culture”, The Beacon, 2018-11-19.