One of the reasons I’m in favour of small government is because big government tends to be remote government, and remote government is unaccountable, and, as a wannabe world government, the UN is the remotest and most unaccountable of all. If the sentimental utopian blather ever came true and we wound up with one “world government”, from an accounting department point of view, the model will be Nigeria rather than New Hampshire.
Mark Steyn, “Would you trust these men with $64bn of your cash? Of course not”, Telegraph Online, 2005-02-06.
May 5, 2021
QotD: The United Nations
May 3, 2021
History Summarized: Pope Fights 2 — The Reformation
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 26 Apr 2019Thank you to our Patron Peter Bemis for commissioning this video! To support the channel, head over to Patreon.com/OSP
You’ve seen the Double-Pope matchup, but what about the Double-Christianity face-off? Today’s Pope Fights covers the history and aftermath of the Protestant Reformation and Catholic Counter-Reformation.
FURTHER READING, from shortest to longest books:
The Reformation: A Very Short Introduction — https://www.amazon.com/Reformation-Ve…
Christianity In The West (1400-1700) — https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/019…
The Reformation: A History — https://www.amazon.com/The-Reformatio…DISCORD: https://discord.gg/ZufVWse — Come one come all to the official OSP discord server!
MERCH LINKS:
Shirts – https://OverlySarcasticProducts.Threa…
All the other stuff – http://www.Cafepress.com/OverlySarcas…OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter @OSPYouTube!
April 21, 2021
Hitler’s Money and How He Stole It – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 20 Apr 2021On paper, Hitler never made a lot of money. Yet he became one of the wealthiest people of his time. This is how he stole his fortune.
Between 2 Wars: Zeitgeist!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KThHc…
Hitler Never Gave the Order – So Who Did? – WW2 Special
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uQsGU…
The Nazis: Most Notorious Art Thieves in History – WW2 Special: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tXvo-…
Why the Nazis Weren’t Socialists – “The Good Hitler Years” | BETWEEN 2 WARS I 1937 Part 2 of 2
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YHAN-…Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sources
—
Hosted by: Spartacus Olsson
Written by: Joram Appel and Spartacus Olsson
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Joram Appel
Edited by: Karolina Dołęga
Sound design: Marek KamińskiColorizations by:
– Daniel Wiess
– Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
– KlimbimSources:
Picture of building appartement on Prinzregentenplatz 16, Munich in 1910. courtesy of Stadtarchiv München, DE-1992-FS-NL-PETT1-2847 https://stadtarchiv.muenchen.de/scope…
– Bundesarchiv
– National Archives NARA
– Imperial War Museum: IWM Art.IWM PST 4099
– United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
– Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
– Nationaal Archief
– The picture of the Eagle’s Nest in 2020 courtesy of Marcus Hebel from Wikimedia – https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
– The picture of the Eagle’s Nest in 2014 courtesy of Nordenfan – from Wikimedia https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
– Icons from The Noun Project: barracks by Smalllike, Cook by Alice Design, Farm by Laymik, football field by Mavadee, House by Abhimanyu Bose, Kitchen by RD Design, Library by Adrien Coquet, Housekeeper by Richie Romero, Old Car by Halfazebra Studio, Pool by Loritas Medina, Projector by Ralf Schmitzer, Waiter by chris dawson, Woman by Deemak Daksina, Woman by Wilson Joseph, Woman hat by Xinh Studio, Woman With a Hat by Graphic EnginerSoundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
– “The Inspector 4” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “London” – Howard Harper-Barnes
– “Other Sides of Glory” – Fabien Tell
– “Rememberance” – Fabien Tell
– “Deviation In Time” – Johannes Bornlof
– “Break Free” – Fabien Tell
– “March Of The Brave 10” – Rannar Sillard – Test
– “Ominous” – Philip Ayers
– “Symphony of the Cold-Blooded” – Christian Andersen
– “Please Hear Me Out” – Philip AyersArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
January 6, 2021
The Use and Abuse of the US Postal System (feat. Mr. Beat)
The Cynical Historian
Published 10 Oct 2020Thanks to Private Internet Access for sponsoring this video. Click here to get 77% off and 3-months free: http://www.privateinternetaccess.com/…
We’ve been seeing a lot of coverage about the post office here in the United States. A lot of folks talk about the history of it, but generally in a piecemeal fashion. The fact most of this commentary lacks is that the post office has always been a political tool, from its beginnings even before the US Constitution. Interestingly enough, what it has been used for over the years has changed substantially, but it is always a harbinger of the up and coming dominant ideology. The post office is a cornerstone of our democracy. The postal system in the United States is uniquely important.
Check out Mr. Beat’s video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=favVdKa6cRQ
————————————————————
Connected videos:
3:30 – 1776 | Based on a True Story: https://youtu.be/xY4Te8Qm07A
9:15 – What caused the Mexican-American thing? https://youtu.be/HTmSN4Exci0
9:15 – What Caused the Texas Revolution? https://youtu.be/lDWH-DC74Pk
9:25 – California Gold Rush: https://youtu.be/W1dmyx6LBKA
9:30 – History of California: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
11:30 – The Sectional Crisis: https://youtu.be/Ff2AKILyi0o
14:05 – History of Voting by Mail: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=favVd…
18:25 – Trains and Oil in California: https://youtu.be/0Ef0Ir-hbFc
18:30 – The History of Early Flight: https://youtu.be/sPgxuD0uYYE
20:35 – US Veterans History: https://youtu.be/ANUqaNykuRs
————————————————————
references:
The United States Postal Service: An American History (Washington, DC: United States Postal Service, 2020). https://about.usps.com/publications/p… [PDF]USPS’s website has a trove of information on their history: https://about.usps.com/who-we-are/pos…
The national postal museum is run by the Smithsonian and includes numerous research articles available to anyone on their website: https://postalmuseum.si.edu/research-…https://www.nationalgeographic.com/hi…
————————————————————
Support the channel through PATREON:
https://www.patreon.com/CynicalHistorian
or by purchasing MERCH: teespring.com/stores/the-cynical-hist…
LET’S CONNECT:
Discord: https://discord.gg/Ukthk4U
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Cynical_History
Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/CynicalHistory/————————————————————
Wiki: The United States Postal Service (USPS; also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service) is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the United States, including its insular areas and associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the United States Constitution.
The USPS traces its roots to 1775 during the Second Continental Congress, when Benjamin Franklin was appointed the first postmaster general. The Post Office Department was created in 1792 with the passage of the Postal Service Act. It was elevated to a cabinet-level department in 1872, and was transformed by the Postal Reorganization Act of 1970 into the United States Postal Service as an independent agency. Since the early 1980s, many direct tax subsidies to the USPS (with the exception of subsidies for costs associated with disabled and overseas voters) have been reduced or eliminated.
————————————————————
Hashtags: #history #USPS #USMail
December 12, 2020
Trains and Oil | California History [ep.8]
The Cynical Historian
Published 4 Jul 2019After a long hiatus, here is the return of the History of California series. For those who haven’t seen the previous episodes, here’s the playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Today we’re going over the history of transcontinental railroads, monopolistic practices, and crude oil production in California.
————————————————————
references:
eds. Richard Francaviglia and David Narrett, Essays on the Changing Images of the Southwest (Arlington: University of Texas at Arlington, 1994). https://amzn.to/2JwNiHkWilliam H. Goetzmann, Army Exploration in the American West, 1803-1863, new ed. (1959; Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 1979). https://amzn.to/2K8tslY
Paul Sabin, Crude Politics: The California Oil Market, 1900-1940 (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005). https://amzn.to/2W16gtt
Jules Tygiel, The Great Los Angeles Swindle: Oil, Stocks, and Scandal During the Roaring Twenties (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1996). https://amzn.to/2ASH7Z0
Richard White, Railroaded: The Transcontinentals and the Making of Modern America (New York: W.W. Norton, 2011). https://amzn.to/2zkURO3
————————————————————
Support the channel through PATREON:
https://www.patreon.com/CynicalHistorianLET’S CONNECT:
Discord: https://discord.gg/Ukthk4U
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Cynical_History
————————————————————
Wiki: The history of the Southern Pacific stretches from 1865 to 1998. For the main page, see Southern Pacific Transportation Company; for the former holding company, see Southern Pacific Rail Corporation. The Southern Pacific was represented by three railroads. The original company was called Southern Pacific Railroad, the second was called Southern Pacific Company and the third was called Southern Pacific Transportation Company. The third Southern Pacific railroad, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, is now operating as the current incarnation of the Union Pacific Railroad.The story of oil production in California began in the late 19th century. In 1903, California became the leading oil-producing state in the US, and traded the number one position back-and forth with Oklahoma through the year 1930. As of 2012, California was the nation’s third most prolific oil-producing state, behind only Texas and North Dakota. In the past century, California’s oil industry grew to become the state’s number one GDP export and one of the most profitable industries in the region. The history of oil in the state of California, however, dates back much earlier than the 19th century. For thousands of years prior to European settlement in America, Native Americans in the California territory excavated oil seeps. By the mid-19th century, American geologists discovered the vast oil reserves in California and began mass drilling in the Western Territory. While California’s production of excavated oil increased significantly during the early 20th century, the accelerated drilling resulted in an overproduction of the commodity, and the federal government unsuccessfully made several attempts to regulate the oil market.
————————————————————
Hashtags: #history #California #trains #oil
November 8, 2020
QotD: Tribal and post-tribal economies
… it was a problem of permitting, by and large. Portugal isn’t as bad, mind, nowhere near but in the seventies a lot of places were designated “green belts” everywhere, so that to build on them (and you had to build on them, or you were stymied in growth) you had to know who to bribe, and of course have the money to do it. This isn’t the only reason why favelas end up housing even the middle class. There’s a ton of other reasons, including but not limited to land ownership and property rights, and a shit-ton of stuff. But permitting is part of it.
This is because people don’t view their public posts as something they do to make society better/serve society or even do a job, but as a way to enrich themselves/benefit their friends/make it easier to make money in the future.
Everything, from truly shoddy workmanship to rushed, corner/cutting work, to outright corruption comes from viewing a job not as something you take pride in and work to do your best at, but from viewing a job as an opportunity to enrich yourself and your family while doing as little work as humanly possible. In fact in some societies, this is viewed as a duty. As someone in comments cited there are places in Africa where locals can’t run a shop, because all their relatives near and distant will expect to be given merchandise for free … or even money out of the till.
A lot of this is because the idea of the individual as independent of the tribe and the family is a very new thing in most of the world. We kind of have a head start on it because we are/are descended from those who left family and tribe behind.
[…]
Also in most of the world working for money is vaguely shameful. Particularly so if you’re working for someone else. […] And even here not only does that attitude persist, but it’s trying to make itself normal. Particularly in politics.
So, take pride in what you do, and do the best job you can. It’s not just important for you, it’s a building block of society. Do the best you can, and control as much as you can, so maybe you will have just reward which is an incentive to do better.
This way is civilization built. This way do things actually improve.
Sarah Hoyt, “BUILD!”, According to Hoyt, 2018-07-25.
October 19, 2020
Sarah Hoyt – “… I’ve been feeling like I’m at the end of a Bond movie, and the villain is telling me his big master plan and how Western Civilization is tied to the train tracks and can’t escape”
In the latest Libertarian Enterprise, Sarah Hoyt explains why she’s not expecting the US federal election next month to resolve anything, at least not in a positive way:
At this point I hold about a 10% chance the Democrats/Socialists/Communists (interchangeable now that the masks are off) don’t fraud their way into full power, pack the court and rip our system apart, to install (yet again) a form of communism. This is complicated by the fact that a lot of them are in China’s pockets. Or rather, China has been filling their pockets for a long while. We might find ourselves working for racist, hegemonic overlords, besides suffering all the ills of a descent into communism. (By the way, they’ve already been doing this to some extent to the less fortunate countries, including most African countries. The left in the US and Europe believes this is benevolence. And that Chinese aren’t racist. I wouldn’t believe it, if it hadn’t been said to me over and over.)
There is maybe another 25% of chance we’ll find ourselves in CW II, now with even more foreign interference. What comes out of that, G-d only knows, and I’m not Him. Which is good, because I have trouble enough being me.
And there is a very strong chance that even if Trump wins the White House, besides continuing to have to drive a car where the wheel is disconnected (the extent of which I wasn’t even fully sure of until this month) he won’t do more than delay the crash.
Sometimes here, and particularly at insty, because I tend to do that really late at night when I’m exhausted and less able to control my moods, you’ll catch a hint of how hopeless I feel our situation to be.
In fact since the lockdown, I’ve been feeling we were screwed. That the lockdown was imposed all over the world on such flimsy evidence, that countries and churches, and every cultural institution not only submitted to it but kept telling the people how much it was needed sent me into a deep depression from which I haven’t fully recovered. (Again, the evidence that this virus was MAYBE as bad as the flu has been before our eyes since the beginning. You don’t need special equipment to see it. The homeless were congregating and not dying in droves. The people in slums in the third world weren’t dying at a higher rate than usual. And there were the numbers from the Diamond Princess. Which some idiot here tried to justify with “but they got the best treatment.” In a floating petri dish. With no special equipment. May G-d have mercy on the soul of every idiot who bought that bullshit.).
This last week, on the other hand, I’ve been feeling like I’m at the end of a Bond movie, and the villain is telling me his big master plan and how Western Civilization is tied to the train tracks and can’t escape.
Oh, not the massive corruption of the Biden crime family. I mean seriously. Any of you who didn’t know already that Crackhead McStripperbang wasn’t being paid for foreign countries for his services must have been living under a rock.
Not even the ridiculous, immediate coordination with which our tech overlords moved to clamp down on that information and preventing it from reaching the virgin ears of most of our willfully and willingly ignorant countrymen.
No, what discouraged me most was the “sexual preference” suddenly becoming a slur and Webster dictionary falling in line. (Seriously, guys, sexual preference goes way beyond orientation. For instance, my sexual preference is monogamous and with someone I love. If you think that there’s no preference involved, you must think people have absolutely no control over their impulses.) Because that bullshit couldn’t happen, even in the most totalitarian of conspiracies.
And that’s the terrifying thought. These people are no more conspiring than your breaklines being cut are a conspiracy not to stop the car.
They are a result of deep inlaid propaganda and misseducation which cause a lot of people to try to fall into line with the “word from above” and be “right” with those they view as the smart people and the masters of society.
October 18, 2020
The diplomatic spat with China is “forcing the prime minister to bring out the biggest guns in his arsenal: his really serious socks”
The Line shows just how seriously Justin Trudeau is taking China’s most recent not-so-veiled threats against Canadians in Hong Kong:
The warm glow of a good feed faded quickly in Ottawa, alas, where our nice little vacation from history continues its unravelling apace. China’s ambassador to Canada is issuing increasingly dire threats to the safety of our citizens, specifically the hundreds of thousands of Canadians living in Hong Kong, forcing the prime minister to bring out the biggest guns in his arsenal: his really serious socks, a very frowny photograph by Adam Scotti, and, we expect, the imminent announcement that on top of all her current duties, Chrystia Freeland will be appointed Progressive Minister In Charge Of Figuring Out What The Hell We Should Do About China But Not In A Way That Offends Anyone The Middle Class Build Back Green Error Error Program Alarm—
Whoa! Sorry! The Freeland Job Generator glitched again. No surprise, considering the miles Trudeau has put on it in only five years. Let’s hope it doesn’t give out entirely — we’d need 47 years to procure another one.
Anyway, as to the matter at hand, your Line editors are pragmatic folk. Canada can’t punch at the same level as China; under Mr. Trudeau, indeed, despite all our for-Liberal-egos-only preening about Canada being back, we can’t even punch at the same level as Ireland and Norway. But it’s time Canadians face facts: we can either continue pretending that China’s increasingly aggressive and threatening behaviour is a problem that will go away if we ignore it long enough, or we can at least pretend that we have balls and take what actions we can. Obviously we’re not going to send a fleet to parade up and down their coast, but there are things we can realistically do, and we aren’t. Australia, for instance, also in Beijing’s sights, has rolled out a series of measures to curtail China’s substantial influence there. Canada ought to be doing the same. And we could start by immediately banning Huawei, and encouraging every other country that would listen — which doesn’t seem to be many — that they should too.
Do we expect the Liberal government to do this? No. Making money shilling for the Chinese regime is the best thing to happen to post-politics Liberals since Ontario’s air ambulance service. But they should do this. And the delay is only gonna make it hurt more when events eventually force us to accept that China is not our friend, never has been, and never will be under the current political leadership.
October 17, 2020
September 5, 2020
Beginning the transition from personal rule to the modern bureaucratic state
Anton Howes discusses some of the issues late Medieval rulers had which in some ways began the ascendency of our modern nation state with omnipresent bureaucratic oversight of everyone and everything:
… the bureaucratic state of today, with its officials involving themselves with every aspect of modern life, is a relatively recent invention. In a world without bureaucracy, when state capacity was relatively lacking, it’s difficult to see what other options monarchs would have had. Suppose yourself transported to the throne of England in 1500, and crowned monarch. Once you bored of the novelty and luxuries of being head of state, you might become concerned about the lot of the common man and woman. Yet even if you wanted to create a healthcare system, or make education free and universal to all children, or even create a police force (London didn’t get one until 1829, and the rest of the country not til much later), there is absolutely no way you could succeed.
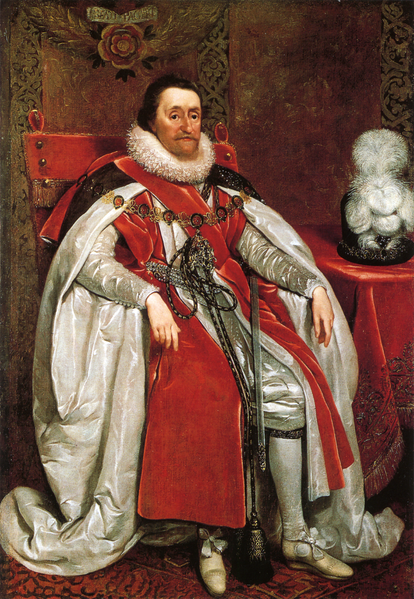
King James I (of England) and VI (of Scotland)
Portrait by Daniel Myrtens, 1621 from the National Portrait Gallery via Wikimedia Commons.For a start, you would struggle to maintain your hold on power. Fund schools you say? Somebody will have to pay. The nobles? Well, try to tax them — in many European states they were exempt from taxation — and you might quickly lose both your throne and your head. And supposing you do manage to tax them, after miraculously stamping out an insurrection without their support, how would you even begin to go about collecting it? There was simply no central government agency capable of raising it. Working out how much people should pay, chasing up non-payers, and even the physical act of collection, not to mention protecting that treasure once collected, all takes substantial manpower. Not to mention the fact that the collecting agents will likely siphon most of it off to line their own pockets.
[…]
It was not until 1689, when there was a coup, that an incoming ruler allowed the English parliament to sit whenever it pleased. Before that, it was convened only at the whim of the ruler, and dispersed even at the slightest provocation. In 1621, for example, when James I was planning to marry his heir to a Spanish princess, Parliament sent him a petition asserting their right to debate the matter. Upon hearing of it, he called for the official record of parliamentary proceedings, personally ripped out the page with the offending vote, and promptly dissolved the Parliament. The downside, of course, was that James could not then acquire any parliamentary subsidies.
Ruling was thus an intensely personal affair, of making deals and finding ways to circumvent deals you had inherited. Increasing your capabilities as a ruler – state capacity – was thus no easy task, as the typical ruler was stuck in an essentially medieval equilibrium. Imposing a policy costs money, but raising money involves imposing policy. Breaking out of this chicken-and-egg problem took centuries of canny leadership. The rulers who achieved it most would today seem hopelessly corrupt.
To gain extra cash without interference from Parliament, successive monarchs first asserted and then abused their ancient prerogative rights to grant monopolies over trades and industries. They eventually granted them to whomever was willing to pay, establishing monopolies over industries like gambling cards or alehouses under the guise of regulating unsavoury activities. They also sold off knighthoods and titles, and in 1670 Charles II even made a secret deal with the French that he would convert to Catholicism and attack the Protestant Dutch, all in exchange for cash. Anything to not have to call a potentially pesky Parliament. At times, the most effective rulers even resembled mob bosses. Take Elizabeth I’s anger when a cloth-laden merchant fleet bound for an Antwerp fair in 1559 was allowed to depart. Her order to stop them had not arrived in time, thus preventing her from extracting “loans” from the merchants while she still had their goods within her power.
August 1, 2020
“All style and no substance made it the perfect match for Trudeau”
Andrew Lawton on the Prime Minstrel’s performance in “explaining” his role in the WE scandal:
“Don’t look at me – I’m just the prime minister.”
That about sums up Justin Trudeau’s defense in a Canadian scandal starring grifters, shell corporations, virtue signallers and a federal ethics probe.
The WE-Scam, as it’s come to be known in Canadian circles, is, on its surface, a simple one.
Trudeau’s government created a $912 million government program to pay students to volunteer – formerly known as “working” if memory serves – and outsourced the administration of it to WE Charity, one of those purported international development charities more known for holding glitzy, celebrity-filled parties than digging any wells in Africa.
All style and no substance made it the perfect match for Trudeau.
WE would have netted about $44 million from the program had the government not pulled the plug amid the backlash. The charity would also have had a budget to pay teachers up to $12,000 each to funnel their students into the paid volunteer channels.
The program itself was a boondoggle, but bad policy became a scandal because Trudeau and virtually everyone in his immediate family have personal and financial connections to WE, as do at least two of his cabinet ministers, not to mention his chief of staff – all of whom say their relationships had nothing to do with WE getting the sole-sourced contract.
After weeks of ducking scrutiny from his political opponents, Trudeau made a rare appearance before the parliamentary finance committee Thursday, though his testimony was heavy on the sanctimony and light on the details.
July 30, 2020
Membership in the Laurentian Elite isn’t about intelligence, it’s about power and status
In The Line, Andrew Potter wonders why Canadian political elites tend to be so … dumb:
Recent events in Canadian federal politics have raised anew the familiar conundrum: why are high status people so stupid?
Anyone who has had much interaction with high status individuals is familiar with the phenomenon. It isn’t the shallow ignorance of the merely uneducated, or the malevolent brainlessness of the criminal class. It’s not even your bog-standard lack of intelligence. No, high class stupidity is of a very special type: A sort of studied lack of interest in facts, an offhand relationship with norms, an outright animosity to new ideas.
But it is important to specify just what we mean by “high status,” because status means different things to different people. (Indeed, how you define “status” is one of the key markers of class differences in Canada.) For some people status is defined by money or wealth, for others it is a function of education, while for still others it is a matter of taste. And even if you are sure it comes down to money, there are clear status differences based on how you got rich. Everyone instinctively understands the difference between the guy who got rich off a chain of used car dealerships and the one who made his bundle selling his dotcom startup, and there’s a reason why “nouveau riche” is a derogatory term.
And so the high-status individuals we are talking about here are the highest of high, the upperest of upper, the ones whose wealth is inherited, whose lives are defined by their privilege, and for whom the question of which rung of the status ladder they stand upon never arises, because there is no one above them.
Which brings us to the Liberal government, and in particular to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, Minister of Finance Bill Morneau and the scandal over the sole-sourced contract (sorry, “contribution agreement”) with a branch of the Kielburger-led WE conglomerate. First, Canadaland broke the story two weeks ago that Trudeau’s mother and brother had received almost a quarter of a million dollars in speakers’ fees from the WE organization.
[…]
Trudeau and Morneau are both very wealthy men, and if they were going to get into the business of selling their offices it wouldn’t be to a children’s charity for penny ante sums. No, as a number of columnists have pointed out, what is at work here is not corruption, it is privilege: It probably never occurred to either Trudeau or Morneau that this sort of thing was wrong. And it didn’t occur to them, because they are the sort of people who have spent their lives not worrying about the comings and goings of money and how it may affect their lives.
That is why the defining feature of the WE scandal is not the corruption, but the almost deliberate stupidity that is on display — in particular the lack of interest in basic material facts or in following the rules that govern the lives of most people. Which brings us back to the question we started with.
Update: Corrected the attribution for this … Andrew Potter’s article appeared in The Line, not The Dominion. Apologies for the brain fart…
July 23, 2020
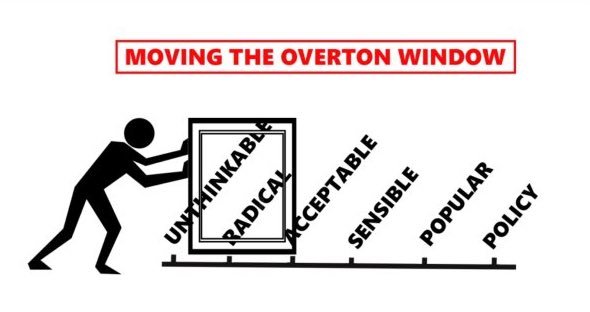
Justin Trudeau and the Overton Window
Ted Campbell explains how Canada’s mainstream media work so hard to move the Overton Window to benefit Justin Trudeau and the Liberal Party:
… this explanation from Politico might help:
The concept of the “Overton window,” the range of ideas outside which lie political exile or pariahdom, was first batted around in a series of conversations by the late free-market advocate Joseph Overton in the 1990s. After Overton’s untimely death in a plane crash in 2003, his friend and colleague at the libertarian Mackinac Center, Joseph Lehman, formalized and named the idea in a presentation meant to educate fellow think-tank warriors on the power of consistent advocacy. Ring the bell loudly for your idea, no matter how unpopular, and back it up with plenty of research and evidence, so the thinking went. Today’s fringe theory can become tomorrow’s conventional wisdom by the shifting of the finely tuned gears that move popular opinion; to Overton and Lehman the role of the think tank was to at least familiarize voters with these ideas, giving them an institutional home when public opinion finally moved their way.
Or, and even more brief visual explanation is:
Anyway, I believe that the Liberal Party of Canada and its allies in e.g. the CBC, The Star, and amongst the others who speak for the Laurentian Elites are working very hard, right now, to move the Overton Window frame of one idea from “Unthinkable” to at least barely “Acceptable.” That idea is that Justin Trudeau’s personal corruption (I believe that’s the right word) is acceptable because the alternative is a Conservative government that is, by Liberal/Laurentian Elite definition, authoritarian (fascist), homophobic, militaristic, racist, and sexist.
That’s right, the Liberal/Laurentian Elites admit that Justin Trudeau is dishonest, that he, unthinkingly, breaks the rules, over and over again ~ because, you see, he’s a really nice person but, sadly, he’s just not very smart. I have even made that case for them. I suggested, almost a year ago, that Justin Trudeau is an intellectual lightweight who is in no way qualified to hold high office … but he has the “second hand” celebrity of a famous name and he’s photogenic, too, and so, in 21st-century Canada he’s electable.
July 9, 2020
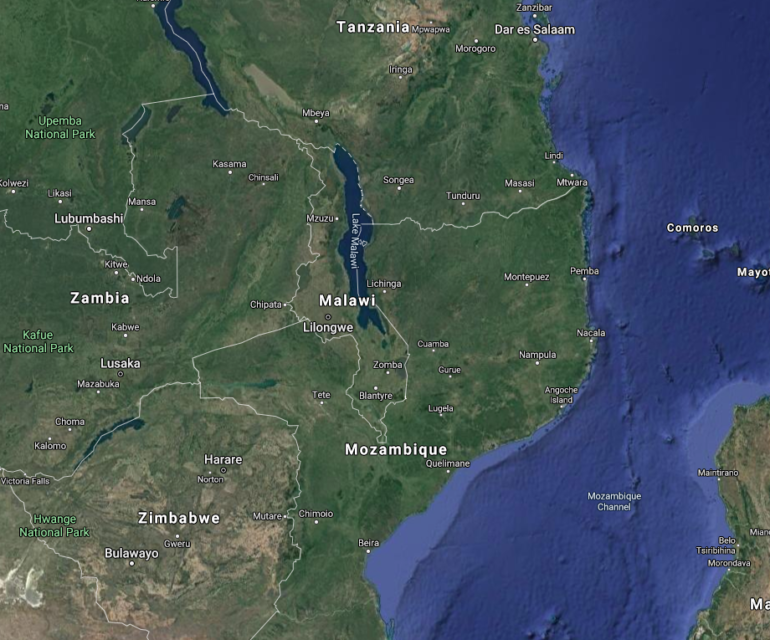
Austin Bay on how Malawi fixed a crooked election
At Strategy Page, Austin Bay recounts the efforts to overturn an election that was clearly fraudulent in the small land-locked African country of Malawi:
Since he retained the title of president, Mutharika believed he controlled the guns and the courts. The protests would fade.
He learned otherwise. Malawi’s military, the Malawi Defense Force (MDF) and the Malawi Police Service, watched the country carefully, keeping order but not taking sides. The opposition appealed to Malawi’s highest court, the Constitutional Court. MDF commanders made it clear their service, as protectors of the constitution, would protect the court’s justices and respect the court’s decision.
Ignoring intimidation and enticements (Mutharika offered splendid early retirement), in February 2020, the court annulled the 2019 results as tainted and ordered new elections in June 2020 — the Fresh Presidential Election.
MDF soldiers prepared to secure the FPE’s paper ballots. In a June briefing, an MDF general told motorists to “maintain a distance of at least one kilometer between them and vehicles” carrying ballots. Enter the security zone and get a warning, but “(overtly) following the vehicles can lead to loss of lives if one is not careful.” Beware political thugs — MDF weapons prevent ballot hijacking.
Voters need protection, too. On June 22, MDF soldiers in central Malawi detained 16 men local citizens identified as intruders seeking to disrupt the vote. When police officers questioned the 16, they admitted they worked for Mutharika’s governing Democratic Progressive Party.
On June 23, opposition leader Chakwera received 60% of the vote in the untainted do-over. Mutharika got 38%. An MDF contingent immediately began protecting Chakwera.
Voting irregularities occur in mature democracies. However, election fraud does severe harm to developing nations where the disenfranchised have little or no systemic recourse and free speech is risky. Hope and nascent civil participation give way to wrath and alienation, which produce violence and destruction, not stability and economic development.
In the six decades since decolonization, election rigging by sub-Saharan Africa elites has stunted economic and social progress in nations whose people deserve far better (see Ghana). Disregard of constitutional law and violent intimidation of opposition voters by the party in power inevitably accompany election theft. Burundi and Congo are examples.