The blunt teaching of history is that socialism is not an advanced stage in the evolution of human society but one of its most primitive stages. A highly articulated form of socialism was practiced among the Incas, the tribe which Pizarro found in control of Peru when he landed there in 1527. All produce, whether agricultural, pastoral or industrial, was the property of the state … In fact, the Incas had not only “communal ownership of the means of production” but a “planned economy”. All the basic features of socialism were present, and the feature which has specially attracted the attention of the archaeologist is that the Incas were in effect a huge bureaucracy … [T]he lesson of history is clear that communal ownership is normal among primitive people, and the institution of private property in the “means of production” is the first big step on the road to civilization.
Ivor Thomas, The Socialist Tragedy, 1951.
March 4, 2026
February 5, 2026
The Mote in God’s Eye: A No-Win Scenario
Feral Historian
Published 26 Sept 2025For whatever reason books by [Larry] Niven and [Jerry] Pournelle always end up being a lot harder to cover than I expect. It’s not that the core ideas are buried in dense convoluted storytelling or unusually compelling characters (often quite the opposite) but rather I think that the core ideas are always a little uncomfortable to face head-on. And Mote is great example.
Niven and Pournelle create a scenario not only of the cyclical rise and fall of a civilization, but one that through a combination of biological and cultural factors points to the impossibility of long-term coexistence between Humanity and the Moties.
00:00 Intro
01:26 Aristocracy and Contact
04:11 The Moties
08:48 Crazy Eddie
10:18 The Middle Path?
12:53 The Gripping Hand
(more…)
December 7, 2025
“Anglofuturism” – slogan or beacon of hope?
At Without Diminishment, Robert King argues for Anglofuturism as the most hopeful path forward from the morass all of the Anglosphere seems to be bogged down in:
Born in the digital backwaters of podcasts and Substacks, Anglofuturism has climbed into public view like a rocket nearing the King Charles III Space Station, gathering both attention and indignation as it ascends.
The New Statesman mutters about it being rooted in “nostalgia“, while the far-left activist group Hope Not Hate insists it is something deeply sinister. Yet their agitation merely confirms a familiar sequence. First, they ignore you, then they laugh at you, then they fight you, and then you win.
At its essence, Anglofuturism is a project of civilisational renewal.
It begins with the conviction that Britain’s decline is not destiny but a decision, and the consequence of decades of political miscalculations that consider the national story to be over, Britain’s very own “end of history”.
Just turn on the news and you will see evidence for this everywhere. Strategic islands like the Chagos Islands surrendered to the vassals of hostile powers. A once-thriving energy sector crippled by the ritual self-flagellation of net zero policies, despite abundant North Sea oil resources.
The capital city of London, once envied for its composure, now deafened by the shrill chants of imported grievances, “From the river to the sea”. Britain was once a country whose streets were said to be paved with gold, according to the legend of Dick Whittington.
Today, they are paved with boarded banks, betting slips, and vape shops. The country’s future is already playing out in London, a place where the nation of Britain has faded into the idea of “the Yookay”. Britain is told that because it once colonised, it must now invite colonisation, that because it once conquered, it must now submit.
The result is a people bending ever lower in the hope of forgiveness from a self-appointed virtuous minority at home, and from the ever-growing numbers of strangers who now claim the country as their own.
Anglofuturism is the vanguard against this ideology. It insists that love of one’s civilisation is a duty, not a sin. It binds identity to optimism, and pride to ambition. It seeks to remind Britons that its best days may yet lie ahead, but only if it learns once more to have confidence in itself.
[…]
The policy of splendid isolation simply will not work for the twenty-first century.
Enter CANZUK, the proposed alliance of Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. Four constitutional monarchies, four democracies, and four maritime powers linked by law, language, and lineage. Together they would represent over 140 million people and a combined GDP exceeding $6 trillion. It would be a realm on which, once again, the sun would never set.
Our shared day of remembrance on November 11 is a reminder that we partake in traditions born of shared sacrifice.
Such a bloc would not be a re-creation of empire, but a confederation of equals who share the responsibilities of defence and trade, coordinating space and science, and projecting stability from north to south and east to west.
It could stand apart from American turbulence, Chinese authoritarianism, and European stagnation, and be a new civilisational pole rooted in innovation and freedom under common law. It could even be a new contender to lead the free world.
Britain is still a nation successful at exporting ideas like capitalism, liberalism, and, regrettably, Blairism. Anglofuturism could be its most powerful export to the Anglosphere yet.
For those of us at the edge of that world, in Cape Town, Perth, or Vancouver, the message of Anglofuturism is that our story is not over. Our civilisation may be weak, even fading, but it can be revived. Doing this will demand the same courage that built it, in the spirit of the pioneers and soldiers, the engineers and thinkers who shaped continents and defended freedom when it was under siege.
November 5, 2025
A minor gaming distraction
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, Matt Gurney takes a few minutes while waiting for the impending catastrophe of the federal budget to be released to talk about a game I’m quite familiar with (and generally share his opinions on):
It’s budget day. My job is only going to get busy in the afternoon and evening. So now is a good time to inflict a non-news and non-political tweet on you. I want to talk to you all briefly about Civilization 7, which has had a troubled launch.
Some of you may follow me closely enough to know I’m a hardcore Civ fan. I’m a wannabe gamer. I love gaming. I could get really into gaming. But I don’t have the time. My preference is for games that are very deep and immersive and require hours of time for a single gaming experience. My life actually only enables me to basically do the opposite: a quick game on my phone that kills five or 10 minutes.
Civ is my guilty pleasure. I’ve played every major iteration of it since the first. And I was SUPER excited for the release of Civilization 7 earlier this year. The company that owns the rights, Firaxis, did a really interesting pre-release marketing job. They built a lot of buzz.
The game itself, which I obviously preordered and played on the day it released, was disappointing. It looked good, but it was very shallow. Every Civ iteration grapples with the challenge of needing to improve on/enhance the game experience compared to earlier releases, but also with the problem of complexity. If you just keep layering on new functions, you eventually make the game unplayable. So there’s a natural tension there. But 7 was still weirdly sparse. There were very basic user interface issues. Fonts were very small, colour choices led to a lot of struggle making out details. It all looked beautiful at a distance until you were actually trying to absorb any information, info necessary to effectively play the game, at a glance. It was impossible. Also, and this is a separate but related problem, some very basic functions and information necessary for gameplay simply wasn’t explained. You kind of had to intuit things.
There were big, structural changes to the gameplay as well. How the game works is very different from earlier iterations. These changes were very controversial — seemingly hated, to be honest. I didn’t actually hate them. I didn’t always love them, but I was pretty open minded to them and kind of liked some of the new mechanics.
But. Ahem. The game itself regressed in some key ways, compared to its predecessor, Civ 6. A small example: religious warfare. For non-players, in Civilization, you can control units for your empire and you move them around the map. Military units can fight other military units, and can seize and defend territory. Religious units were a totally different game mechanic that players would use to export their religion, and to prevent their own cities from being converted. It added a really fun and elegant layer to the game, and one that could be meaningful enough to swing outcomes in a big way.
Civ 7 just nerfed that. Religion is useless. Worse, it’s annoying.
The company has been very aggressive at rolling out updates to fix some of these issues. They’ve also been very open in communicating what they’re working on to the audience. I admire that. I really do. But the numbers don’t lie. Civ 7 is, today, drawing maybe 15-20% of the audience that Civ 6 did. (Using Steam Charts for those figures.) I don’t know if this is a flop for Firaxis, but it has to be a disappointment verging on a disaster.
They’re rolling out a lot of updates and new content to try and fix these issues. And I think they’re making strides. But, like, yikes. Every time they announce a new update, I’m shocked by how much of that stuff should have just been in the game in the first place.
I’m not a gaming expert, like I said. I wish. I’m also not an expert in gaming as a business. I’m just a guy who loves playing Civ. I’ve stuck with 7 since it was released and I’ve given every major update a fair chance. I’ve had fun playing the game. But I just can’t deny that 6 was much better, more playable, and more fun. And I don’t know how much more time the developer has before even hardcore fans like me just give up and go back to 6 permanently.
Anyway. This is what happens when all the news is due to come out later in a day.
Thank you for your attention to this matter!
Matt is more patient with Firaxis than I am, I have to admit. I downloaded and played Civilization VII on release day … played a few rounds of a couple of different civilization/leader combos … played one up to the new “change your entire civilization to a totally different one in a new age” mechanic, saved and quit the game. I’m sure I’ll play again at some point, but VII didn’t grab my attention and interest the way all the earlier iterations had done and I hate hate hate the swapping civilizations gimmick with a passion because it ruins my immersion in the civilization I’m trying to build. But I’m pretty far from being the target market for this game, so take my dissatisfaction with a shaker of salt.
October 18, 2025
QotD: Civilizational survival after the Bronze Age Collapse
If post-Collapse Egypt is Britain, then perhaps post-Collapse Phoenicia is America: a relative backwater, dwarfed by the Great Powers of its day, that suddenly leaps to global prominence when the opportunity arises … but in doing so, changes in some very fundamental ways. Which raises a question about Cline’s subtitle, “The Survival of Civilizations”: what does it actually mean for a civilization to survive?
Sometimes the answer is obvious. The Assyrians and Babylonians clearly survived the Collapse: if you compare their architecture, inscriptions, artwork, settlement patterns, and political structures from the Late Bronze Age to the Iron Age, they are recognizably the same people doing the same things and talking about them in the same way. The Egyptians, too, are plainly the same civilization throughout their (very long!) history, even if they were notably weaker and less organized after the Collapse. The Hittites, just as obviously, did not survive (at least not outside their tiny rump states in northern Syria). But the Greeks and the Phoenicians are both murkier cases, albeit in very different ways.
On the one hand, Mycenaean civilization — the palace economy and administration, the population centers, the monumental architecture, the writing — indisputably vanished. The Greeks painstakingly rebuilt civilization over several hundred years, but they did it from scratch: there is no political continuity from the Mycenaean kingdoms to the states of the archaic or classical worlds. And yet as far as we can tell, there was substantial cultural continuity preserved in language and myth. Admittedly, “as far as we can tell” is doing a lot of work here: Linear B was only ever used for administrative record-keeping, so we can’t compare the Mycenaeans’ literary and political output to their successors the way we can in Assyria or Egypt. We can’t be sure that the character, the vibe, the flavor of the people remained. But the historical and archaeological records of the later Greeks contain enough similarities with the descendants of the Mycenaeans’ Indo-European brethren that the answer seems to be yes.
By contrast, civilization never collapsed in central Canaan. No one ever stopped having kings, writing, building in stone, or making art. The Bronze Age population centers were continuously occupied right up to … well, now. And yet their way of life shifted dramatically, to the point that we call them by a new name and consider them a different people. Cline thinks this is a success story: borrowing an analytical framework from a 2012 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report, he praises their “transformation”,1 which “include[d] actions that change the fundamental attributes of a system in response to actual or expected impacts”. (The Assyrians, by contrast, merely “adapted”, while the Egyptians barely “coped”.) But does there come a point when the change is so great, so fundamental, you’re no longer the same civilization? Can the Ship of Theseus really be said to have “survived”?
In the final section of his book, titled “Mycenaeans or Phoenicians”, Cline asks how we’ll react to the societal collapse we all sort of know is coming sooner or later. Our world just is too complicated, too interconnected, to survive a really massive shock (or, as in the Late Bronze Age, a “perfect storm” of smaller ones). Even the relatively mild disruptions of the past few years have revealed fragilities and vulnerabilities that we’ve done nothing to shore up since. Of course, he has an answer: Transform! Innovate! Flourish amidst chaos! Become a new iteration of yourself, like the bog-standard Canaanite cities that reinvented themselves as an Iron Age mercantile superpower and turned the Mediterranean into a “Phoenician lake”. But at what price?
Or, to think of it another way, what would you prefer for your society five hundred years from now?
Behind Door Number One: governmental collapse, abandonment of the population centers, dramatic reduction in societal complexity, and then a long, slow rebuilding where your time and your people are remembered only as myth — but when civilization is restored, it’ll be by people whose the desires, values, attitudes, and beliefs, their most basic ways of understanding the world, are still recognizably yours. They may have no idea you ever lived, but the stories that move your heart will move theirs too.
And behind Door Number Two: expansion, prosperity, and a new starring role on the world stage — but a culture so thoroughly reoriented towards that new position that what matters to you today has been forgotten. Do they remember you? Maybe, sort of, but they don’t care. They have abandoned your gods and your altars. Those few of your institutions that seem intact have in fact been hollowed out to house their new ethos. A handful of others may remain, vestigial and vaguely embarrassing. But boy howdy, line goes up.
Obviously, given our druthers, we’d all be the Assyrians: seize your opportunities, become great, but don’t lose your soul in the doing. But if it comes down to it — if, when the IPCC’s warning that “concatenated global impacts of extreme events continues to grow as the world’s economy becomes more interconnected” bears out, the Assyrian track isn’t an option — then I’d take the Greek way.
I don’t care whether, on the far side of our own Collapse, there’s still a thing we call “Congress” that makes things we call “laws”. Rome, after all, was theoretically ruled by the Senate for five hundred years of autocracy as all the meaning was leached from the retained forms of Republican governance. (Look, I’m sorry, you can call him your princeps and endow him with the powers of the consul, the tribune, the censor, and the pontifex maximus, but your emperor is still a king and the cursus honorum has no meaning when the army hands out the crown.) I don’t even really care if we still read Shakespeare or The Great Gatsby, although it would be more of a shame to lose those than the Constitution. But I do care that we value both order and liberty, however we structure our state to safeguard them. I care that we’re the sort of people who’d get Shakespeare and Fitzgerald if we had them around. Maybe we should start thinking about it before our Collapse, too.
Jane Psmith, “REVIEW: After 1177 B.C., by Eric H. Cline”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2024-07-08.
- “Transformation” is always a term worth taking with a pinch of salt because so often it’s a euphemism for “total civilizational collapse”. In the chapter on the Hittites, for example, Cline quotes one archaeologist to the effect that “[a] deep transformation took place in the former core of the empire around the capital Hattusa, resulting in a drastic decrease in political complexity, a shift to a subsistence household economy and a lack of evidence for any public institutions”. Relatedly, one of my children recently transformed a nice vase into a pile of broken glass.
In this case, though, Cline really does mean transformation.
October 17, 2025
Civilizational collapse is … female
On her Substack, Janice Fiamengo addresses the unpalatable contention that female power leads to civilizational disaster:
Multiple surveys (see, for example, with thanks to James Nuzzo, here, here, here, here, here and here) suggest that when women hold power, they pursue typically feminine preferences and policies. Female-led institutions become more oriented to social justice than objective truth. Feelings matter above facts, context above law, and victimhood above expertise.
Protecting and promoting the allegedly vulnerable — through censorship, shaming, coercion, or lawbreaking/lawfare — becomes a greater priority than excellence or impartiality. Truth-tellers find themselves cancelled, Nobel prize winners reduced to tears, laws and policies applied unequally, white men accused and vilified, criminals cossetted, mental illnesses affirmed, and destructive policies embraced. No one who has paid attention over the past 20 years can be surprised by the findings.
Moreover, our ability to discuss this feminine revolution in values is hampered by the very logic of the revolution, as I will show. Both women and men, deeply disinclined to “harm” women, fail to confront the problem adequately.
Two discussions of the subject — an essay by two social psychologists at Quillette and, more recently, a conference speech by a feisty conservative woman — draw a line under the seeming inevitability of the west’s collapse. Even faced with that alarming prospect, most pundits cannot bear to imagine an alternative to the female-led assault on our core institutions.
Cheering on Women’s Empowerment
A 2022 article in Quillette, “Sex and the Academy“, provides a stark illustration of my thesis. The subtitle rules out the very conclusion the data supports, with the authors emphasizing that “The inclusion of women in higher education is a great achievement for Western liberal societies. How is this changing academic culture?”
The “great achievement”, as it turns out, will almost certainly be a lethal one.
The article was written by two academics, Cory Clark and Bo Winegard, both PhDs in social psychology. Winegard, a male scholar, had an unfortunate run-in with academic orthodoxy that led to his loss of employment; Clark, a female scholar, has a secure academic position. Both authors express enthusiasm for the takeover of academia by women even as they point out its damaging consequences. Neither one advocates any form of resistance, no matter how mild, to feminine academia’s assault on truth.
Summarizing the results of many surveys, Clark and Winegard demonstrate that while a majority of men favor free speech and the advancement of knowledge over emotional comfort, a majority of women prefer conformity, safety, and the protection of victim groups’ feelings. Not all women are indifferent to the traditional underpinnings of western civilization (and not all men support those underpinnings), but the general trends are clear.
Women are significantly more likely than men to support the cancellation of controversial speakers or the suppression of controversial research.
Women also tend to favor the existence of snitch lines to report people who cause offence. Women are more supportive than men of diversity quotas that exclude white men from consideration for prizes, positions, and promotions. (It would be interesting to know how many white women support diversity quotas that exclude white women from consideration for prizes, positions, and promotions.)
[…]
Asserting that both sides are pursuing worthy goals, the authors downplay the shock value of the findings, which show that women are, overall, less interested in truth and accuracy than men are. Imagine assessing such a finding as anything but catastrophic. Imagine calling the disregard for truth moral.
In place of truth, women value a utopian ideology that they perceive — usually without any consistency or adherence to fact, but nonetheless granted by Clark and Winegard — as “morally desirable”. But morally desirable for whom, and to what end? The use of the phrase, a misnomer, demonstrates how thoroughly the authors themselves are in thrall to the corrosive feminine culture they examine.
There is nothing moral (or generally desirable) about the suppression of truth-seeking research when it conflicts — or is perceived to conflict — with an allegedly emancipatory social goal. There is nothing morally desirable or indeed “protective” about shouting down an academic speaker because of the alleged harm of the speech. Naturally, social justice proponents would be outraged if their speeches were shouted down or their research blocked and censored.
I saw a link to this Helen Andrews article which seems to go well with Janice Fiamengo’s article linked above describing the “Great Feminization”:
… Cancel culture is simply what women do whenever there are enough of them in a given organization or field. That is the Great Feminization thesis, which the same author later elaborated upon at book length: Everything you think of as “wokeness” is simply an epiphenomenon of demographic feminization.
The explanatory power of this simple thesis was incredible. It really did unlock the secrets of the era we are living in. Wokeness is not a new ideology, an outgrowth of Marxism, or a result of post-Obama disillusionment. It is simply feminine patterns of behavior applied to institutions where women were few in number until recently. How did I not see it before?
[…]
The substance fits, too. Everything you think of as wokeness involves prioritizing the feminine over the masculine: empathy over rationality, safety over risk, cohesion over competition. Other writers who have proposed their own versions of the Great Feminization thesis, such as Noah Carl or Bo Winegard and Cory Clark, who looked at feminization’s effects on academia, offer survey data showing sex differences in political values. One survey, for example, found that 71 percent of men said protecting free speech was more important than preserving a cohesive society, and 59 percent of women said the opposite.
The most relevant differences are not about individuals but about groups. In my experience, individuals are unique and you come across outliers who defy stereotypes every day, but groups of men and women display consistent differences. Which makes sense, if you think about it statistically. A random woman might be taller than a random man, but a group of ten random women is very unlikely to have an average height greater than that of a group of ten men. The larger the group of people, the more likely it is to conform to statistical averages.
Female group dynamics favor consensus and cooperation. Men order each other around, but women can only suggest and persuade. Any criticism or negative sentiment, if it absolutely must be expressed, needs to be buried in layers of compliments. The outcome of a discussion is less important than the fact that a discussion was held and everyone participated in it. The most important sex difference in group dynamics is attitude to conflict. In short, men wage conflict openly while women covertly undermine or ostracize their enemies.
Bari Weiss, in her letter of resignation from The New York Times, described how colleagues referred to her in internal Slack messages as a racist, a Nazi, and a bigot and—this is the most feminine part—”colleagues perceived to be friendly with me were badgered by coworkers.” Weiss once asked a colleague at the Times opinion desk to get coffee with her. This journalist, a biracial woman who wrote frequently about race, refused to meet. This was a failure to meet the standards of basic professionalism, obviously. It was also very feminine.
Men tend to be better at compartmentalizing than women, and wokeness was in many ways a society-wide failure to compartmentalize. Traditionally, an individual doctor might have opinions on the political issues of the day but he would regard it as his professional duty to keep those opinions out of the examination room. Now that medicine has become more feminized, doctors wear pins and lanyards expressing views on controversial issues from gay rights to Gaza. They even bring the credibility of their profession to bear on political fads, as when doctors said Black Lives Matter protests could continue in violation of Covid lockdowns because racism was a public health emergency.
[…]
The Great Feminization is truly unprecedented. Other civilizations have given women the vote, granted them property rights, or let them inherit the thrones of empires. No civilization in human history has ever experimented with letting women control so many vital institutions of our society, from political parties to universities to our largest businesses. Even where women do not hold the top spots, women set the tone in these organizations, such that a male CEO must operate within the limits set by his human resources VP. We assume that these institutions will continue to function under these completely novel circumstances. But what are our grounds for that assumption?
The problem is not that women are less talented than men or even that female modes of interaction are inferior in any objective sense. The problem is that female modes of interaction are not well suited to accomplishing the goals of many major institutions. You can have an academia that is majority female, but it will be (as majority-female departments in today’s universities already are) oriented toward other goals than open debate and the unfettered pursuit of truth. And if your academia doesn’t pursue truth, what good is it? If your journalists aren’t prickly individualists who don’t mind alienating people, what good are they? If a business loses its swashbuckling spirit and becomes a feminized, inward-focused bureaucracy, will it not stagnate?
If the Great Feminization poses a threat to civilization, the question becomes whether there is anything we can do about it. The answer depends on why you think it occurred in the first place. There are many people who think the Great Feminization is a naturally occurring phenomenon. Women were finally given a chance to compete with men, and it turned out they were just better. That is why there are so many women in our newsrooms, running our political parties, and managing our corporations.
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, John Carter comments on Helen Andrews’ article:
One thing Helen misses in this otherwise excellent analysis is the role played by prestige. Cancel culture was enabled by the unique circumstance of women weaponizing the prestige of freshly feminized legacy institutions. So long as those institutions retained their prestige, what the people who ran them said really mattered.
Unfortunately for the ladies (but luckily for civilization), this is self-limiting, because prestige is fundamentally an emergent property of masculine competence hierarchies. We see this demonstrated whenever a profession becomes coded as women’s work: its prestige immediately crashes. Feminists have complained about this for years, though of course they misunderstand the mechanism (prestige is a component of male sexual attractiveness, but not of female, and this is biologically hard-wired).
This prestige collapse is now affecting essentially every coopted, feminized institution — universities, news media, publishing houses, movie studios, large corporations, various government agencies, hospitals, courts, churches, all of them wield far less cultural power than they did even a few years ago. The only people who really care what these legacy institutions say are the women who took them over. To everyone else, the angry sounds they make are nothing more than background noise.
This is probably the main reason for the vibe shift. Once the prestige of feminized institutions declined below a certain threshold, their ability to enforce social consensus began to evaporate.
It’s also probably no accident that the Trump administration seems to care a lot more about what the anons of the Online Right say than it does about the opinion of the universities or the news media. All the intelligent young men got pushed out of the institutions, and those ionized particles of free male energy then began to self-assemble online into an ad hoc competence hierarchy where prestige is measured by clout rather than professional degrees, job titles, or institutional affiliations. The anon swarm is entirely informal, meaning that its outcomes are not amenable to antidiscrimination legislation or to procedural manipulation; you can screw with the algo all you want but you can’t actually force people to care what women say just because they’re women (thereby placing women into the position of openly trading in thirst, which gets them attention but certainly doesn’t mean that anyone has to pretend to take them seriously).
All that’s happened so far is that people’s attention has been redirected away from crazy woke females and towards the influencers of the online right. The fever has broken but society is a long way from recovered. The institutions are still under the control of crazy woke females, and this is extremely bad, especially because they are – for biological reasons related to childlessness — only going to get crazier as time goes on. Fortunately no one really cares what they say anymore, so as they throw tantrums as the institutions are reclaimed over the next decade or so, their protests won’t register as anything but irrelevant toddler noise.
September 24, 2025
QotD: The political divisions of humanity
… the various divisions between human beings — communists vs. fascists vs. loyal American patriots — we have lived with all our lives are less important, less fundamental, than the basic one that Heinlein identified: “The human race divides politically into those who want people to be controlled and those who have no such desire”. Call the first group authoritarians or feudalists and the second, generic libertarians.
The first time, in the history of Western Civilization, that this became an issue, was the Renaissance/Reformation. Information suddenly came flooding, unbidden, into Europe, from North Africa, through Galileo’s telescope, out of Gutenberg’s printing press, and a dozen other undesirable, unlicensed, and deplorable sources. It must have been a nightmare for the aristocrats who considered themselves to be in charge, the kings and barons and bishops and bullies. They struggled in vain to get it back under control. They got the Church to condemn it. They intimidated and tortured its emissaries when they could. They invented universities to get a handle on it, a collar around its neck, but it was a lost cause. In just a couple of centuries (compared to the previous 500 generations), people — ordinary people; who the hell did they think they were? — came to know too much for the good of Authority.
And they soon proved it, in the American Revolution, which told 10,000 years of kings to go to hell, and the French Revolution, which cut to the chase and removed their overly-pampered heads. I have actually seen the blade. Many other revolutions followed, worldwide, and people began to learn, slowly and awkwardly, to live their own lives. The one good thing to come out of the brutal and deceitful Russian Revolution was the ultimately individualistic philosophy of refugee Ayn Rand.
Otherwise, it was a naked attempt by the authoritarians, the feudalists, to regain control of the masses that the Czar had clumsily let slip through his overly-manicured fingers. Whenever human beings have clashed over whether their lives should be controlled by others or not, it has almost certainly been a matter of who gets to be the next king, baron, bishop, commissar, etc., a battle between liberated entities and those who would restore feudalism.
L. Neil Smith, “The Deep State”, Libertarian Enterprise, 2019-04-14.
August 7, 2025
QotD: The lost-then-found-again Hittite civilization
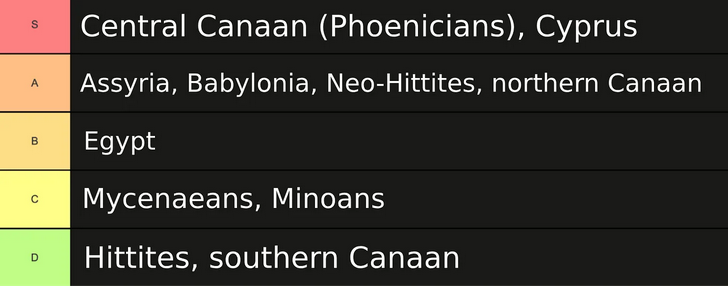
… Mycenaean Greece was as much an outlier as sub-Roman Britain: the civilizational collapse in the Aegean was unusually prolonged and severe compared to the fates of many of the other peoples of the Late Bronze Age. Here I have helpfully reformatted Cline’s chart of how resilient the various societies proved:
Let’s take a brief tour through the various fates of these societies. I’ll come back to the Phoenicians at the end, because their example raises interesting questions when considered in contrast with the Mycenaeans. For the moment, though, let’s begin like civilization itself: in Mesopotamia.
Before the Late Bronze Age Collapse, the Assyrian and Babylonian empires had numbered among the Great Powers of the age: linked by marriage, politics, war, and trade to the other mighty kings, they spent much of their time conducting high-level diplomacy and warfare. As far as we can tell, they did well in the initial collapse: there’s a brief hiatus in Assyrian royal inscriptions running from about 1208 to 1132 BC, but records resume again with the reign of Aššur-reša-iši I and his repeated battles with his neighbor to the south, the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar I (no relation). But although the kings of the late twelfth century continued much as their Bronze Age predecessors had — waging war, building palaces, going hunting, accepting tribute, collecting taxes, and ordering it all recorded in stone and clay — the world had changed around them. No longer were there huge royal gifts sent to and from fellow great kings, “My Majesty’s brother”1 overseas; now their diplomatic world consisted of tiny petty kings of nearby cities who could be looted or extorted at will.
Mesopotamia didn’t escape unscathed forever: beginning around 1080 BC, texts begin to record severe droughts, invading Aramaeans, and total crop failures. There was a major drought in 1060 BC, and then both the Assyrian and Babylonian records record further drought every ten years like clockwork — sometimes accompanied by plague, sometimes by “troubles and disorder” — until the end of the eleventh century BC. Most of the tenth century was equally dire, with chronicles recording grain shortages, invasions, and a cessation of regular offerings to the gods.
But unlike the Mycenaeans, and in spite of real suffering (ancient Babylonia is estimated to have lost up to 75% of its population in the three hundred years after the Collapse), both Mesopotamian empires were able to hang on to civilization. There were still kings, there were still scribes, and there were still boundary stones on which to record things like “distress and famine under King Kaššu-nadin-ahhe”. And when conditions finally improved, Assyria and Babylonia were both able to bounce back. When at last the Assyrian recovery began under Aššur-dan II (934-912 BC), for example, he (or more realistically, his scribe) was able to write: “I brought back the exhausted people of Assyria who had abandoned their cities and houses in the face of want, hunger, and famine, and had gone up to other lands. I settled them in cities and homes which were suitable and they dwelt in peace”. Clearly, Assyria still retained enough statehood to effect the sort of mass population transfer that had long been a feature of Mesopotamian polities.2
Over the next few centuries, the Neo-Assyrian Empire would come to dominate the Near East, regularly warring with (and eventually conquering) Babylon and collecting tribute from smaller states all over the region. At its peak, it was the largest empire history had ever known, covering a geographic extent unsurpassed until the Achaemenids. The Babylonians had to wait a little longer for their moment in the sun, but near the end of the seventh century they overthrew their Assyrian overlords and ushered in the Neo-Babylonian Empire. (Less than a century later, Cyrus showed up.)
So how did Babylon and Assyria hold on to civilization — statehood, literacy, monumental architecture, and so forth — when the Greeks lost it and had to rebuild almost from scratch? Unfortunately, Cline doesn’t really answer this. He offers extensive descriptions of all the historical and archaeological evidence for the diverse fates of various Late Bronze Age societies, but only at the very end of the book does he briefly run through the theories (and even then it’s pretty lackluster). He does have a suggestion about the timing — the ninth century Assyrian resurgence lines up almost perfectly with the abnormally wet conditions during the Assyrian megapluvial — but why was it the Assyrians who found themselves particularly well-positioned to take advantage of the shift in the climate? Why not, say, the Hittites?
Sometime around 1225 BC, the Hittite king Tudhaliya IV wrote to his brother-in-law and vassal, Shaushgamuwa of Amurru, that only the rulers of Egypt, Babylonia, and Assyria were “Kings who are my equals in rank”.3 A mere thirty years later, though, his capital city of Hattusa would lie abandoned and destroyed. Modern excavators describe ruins reduced to “ash, charred wood, mudbricks and slag formed when mud-bricks melted from the intense heat of the conflagration”.
And with that, the Hittites essentially vanished from history.
They were so thoroughly forgotten, in fact, that when nineteenth-century archaeologists discovered the ruins of their civilization in Anatolia, they had no idea who these people were. (Eventually they identified the new sites with the Hittites of the Bible, who lived hundreds of years later and hundreds of miles to the south, out of sheer ¯\_(ツ)_/¯.)4
What happened to the Hittites? Well, Cline suggests the usual mélange of drought, famine, and interruption of international trade routes, as well as a potential usurpation attempt from Tudhaliya’s cousin Kurunta, but the actual answer is that we’re not sure. Given the timing, they may have been the first of the Late Bronze Age dominos to fall; given the lack of major rivers in central Anatolia, they may have been uniquely susceptible to drought. Hattusa may have been abandoned before the fire — its palaces and temples show little sign of looting, suggesting they [may] already have been emptied out — but many other sites in the Hittites’ central Anatolian heartland were destroyed around the same time, and some of those have bodies in the destruction layer. But whatever the order of events, Hittite civilization collapsed as thoroughly and dramatically as the Mycenaeans’ had done, and with a similar pattern of depopulation and squatters in the ruins. Unlike the Mycenaeans, though, the Hittites would never be followed by successors who inherited their culture; the next civilization of Anatolia was the Phrygians, who probably arrived from Europe in the vacuum following the Hittites’ fall.
There was one exception: in the Late Bronze Age, cadet branches of the Hittite royal family had ruled a few small satellite statelets in what is now northern Syria, and many of these “Neo-Hittite” polities managed to survive the Collapse. A tiny, far-flung corner of a much greater civilization, they nevertheless outlasted the destruction of their metropole and maintained Hittite-style architecture and hieroglyphic inscriptions well into the Iron Age.5 (They would be swallowed up by the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the late eighth century BC.) And though the Neo-Hittite kings ruled over tiny rump states, we’re now able to translate inscriptions in which they referred themselves by the same titles the Bronze Age Hittite “Great Kings” had employed. The records of their larger neighbors, which had a much greater historical impact, seem to have followed suit: the Neo-Hittites in Syria probably actually were the Hittites of the Bible! Chalk up another one for nineteenth century archaeology.
Jane Psmith, “REVIEW: After 1177 B.C., by Eric H. Cline”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2024-07-08.
1. I really think we should bring back monarchs referring to themselves as “my Majesty”. So much cooler than the royal “we”. Or combine them: “our Majesty”!
2. The Babylonian Captivity, much later in the Iron Age, was far from historically unique.
3. The list actually reads, “the King of Egypt, the King of Babylonia, the King of Assyria,
and the King of Ahhiyawa” — the strikethrough appears in the original clay tablet! A generation earlier, under Tudhaliya’s father Hattusili III, the Hittite texts had consistently referred to the king of Ahhiyawa as a “great King” and a “brother”, but apparently the geostrategic position of the Mycenaean ruler had degraded substantially.4. We now know that the Hittites spoke an Indo-European language and referred to themselves “Neshites”, but the name has stuck.
5. I went looking for a good historical analogy for the Neo-Hittite kingdoms and discovered, to my delight, the Kingdom of Soissons, which preserved Romanitas for a few decades after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The Neo-Hittites lasted a lot longer.
July 15, 2025
American (religious) exceptionalism
Christianity has been in retreat across the western world for decades, with the United States being the laggard in abandoning the faith. Canada is closer to the western European rate of secularization. On Substack, Fortissax explains why it has become uncommon to find a believing Christian outside the US in response to a query on X about people turning to various neopagan faiths:
First, I believe there are two factors at play. One is the divide between the United States and the rest of the Western world. The United States still has the highest percentage of weekly churchgoers in the West, at around 24 percent. In the U.S., Christianity remains a living tradition. Millions still attend church, or at least try to. Many people share a common faith, believe in God, and are familiar with Christian references in public life, politics, and law. In contrast, in countries like Canada and much of Europe, regular church attendance is closer to 5 percent. That number often includes recent immigrants who tend to be more socially conservative. Among native-born Canadians and Europeans, especially in urban areas, church attendance is even lower. Religion in these places is often kept alive only by older or rural populations. Among the youth, it has largely faded. Second, many Western countries have experienced secularization for much longer.
I believe this first one is not obvious to a majority of people. There are significant cultural differences and experiences within in the United States and outside of it. I believe it would be appropriate to say that the U.S. is still a Christian country, and not just nominally, regardless of whether or not it was established on Lockean principles and Greco-Romain inspiration (some would say revision), of the liberal enlightenment. Sure, the faith is not what it used to be, but probably the majority of Americans at least understand Christian references in common parlance.
I can share a personal anecdote that I believe is fairly typical.
I was born and raised in a region where Christianity had long disappeared from everyday life, following a slow process of state secularization. My great-grandfather was Catholic, but he changed denominations to marry my great-grandmother in the 1930s. It was a utilitarian choice. He believed in God but didn’t care for the petty tyrannies of ethnic and cultural association by denomination. His son, my grandfather, saw hypocrisy in both Catholic and Protestant institutions. As a boy, he was told he could not be friends with a Protestant by a the Catholic priest of his best friend, and he was kicked out of the house by his mother for attending Catholic mass with his girlfriend, even though his father had once been Catholic. My parents were irreligious agnostics. They were not hostile to Christianity, just indifferent, because they were not raised in it. As for me, I grew up in a post-liberal, post-Christian society. I believe in the divine and understand the importance of religion to civilization, but I have no living connection to what came before. In my country of Canada and among my people, Christianity is no longer part of the cultural fabric. I believe this to be the case in Western Europe as well.
There is a common joke that if someone likes paganism so much, they should try the most pagan tradition of all: converting to Christianity. But the unfortunate reality is that secular liberalism has exercised a longer and deeper influence in the modern West than many realize. In response, one could just as easily say that the most Christian tradition of all is converting to secular liberalism, which has formally shaped the cultural and institutional framework of the West for more than 275 years.
For people raised in multi-generational secularized liberal contexts, there is nothing to return to. Christianity is not a living tradition. They cannot come home to Jesus the way many Americans still can, and they cannot undo the liberal Enlightenment. They can only move forward through it. At best, something new might be reinterpreted or reformed from its remnants. But Christianity was never part of their lived experience. It was not seen, heard, or practiced. Churches were never attended. Christmas and Easter functioned as civic holidays focused on family rather than faith. Christianity resembled a historical artifact, something like a beautiful mantelpiece in an old house. It had aesthetic and historical value, but no emotional, cultural, or spiritual presence. This situation is common in much of the non-American West.
This is why many contemporary efforts at Christian revival often feel disconnected. They are built on the assumption that secular individuals are lapsed believers who simply need to be reminded of what they once knew. But these individuals are not returning exiles. They are cultural natives of a secular world. They did not lose the faith, it was never given to them. There were no prayers at the dinner table, no hymns embedded in childhood memory, no sacred calendar shaping the flow of life. Organized religion belonged to the past, replaced with secular civic cults they’re largely unaware of. It was something other people had, something no longer meant for them. This group is not necessarily hostile to Christianity. In many cases, they admire it. They recognize its role in shaping art, architecture, law, and moral tradition. When foreigners attack these, they defend them. They understand its civilizational significance. But the faith speaks a language they do not understand. Its metaphors do not resonate. Its moral claims appear without context. Its stories feel distant.
A useful comparison can be found in the Heliand, a ninth-century Old Saxon gospel poem that re-imagined the life of Christ using the language and imagination of Germanic warrior culture. In that version, Christ is not a wandering teacher from a distant land, but a noble chieftain surrounded by loyal retainers. His mission is framed in terms of honor, loyalty, kinship, fealty, and sacred duty. The gospel message is not altered in its substance, but it is reshaped so that it resonates with the values, social structures, and poetic traditions of a people for whom neither Scripture nor Roman religious order had any living relevance.
This work was part of a broader process of the Germanization of Christianity, a phenomenon that has been studied in detail by scholars like James C. Russell and Fr. G. Ronald Murphy, SJ. Russell, in The Germanization of Early Medieval Christianity, argues that the conversion of the Germanic peoples did not consist merely in the passive reception of Christian doctrine, but in a complex synthesis between Germanic folk-religious consciousness and Christian metaphysics. The resulting Christianities of the early medieval West were distinct, rooted in local mythic frameworks, and expressed through tribal loyalty, sacrificial kingship, and heroic virtue. Murphy, in works such as The Heliand: The Saxon Gospel, explores how the Heliand uses alliteration, formulaic verse, and martial imagery to make Christ intelligible to a newly converted warrior society. He shows how the gospel was not just translated into the Saxon tongue, but into the Saxon soul.
This is the historical precedent that today’s Church must study carefully. The peoples of early medieval Europe were not apostates. They were unbaptized, uncatechized, and culturally alien to Christianity. They were brought into the faith through through cultural immersion. Christianity did not ask them to surrender their world entirely. It entered their world, dignified their heroic values, and redirected them toward the divine. Only then did conversion become possible.
Even those outside the Church understand that this work is urgent. The crisis of meaning in secular liberal societies is visible. The desire for transcendence, rootedness, and spiritual structure has not disappeared. It has been redirected into political identity, consumer behavior, and digital escapism.
If Christianity is to succeed, the same kind of work is needed today. Christianity must once again become a missionary faith. This time, the mission field is not a remote foreign land, but the secularized cities and postmodern suburbs of the Western world. The people being addressed are cultural outsiders. Many were born into environments where the gospel was never lived, never spoken, never embodied. Christianity was not abandoned. It was never truly encountered.
A future for Christianity in the West will not be built on appeals to lost memory or civilizational guilt. It will not be recovered through progressive accommodation or through aesthetic traditionalism that treats churches, vestments, and relics as ornaments of cultural decline. It will only re-emerge through an act of deep cultural translation. That act must begin with an honest assessment of what has been lost, and a willingness to reframe the sacred in terms that can again be understood.
The alternative is a continued descent into spiritual confusion and civilizational forgetfulness. Christianity may continue to grow in the Global South. It may endure as a global religion. But in the West, it will only live again if it learns how to speak, once more, to those who were never taught how to listen.
Looking in from the outside, it seems to me that the majority of Christian priests and ministers have already made their peace with the inevitable extinction of their faith and far too many of them are actively working toward that end. Feminist and progressive currents move far more local Christian leaders than the message of the faith itself, hence any hopes of western Christianity reforging itself depend on a tiny minority of the clergy.
July 12, 2025
QotD: Ancient empires
The earliest “empires” were Security oriented. A band of hunter-gatherers — who had no concept of individual property, and just took whatever they needed from the environment — finally settled, and became farmers. Fencing and cultivating and irrigating, and building surpluses which could be traded for items that would improve living standards. (Farmers in areas that CAN’T store surplus — mainly tropical areas with year round crops — never made it further than village level agriculture, whereas farmers in areas with storable annual crops like grain — which can be stored and TAXED — went on to found empires …)
Unfortunately the initial problem with being farmers surrounded by hunter-gatherers who don’t understand property, is that such hunter-gatherers look at those nicely fenced grains and enclosed cows and sheep and goats as wonderfully convenient places to hunter-gather … (There is a reason the boundaries between hunter-gatherers and farmers are violent places, and all the crap written about “frontier wars” and extermination and the rest is just a shorthand for — these two cultures cannot co-exist peacefully … Nomads are different … they trade, therefore they understand property, therefore they can co-exist with farmers — though they will still raid where they can, be they Mongol or Viking!)
So farmers immediately face a law and order issue, which can only be solved if there is enough surplus available to provide a tax base that will allow an authority figure (chief, king, emperor, etc.) to employ people to provide protection. At village level that is usually a warrior caste who can keep the competition at bay, but once surplus gets to a level that allows higher tech, that will mean states or empires.
To put that in perspective, if your local community collects a surplus, and can afford a local chief/lord/king to provide protection, the resulting tax system is almost always (in recorded human cultures) based on a percentage of production. (In fact the earliest versions of written communication are almost always record keeping for crops and taxation.) This means that the local lord immediately has both the majority of excess funds locally, and a strong incentive to increase local production so his take will increase.
When I ask the average class of secondary school students what sorts of things the local lord could invest in to improve productivity, they get the idea pretty quickly. Irrigation for fields; animals for farm work; blacksmiths for tools and axles; wheelwrights; roads; bridges; mills; markets; guards; etc. This list is common to most parts of Europe, Africa, Asia, Central and South America and Australasia. The only places it never develops are the very early farming communities in places like New Guinea that have no storable or taxable food items to allow such a development.
So all early farming societies that can tax — without exception — become tax based hierarchical cultures. Some are even referred to as kingdoms or empires. And they are based on the idea of keeping the farmers safe, so they can be taxed.
These early empires are all Security empires. In the Middle East they are often shown as large sprawls across the map, but such sprawls are fairly fanciful. In practice they usually refer to rich farm based river valleys, with an extended hinterland based on nomadic tribes that are trading with/employed by/or paid tribute to by the “imperial authority” simply to keep other outsiders at bay.
Traditionally they fall when their hinterland nomadic allies are not strong enough to keep outsiders at bay, or become strong enough themselves to try a bit of conquest. At which point of course the conquerors find that they have to adopt the systems of the despised lowlanders they have just conquered if they are to keep the loot coming in and the system going. (One of my favourite historical analogies is the nomadic conquerors crucifying the old king on the walls of his palace and sneering that he could watch his city burn, only for him to point out that it isn’t his city anymore, it’s their city that’s burning …)
Nigel Davies, “Types of Empires: Security, Conquest, and Trade”, rethinking history, 2020-05-02.
March 27, 2025
QotD: Did humans domesticate plants, or was it the other way around?
In Sapiens: A brief history of humankind, Yuval Noah Harari locates the agricultural revolution to a period roughly some 10,000 years ago when humankind, having survived as a hunter and forager for over two million years, began to domesticate various plants and animals, thus to have a better control over its food supply. Harari calls this revolution “history’s biggest fraud” because he believes that what actually happened here is that plants, like wheat, domesticated human beings rather than the other way round, crops turning people into its willing slaves. Humans ended up doing back-breaking work in the fields so that crops like wheat could spread themselves over every corner of the planet.
Of course, the cultivation of crops enabled human beings to produce far more calories per unit of territory than foraging ever could. And this enabled the human population to expand exponentially, thus putting even more pressure on the food supply, thus necessitating an even greater emphasis on agriculture. Alongside this deepening spiral there were other unintended consequences as well. As Harari puts it: “Nor did the farmers foresee that in good years their bulging granaries would tempt thieves and enemies, compelling them to start building walls and doing guard duty”.
Giles Fraser, “The Magnificent Seven is a post-liberal idyll”, UnHerd, 2020-04-01.
October 11, 2024
“[T]he past is like a thriving civilization; they do things better there”
Another recommended link from the “Your Weekly Stack” set of links to interesting posts on Substack. This, like the previous post, is from an author I hadn’t read before and thought was worth sharing with you.
This is from The American Tribune, making the case that modern Americans (and westerners in general) are in a similar situation to the white minority in Rhodesia:
We stand today in the ruins of civilization. Much as the 9th Century Anglo-Saxons looked at the stone works of the Romans and thought they must have been giants,1 or the Greeks of the post-Sea Peoples Dark Age saw the works of the Minoans and Myceneans and thought only Cyclopses could have constructed such structures,2 we stare at the achievements of the 19th and early 20th Centuries in near-disbelief.
The moon hasn’t been stepped upon since the 70s. Mars remains uncolonized. Municipal infrastructure like water treatment and provision is falling apart and the government either can’t or won’t respond to natural disasters.3 Whereas we once built beautiful buildings that lasted for centuries, structures such as Chatsworth and the Horse Guards Building of Whitehall, now we have ugly structures of concrete and steel that are falling apart already.4
The situation as regards crime and squalor is even worse. As Curtis Yarvin notes in “An Open Letter to Open-Minded Progressives”:
If you read travel narratives of what is now the Third World from before World War II (I’ve just been enjoying Erna Fergusson’s Guatemala, for example), you simply don’t see anything like the misery, squalor and barbarism that is everywhere today. (Fergusson describes Guatemala City as “clean”. I kid you not.) What you do see is social and political structures, whether native or colonial, that are clearly not American in origin, and that are unacceptable not only by modern American standards but even by 1930s American standards.
So whereas Guatemala was once clean, now America’s cities are towers of concrete surrounded by piles of refuse, mobs of zombie-like drug addicts living on the streets,5 and infested with criminals of both the petty and highly violent variety. As Hartley put it, “The past is a foreign country; they do things differently there”. More accurately, the past is like a thriving civilization; they do things better there.
In short, we, like those in the Belgian Congo after the Belgians left, live in an “Empire of Dust” where much of what remains is the ruin of a prior civilization destroyed not because it didn’t work, but because the demented ideology of the present conflicted with its continued, functional existence.6
What happened? A sort of decolonization inflicted upon the Great Powers themselves — namely America, Germany, Britain, and France — after the outlying colonies had long been destroyed. The decay of law and order, the promotion of anti-white hatred, the decay of infrastructure, and the filling of positions with corrupt thugs rather than honorable gentlemen,7 all of it is more or less what happened to the colonies in the ’50s and ’60s. Further, it is similar to what happened later on in South Africa, where a collection of communists, leftists, and NGOs with like mindsets and funded by those like George Soros turned a formerly thriving civilization into what now amounts to a land like Mad Max but with more murder.8
But while the South Africanization of America is certainly an issue that we face,9 it’s not the most accurate comparison to our present problem. South Africa was, when it fell, filled with decades of racial hatred sparked by decades of apartheid that ended only then (though was somewhat overblown), something that Europe never had and nowhere in America has had in over half a century. That unique circumstance created a degree of hatred that was overpowering and, though one with which we largely disagree, understandable. We, then, are somewhat different in terms of where we are and what is happening.
1. https://espace.library.uq.edu.au/data/UQ_363155/s40110183_phd_final_thesis_copy.pdf
2. See The Glory that Was Greece by Stobart
3. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jackson,_Mississippi_water_crisis; https://nypost.com/2024/10/03/us-news/north-carolina-hurricane-victims-slam-biden-harris-admin-as-fema-response-sputters/
4. See, for example, https://www.vintagebuilding.com/houses-longer-houses/
5. See, for example: https://youtu.be/9iSkKkzabnM
6. This is what the phrase “empire of dust” comes from: https://www.imdb.com/title/tt2148945/
7. https://www.theamericantribune.news/p/the-death-of-the-gentleman-and-the
8. https://www.theamericantribune.news/p/george-soross-hand-in-south-africas
9. I wrote an article on this for Tablet: https://www.tabletmag.com/sections/news/articles/united-states-south-africa-racial-justice
September 12, 2024
QotD: The collapse of early civilizations in Mesopotamia
Early states were pretty time-limited themselves. [In Against The Grain,] Scott addresses the collapse of early civilizations, which was ubiquitous; typical history disguises this by talking about “dynasties” or “periods” rather than “the couple of generations an early state could hold itself together without collapsing”.
Robert Adams, whose knowledge of the early Mesopotamian states is unsurpassed, expresses some astonishment at the Third Dynasty of Ur (Ur III), in which five kings succeeded one another over a hundred-year period. Though it too collapsed afterward, it represented something of a record of stability.
Scott thinks of these collapses not as disasters or mysteries but as the expected order of things. It is a minor miracle that some guy in a palace can get everyone to stay on his fields and work for him and pay him taxes, and no surprise when this situation stops holding. These collapses rarely involved great loss of life. They could just be a simple transition from “a bunch of farming towns pay taxes to the state center” to “a bunch of farming towns are no longer paying taxes to the state center”. The great world cultures of the time – Egypt, Sumeria, China, whereever – kept chugging along whether or not there was a king in the middle collecting taxes from them. Scott warns against the bias of archaeologists who – deprived of the great monuments and libraries of cuneiform tablets that only a powerful king could produce – curse the resulting interregnum as a dark age or disaster. Probably most people were better off during these times.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Against The Grain“, Slate Star Codex, 2019-10-15.
July 10, 2024
After 1177 B.C.
Jane Psmith reviews the follow-on book from Eric Kline’s bestseller about the Bronze Age Collapse, After 1177 B.C.: The Survival of Civilizations:
Sometime around 1150 BC, the dense network of politically, economically, and culturally interdependent states around the eastern Mediterranean collapsed. In 2014, GWU archaeologist Eric Cline wrote a book about it. And then, surprisingly, it became a bestseller.
Okay, maybe it’s not that much of a surprise: most people can recognize an obvious historical analogy when it hits them over the head, and the globalized1 state system of the Late Bronze Age has extremely clear parallels to the modern day. An interconnected and cosmopolitan world? Centralized state bureaucracy? High-level diplomacy between ruling elites? A technologically complex civilization enabled by extensive international trade along lengthy and elaborate supply chains? Well, gosh, that seems remarkably familiar. An audience that had just weathered a global financial crisis (and, later, a global pandemic) was perfectly poised to appreciate Cline’s exploration of the fragility of complex systems. No wonder it sold! (A copy entered the Psmith household in early 2020 for, uh, obvious reasons.)
Cline’s basic argument in the book was that the Collapse was due not to any single cause but to a “perfect storm” of calamities: drought and accompanying famine, earthquake, internal rebellion, external invasion. These were all problems that the civilizations of the Bronze Age Mediterranean had faced and survived in the past, but under their combined onslaught the most fragile parts of the system at last began buckle. When one society disintegrated, its sudden absence from the interconnected global economy became a new stressor on its surviving neighbors — until at last, domino-like, the whole thing came down.2 It would be decades, or in some places centuries, before the standard of living returned to anything like its previous level, and it would be nearly five hundred years before an international system as complex and sophisticated as the world of the Late Bronze Age emerged.
Now, a decade after his original book, Cline has a sequel exploring what happened after the Collapse. Which civilizations were able to rebound to something approaching their former glory, which barely managed to limp along into the Iron Age, and which vanished into the sands of time? And, more importantly, why?
This is a much more difficult story to tell. The original 1177 B.C. spent much of its page count on the zenith of Bronze Age civilization, the 15th through 13th centuries BC, to explain what it was that did the collapsing. It’s a sweeping tale, full of wonderful stories and fascinating digressions into the historicity of the Trojan War (yes) and the Exodus (not archeologically substantiated) as well as being a compelling portrait of a complicated set of societies. Cline’s narrative darts from Egypt to Assyria to the Aegean to the Hittites, treating each in turn as he moves forward through time towards what we all know is coming.
But chronological framing is impossible for the sequel. There is, definitionally — there can be — no grand narrative of regional divergence after the fall of a “world-system“. The fate of Mesopotamia is no longer linked to that of Greece; there are no more Cretan envoys in New Kingdom tomb reliefs, no more battles between the Hittite Great King and the wanax of a Mycenaean palatial center, no more Uzbek tin shipwrecked off the coast of Anatolia. Once the ties are cut, each story must stand alone, and accordingly Cline gives each region its own chapter.
Alas, this is a lot less fun to read.
1. For sufficiently small values of “globe”. But larger than you might expect!
2. The revised 2021 edition apparently gives a larger role to climate factors, especially the 3.2kya megadrought, but that’s not the one I read and anyway the other elements were still present.
May 21, 2024
Tribalism
Theophilus Chilton pulls up an older essay from the vault, discussing tribalism, how it likely arose, and examples of cultures that relapsed into tribalism for various reasons:
In this post, I’d like to address the phenomenon of tribalism. There can be two general definitions of this term. The first is attitudinal – it refers to the possession by a group of people of a strong ethnic and cultural identity, one which pervades every level and facet of their society, and which serves to separate (often in a hostile sense) the group’s understanding of itself apart from its neighbours. The second definition is more technical and anthropological, referring to a group of people organised along kinship lines and possessing what would generally be referred to as a “primitive” governmental form centered around a chieftain and body of elders who are often thought to be imbued with supernatural authority and prestige (mana or some similar concept). The first definition, of course, is nearly always displayed by the second. It is this second definition which I would like to deal with, however.
Specifically, I’d like to explore the question of how tribalism relates to the collapse of widely spread cultures when they are placed under extreme stresses.
There is always the temptation to view historical and pre-historical (i.e., before written records were available) people-groups which were organised along tribal lines as “primitives” or even “stupid”. This is not necessarily the case, and in many instances is certainly not true. However, tribalism is not a truly optimal or even “natural” form of social organisation, and I believe is forced onto people-groups more out of necessity than anything else.
Before exploring the whys of tribalism’s existence, let’s first note what I believe can be stated as a general truism – Mankind is a social creature who naturally desires to organise himself along communal lines. This is why cities, cultures, civilisations even exist in the first place. Early in the history of Western science, Aristotle expressed this sentiment in his oft-quoted statement that “Man is by nature a political animal” (ὁ ἄνθρωπος φύσει πολιτικὸν ζῷον). This aphorism is usually misunderstood, unfortunately, due to the failure of many to take its cultural context into account. Aristotle was not saying that mankind’s nature is to sit around reading about politicians in the newspaper. He was not talking about “politics” in some sort of demotic or operational sense. Rather, “political” means “of the polis” [” rel=”noopener” target=”_blank”>link]. The polis, in archaic and classical Greece, was more than just a city-state – it was the very sum of Greek communal existence. Foreigners without poleis were not merely barbarians, they were something less than human beings, they lacked a crucial element of communal existence that made man – capable of speech and reason – different from the animals and able to govern himself rationally. “Political” did not mean “elections” or “scandals”, as it does with us today. Instead, it meant “capable of living with other human beings as a rational creature”. It meant civilisation itself. Tribalism, while perhaps incorrectly called “primitive”, nevertheless is “underdeveloped”. It is in the nature of man to organise himself socially, and even among early and technologically backwards peoples, this organisation was quite often more complex than tribal forms. While modern cities may be populated by socially atomised shells of men, the classical view of the city was that it was vital to genuine humanity.
My point in all of this is that I don’t believe that tribal organisation is a “natural” endpoint for humanity, socially speaking. The reason tribes are tribes is not because they are all too stupid to be capable of anything else, nor because they have achieved an organisation that truly satisfies the human spirit and nature. As the saying goes, “The only morality is civilisation”. The direction of man’s communal association with man is toward more complex forms of social and governing interactions which satisfy man’s inner desire for sociability.
So why are tribal peoples … tribal? My theory is that tribalism arises neither from stupidity or satisfaction, but as a result of either environmental factors such as geography, habitability, etc. which inhibit complexification of social organisation, or else as a result of civilisation-destroying catastrophes which corrode and destroy central authority and the institutions necessary to maintain socially complex systems.
The first – environmental factors – would most likely be useful for explaining why cultures existing in more extreme biomes persist in a tribal state. For example, the Arctic regions inhabited by the Inuit would militate against building complexity into their native (i.e. pre-contact with modern Europeans) societies. The first great civilisations of the river valleys – Egypt, Mesopotamia, the Indus valley, and China – all began because of the organisation needed to construct and administer large scale irrigation projects for agriculture. Yet, the weather in the Arctic precludes any sort of agriculture, as well as many other activities associated with high civilisation such as monumental architecture and large scale trade. The Inuit remained tribal hunter-gatherers not because they were inherently incapable of high culture, but because their surroundings inhibited them from it. Likewise, the many tribal groups in the Rub’ al-Khali (the Empty Quarter of the Arabian peninsula) were more or less locked into a semi-nomadic transhumant existence by their environment, even as the racially and linguistically quite similar peoples of Yemen and the Hadramaut were developing complex agricultural and commercial cultures along the wadis.
However, I believe that the more common reason for tribalism in history is that of catastrophes – of various types, some fast-acting and others much slower – which essentially “turned the world upside down” for previous high civilisations which were affected by them. I believe that there are many examples of this which can be seen, or at least inferred, from historical study. I’ll detail five of them below.
The first is an example which would formerly have been considered to fall into the category of tribes remaining tribal because of geographical factors, but which recent archaeological evidence suggests is not the case. This would be the tribes (or at least some of them) of the Amazon jungles, especially the Mato Grosso region of western Brazil. Long considered to be one of the most primitive regions on the planet, one could easily make the argument that these tribes were such because of the extreme conditions found in the South American jungles. While lush and verdant, these jungles are really rather inhospitable from the standpoint of human habitability – the jungle itself is extremely dense, is rife with parasites and other disease-carriers, and is full of poisonous plants and animals of all kinds. Yet, archaeologists now know that there was an advanced urban culture in this region which supported large-scale root agriculture, build roads, bridges, and palisades, and dammed rivers for the purpose of fish farming – evidently the rumours told to the early Spanish conquistadores of cities in the jungle were more than just myth. This culture lasted for nearly a millennium until it went into terminal decline around 1550 AD, the jungle reclaiming it thoroughly until satellite imaging recently rediscovered it.
What happened? We’re not sure, but the best theory seems to be that diseases brought by Europeans terminated this Mato Grosso culture, destroying enough of its population that urban existence could no longer be sustained. The result of this was a turn to tribalism, a less complex form more easily sustained by the post-plague population. The descendants of this culture are the Kuikuro people, a Carib-speaking tribe living in the region, and probably also other tribes living in the greater area around the Matto Grosso. In the case of the Mato Grosso city culture, the shock of disease against which they had no immunity destroyed their population, and concomitantly their ability to maintain more complex forms of civilisation.
The conical tower inside the Great Enclosure at Great Zimbabwe.
Photo by Marius Loots via Wikimedia Commons.The second example would be that of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe, centered around its capital of “Great Zimbabwe,” designated as such so as to distinguish it from the 200 or so smaller “zimbabwes” that have been scattered around present-day Rhodesia and Mozambique. Great Zimbabwe, at its peak, housed almost 20,000 people and was the nucleus of a widespread Iron Age culture in southern Africa, and this Bantu culture flourished from the 11th-16th centuries AD before collapsing. It is thought that the decline of Zimbabwean culture was due to the exhaustion of key natural resources which kept them from sustaining their urban culture. The result, if the later state of the peoples in the area is any indicator, was a conversion to the tribal structures more typically associated with sub-Saharan Africa. The direct descendants of the Zimbabwean culture are thought to be the various tribes in the area speaking Shona, a Bantu language group with over 8 million speakers now (post Western medicine and agriculture, of course). Once again, though, we see that when conditions changed – the loss of key resource supports for the urban culture – the shock to the system led to a radical decomplexification of the society involved.